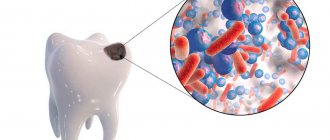
Until the age of 7, caries is observed in 80% of cases. This disease begins to develop as soon as teeth erupt. Many parents deliberately do not notice this problem. But practice shows that both baby and permanent teeth need treatment. If the situation is neglected, you can get a purulent infection, pulpitis and other equally serious problems. In addition, treating caries does not necessarily mean drilling. Today, low-penetration techniques have been developed for children. This is fluoridation, silvering, infiltration.
Rules for the treatment of baby teeth
- Anesthesia takes place in 2 stages. This is necessary so that the baby does not feel anything and is not afraid. First, a gel or spray and lidocaine are applied to the gums. Only then is the injection given. For this, the finest needles are used.
- Tissues affected by caries are carefully removed using a special hand tool.
- A safe concentration of anesthetic in the drug is maintained. For Lidocaine it is 2%, for Articaine – 4%. The amount of the drug is selected depending on the weight of the child. Apply from ½ to 1/6 of the standard adult dose. Anesthetics containing adrenaline should not be used for children under 4 years of age.
- Treatment of caries is carried out in sessions. Each should last no more than 30 minutes. Otherwise, the baby will get tired and become capricious.
- Filling materials are used that can be applied in one go. They contain fluoride and other minerals to strengthen teeth.
“Permanent 6th teeth erupt in children aged 5-6 years and, as a rule, are affected by caries first. Teach children how to use toothbrushes and toothpastes correctly, which will prevent plaque from accumulating in deep fissures.”
Rita Martikovna Meliksetyan, Dentist therapist, orthodontist, pediatric dentist, 19 years of work experience
Modern methods of treating primary teeth in children aged 2 to 4 years
Modern parents believe that treating a child’s teeth is a waste of time, because over time, milk teeth will be replaced by permanent, healthy teeth without caries.
But every pediatric dentist will call this opinion erroneous, since caries negatively affects not only the oral cavity, but also the condition of other organs and systems of the small patient. The reasons for the development of childhood caries are different. How do young children have their teeth treated today in the Russian Federation? This is done using a gentle method and using only the latest developments in dentistry. Therefore, during this procedure the baby does not experience any discomfort, much less fear.
From 2 to 4 years of age, pediatric dentistry uses the method of silvering baby teeth. A specially developed medicine is applied to the already damaged enamel. The drugs of choice are Saforide and Argenate - they contain 30% silver. After application, the dentin canals close and the spread of bacteria that cause caries stops. This procedure does not bother the baby at all, and he calmly sits for the required time in the chair.
The fluoridation procedure helps eliminate caries in children as reliably as the first method. There are two ways to go here. The first is the application of a fluoride-containing preparation with a brush to the tooth enamel. The second is treatment with a tampon, which is soaked in a special liquid. It contains copper and calcium hydroxide.
Dental treatment today is neither painful nor scary, and this is the main difference between dental offices and those that existed 20 or even 30 years ago. We use modern, effective anesthetics with different flavors, silent drills, and multi-colored fillings, the color of which the child can choose himself.
How is childhood caries diagnosed?
Tooth decay occurs much faster in children. This process takes several months. All due to weak enamel of baby teeth. They are permeated with many micropores through which bacteria penetrate. Therefore, you need to undergo a dental examination at least once every 3-4 months.
At different stages of caries, its symptoms differ:
- Initial stage. White spots appear on the tooth enamel, which then turn yellow and become rough. There is no pain, although the tooth may react to hot and cold. To eliminate initial damage, you do not need to drill the tooth. In such cases, it is possible to restore the enamel without filling.
- Middle stage. A “hole” is formed at the site of damage to the enamel. Food debris and softened dectin accumulate in it. In such cases, a cavity is formed and a filling is placed to prevent further decay.
- Deep stage. Not only the enamel is destroyed, but also the bone tissue of the tooth. The damage is noticeable to the naked eye. Deep caries can be cured with fillings, but sometimes even this does not help. In some cases, it is necessary to remove a baby tooth.
Diagnosis of carious lesions is carried out visually or using a special probe. If the “hole” is located in a remote place, an oral camera or x-ray is used. In the initial stages of caries, a special composition is used, which is applied to all teeth. It turns the affected areas pink or blue. This method has no side effects.
What should you do if your child has toothache?
If acute pain appears, it is necessary to examine the oral cavity and try to find out the approximate cause of the appearance and nature of the pain, and then give the child an anesthetic that has been approved by a pediatrician specifically for your baby. Under no circumstances should you resort to using remedies recommended by strangers, as each medicine is tolerated differently by individuals and can cause serious complications, including death. Next, you should immediately consult a dentist.
You should not delay treatment, as inflammatory and purulent processes in children develop very quickly, spread to nearby tissues and cause extremely negative consequences.
If a child experiences acute toothache, you should consult a dentist.
If the nature of the pain is unexpressed, periodic, you should schedule a visit to the dentist in the near future as planned. Treatment outside of an exacerbation is better and more effective, so you should not delay seeing a doctor. The health of baby teeth guarantees not only a quiet life for the baby, but also the correct and complete eruption of healthy permanent teeth. After tooth extraction, how long after you can eat, read on our website
Treatment of caries in early childhood
- Fluoridation. The second name of this method is remineralization. This is the saturation of the affected areas of enamel with minerals, its restoration. The tooth surface is treated with a special composition containing calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and other elements. The effect of this treatment lasts for about six months. Fluoridation is indicated for children from 6 years of age.
- Silvering. This method is outdated, but is still sometimes used. The surface of the tooth is coated with a 30% solution of silver nitrate, which destroys bacteria that cause caries. The procedure is absolutely painless. But after it the teeth become black, which can cause complexes in the child.
- Infiltration. A special gel is applied to the affected area of the tooth, which softens the tissue. Afterwards they are washed with an abrasive mixture. The area is then dried and covered with Icon Liquid Filling. The material hardens under a curing lamp.
- Ozone therapy. Ozone under pressure in a gaseous state is applied to the area of the tooth affected by caries. This does not cause any pain. The duration of the procedure is 10-20 seconds. Ozone destroys bacteria that cause tooth decay. After ozone therapy, tooth decay stops.
- Filling. The installation of fillings on baby teeth begins with the removal of dead tissue from the cavity. This is done with hand tools or a drill. The cavity is disinfected with a special composition and hermetically sealed. Upon completion, the surface of the filling is ground.
The filling material should be no harder than enamel. Otherwise, protrusions will form along the edges. Therefore, glass ionomer cements are used for children. They wear evenly and naturally together into enamel.
Some clinics use colored fillings for fillings. They are made from compomer and have no side effects.
When should baby teeth be removed?
But sometimes the removal of a temporary tooth cannot be avoided. The doctor may insist that the question of whether to treat or remove a baby tooth should be decided in favor of removal. If his position is justified, then begin to prepare the child for this procedure. But if in doubt, it is better to get advice from several specialists.
The need to remove a baby tooth may arise in the following cases:
- the development of caries, caries, after which the tooth is difficult to cure - sometimes carious cavities in children's teeth become so huge that there can be no talk of treatment;
- severe forms of periodontitis or pulpitis, especially if there is a threat of damage to the permanent tooth germ - serious inflammatory processes of dental tissues can harm the child’s body as a whole, so sometimes in such cases a decision is made to remove the tooth;
- the appearance of a permanent tooth next to the milk tooth - when there is early eruption of a permanent tooth, which is hampered by a milk tooth that has not yet fallen out, the temporary tooth must be urgently removed;
- the development of a cyst at the roots of a tooth is a fairly serious diagnosis, the treatment of which requires immediate tooth extraction;
- formation of a fistula on the gum - in this case it is also impossible to carry out treatment without first removing the tooth at the site of the fistula.
It should be noted that the removal of a baby tooth is considered premature when the eruption of a permanent tooth in this place will have to wait more than a year. At what age do certain teeth change, check with your dentist.
How is caries of permanent teeth treated in children?
Caries on permanent teeth is treated as in adults. The main method is filling. Photocomposites are the most successful for sealing the affected cavity. These are materials that do not differ in color or texture from teeth. Filling takes place in several stages:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Removing dead tissue using a drill and cleaning the cavity.
- Rinsing the tooth with an antiseptic.
- Air drying.
- Application of phosphate cement insulating gasket.
- Filling with composite materials in several layers, each of which must be dried with a special lamp.
For shallow caries, infiltration, remineralization or ozone therapy can be used. Silver plating is contraindicated.
Do baby teeth need to be treated and how are they treated?
Why is it worth treating baby teeth?
Children's enamel is not strong enough and mineralized, so it is very susceptible to inflammatory and destructive processes.
Insufficiently thorough oral hygiene can lead to oral diseases that develop quickly and lead to unpleasant consequences. This has a negative impact on permanent teeth in the future. Harmless, at first glance, caries can provoke the occurrence of more complex diseases in the form of periodontitis and cysts, cause inflammation of the gum tissue and lead to a general deterioration in health due to decreased immunity. Another, not always obvious, reason why it is worth treating baby teeth is the impact of their condition on the child’s bite in the future. What is the relationship? It's simple. Often caries develops very quickly and rapidly reaches a stage at which it is impossible to save the tooth. In this case, the dental unit must be removed. If a baby tooth is removed and the molar bud has not yet formed, this area is empty until the natural eruption of the permanent tooth. At the same time, the teeth adjacent to the removed unit gradually begin to shift, compensating for the resulting distance. Accordingly, when the permanent unit begins to erupt, it does not have enough space, and it moves the row. To prevent such a situation from arising, it is important to treat milk breasts in a timely manner in order to preserve them until they naturally change to permanent ones.
How are baby teeth treated? We describe the features of the procedure.
How are baby teeth treated?
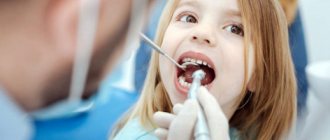
It is recommended to visit a pediatric dentist with your child from the appearance of the first tooth. It is not necessary to wait for visible caries to appear; regular examinations and prevention will help minimize the risk of inflammation. A visit to the clinic always begins with meeting the doctor and adaptation in a playful way so that the baby gets used to and feels comfortable in the new environment.
The doctor makes a decision on how to treat caries of primary teeth after examining and identifying the extent of the inflammatory process. At the white spot stage, treatment takes place without drilling: by polishing and strengthening the enamel with a special compound. Superficial caries is most often eliminated without an injection - pain relief is carried out with a special gel. In case of deep caries, removal of the affected areas is carefully performed after anesthesia with an injection.
In advanced cases, removal may be required. But the position of doctors is to try as much as possible to preserve natural teeth. Therefore, they will do everything possible to correct the situation with conservative treatment.
Is it painful to treat baby teeth?
Why weren't baby teeth treated before?
In most cases, due to myths about dentists formed in society. And still, some parents put off going to the pediatric dentist because they are afraid that the child will experience pain and fear. Such emotions may negatively affect future attitudes towards doctors. It is worth noting that modern dentistry has changed a lot in recent years and treating teeth has become no longer painful. Anesthetic gels and pastes are successfully used, which eliminate discomfort during superficial treatment or during an anesthetic injection when more serious treatment is required. Pediatric dentists have the skills of a psychologist, so they can put a small patient at ease, reduce the degree of tension and fear in a place that is unusual for a child. You need to treat baby teeth and it doesn’t hurt, so don’t put it off!
Each child is an individual, each situation is unique. Therefore, the dentist will be able to give precise recommendations on oral care and necessary treatment after the examination. Contact pediatric dentist-therapists at the medical and research center in Yekaterinburg. We will find an approach to your baby and, if necessary, provide effective treatment. Always happy to help!
Still have questions?
Ask them to our doctor
Anesthesia for the treatment of childhood caries
Local anesthesia. Used in the vast majority of cases. There are 2 types: application and injection anesthesia. The first does not involve an injection. The risk here is that the child may swallow saliva containing lidocaine. Injections are safer and more effective.
Anesthesia. Used if the child is restless or simply afraid to have their teeth treated. This method is common in the West. Many parents are afraid of memory impairment due to general anesthesia. However, this happens extremely rarely. In addition, general anesthesia becomes the only option when you need to fill several teeth at once in one trip to the dentist. After all, this can take 2 or more hours. Before general anesthesia is administered, the child must undergo the following tests:
- Blood biochemistry.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Electrocardiography.
- Blood for sugar.
Before the introduction of general anesthesia, you cannot eat for 6 hours, and drink for 4 hours. The child is gently put to sleep using a sedative gas containing sevoflurane. To wake him up, it is enough to increase the oxygen supply. This can be done at any time. After recovery from anesthesia, all reflexes are restored within the first 15 minutes.
How are baby teeth different from molars?
Baby teeth appear at the age of six months. First, the central incisors erupt on the lower jaw, then on the upper jaw. By about 2.5 years old, the baby already has a full, white-toothed smile. His mouth contains 20 milk teeth, which will serve the child for several years.
After about six years, temporary teeth begin to be replaced by permanent teeth. When the baby brings the first “trophy” to his parents, it causes sincere joy and tenderness. And also the desire to carefully examine what the baby is holding in his fist. And while studying the tooth, parents can draw several wrong conclusions.
pixabay.co/
The first is that baby teeth have absolutely no roots. This impression is created because the root shoot of a fallen tooth is usually located on only one side, and sometimes it does not exist at all. In fact, primary incisors and molars, of course, have roots, but over time they become smaller.
This occurs in order to ensure a natural and painless process of changing the dentition. When the time comes to change the bite, the roots of the baby teeth gradually dissolve. And thanks to this, the indigenous ones “push out” their predecessors from the gums, taking their place.
The second incorrect conclusion may be related to the size of the tooth. It seems incredible that such a “baby” could have the same structure as an “adult” native.
“The structure of baby teeth is almost the same as permanent teeth,” comments Natalya Terentyeva. “They have roots, root and coronal pulp, root canals through which nerve fibers pass. Milk teeth differ from molars in that their enamel is weakly mineralized, which means it is more susceptible to destruction and the development of carious processes.”
Complications of childhood caries
It is important to treat baby teeth. After all, deep caries can penetrate the tissue so much that it damages the permanent dentition. In addition, the condition of temporary teeth subsequently affects the child’s bite. Removal leads to abnormal growth of the jaw. As a result, permanent teeth may appear out of place. Because of this, the child will have to wear braces.
Deep caries leads to inflammation of the pulp, periodontitis, and the formation of basal cysts. Treating these problems is very difficult and painful. It requires root canal filling.
If periodontitis starts, it can cause an abscess and even osteomyelitis. This is already dangerous for the child's life.
How do children's teeth work?
Children have an order of magnitude smaller teeth than adults. In addition, they are much smaller in size than permanent ones, are less durable, and are easily susceptible to the destructive influence of caries.
Pulp - loose fibrous tissue that fills the internal cavity of the tooth - occupies a very large space and is covered with a relatively thin protective layer. It is where blood vessels and nerve endings pass. This means that there are nerves in baby teeth and they can hurt no less than molars.
As for the characteristics of the root system, it is less developed in children than in adults. This is due to the need for root resorption during the period of change of bite .
Dentists never tire of repeating: baby teeth are complex systems in structure, and their condition affects the health of future molars. This is why most people who ignore the need to visit the dentist in childhood have serious dental problems at a young age.
Many parents do not pay enough attention to the health of their children's smiles. They explain their position by the fact that very soon the roots will resolve anyway, and the crown will collapse. But thinking like that is irrational and even dangerous. The inflammatory process can move to the root germ, then there is no need to talk about any healthy change.
Moreover, it is inhumane to deny children dental treatment. Indeed, with severe tissue destruction, they will begin to experience unbearable pain. If you treat caries at an early stage of its development, serious problems are guaranteed to be avoided.
Our patients
Patient recommendations
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Alekseeva O.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Zolotareva S.V.
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Vera
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Recommendations from patient Mikhail Ivanovich
Akhmedkhanov Said Rashidovich
Dental surgeon, general dentist, implantologist, orthopedic dentist, dental therapist.
Make an appointment 8 (499) 520-98-70
Make an appointment
Collapse