Teeth are hard tissue formations with high strength that last for a long period of time. The shape and location of individual units affects their functions:
- primary mechanical processing of food is carried out with the help of saliva (chewing, formation of a food bolus);
- formation of sounds (diction);
- protection of the body (prevent harmful microorganisms from entering internal organs).
Many external and internal factors influence when a person’s teeth begin to erupt and until how many years they grow. Among them are the nature of nutrition, the quality and composition of drinking water in the region of residence, hot (cold) climate.
Symptoms that indicate that the process has begun:
- Some children experience an increase in temperature (up to 38). In this case, you should not hesitate; it is better to seek advice from your doctor.
- Unpleasant sensations in the gums.
- The space between the teeth increases.
- The roots begin to dissolve (The roots of baby teeth are much shorter than those of permanent teeth. When the process reaches the neck, a tooth change occurs).
- Gums are bleeding.
Until what age do molars grow?
The process of replacing milk rudiments with permanent ones is extended over time. It can begin at age 6 and continue until age 14. Most often, permanent units fully grow by age 12. The first eight is usually achieved at the age of 18-20. It happens that wisdom teeth come in at 35 and 45 years old. Third molars may not appear at all. After all, the jaw of a modern person is slightly smaller in size than that of our distant ancestors.
As the permanent dental organ appears and grows, its roots thicken and their length increases. Enamel forms slowly. This takes about two years. The root masticatory organ usually appears without pain. Approximate growth periods:
- Central incisors – period from 6 to 8.5 years;
- The lateral incisors appear at 7.5 - 9 years of age;
- Fangs emerge at 9, 5, or even 12 years of age;
- Premolars appear by 10 years of age, and may appear even at 12 years of age;
- First molars – period from 6.5 to 7.5 years;
- Second molars – from 11 to 13 years;
- Wise units appear by the age of 17, and may even appear by the age of 21.
These norms are conditional. There is no need to worry if there are minor deviations. The formation of dentition occurs in different ways, depending on a number of factors.
Everything has its time
One of the most frequently asked questions to our doctors from mothers is: “In what order do teeth begin to fall out?”
It usually starts at the age of 5 years. The very first teeth that undergo this process are the incisors, then the fourth and fifth teeth of the row, then the canines. To make it more clear to you, here is a diagram of the loss and eruption of baby teeth:
Don't worry if your child is over 5 years old and his teeth aren't starting to change. Each child’s body is individual, and much depends on nutrition, dental care, daily routine, and climatic conditions. In girls, the loss of baby teeth begins a little earlier than in boys. If you are still worried, then contact your dentist and conduct an unscheduled examination.
I would also like to note the timing. Complete replacement of milk teeth with molars occurs within 6-7 years. There is no need to specifically tear them out or loosen them. Everything will happen naturally.
The doctor prescribes removal only if the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, but the root tooth is already beginning to grow.
Popular types of x-rays of baby teeth in children
Modern pediatric dentistry allows us to solve any problems with baby teeth. But in order to consider the disease and make a correct diagnosis, it is not enough just the child’s complaints and his description of pain and discomfort. In order for treatment to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to build a treatment plan based on diagnostic data that can be obtained after one of four popular types of radiography:
- Sighting (periapical). Indicated in cases where clarification is necessary on one or more adjacent teeth (from 1 to 3). Provides data about the units themselves, their roots and surrounding soft tissues.
- Occlusal (palatal). As a result, the attending physician receives a complete projection of one of the child’s jaws. The technique is used to determine possible malocclusions and anomalies of the dentition in general.
- Panoramic (orthopantomogram). Allows scanning of the entire oral cavity. An orthopantomogram for children is indicated for a detailed study of pathologies of the upper and lower jaw, the temporomandibular joint and the maxillary sinuses. The results of such an x-ray are necessary for further dental correction. This type of examination is prescribed for children with a fully formed dental system, that is, from about 9 years old.
- 3D pictures. A three-dimensional X-ray image of children's primary teeth allows us to obtain data on all units (existing and not yet erupted). The entire maxillofacial area is subject to examination. The photographs can be used to evaluate the structure of the entire skeletal system of the jaws, the condition of the root system (including pathologies), inflammation in soft tissues, etc. Such dental x-rays are prescribed for the purpose of making a diagnosis and as a control study after canal filling.
Depending on the existing problems with baby teeth, the child may be prescribed one specific or several different types of examination. The attending physician will definitely explain the advisability of obtaining images and the need for x-rays.
You might be interested in:
Dental diagnostics
Pediatric orthopantomogram
3D image of teeth
Features of baby teeth
Now I will answer another very popular question: “how do baby teeth differ from molars?”
These are the baby's very first teeth. They appear before the age of three, and begin to erupt until there are 20 teeth. See the photo above for the cutting diagram.
They do not have such deep roots as permanent teeth, have a more rounded shape and smaller size, and are white in color, while permanent teeth have a yellowish tint. By location, they are directed vertically, and the radicals are slightly outward.
Wisdom teeth cannot be milk teeth, because they grow into deep roots only by the age of 18-20, and sometimes later.
Which teeth should an eight-year-old child have?
Every child who has reached the age of eight should normally have the following permanent teeth - 4 lower and 4 upper incisors, sixth molars. Sometimes there may be individual deviations in teething within plus or minus six months.
Why is it necessary to treat caries in childhood if you then have to remove baby teeth with filled roots?
If an empty space forms in the dentition, this contributes to the fact that the remaining milk teeth shift, and along with them, the rudiments of permanent teeth also shift and they begin to grow incorrectly under them - in one place the formation of cracks begins, and in another - the teeth fit alone another. A filled, treated baby tooth will save space for a permanent tooth. Untreated teeth infect the rudiments of permanent teeth with infection, which causes their deformation and even complete absence.
Daily doctor's advice on caring for baby teeth:
- Start brushing your baby's teeth only after they have erupted; use a special brush for babies.
- When your child turns one year old, buy a brush with soft bristles and toothpaste without fluoride; it will not harm the child if he swallows it.
- Brush your baby's teeth 2 times a day (morning and evening)
- Don't put off going to the dentist. They should be regular, even if there are no signs of concern.
- Include more fresh greens, fruits and vegetables in your diet.
First teeth
When to expect
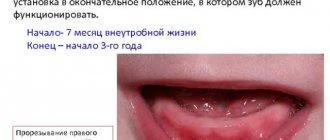
The baby's milk teeth are formed at the 7th–8th week of intrauterine development, and the permanent ones at the end of the 4th month of pregnancy. In total, a child develops 20 baby teeth, while 32 permanent teeth. To provide the baby with a Hollywood smile, the expectant mother needs to eat properly throughout the nine months of pregnancy. There are no calcium preparations that are 100% absorbable, so it is very important to get “natural” calcium from food, especially cottage cheese. And, of course, the pregnant woman herself needs to have all her teeth treated - now there are very gentle technologies for this.
The eruption of the first milk teeth in most cases begins at 3–8 months of the baby’s life and ends closer to three years. But it also happens that children are born with one or two teeth, or teeth may erupt in the first weeks of life. Often the timing of teething depends on genetic characteristics, but much more strongly on other factors. Diseases of the baby also affect the teeth (for example, with rickets, frequent ARVI and dyspepsia, teeth erupt later). It’s worth paying attention to the nature of your diet, the quality of drinking water, even the climate! On average, northern residents start teething a little later than southerners. Sometimes teething is delayed, and the first tooth appears closer to a year. Usually there is nothing wrong with this. It is believed that it is not so much the timing that speaks about a child’s health, but rather the order in which teeth erupt. If it is broken, pay attention to this fact and show the baby to the pediatric dentist.
The process has started
The fact that the teething process has begun is indicated by profuse salivation. In addition, the baby begins to put into his mouth everything that comes to hand. This means that the gums are itchy, causing him discomfort. Trying to relieve the itching, the baby instinctively acts correctly - micromassage of the gums improves microcirculation in them, teeth erupt easier and faster. During this period, provide your child with teethers: hypoallergenic silicone toys filled with water. The teether should not be cooled in the freezer - only in the refrigerator: otherwise the baby will get hurt on a hard surface. If the gums are very swollen and the baby is crying in pain, use special dental gels that have a mild local anesthetic effect.
For most children, the teething process goes quite smoothly. There may be short periods of anxiety, disturbances in daily routine and nutrition. Sometimes even teething is accompanied by diarrhea, runny nose, cough and fever. And during the period when teeth appear, the baby is vulnerable to all kinds of infections. The baby’s immunity is weakening these days, and it is easier for him to “catch” the virus, so you should not attribute the deterioration of the condition only to the teeth. If a child has a fever when a tooth is being cut, you need to look for another inflammatory source in the body.
At 6 months
The baby usually boasts central lower incisors. This is a reason to start brushing your teeth. Why so early? Baby teeth are small and sharp, have an uneven wavy edge, stand close to each other and, as a rule, have a yellowish tint. These teeth have a low degree of mineralization. Their enamel and dentin are very thin. All this contributes to the rapid occurrence and spread of caries. In order to prevent it, you need to regularly brush your teeth: for this you can use various massage brushes, which not only accustom the child to hygiene, but also facilitate the teething process itself. We immediately teach you how to brush your teeth correctly - from the gums to the edges, with slightly “sweeping”, semicircular movements, and in no case horizontally. If possible, brush your teeth after every meal (and at least twice a day). Isn't there such a possibility? Give the baby something to drink - the water will wash away any remaining food.
At 8 months
The upper central incisors usually erupt.
At 9 months,
the upper lateral incisors appear.
At 11 months,
many children's lower lateral incisors are already in place!
By the age of one year, a baby normally already has eight teeth
.
But there may not be any - delayed teething occurs in 25% of cases with normal psychomotor development of the child. In extremely rare cases, the absence of teeth is associated with adentia - the absence of their rudiments. This can be checked by a pediatric dentist using radiovisiography. By 13–15 months,
the upper first molars appear first, followed by the lower ones.
From the age of one year, your baby can brush his teeth with children's toothpaste and a special children's brush. The service life of the brush is no more than 2 months, even if it looks like new. Many kids swallow the tasty pasta. There is no need to be afraid of this if it is for children and its quantity is no more than a pea. Of course, until 2–2.5 years of age, teeth brushing should be done with the help and then under the watchful supervision of the mother.
At 18 months
fangs erupt.
Typically, these teeth cause more problems than others; their eruption is more painful, and this process is often accompanied by discomfort. At 20 months,
the second molars erupt.
And sometimes already at this age the mother can notice the first problems. Doctors reassure: carious baby teeth are not a reason to worry that permanent teeth will also be bad. As practice shows, there is no pattern here. Of course, if parents do not neglect disease prevention and dental hygiene. At 2.5 years old, a child normally has a full set of baby teeth.
There are 20 of them - 10 on each jaw .
Baby teeth don’t last very long – soon they will begin to fall out and permanent ones will appear in their place. Usually the change of teeth begins at about 5–6 years and lasts until the age of 20, when wisdom teeth erupt.
Starting from 6 months, you must come for a preventive examination twice a year. When this becomes a habit, the baby will not be afraid of doctors, and by the age of 7–8 years (when a visit to the clinic can no longer be avoided) he will sit completely calmly in the dental chair
In order for your baby’s teeth to grow strong and healthy, you need to start taking care of them almost before conception. It’s also better to meet the dentist early
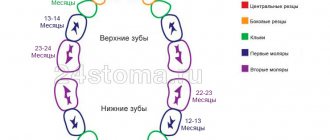
Timing of eruption and loss of baby teeth
| Upper teeth | |||
| Tooth name | Period of eruption | Teething order | Drop date |
| Central incisor | 8 months – 1 year | 2 | 6–7 years |
| Lateral incisor | 9 months – 1 year 2 months | 3 | 7–8 years |
| Fang | 1 year 3 months – 1 year 10 months | 7 | 10–12 years |
| First molar | 1 year – 1 year 6 months | 5 | 9–11 years |
| Second molar | 2 years – 2 years 8 months | 10 | 10–12 years |
| Lower teeth | |||
| Central incisor | 6 months –10 months | 1 | 6–7 years |
| Lateral incisor | 10 months –1 year 4 months | 4 | 7–8 years |
| Fang | 1 year 4 months – 2 years | 8 | 9–12 years |
| First molar | 1 year 2 months – 1 year 7 months | 6 | 9–11 years |
| Second molar | 1 year 10 months – 2 years 8 months | 9 | 10–12 years |
Doctor's advice when the process of changing teeth begins:
- After tooth loss, let your baby not eat for 3 hours, and you should also not drink very cold or hot drinks.
- Protect your child from sour, spicy and very sweet, astringent foods. All this has a negative impact on teeth.
- If your baby is bothered by discomfort or pain after a baby tooth falls out, then buy a special gel, but it is better to choose it on the recommendation of a dentist.
- Do not let your child touch the hole where a tooth has fallen out, as it may become infected.
- To soothe your mouth, make a decoction of chamomile.