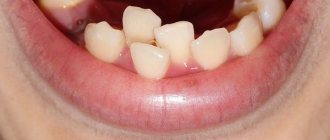
The replacement of baby teeth with molars is a joyful and at the same time exciting period in the life of every child and his parents. He is accompanied by dozens of doubts and questions. Are teeth changing correctly? Why do baby teeth fall out of order? Should they be immediately replaced by molars or can there be free “spaces” left in the mouth for some time? When should you worry and see a doctor?
A pediatric dentist at the “All Ours!” Dentistry answered these questions to a FAN Victoria Arutyunova .
Why do children lose teeth?
The formation of baby teeth in the jaw begins long before the baby is born. And the eruption of the first tooth becomes a real event. This usually happens at six months: parents notice bumps on the lower gum, the baby becomes capricious and restless. And after some time, the mouth is decorated with white “caps” of the first central incisors.
A little later, after two to four months, they are paired with the central incisors on the upper jaw. Then the lateral incisors, canines and molars appear in the mouth. The latter grow up by about two and a half to three years, and by this age most children acquire a complete milk bite. 20 baby teeth will serve the baby for at least another two to three years.
As the baby grows, his jaw also changes. It becomes larger, and if up to three years the teeth were arranged in dense, neat rows, then later gaps will begin to appear between them. Parents should not worry - this is a natural and necessary process. Interdental spaces, called diastemas, are needed so that later molars, larger than baby teeth, can take their place.
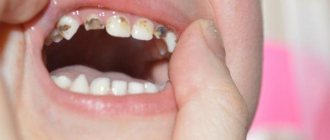
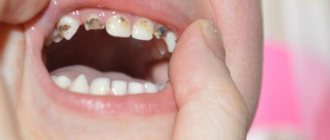
At the age of six or seven years, the changes become even more noticeable. The baby's first tooth may fall out. Usually, the one that appeared first, that is, the central incisor of the lower jaw, falls out first. This event indicates that the milk bite will begin to change into a permanent one. The baby’s body will need time to completely renew its dentition. This takes on average four to five years, and there is no need to rush things.
pixabay.com/
Parents are often worried that their children’s teeth are already actively changing, but their baby still walks around with a full, milky smile. These experiences are usually in vain, since nature has not programmed the only correct time for a person to change their bite. The indicated age for the loss of the first tooth is conditional. For some children this happens earlier - for example, at five years old. For others - after seven years, when the baby goes to school. It has been noticed that girls acquire molars earlier than boys. At the same time, the age at which baby teeth fall out is not as important as the correct order.
Is there a pattern for tooth loss?
It is believed that the first permanent tooth appears immediately after the baby tooth falls out. Actually this is not true.
“At the age of five or six years, children’s first molar teeth erupt,” comments a pediatric dentist at the “All Yours!” Dentistry. Victoria Arutyunova. - This is the sixth tooth, which is located behind all the milk teeth. And only after this the change from the milk bite to a permanent one begins.”
This happens in a certain order:
- the first stage at 6-7 years . The central incisors change, first on the lower jaw, then on the upper;
- second stage at 7-8 years . Time to change the second incisors, which will also fall out first at the bottom and then at the top;
- third stage at 8-9 years . There are fangs immediately behind the incisors, but they will not change now. At this stage, the “fours” located immediately behind the fangs should change;
- fourth stage at 9-10 years . Time to change canines, and then molars;
- fifth stage at 10-11 years . By this age, the child should have replaced molars. The process of tooth loss in children is completed.
“At the age of 10-11, the last milk teeth fall out, and the bite becomes permanent,” notes Victoria Arutyunova. - But the growth of molars does not end there. There are still “sevens” and “eights” left - the second painters, who erupt at 12-13 years of age. And also wisdom teeth or third molars, which grow after 18 years. But in general, we can say that by the age of 12, all the teeth in the child’s mouth will be permanent.”
pixabay.com/
Treatment and prevention
Treatment for delayed development of primary teeth always depends on the cause of this phenomenon. The doctor needs to understand what is going wrong in the child’s body and then prescribe treatment specifically for this ailment. It is impossible to cure teeth that do not erupt, because there is always
there is a specific reason why this is not happening. It is also necessary to determine whether the child has any rudiments of teeth at all, because if they do not exist, then other measures will have to be taken.
If teeth erupt early, then parents need to worry about caries not “eating” them prematurely. But if a child does not have chewing organs at one year or 10-11 months, this can be a problem.
Prevention of teething disorders cannot exist, because when a child is born, the parents have a colossal influence on its development, but the entire basis has already been laid, so the main attention should be paid to the health, nutrition and lifestyle of the pregnant woman.
Why is the order of changing teeth important?
First, the incisors, and only then the molars and canines - this order determines the normal course of jaw development and the formation of a correct bite. If teeth fall out in the wrong order, this can lead to malocclusion and subsequent problems.
Malocclusion is not only an aesthetic problem that changes facial features, but a physiological one. As a result, pronunciation and clarity of speech are impaired, the quality of chewing food deteriorates, which can lead to disruptions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Several reasons can cause a disorder in the order of tooth loss:
- trauma - the baby hit himself and knocked out or damaged a tooth, causing it to fall out prematurely;
- diseases of the oral cavity - enamel hypoplasia, caries or pulpitis.
It happens that parents “neglect” the condition of the child’s oral cavity, believing that there is no need to care for or treat baby teeth. They'll fall out soon anyway. This leads to negative consequences.
Firstly, the baby does not develop a culture of oral care. And at an older age, he will not closely monitor the health of his molars, which will cause the active development of carious processes and their early loss.
Secondly, caries of baby teeth is not a harmless disease. It destroys teeth, causing them to fall out earlier, spreads aggressively in the mouth and can infect the molars and molars, which are located in the gums. Caries in children must be treated. And the sooner parents notice white or dark spots on the enamel and the sooner they consult a doctor, the greater the chance that the doctor will “catch” the disease at an early stage. And it will not have time to lead to dangerous consequences for the baby’s health.
If the order of changing teeth is disrupted as a result of injury or illness, you should consult a doctor. It is important to consult a pediatric dentist to help get rid of oral diseases. And also an orthodontist, who will recommend options for correcting the primary bite and select means that do not allow the teeth located next to the freed space to move arbitrarily.
pixabay.com/
What to do if a tooth does not grow after a baby tooth falls out?
Ideally, teeth change as follows. The molar located in the gum begins to move upward. This serves as a signal to the dairy that it is time to make room. Its roots begin to dissolve, and it itself becomes mobile. The baby may feel that the tooth has become loose, but it will not fall out quickly. It takes time for the roots to be reabsorbed; this takes several months. As the molar or molar grows, the roots of the predecessor become smaller and smaller. At some point, it falls out, and in the hole that remains in its place, the cap of the original “replacement” is already visible.
But it also happens that a molar tooth does not replace a lost baby tooth. And this is a reason to consult an orthodontist.
“Such problems can arise if there is not enough space in the child’s bite for the eruption of permanent teeth,” comments pediatric dentist Victoria Arutyunova. - Molars are larger in size than baby teeth. And if the freed up space is not enough for a permanent tooth to erupt, it may remain in the gum.”
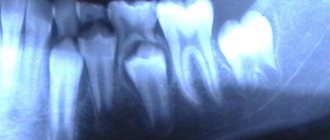
The orthodontist will give you a referral for a panoramic photograph of the jaw. This is a completely painless procedure that will allow you to see the location of all molars in the gums. Based on the image taken, the doctor will offer options for solving the problem. Modern orthodontic techniques help eliminate malocclusion in children of all ages.
pixabay.com/
Is it normal for a baby tooth to have not fallen out yet, but the molar tooth is already growing?
It also happens that a child’s teeth begin to grow “in two rows.” Many parents find this funny and are in no hurry to take their baby to the doctor, waiting until the baby tooth falls out on its own. And this is an erroneous position, which will only add to bite problems in the future.
As a rule, the molar, which grows under a tightly seated deciduous tooth, finds its exit in the gum from the side of the tongue. Incorrect position disrupts the bite. And the longer competitors fight for one place, the more crooked the permanent tooth will grow.
“Such cases are due to the anatomical features of the child’s oral cavity,” notes Victoria Arutyunova. — The permanent tooth is already growing, but the root of the milk tooth has not yet resolved. In this situation, you need to help the child get rid of the tooth, since, as practice shows, it cannot fall out on its own.”
Teething symptoms
The symptoms of pecking baby teeth are the same for all children. The first signs include excessive salivation and inflammation of the gums. Most often, they appear a few weeks before teething, but there are cases when the gums itch from 3 months, which causes discomfort to the baby, and he begins to pull various objects into his mouth.
Often the child experiences indigestion, poor appetite, and sleep disturbances. There are times when the temperature rises slightly, diarrhea, runny nose, and wet cough may appear. Children’s behavior often changes: they become capricious, cry for no reason and ask to be held by their parents.
It happens that these signs indicate other diseases, so it is better not to delay visiting a doctor.
Do baby teeth need to be pulled out?
There may be several reasons for removing baby teeth. Among them is the one mentioned above, when the permanent incisor or canine needs to be given the opportunity to erupt correctly and take its place in the gum. Another reason is the long absence of a molar tooth in place of the fallen milk tooth, which is prevented from appearing on the surface by tightly seated “neighbors.”
These reasons require the supervision of a specialist - an orthodontist, since they usually talk about insufficient jaw width. There was enough space in the mouth for small baby teeth, but there was too little space for larger permanent teeth. You can decide on removal on your own only if the incisor or fang is actively loose, which causes discomfort for the child and bleeding gums. And the only way to get rid of the problem is to pull out a tooth that is no longer needed and does not perform its functions.
If a change in bite occurs with disturbances, you need to consult a doctor. In childhood, the problem is solved by orthodontic treatment: wearing mouth guards or orthodontic devices - special plates. These products help gradually enlarge the jaw to allow the molars to grow properly. Orthodontic treatment is long-term, but painless and effective. The only thing it requires is discipline from the parents and the child himself.
pixabay.com/
Causes of frequent bowel movements
Constipation in a child causes discomfort in the abdominal area.
With the introduction of the first complementary foods, the baby's stool may change. When receiving an unfamiliar type of food, the body tries to adapt to its processing and digestion, so in this case it is normal for a child to poop frequently. This is a consequence of the type of nutrition and restructuring of the body.
You should pay attention to how the baby behaves after eating. If the nature of his behavior becomes restless, he begins to be capricious, press his legs to his stomach, rub his stomach, which means discomfort has appeared in the intestines.
In this case, you will have to wait a while with the introduced type of complementary feeding and try something else. Also, a serious indicator of intolerance (albeit temporary) to a particular type of “adult” product is the appearance of rashes on children’s skin.
For a baby, the food is practically those products that the mother who is nursing him eats, only he receives them in a slightly different form. Therefore, it is natural that when a mother eats a large amount of laxative food, her baby will have more frequent bowel movements.
When breastfeeding, you need to carefully monitor your diet so that the baby receives a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals, and at the same time there is no heavy load on his not yet fully formed intestines.
In addition to nutrition, many factors influence the frequency of a child's stool. The reason your baby poops frequently could be one of the following:
- taking certain medications, including laxatives;
- increased intestinal motility;
- bacterial and viral infections;
- celiac disease (deficiency of enzymes that break down the gliadin protein found in cereals);
- malabsorption syndrome (insufficient absorption of nutrients);
- food poisoning, etc.
Most often, children under the age of one year are susceptible to infection with E. coli. Normally, these bacteria are present in the body of both children and adults. But some of its types, entering the intestines from the external environment with water, air, food, can cause severe disorders of the digestive system.
Rotavirus infection, which affects both adults and children, becomes more active during the cold period - the autumn and winter months. Initial symptoms are similar to those of acute respiratory viral infection, but also include nausea, vomiting, fever and diarrhea - an intestinal upset. Celiac disease is a hereditary disease. Its symptoms appear when the baby begins to eat cereals in the form of porridge, bread, and cookies.
Is it possible for children to lose molars?
In childhood, molars are just emerging, so, of course, they cannot fall out in a healthy baby. Sometimes parents confuse large molars located deep in the jaw with permanent teeth. And they get scared when a child brings such a large tooth in his palm.
You can lose your permanent dentition as a result of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity - periodontitis. Or against the background of scurvy, a rare disease in modern society associated with a chronic lack of vitamin C in the diet.
But despite this, if you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor. After all, bite formation is a responsible process. And if it is carried out under the supervision of a specialist, there is a much greater chance that the teeth will grow healthy, even and beautiful. To do this, you need to undergo regular dental examinations. And if the dentist recommends consulting an orthodontist, you should not refuse this recommendation.
Causes of eruption disorders
If the first teeth of a one-year-old baby have not erupted, the reason most likely lies in impaired fetal development during pregnancy. Pathology of the chewing apparatus in a child may be caused by certain diseases suffered by a pregnant woman in the first trimester. In addition, the formation of the fetal dental system is adversely affected by the bad habits of the mother: smoking, drinking alcohol, drugs and illegal drugs.
Other reasons for delayed teeth may be:
- genetic inheritance;
- poor nutrition of a child at an early age, incorrect introduction of complementary foods, lack of necessary nutritional ingredients in the diet;
- lack of calcium and phosphorus in the baby’s body, lack of vitamin D;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- rickets;
- chronic diseases;
- complete absence of tooth rudiments (congenital adentia) or too compact their arrangement.
The exact cause of the delay in the development of the dental apparatus can be determined by a pediatric dentist after examination and carrying out the necessary tests.