Back to list Previous article Next article
23.11.2021
Tags:
leptotrichia, leptotrichia
Vote
Leptotrichia are gram-negative anaerobic bacteria. In Latin they are called Leptotrichia. Previously they were called leptothrix. The appearance of microorganisms resembles long and thick rods, slightly curved in the middle, ranging in size from 1 to 15 microns. The ends are straight or pointed. During their life, bacteria often form groups. Colonies look like threads. They often form capsules. For the growth and reproduction of leptotrichia, optimal temperature conditions are required - from 35 to 37 degrees. Celsius. At temperatures below 25° or above 45°, no growth is observed. An additional condition is the need for the presence of carbon dioxide and the absence of oxygen.
How dangerous is leptothrix and where does it come from?
Long-term parasitism of the bacterium on the oral mucosa leads to infection of nearby tissues and the development of leptotrichosis sepsis. Often manifested in the form of oral stomatitis. Some experts consider leptotrichosis to be similar to HIV infection.
The disease was found in 5% of women undergoing gynecological tests - vaginal smears. Recent foreign studies have made it possible to determine the connection between leptotrichia and bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis). The established connection suggests that leptothrix is one of the signs of asymptomatic vaginosis in women.
It is quite easy to catch this infectious pathogen. The microorganism is transmitted sexually and domestically: through the water of stagnant reservoirs, insufficiently clean tap water, dirty bed linen, towels, etc. That is, it is possible to infect a sexual partner with leptotrichosis during sex. It is advisable for both to undergo treatment.
There is an opinion that intrauterine devices are a common cause for the development of the disease.
Back to contents
What is leptothrix
Leptothrix (Leptothrix from Leptos thin + thrix hairs) or in modern terminology leptotrichia (Leptotrichia) is an anaerobic gram-negative bacterium belonging to the family Fusobacteriaceae, forming thin threads or “chains” (trichiae) with segmented ends and a thickening in the center with a diameter of 0.2 - 0.4 microns, which do not branch or bud. Leptorix is characterized by a microscopic sign - “dot-dash”. Optimal growth of the microorganism occurs in the presence of an increased concentration of CO2
| The previously used term Leptothrix (Leptotrichia) vaginalis is not currently used, since it has been established that there are several representatives of the genus Leptotrichia, which are found in the vagina, and they are separated into independent species, for example - Leptotrichia goodfellowii, Leptotrichia hofstadii, Leptotrichia shahii, Leptotrichia wadeii, etc. Therefore, they are designated by the generic term Leptothrix (Leptotrichia) species (spp.) |
Leptotrichosis is not a sexually transmitted disease and vaginal leptotrichosis is not transmitted to men. But why then, you ask, are issues related to leptothrix discussed on the site about sexually transmitted infections?
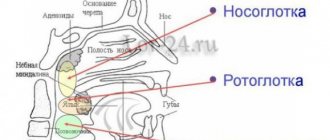
Firstly, leptothrix is often found in mixed sexual infections - trichomoniasis, chlamydia, candidiasis and bacterial vaginosis - i.e. its detection (and it is easily diagnosed by microscopy) should alert the doctor and provide for further more in-depth examination (PCR, bacteriological culture). Secondly, leptotrichosis of the oropharynx is classified as an HIV-associated disease (it is also often found in patients with a significant decrease in immunity, cancer patients, and people with blood diseases).
Third, recent studies have established the role of leptothrix (in modern terminology - leptotrichia) in the development of choriamnionitis, spontaneous abortion, postpartum sepsis, bacteremia in newborns and septic arthritis.
Leptothrix in a smear during pregnancy: diagnosis and consequences
It is worth noting a bacterium from the same family - Leptotrichia amnionii. French scientists managed to isolate it from the amniotic fluid of women who gave birth prematurely. The bacterium caused chorioamnionitis - inflammation of the membranes. The result of this was premature rupture of amniotic fluid and termination of pregnancy.
But the negative impact on the fetus did not stop there. In addition to prematurity and all the problems associated with it, bacteremia was recorded in infants, the presence of the same infectious pathogens in the blood as in the amniotic fluid (water).
Apparently, the bacterium has this effect due to a physiologically determined decrease in the mother’s immunity during pregnancy.
Only the attending physician, a gynecologist who is managing the pregnancy, can confirm or refute the diagnosis. Expectant mothers undergo flora smears at least twice during pregnancy. And if the analysis turns out to have a lot of leukocytes, a competent doctor will prescribe another, additional test - vaginal culture . It is also called cultural research. It takes about a week to complete. Task: to identify which specific microorganisms caused the inflammatory process and which antibiotics they are sensitive to, that is, to prescribe the most effective drug.
It is in the culture that Leptothrix is detected. It must be treated necessarily in the presence of symptoms and (or) in case of confirmation of its subtype - amnionii, even a small amount of which can lead to fetal death.
The PCR test, which is also taken by expectant mothers, helps to identify hidden sexually transmitted infections. They often occur in parallel with leptotrichosis and are dangerous for the fetus.
Back to contents
Causes
The provoking factors causing leptotrichosis are:
- Diseases of the immune system, incl. AIDS.
- Fungal infections, candidiasis.
- Diabetes.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diseases of the oral cavity leading to degeneration of the epithelium of the mucous membrane.
- Metabolic disorders, carbohydrate-protein metabolism.
- Lack of vitamins C and B.
- Taking certain medications (corticosteroids, antibiotics).
Insufficient oral hygiene can also provoke the development of the disease. It is especially often the cause of leptotrichosis in children.
Clinical picture: symptoms and signs
Affecting the mucous membranes of the vagina and cervix, the pathology manifests itself as a gray coating on the walls, and vaginal discharge also becomes gray. And in addition, redness, itching and burning, which intensify during sex. The female body does not show any other reactions. At least in the “non-pregnant” state and with normal immunity.
If a woman has concomitant inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, for example, endometritis, parametritis, salpingitis, then broader symptoms are possible. This is an increase in temperature to 39-40 degrees, headache and muscle pain, dehydration. General intoxication of the body occurs. Such symptoms appear mainly in expectant mothers when leptothrix enters their blood. The same bacterium provokes severe abdominal pain in them. The amniotic membranes are also affected. A child becomes infected with the bacteria in utero .
Back to contents
How is leptotrichosis diagnosed and treated?
The diagnosis is based on a characteristic microscopic picture: the detection of chains of bacteria in the form of a dot-dash. To confirm the diagnosis of a disease associated with Leptotrichia amnionii, culture is used (unlike other leptotrichia, it is not cultured on blood agar) and PCR (16S rDNA). Standard treatment for leptotrichosis has not currently been developed. In typical cases, antibiotic therapy is used. Sensitivity of leptotrichia to beta-lactam antibiotics, clindamycin, metranidazole, tetracycline and chloramphenicol, and resistance to macrolides, aminoglycosides and fluoroquinolones have been noted.
Treatment regimens for leptothrix during pregnancy and beyond
When treating vaginal symptoms of pathology, standard regimens are used to combat bacteria. In the acute phase of the disease, topical antifungal drugs (vaginal suppositories and tablets) are used:
- "Gyno-travogen" (iconazole nitrate) - vaginal suppositories (0.6 g), 1 time per day;
- "Clotrimazole" - tablets (0.1–0.2 g), cream (1–2%);
- "Miconazole", "Gynodactarin" - suppositories (0.1 g);
- "Econazole", "Ginopevaril" - suppositories (0.15 g).
To get rid of bacteria throughout the body, systemic drugs are used, they guarantee relief from vaginal symptoms:
- “Orungal” - take a course of capsules (0.1 g) for 3 days;
- "Ketoconazole" - tablets (0.2 g) 5 days;
- "Diflucan" - capsules (0.05–0.15 g).
Antifungal antibiotics are also used:
- “Pimafucin” - a course of tablets, designed to be taken 4 times a day, 1 piece, 7-12 days;
- "Amphoglucamine" - tablets, 2 times a day, 1 piece, 10-14 days;
- “Nystatin” - tablets (500 thousand units) 4 times a day, course - 2 weeks;
- Clindamycin is an antibiotic for oral administration, the dosage depends on the severity of the disease.
Broad-spectrum antimicrobial and combination drugs:
- metronidazole - tablets for oral administration, 500 mg 2 times a day for a week;
- Terzhinan - vaginal tablets, course on average 10 days.
Vaginal antiseptics:
- "Hexicon" (chlorhexidine);
- "Betadine" (povidone-iodine).
1-2 times a day for a week.
After treatment with any vaginal antimicrobial drugs, the amount of beneficial flora and lactobacilli in the vagina decreases; you can simply wait until everything returns to normal on its own or use drugs to restore the microflora:
- "Lactozhinal";
- "Acilact";
- "Lactonorm";
- "Vagilak";
- "Gynoflor" and the like.
For the treatment of pregnant women, it is permissible to use only a local type of therapy - suppositories, vaginal balls, creams, etc. Other drugs can harm not only the health of the mother, but also the unborn child.
The pathology is usually asymptomatic and the detection of leptothrix bacteria in a smear (if there are no signs of an inflammatory process) is not at all a reason for immediate treatment, since it is also detected in healthy people. This is an opportunistic microorganism. The only exceptions are expectant mothers and a certain subspecies of bacteria.
If you need to undergo treatment for dysplasia, “cauterize the erosion”, and leptothrix is detected in the smear, while the number of leukocytes is normal, there are no inflammatory manifestations - this is not a reason to postpone the procedure.
Back to contents
This is also interesting
- Tank culture from the cervical canal for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics
- What does coccobacillary flora mean, does it need to be treated and how?
- Streptococcus agalactiae in a smear from the vagina, urethra and cervical canal - what to do if detected
Reviews and comments
- Mikhail 41 years old:
March 27, 2022 at 4:44 pmHello. A year ago I saw a dermatologist about seborrheic dermatitis and cheilitis. I was treated with antifungal tablets for 1 month. Symptoms appeared after some time and appeared again. The dermatologist looked at the root of the tongue and said that it was covered with a yellowish-brown coating, then she prescribed a smear from the root of the tongue. They found leptotrichia. She prescribed metronidazole. Now about a year has passed. The tongue is yellowish-brown again, the drool is yellow. The immune system is weak, stress. A year ago I donated blood: lymphocytosis, neutropenia. The hematologist-oncologist said that he didn’t see anything wrong. That there were signs of an infectious inflammatory process. And to re-donate the blood in a month. But he didn’t send it. 2 months ago I took ampicillin for 7 days because of acute respiratory viral infection. I am taking antipsychotics. Now my tongue is yellowish-brown again. I have stomatitis. Tell me how to get rid of leptothyrichia posta
Answer
Routes of infection with leptotrichia and risk factors
Leptothrix in a smear (treatment is carried out using complex methods, traditional medicines and folk remedies are used) is found in a person’s mouth or in a woman’s vagina. Representatives of the stronger sex rarely encounter leptotrichosis. Most men are carriers of pathogens.
The following people are at risk:
- patients with oncological pathologies;
- women who have an intrauterine device (IUD);
- people with a weakened and exhausted body;
- HIV-infected patients;
- patients with hematological pathologies.
Infection of the body rarely occurs during sexual intercourse. The main route of infection is swimming in open water and dirty pools. The likelihood of infection increases significantly if urination occurs while swimming. The risk of infection remains even when carrying out daily hygiene procedures in which tap water is used.
Side effects and contraindications
Terzhinan does not cause exacerbations of existing chronic pathologies. Due to the lack of systemic action, it does not interact with other medications. In rare cases, its use may cause itching and irritation of the mucous membranes. The only contraindication is individual intolerance to one or more components. Its signs:
- severe burning sensation;
- redness of the integument;
- swelling of the mucous membrane or severe pain at the injection site.
In isolated cases, Prednisolone in tablets can provoke erosive lesions of the vaginal walls. In addition, this hormone requires careful use of the drug for hypothyroidism, diabetes, and cardiovascular pathologies.