232 teeth, both embryonic and fully grown, were removed from the mouth of an Indian teenager in a clinic in Mumbai, India. Hyperdontia is the diagnosis the doctors gave him after all the clarifying procedures and exclusion of a malignant neoplasm. And all the supernumerary teeth were extracted during a 6-hour operation. The guy recovered and then returned home, taking his former hyper set of teeth with him as a souvenir.
Hyperdontia may also be called in different sources:
- Polyodontia.
- Supradentia.
- Hyperdentia.
Causes of hyperdontia
Experts do not have a unified theory for the occurrence of this abnormal dental condition. There are 4 recognized versions of the causes of hyperdontia, each of which has the right to exist:
- Embryonic splitting of the root germ of the tooth. It can only be considered as a version if a single, or at most double, splitting occurred. This means that the failure to duplicate the roots of the teeth occurred in the womb, before childbirth, and was caused by some illness during this period.
- Formation of tooth germs beyond the set provided by nature. The reason is the same as in the theory of embryonic splitting during the prenatal period of development. Only the mother had to suffer a very serious illness with treatment with potent drugs. Or in the area of her residence, a critically unfavorable environmental situation is observed from year to year.
- Heredity factor. If the parents had hyperdontia, the risk of its manifestation in the child increases by 2-3 times.
- Manifestation of atavism. Our distant primitive ancestors had not 4, but 6 incisors in each jaw in their mouths. Proponents of the theory of atavism believe that this is an attempt by nature to return the body to its original version of development. True, the atavistic theory cannot explain the appearance of extra molars.
Judging by the statistics collected on hyperdontia, the theory of environmental pollution has the greatest chances. Which, however, is quite consistent with the 2nd and 3rd hypotheses. This is supported by the fact that now the frequency of such developmental disorders has increased, and on a global scale, cases of hyperdontia account for up to 2% of the total number of inhabitants. A huge number if you think about and remember the total number of inhabitants of the Earth.
Spreading
Normally, a person should have 20 baby teeth in childhood, which are replaced by 32 teeth, starting in adolescence. But for the reasons stated above, hypersets with two, four or more redundant teeth can be formed. 2% of people susceptible to this pathology is the total number. But among them it is possible to identify groups in which supernumerary teeth erupt in numbers of no more than two.
The location of such extra teeth (mainly incisors) is the upper jaw, with a shift of the supernumerary units towards the palate. Such people, of the total number of people susceptible to hyperdontia, are about 48%.
The second group is characterized by the growth of canines or premolars, also on the upper jaw. Incomplete teeth appear in them in the amount of one or two.
More than four, six, eight, etc. extra teeth grow only in a rare minority, with hypersets located in the lingual part of the oral cavity.
The remaining cases occur due to the unsystematic appearance of teeth in the lower jaw, on the side of the tongue, lips and cheek.
What does it look like
The main symptom or sign is the presence of extra teeth or even a hint of their appearance in the form of a painful swelling in the mouth. In such cases, the first thing they do is targeted radiography, which allows one to clearly diagnose problems in the area of 4-5 teeth.
If this method turns out to be ineffective, an orthopantogram is used, which reflects a more complete picture of the condition of the roots of the teeth and jaw bones. And to obtain a 3D picture of the condition of the roots and crowns, you can make a computer tomogram.
This anomaly can appear at any age. True, in adults and children the clinical picture of the development of the disease can manifest itself differently.
In children
Extra teeth can come out in the first few months of a child’s life, that is, in full accordance with the timing. But their number will be doubled. Although there have been cases of the appearance of such teeth immediately after the birth of the baby, in the first weeks and even days of its existence.
Both the baby and the mother suffer from such a “toothy” because:
- When teeth grab the nipple, wounds and cracks appear on it.
- In a child, the unpleasant sensations from teething intensify many times over.
- Poor milk flow due to improper latching of the breast.
- The child has difficulty sucking milk.
Manifestations of hyperdontia in an infant can be expressed in:
- Poor nasal breathing due to swelling of the nasal mucosa.
- Severe drooling.
- The gum tissue is swollen and painfully red.
- The temperature rises to low-grade levels, that is, up to 38⁰C, for several days.
If the case is advanced, then the symptoms change to the following signs:
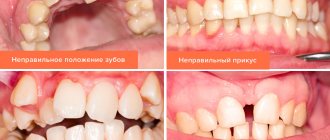
- diction is impaired;
- an incorrect bite is formed;
- due to injury to the mucous membrane of the tongue and the inner surface of the cheek, wounds regularly form on them;
- there is no complete closure of the main dentition.
All this will be especially pronounced if extra teeth begin to grow in the area of the upper palate. Hyperdontia especially hinders children who have begun to develop speech. The first consequence of the appearance of extra teeth will be a lisp due to the fundamental impossibility of pronouncing sounds correctly. After all, teeth that have grown outside the dentition will not allow the tongue to take the correct position when trying to pronounce hissing, voiceless, and voiced consonants. No speech therapist can help solve this problem.
And the presence of extra teeth at primary school age (especially if they immediately catch the eye during a conversation) can serve as a subject of ridicule and even bullying from peers. Which is also fraught with deep psychological problems.
In adults
Abnormal dental development in adults may have the same symptoms as in children. But because the tissues of the oral cavity have already been formed and have essentially stopped in their growth and development, additional symptoms may include:
Dystopian teeth
That is, additional teeth whose growth has stopped and the bite has already been formed. And there is no longer room for the growth of other teeth.
- The growth of extra teeth occurs in the roof of the mouth or in the lingual (tongue-facing) part of the gum. Moreover, in the upper jaw - in the lower jaw, cases of germination of extra teeth are recorded much less frequently.
- The teeth have an incorrect turn, an atypical angle of inclination, and are curved.
- The teeth adjacent to the abnormal swelling become loose.
- In the area of tooth growth, protrusion of the jaw bone is observed.
- The gums often become inflamed, and X-ray examination at the initial stages of the anomaly reveals deformations of the jaw bones - even before the roots of extra teeth form.
In adults, dystopic teeth become a source of psychological problems. Such people are often withdrawn and unsociable. And psychological problems then turn into chronic forms of diseases of the digestive, nervous and endocrine systems.
Impacted teeth
This term refers to teeth that are unable to erupt and remain in the bone tissue of the jaw. A person often does not even suspect their presence until they make themselves felt with all sorts of complications. Namely:
- Loosening of normal, healthy-looking teeth.
- When an impacted tooth is located close to the edge of the jaw, a subcutaneous or axillary protrusion appears on the face.
- At any time of the day, aching pains can appear and just as suddenly disappear.
The most difficult moment is the appearance of supernumerary teeth in place of impacted third molars, or “wisdom teeth.” Which cannot germinate due to the presence of supernumeraries. Because third molars have a large area of chewing surfaces, such attempts to erupt lead to overstraining of the gum tissue and even entangling of the roots of other teeth during the growth process. The consequences of this can manifest themselves in the form of inflammation of the roots of all molars up to and including the premolar.
Types of hyperdontia
There are several of them. And they differ in the degree of inconvenience for their wearer and in the possible consequences. And even according to the subjective feelings of people who have been diagnosed with this disease.
Typical hyperdontia
This pathology is characterized by the presence of extra teeth that began to grow without leaving the dentition in the mouth. Since two normal-sized teeth would be cramped, such teeth, called twins, are reduced in size. This is expressed in the reduction of their coronal part.
The cause of this anomaly is most often heredity.
Atypical or atypical
This pathology with an increase in the number of teeth is characterized by the growth of extra teeth outside the dentition. Usually on the palate, where they can take up almost all the available space. Or the lateral surfaces of the jaw arches, most often from the side of the tongue. It is a very rare form of pathology.
Real (true)
Supernumerary permanent teeth in this type of hyperdontia appear from the formation of excess root buds or when the roots split in the initial stage of their growth. It does not cause significant inconvenience as long as both teeth in a pair of “twins” are healthy. Problems arise if at least one is affected by caries, the treatment of which can be difficult due to the intertwining of the roots of such teeth. For the same reason, there are difficulties with their removal.
False hyperdontia
Probably the most harmless of all, from the “it will go away on its own” series. Although, of course, medical supervision is mandatory in order to avoid developmental complications. It occurs when a child’s bite changes due to the replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones. It occurs when a permanent tooth erupts, when the milk tooth has not yet fallen out. Corrected after the loss or removal of a baby tooth. The decision to remove is made by the doctor.
The long-term coexistence of missing baby teeth and new, permanent ones is not such a rare phenomenon. This happens due to the inattention or even frivolity of parents who missed such an important stage in the development of the child. Especially if the growth of permanent teeth occurs painlessly.
In children
Young mothers need to be especially careful and identify hyperdontia early. Extra teeth can appear very early - in infancy, so they should not be confused with complete baby teeth, which will subsequently be susceptible to their pathological effects. Parents need to be very careful and seek advice from a pediatrician in case of abnormal position and shape of the tooth, as well as if the child has:
- gums become red;
- the temperature has risen;
- increased salivation;
- broken stool;
- does not latch onto the nipple well during breastfeeding;
- pain occurs.
Types of teeth with hyperdontia
Supernumerary teeth in hyperdontia can be divided into several types according to their location in the mouth:
- Spiny. May form on the upper jaw. Localization - between the central and lateral incisors, within the immediate limits of the main dental arches. They are called spiky because of the presence of very sharp ends.
- Additional premolars. They grow from the cheek side within the normal molar units of the dentition.
- Extra fangs. These grow on the upper jaw, in 99% of cases - on the side of the cheek and lip.
- Additional premolars. The localization area of these additional teeth is the lower jaw, on the cheek side.
Additional and primary teeth may fuse. There are 4 types of such merger:
- Bedding. The enamel of both teeth, twin neighbors, grows in the form of tubercles over the entire tooth surface.
- Root merge. The crown parts are located separately, but the roots are fused together.
- Coronal fusion. The root system of each tooth is separate, but the crown part is fused and has one common enamel “shirt”.
- Complete fusion of twin teeth. The crowns, which have a common enamel coating, and the roots are fused together.
Diagnostics
Identifying erupted supernumerary teeth is not difficult. Often, patients themselves, already at the initial examination, complain that they have a tooth that should not be there.
The situation is more complicated with hyperdontia with impaired eruption . In such cases, the main diagnostic method is x-ray (panoramic radiography). It allows you to clearly visualize all dental elements, both normal and supernumerary, as well as their location. The disadvantage of the technique is that the X-ray image is flat and cannot be used to characterize the exact relative position of all teeth and their root systems. Therefore, patients often undergo additional computed tomography .
Treatment of hyperdontia
It happens that there is no need to treat such an anomaly at all: if the teeth do not extend beyond the dentition, do not disturb their shape and do not injure the mucous membrane. In other cases, the presence of supernumerary teeth in the mouth requires serious intervention. Usually a dental surgeon.
It can not only remove unnecessary teeth that clearly interfere with normal life, but also help the necessary teeth to emerge. And the orthodontist will help correct the bite.
Extra teeth must be removed if:
- Milk teeth do not allow permanent teeth to erupt normally, and a growing person retains a “milk bite.”
- In the dental arch, the teeth are positioned incorrectly, grown with displacement and a strong inclination. This phenomenon is called dystopia.
- The crown is stuck in the gum or bone and cannot erupt. This is called retention.
Such pathological cases in dentistry can be treated without difficulty. If, of course, the patient turned to the appropriate doctor on time. Although there are nuances associated with each specific person.
The question of removing extra teeth is decided by the doctor based on: the stage of formation of the dental system, the inclination of the supernumerary tooth, what consequences and defects are predicted from a particular situation.
Sometimes, if supernumerary teeth:
- interfere with normal eruption;
- contribute to the formation of three – abnormal gaps between the teeth, causing caries in the gum pockets, and diastema – an extra-wide interdental space;
- impacted ones are not capable of eruption due to the fact that they are incorrectly formed and strongly inclined;
- may cause bite defects.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of polyodontia is carried out exclusively by a specialized doctor - an orthodontist, who conducts a preliminary examination of the oral cavity and dentition, refers the patient to x-rays (orthopantomography) and analysis of anthropometric casts of teeth made of plaster. Such models are made for a more detailed study of a specific anomalous phenomenon, on the basis of which a diagnosis is then made and treatment is prescribed.
Table of normal human teeth. Deviation from the norm - polyodontia
When examining plaster models made on the basis of dental casts, the doctor measures the size of the teeth, and then analyzes the data obtained based on a special table by Wetzel and Ustimenko. The length of each row of teeth must be measured. This indicator may fluctuate depending on such characteristic individual characteristics of a person as crowding of teeth or the presence of large gaps between them. In the first case, the length will be less than normal, and in the second, a little longer. To diagnose asymmetry, the distance from the midline of the palate (or hyoid frenulum) to the far point of the dentition in one direction or the other is determined.
When to expect supernumerary teeth to appear?
Always. And not just during and immediately after the baby teeth period. This is especially true in cases of hereditary occurrence of such an anomaly. The most common growth zones for supernumerary teeth are the upper incisors, canines, premolars and first molars. It is possible that such teeth will appear not only within the dentition, but also in the area of the upper palate. But the same supernumerary teeth, but within the lower jaw, are found 5-6 times less often.
Sometimes a deep location in the thickness of the jaw can cause extensive trauma if the tooth is “not going” to leave the place of its growth point due to the obstruction of surrounding tissues. Then the surgical intervention is postponed (if not canceled altogether), and orthodontic devices are placed on the dentition.
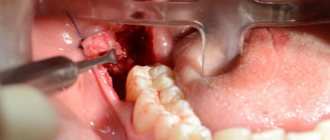
Removal of extra teeth
If the abnormal tooth is located in a simple place, then its removal is carried out in the standard way using forceps. When polyodontia has manifested itself in hard-to-reach places, the extra tooth has several roots or it has not fully erupted, removing it is much more difficult. Most likely, you will have to cut the gum, make a so-called hole to get to the hidden root, then apply sutures to the damaged tissue, apply medicinal treatment after removal, etc. In any case, the surgical procedure for removing supernumerary teeth is accompanied by anesthesia. There are therapy methods using orthodontic treatment.
In the case when the abnormal tooth is located close to the main dentition and it is possible to integrate it into this row, the use of braces is effective. In addition, treatment by an orthodontist may also be indicated after the removal of a supernumerary tooth in order to correct a previously disturbed bite.