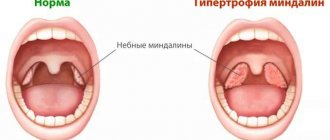
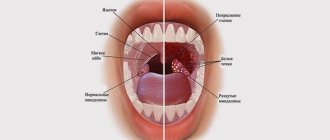
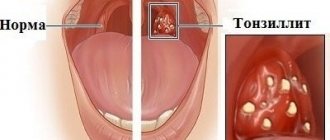
Plugs in the palatine tonsils (or tonsils) are purulent accumulations in the lacunae of the tonsils. In medicine you can find other names for this pathology: purulent plugs, caseous plugs.
Most corks are white, but can have a yellow, brown or gray tint, depending on their composition.
Tonsil plugs may be soft to the touch or harder if they contain a large amount of calcium. Their size varies from a few millimeters to a centimeter. Both men and women are equally susceptible to their appearance, regardless of age.
Some patients mistakenly think that this condition does not need to be treated. But this is fundamentally wrong! The presence of purulent accumulations in the palatine tonsils contributes to the development of complications (not only in the upper respiratory tract, but even in the joints, kidneys and heart!).
Why does an accumulation of pus occur in the tonsils? How to treat tonsil plugs? And is it possible to carry out treatment at home? You will find answers to all your questions in our new article.
Tonsil plugs: causes
To find out the etiology of the occurrence of purulent accumulations in the tonsils, you need to understand what role the palatine tonsils play in the body.
The tonsils are an important organ of the human immune system, which is the first to stand in the way of bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth. As soon as “strangers” reach the surface of the tonsils, they begin to intensify the production of leukocytes, which enter into battle with pathogenic microorganisms. As a result of such “battle actions”, dead leukocytes, bacteria, and epithelial remains accumulate in the lacunae of the tonsils. Over time, minerals accumulate here, and the contents of the lacunae begin to harden, forming caseous plugs.
The main cause of traffic jams is chronic tonsillitis. But they can also form in the palatine tonsils for various reasons:
- accumulation of staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci and other bacteria;
- in people who have a weak immune system;
- frequent sore throats;
- the presence of herpes virus and fungi in the body;
- dental problems (caries);
- viral infections (flu, ARVI).
Each of the above reasons can provoke inflammation of the tonsils. The risk of accumulation of caseous masses in the lacunae of the tonsils is increased by unhealthy diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Traffic jams do not form just like that, for no reason. They are a consequence of another disease and signal that an inflammatory process is underway in the body.
Classification
Experts distinguish two types of tonsil cysts:
- Retention - formed after blockage of the ducts of the glands of lymphoid tissue, have a classic round shape, a thin capsule, filled with serous or purulent secretion. After emptying (evacuation of contents or spontaneous breakthrough), they are filled again.
- Dermoid or congenital - formed during intrauterine development, inclusions of embryonic tissue are always found in them. These true tumors, caused by genetic causes or harm suffered by the mother during pregnancy, are very rare. The capsule is usually dense and the contents are viscous.
Symptoms
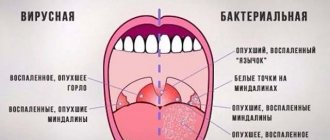
Small accumulations, as a rule, do not cause significant symptoms. With large accumulations, the patient may experience the following symptoms of inflammation:
- bad breath;
- whitish dots are clearly visible on the surface of the tonsils;
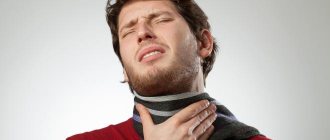
- persistent sore throat;
- pain while swallowing;
- body temperature may be increased to 37-37.7 degrees;
- a feeling of discomfort at the site of accumulation of purulent masses;
- swollen tonsils;
- weakness, lethargy, general malaise;
- decreased performance;
- loss of appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain may radiate to the ears.
Traffic jams appear gradually, so in the early stages of the disease the patient experiences only discomfort when swallowing and a sore throat.
This condition is extremely dangerous for pregnant women! In addition to the fact that it has a detrimental effect on the general condition of the expectant mother, it can negatively affect the development of the fetus and, in the worst case, provoke a miscarriage. Therefore, it is extremely important to contact an otolaryngologist in time to receive competent recommendations on how to effectively treat tonsillitis during pregnancy and avoid complications.
Removal in adults
Methods for removing papilloma are prescribed depending on the patient’s health condition.
Pregnant women are contraindicated:
- use of radiofrequency method;
- ultrasound;
- chemical means.
Radiotherapy is not used if there are:
- cardiovascular disorders;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- malignant neoplasms.
Additional contraindications for prescribing electrocoagulation include blood clotting disorders and individual intolerance to electrical procedures.
But what a tonsil abscess without fever looks like and what can be done about such a problem is indicated here.
Help yourself?
The biggest mistake most patients make is overconfidence that caseous plugs can be removed at home using improvised means. They use a whole arsenal of objects that are absolutely not intended for this: spoons, forks, toothpicks... At best, such amateur activities simply will not bring results, at worst, they will cause injury to the surface of the tonsils and provoke severe bleeding, swelling and inflammation! This will most likely be followed by a sore throat! Plus, if you press incorrectly with a hard object on the accumulation of pus, you can push it even further into the thickness of the tonsil.
Some people try to gargle, believing that gargling will bring relief. Yes, the feeling of discomfort in the throat temporarily passes, but the accumulations of pustules do not disappear, because the rinsing solution comes into contact only with the surface of the tonsils, and getting inside it is extremely problematic, or rather, impossible. Therefore, this method is also not effective.
The best method to get rid of traffic jams is to consult an otolaryngologist!
Our doctors
Gogolev Vasily Gennadievich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist
20 years of experience
Make an appointment
Zharova Galina Gennadievna
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, member of the European Society of Rhinologists, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Debryansky Vladimir Alekseevich
Doctor - otorhinolaryngologist, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Possible complications
As already mentioned, the presence of clusters of caseous masses is not as harmless as it might seem at first glance. The danger of this condition is that pathogenic microflora from the lacunae of the tonsils can spread to other organs beyond the tonsils and provoke various kinds of complications:
- Peritonsillar abscess of tissue around the tonsils. A severe inflammatory process starts in the tissues around the tonsils. A patient with this condition experiences a sore throat. He can't help but feel like there's a foreign object stuck in his throat. There are difficulties with swallowing and wide opening of the mouth (trismus of the masticatory muscles). Periodically, the patient has a fever, and other unpleasant symptoms of intoxication of the body appear. In this case, only opening the peritonsillar abscess, sometimes with the simultaneous removal of the tonsils (abscessonsillectomy), will help improve the patient's condition.
- Cervical phlegmon is an infection of the tissue of the neck. The patient experiences severe pain at the site of inflammation, and the body temperature rises to 40°C. The danger is that a purulent infection can enter the blood and cause sepsis and purulent damage to other organs. The abscess can also descend into the mediastinum - the case where our heart is located. This inflammation is called mediastinitis. This is a disease with an extremely high mortality rate!
- Sepsis (blood poisoning), caused by infection in the blood. This condition is extremely dangerous for humans and requires urgent hospitalization.
- Kidney diseases.
- Joint diseases.
- Heart diseases.
Forms of tonsillitis
Tonsillitis (or sore throat) is an inflammation of the tonsils, often accompanies colds.
Types of sore throats
Sore throats are acute:
- Banal (vulgar or typical) tonsillitis: there are catarrhal, follicular, lacunar, mixed.
- Atypical tonsillitis: herpetic, Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent's tonsillitis, phlegmonous, fungal and mixed forms. Usually they are severe, as they appear against the background of decreased immunity.
- Sore throats associated with infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, sore throat due to HIV infection and others).
- Angina in blood diseases: monocytic, agranulocytic, tonsillitis in leukemia.
Tonsillitis can also be chronic (compensated and decompensated)1.
Interesting fact!
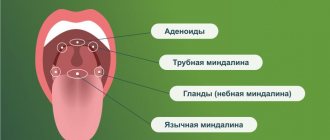
Our defense against infections is located in the pharynx - an anatomical structure consisting of lymphoid tissue. The lymphoid elements in the pharynx are located around the pharynx in the form of a ring, so it was called the “lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring” by Waldeyer-Pirogov. It is formed by two palatine tonsils (those that are sometimes called “tonsils”), one pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal (located on the back wall of the pharynx), one lingual (a collection of lymphoid follicles at the root of the tongue) and two tubal (located in the thickness of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx near the openings eustachian tubes). Tubal tonsils are most pronounced in children under 5-7 years of age, and later undergo reverse development. In adults, due to their small size, they are almost invisible.
The pharyngeal ring is an additional barrier for bacteria between the external and internal environment of the body. These structures also produce antibodies and lymphocytes - immune response cells.
Acute tonsillitis
This is an acute inflammatory disease of the palatine tonsils. Their mucous membrane becomes swollen, hyperemic, and purulent deposits may appear in the crypts of the tonsils. But depending on the factors that caused the disease and the patient’s condition, the process is not limited to damage to the tonsils alone. A severe infection can take over the entire body. The most dangerous complications are rheumatic heart defects, joint damage, kidney damage (glomerulonephritis). Therefore, self-medication can be dangerous. For correct diagnosis and effective treatment, you need to consult a specialist.
Purulent tonsillitis is one of the forms of tonsillitis and can be a complication of acute or chronic tonsillitis. It is characterized by the presence of purulent discharge in the crypts of the palatine tonsils. Most often accompanies a bacterial infection. Improper treatment can lead to chronicity of the process.
Chronic tonsillitis is a persistent chronic inflammation of the tonsils, characterized by recurrent exacerbations in the form of tonsillitis, a sluggish course, and a decrease in the body's resistance to infection. Slight hypothermia or draft causes exacerbation of tonsillitis. Many factors play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory process in the tonsils. Most often the disease occurs after repeated sore throats. Chronic tonsillitis is of two types: compensated and decompensated. This is important for further treatment tactics.
With compensated chronic tonsillitis, examination reveals some looseness of the tonsils, hyperemia, swelling, purulent plugs or plaque in the crypts of the tonsils, but this process is limited to the tonsils and does not spread beyond its boundaries. This precarious balance between local immunity and the body’s resistance on the one hand, and the presence of pathogenic organisms in the inflamed tonsils on the other, can shift towards decompensation if the course of the disease is unfavorable. With decompensated chronic damage to the lymphoid apparatus of the pharynx, local signs of chronic tonsillitis are usually clearly expressed. With this form, exacerbations often occur in the form of sore throats, peritonsillitis, peritonsillar abscesses, regional lymphadenitis, and in clinically advanced cases, disturbances in the functioning of other organs and systems (kidney pathology, formation of cardiac flow, articular syndrome, damage to the nervous system).
Up to contents
Treatment of tonsil plugs
When contacting an ENT doctor, the patient is offered conservative treatment, which includes washing the tonsils, physiotherapeutic procedures and drug therapy.
There are two methods of rinsing: removing pus with a syringe and hardware rinsing. The method using a syringe is used much less frequently if the patient has a strong gag reflex. The most effective method is to wash the tonsils using a vacuum method using the Tonsillor apparatus. In our ENT clinic, we use a special vacuum attachment for this, which has no analogues today! With the help of this attachment, it is possible to effectively and painlessly wash the entire contents of the lacunae of the tonsils, and improve the patient’s condition after the first session.
Removal in children
In children, surgery to remove growths is performed under local anesthesia.
To eliminate papillomas, use:
- cryogenic method;
- electrocoagulation;
- ultrasound.
These methods are the least traumatic, painless, and heal quickly.
Contraindications for treatment:
- presence of open wounds in the mouth;
- temperature;
- cold intolerance;
- blood diseases.
Removal by chemical means is not prescribed. The use of the radiofrequency method, laser and conventional scalpel is limited.
But how the vacuum rinsing of the tonsils occurs and what the price of such a procedure is, is described here.
Diagnostics
Papillomatosis is diagnosed using several methods at once, allowing not only to determine the presence of growths, but also the location of their distribution, the degree of organ damage and size.
Diagnostic methods:
- visual examination by an otolaryngologist using a laryngoscope - a special device for examining the throat;
- examination of the throat using an operating microscope - microlaryngoscopy;
- radiography and computed tomography;
- to identify disturbances in the functioning of the vocal apparatus, in particular, the ligaments, laryngostroboscopy and electroglottography are used;
- analysis of material obtained from biopsy of growths;
- removed papillomas are examined for histology - the presence of cancer cells.
Blood must be taken for analysis.
Papilloma in the throat is detected by a doctor during a visual examination. To clarify the extent of the spread of the disease, it may be necessary to examine the larynx using a laryngoscope.
Infectious granulomas and malignant neoplasms give a similar visual picture, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected tissue is performed, followed by histological examination of the material. The patient may also be prescribed a blood test for HPV to determine the strain of the virus.