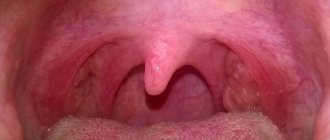
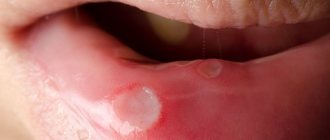
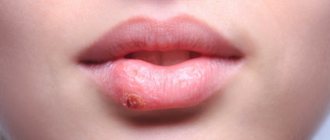
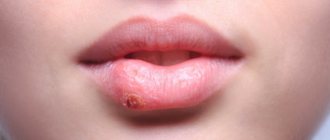
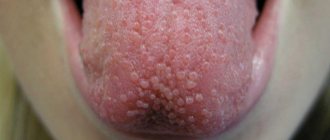
Chronic tonsillitis is a chronic inflammation of the tonsils.
The palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils) are an important part of the human immune system.
Bacteria, viruses, and microscopic fungi enter us with food and air. They settle on the mucous membranes, where they are picked up by a constant current of mucus, and this “river” flows in the direction of the oropharynx, just where the tonsils are located behind the palatine arches.
The palatine tonsils are like a sponge. They are dotted with gaps. When we swallow a bolus of food soaked in infected mucus, this mucus enters the lacunae of the tonsils. There, foreign microorganisms are attacked by the guard cells of the primary immune response: neutrophils and macrophages. The latter not only kill the infection, but also “cut” it into small molecular fragments, on which young cells of the secondary immune response—lymphocytes—are then “trained.” Prepared and trained lymphocytes emerge from the tonsils and “spread” throughout the mucous membranes of the pharynx and nose, forming a fairly reliable secondary specific defense.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
In fact, inflammation occurs constantly in the tonsils - this is their function. But sometimes the protective resources of the tonsils are unable to cope with the infection, and then the inflammation, which gets out of control, turns into a serious disease - tonsillitis.
The acute form of tonsillitis is tonsillitis. Untreated tonsillitis often develops into chronic tonsillitis. Conversely, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis leads to an outbreak of tonsillitis. If a person gets tonsillitis every year or several times a year, then he most likely has chronic tonsillitis.
Sometimes chronic tonsillitis can develop even if a person has not had a sore throat. This is possible if there is a source of infection that can affect the tonsils for quite a long time, for example, untreated caries or chronic sinusitis.
Danger
Tonsillitis is not a disease that can be fatal, but it can cause serious complications. Thus, patients are often diagnosed with:
- peritonsillar abscess;
- formation of ulcers on the tonsils;
- acute rheumatic fever 1-4 weeks after recovery;
- joint inflammation;
- the occurrence of acquired valvular heart defects;
- kidney diseases;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- tonsillar sepsis (infection through the bloodstream spreads throughout the body).
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
The inflammatory process in the tonsils can spread to neighboring organs, and then the person may complain of nasal congestion, sore throat, dry cough, and these secondary symptoms may be predominant.
With chronic tonsillitis, there may also be complaints of pain in the joints (knees, elbows, wrists), especially in the evening and when the weather changes, fleeting pain in the heart, a feeling of palpitations without physical activity, pain in the lumbar region. The ECG may reveal arrhythmia and tachycardia.
Such symptoms are a serious cause for concern, since they can accompany the development of severe autoimmune diseases of the kidneys, heart, and nervous system, which are complications of tonsillitis. This occurs when inflammation in the tonsils causes the immune system to malfunction; as a result, antibodies are produced, but not to the causative agent of the disease, as it should be, but to the heart muscle, joint tissue and connective tissue. When the body's defense system is upset, it tries to destroy the body itself.
The insidiousness of chronic tonsillitis also lies in the fact that it can occur without obvious symptoms. In this case, between outbreaks of sore throat, the person does not complain of anything, although a focus of inflammation remains in the tonsils.
The main symptoms of chronic tonsillitis itself are:
Sore throat
With chronic tonsillitis, there is pain in the throat when swallowing, especially in the morning. The appearance or intensification of such pain can be caused by swallowing cold food or liquid.
Feeling of discomfort in the throat
There may be no pain as such, but there may be discomfort when swallowing, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
Low-grade fever
With chronic tonsillitis, there may be a temperature that does not decrease over a long time (37.2-37.5°C).
Bad breath
Inflammation in the tonsils can manifest as persistent bad breath.
General weakness
Typical manifestations of chronic tonsillitis are increased fatigue, sweating, weakness, and poor health.
Symptoms of the disease
Angina:
- pain in the throat when swallowing;
- increase in body temperature;
- the presence of purulent plugs on the tonsils;
- headaches;
- enlarged lymph nodes and their pain;
- a state of general weakness.
Chronic stage of tonsillitis:
- discomfort and pain when swallowing;
- presence of bad odor from the mouth;
- excessive fatigue;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- sleep disturbance;
- enlargement and tenderness in the cervical lymph nodes.
Treatment methods for chronic tonsillitis
It is very important to defeat chronic tonsillitis: otherwise, there remains a constant source of infection and intoxication of the entire body, not to mention the threat of severe autoimmune complications.
Home methods can reduce the severity of symptoms, but achieving a complete cure is difficult. Tonsillitis is a disease that is too complex in its nature and course. Therefore, if you suspect chronic tonsillitis, you should consult a doctor.
First of all, a comprehensive examination should be carried out to determine the pathogen and the stage of development of the disease.
Before treating tonsillitis, it is necessary to eliminate other sources of infection - cure carious teeth, inflammatory processes in the nose and paranasal sinuses. If your child often suffers from sore throats, then it is very likely that one of the family members is a carrier of the infection. In this case, it makes sense to get the whole family examined.
With complaints corresponding to the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, you can contact a general practitioner (family doctor or therapist) or a specialized specialist - an otolaryngologist (ENT).
Children's appointments are conducted by qualified pediatricians and ENT doctors.
The Family Doctor clinics have the necessary equipment and a staff of qualified specialists to conduct examinations, establish diagnoses and perform all procedures in accordance with the prescribed course of treatment, and, if surgical treatment is required, to perform operations.
In the treatment of chronic tonsillitis the following are used:
Washing the lacunae of the tonsils
The course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis, as a rule, involves washing the lacunae of the tonsils using vacuum drainage. During rinsing, various anti-inflammatory drugs are used that penetrate deep into the tissue, destroying microorganisms that multiply in the tonsils.
Physiotherapy
In parallel with washing the tonsils, physiotherapeutic procedures (treatment with short-wave ultraviolet radiation, magnetic laser therapy, phonophoresis) can be prescribed.
More information about the treatment method
Antibacterial therapy
If chronic tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection, it is treated with antibiotics.
More information about the treatment method
Surgery
If the inflammatory process has gone far enough, surgical treatment methods are used. At JSC “Family Doctor” you can use the modern method of laser tonsillotomy. Laser tonsillotomy is a high-energy treatment of the palatine tonsils, in which only the affected part of the tonsils is removed. The tonsils themselves are preserved, if possible, which is very important for the immune system. In the most severe cases, the tonsils are completely removed.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of tonsillitis in children and adults is made on the basis of anamnesis, ENT examination data and some additional diagnostic measures. During farinoscopy (the condition of the pharynx is assessed under special lighting conditions), hyperemia, swelling and thickening of the palatine arches are determined. In children, pronounced loosening of the tonsils is often observed. The lacunae may contain pus. The doctor also notes an enlargement of the lymph nodes.
To determine the causative agent of tonsillitis, a smear is taken from the back wall of the pharynx and the surface of the tonsils. The resulting sample is sent to the laboratory for microsporation of the material. This allows you to understand which microorganisms provoked tonsillitis (usually staphylococci or hemolytic streptococci).
Additionally, the patient may be given an antibiotic sensitivity test. Its results enable the ENT specialist to select the most effective treatment. Urine and blood tests are also mandatory.
A biopsy for tonsillitis is performed extremely rarely, since lymphocytes are present in both the inflamed and healthy tonsil. The method is used if there is a suspicion of the development of a malignant neoplasm.
Results of a clinical blood test for tonsillitis:
- the ESR level rises to 18-20 mm/h;
- the number of neutrophils in the blood is up to 7-9x109/l;
- the number of immature neutrophils (band neutrophils) increases, metamyelocytes and myelocytes appear (band shift to the left).
In some patients, despite the presence of tonsillitis, tests remain normal.
Surgery. Do I need to have my tonsils removed?
Surgical intervention includes partial tonsillotomy or complete removal of the tonsils - tonsillectomy.
The presence of chronic tonsillitis does not mean that surgery is needed in 100% of cases. Increasingly, ENT doctors are trying to treat patients conservatively.
If frequent tonsillitis is accompanied by the development of paratonsillitis or paratonsillar abscess, then this is a direct indication for tonsil removal.
The tonsils can become so large that they interfere with the patient's swallowing and breathing, so either partial or complete removal of the tonsils is performed.
It is worth noting that the operation should be carried out without an exacerbation!
Tonsillectomy
Chronic tonsillitis can be cured. To get rid of it forever, the tonsils are removed. However, the operation is often postponed, justifying the decision by the participation of these formations in the formation of immunity.
In fact, the mass of the tonsils constitutes only 0.05% of the total mass of lymphoid tissue, which mediates the systemic immune response3. The functions of protecting the respiratory tract from microorganisms penetrating through the mouth and nose are taken over by other tonsils3: paired tubal and unpaired lingual and pharyngeal tonsils. Moreover, the tonsils affected by infection lose their functions1 and turn into a focus of infection that can cause serious illnesses.
The operation is performed in a hospital setting. It involves complete bilateral removal of the tonsils along with the surrounding capsule and often does not require general anesthesia5.
Contraindications to it are:
- blood diseases accompanied by a decrease in blood clotting;
- severe cardiovascular, renal, hepatic and pulmonary insufficiency;
- severe course of hypertension;
- heart problems such as cardiosclerosis with angina pectoris5.
The operation should be postponed if it is necessary to treat acute respiratory viral infections and other infections and concomitant diseases, the exacerbation of which is possible as a result of surgical intervention.
Up to contents
Literature
- D.L. Yalymova, V.V. Vishnyakov, V.N. Talalaev, V.N. Kostyuk. Chronic tonsillitis: diagnosis, classification, treatment. Directory of a polyclinic doctor. 2014; 08: p. 29-31.
- Chronic tonsillitis. Directory of a polyclinic doctor. 2014; 09: p. 43.
- G.S. Maltseva. Chronic tonsillitis: current issues (clinical lecture). Consilium Medicum. 2011; 11: p. 32-38.
- A.I. Kryukov, Yu.V. Better. Sore throat and chronic tonsillitis: the problem of choosing an antibacterial drug in an outpatient setting. Directory of a polyclinic doctor. 2007; 04: p. 42-44.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution.
Up to contents
Surgical removal of tonsils
If we talk about the removal of the tonsils, then the operation to completely remove the tonsil tissue is called a bilateral tonsillectomy.
Partial removal of the tonsils is called a bilateral tonsillotomy.
It is extremely rare that the palatine tonsil is removed routinely on one side. There is also a practice of a number of hospitals (they like to do this in the Pirogov City Clinical Hospital No. 1) of removing the palatine tonsil or tonsils in case of a paratosillar abscess. This operation is called abscessonsillectomy. But it must be remembered that against the background of severe pain caused by an abscess, removal of the tonsil is extremely painful. Due to the purulent process, it is impossible to provide adequate anesthesia. Therefore, it is necessary to anesthetize the peri-almond tissue only with strong anesthetics: Ultracaine and Ultracaine DS-forte.
Routinely, palatine tonsils can be removed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia. Previously, this operation was performed only under local anesthesia.
Fortunately, there is now modern equipment that allows removal of palatine tonsils under general anesthesia or under anesthesia using cold plasma coagulation - Coblator.
Features and causes of the disease
Tonsillitis occurs in acute (angina) and chronic forms. The peak incidence occurs in the autumn or spring. Children get sick twice as often as adults. Due to the structural features of the organs of the peripheral immune system, which include the tonsils of the peripharyngeal ring, they often do not perform a protective function, but themselves become a source of infection due to constant inflammation in them.
Tonsillitis occurs due to a weakened immune defense and in the presence of provoking factors. The development of the disease is promoted by:
- hypothermia of the body;
- bad habits: smoking and alcohol abuse;
- hypo and vitamin deficiencies;
- throat injuries;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the nasal and throat cavities, paranasal sinuses;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- hereditary predisposition to throat diseases;
- hypoplasia of lymphoid tissues and other causes.
The disease can also provoke impaired nasal breathing and concomitant somatic diseases of various organs and systems that affect the overall reactivity of the body.
The causative agents of inflammation of the palatine tonsils are most often adenoviruses, coccal flora (streptococci, staphylococci), chlamydia, rhinoviruses, herpes viruses, parainfluenza.
Acute tonsillitis in pregnant women
The pregnancy period is always accompanied by a physiological decrease in immunity due to complex hormonal changes, therefore, during the period of colds, the body's susceptibility to bacteria and viruses increases or activation of any chronic foci of infection, including chronic tonsillitis, is possible.
throat or acute tonsillitis are extremely undesirable diseases during pregnancy, since treatment of this group of patients can be difficult due to restrictions on the use of most medications, especially antibiotics. Therefore, the prevention of colds during the period of influenza and ARVI is of great importance: avoid crowded places, avoid contact with people with sore throat, thoroughly wash your hands, ventilate rooms, walk in the fresh air.
Pregnant women suffering from chronic tonsillitis without exacerbation are recommended for local treatment in the form of gargling with herbal solutions at home.12
The use of ANY medications, including dietary supplements, is permissible only after consulting your obstetrician-gynecologist!