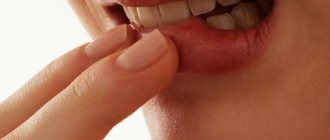
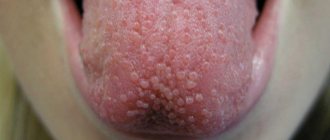
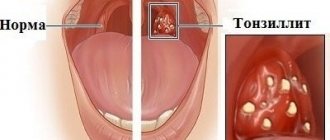
Oral papillomas are benign neoplasms in the oral cavity that grow from epithelial cells. Papillomas are discovered during a dental examination and look like separate growing seals on a small stalk, they are painless and have a white or pale pink color.
This type of neoplasm in the oral cavity is diagnosed most often. About 60% of patients are women aged forty years, about 20% are teenagers of any gender. Often, adults experience the appearance of individual papillomas, while children may experience so-called papillomatosis (multiple papillomas). In half of the cases, papillomas are localized on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Papilloma in the mouth: causes of appearance
The most common cause of this type of tumor is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Factors that provoke the appearance of papillomas in the oral cavity are, for example, constant microdamage to the cheeks and tongue. A relatively small damage is enough for viral particles to penetrate inside and trigger the formation of papilloma. In children, the provoking factor is a too short frenulum of the tongue - the lower incisors injure it, creating a gateway for infection.
When analyzing papilloma under a microscope, it can be noted that this neoplasm is a tumor, which consists of many layers of epithelial tissue, which in some places has become significantly keratinized. In some areas, traces of the appearance of a focus of inflammatory infection can be noted.
Causes of papilloma
This disease is caused by papilloma, a viral infection that has a long latent, that is, hidden, period. The time during which the disease does not manifest itself after the virus enters the body takes from two months to five years. This is the main danger of such a disease, because in such cases immediate intervention by a surgeon is required, and delay can cause death. The main reason for the formation of papilloma on the gums is a decrease in human immunity.
Classification of oral papillomas
Based on the number and concentration of neoplasms, oral papilloma is differentiated from papillomatosis – a massive accumulation of neoplasms in one place.
According to their origin, papillomas are divided into the following types:
- Traumatic (reactive) papilloma. May appear after traumatic effects of a mechanical, chemical or temperature nature. A distinctive and characteristic feature of reactive type oral papilloma is that their growth stops immediately after the irritant that caused them is eliminated.
- True (neoplastic) papilloma. This type of papilloma begins to develop after the mechanism of cell division, growth, and differentiation is disrupted. In most cases, this type of papillomas appears in the distal part of the cheek, in the area located behind the molars and in the area of the pterygomandibular fold.
- Viral papilloma of the oral cavity. May appear after the patient has been infected with the human papillomavirus. This type of infection occurs through direct contact with a carrier of the virus. When the integrity of the oral mucosa is compromised (for example, due to microtrauma), a path for infection appears.
Treatment of oral fibroids
Surgery remains the most effective and most common therapeutic method. The seal is excised using a laser or radio waves. This procedure lasts about half an hour. If the tumor is very large, after its removal the wound is covered with a flap, which is formed by the doctor from the surrounding tissue.
When pathology is caused by taking certain medications, they should be completely eliminated and replaced with alternatives with similar properties. After discontinuation of drugs in such cases, the appearance of the mucous membranes is often restored without outside help, and the likelihood of relapse approaches zero. However, this does not apply to situations where the disease is advanced.
Surgery can also be avoided in case of traumatic effects of orthopedic structures. For example, when a crown, filling, or prosthesis puts pressure on the tissue. Elimination of the provoking factor often leads to a decrease or complete disappearance of a benign formation. Most likely, it will be necessary to dismantle the old structures and replace them with new ones.
On the Internet you can find stories of healing using home remedies. It is worth remembering that the disease cannot be treated with the help of folk recipes. Herbal decoctions and infusions, and other compositions are used only as an auxiliary element of complex therapy.
Treatment of oral papillomas
Diagnosis of this disease includes a collection of the patient’s medical history, as well as a thorough histological examination of removed papillomas.
Treatment of papillomas is only surgical. The neoplasm is excised down to the borders of healthy tissue. Techniques such as electrocoagulation, cryosurgery, sclerotherapy and others are rarely used, since as a result of their implementation it is impossible to conduct a histological analysis of the papilloma removed to the base.
If a large accumulation of papillomatous neoplasms is detected, a combined technique is used: a scalpel is used to dissect the largest number of papillomas accumulated in one place, and single papillomas are removed using electrocoagulation.
If oral papillomas have a viral etiology, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is prescribed along with surgical intervention to prevent relapses.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, relapses may occur with greater or lesser probability. So, if there is a human papillomavirus in the body, the risk of papillomas returning after surgery is quite high.
Papillomas in the throat - treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis
Let's take a closer look at how complete treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis in children and adults occurs, its full cycle, in the Yesong center, in Korea.
Data from the study:
1 OPERATION
“The intratrochlear excision method is the surgical removal of masses of papillomas with the capture of a 2 mm layer of the mucous membrane, including submucosal glands, using minimal cold instruments for children and some adults, with complete removal of the papilloma, especially if the papilloma has re-formed at the site of the scar from a previous operation and CO2 laser applications. Papillomas are excised to a healthy mucous membrane, all infected parts of the mucous membrane are removed.
IMPORTANT: Since papillomas cells can grow deep into the tissue, destroying the membrane barrier, complete removal of the submucosal gland in the affected area is necessary to reduce the risk of relapse.
Next, the surface of the larynx is treated with a 585 nm pulsed color dye laser ( PDL laser) or KTP laser to prevent scarring and stenosis formation. In the study, the use of cold instrumentation followed by treatment with a PDL laser instead of a CO2 laser resulted in a significant reduction in laryngeal scarring. Minimizing the formation of scars and scarring of the vocal folds after surgery is the basis for effective voice restoration in the subsequent recovery period.
After laser treatment, Cidofovir into the affected area to prevent future relapses.
The operation is completed with the “microflap” technique - suturing the vocal cords in order to minimize the adhesive process and possible stenosis of the larynx.”
Laryngoscope 126: June 2016 Kim and Baizhumanova: Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis and Its Treatments. Page 1360-1361
2 OPERATION
On the 4th day after the first operation, a second throat operation is performed . After the first operation, fibrin is formed on the operated surface, in simple words - a film. If it is not removed, it becomes a denser tissue, and adhesions appear, which lead to laryngeal stenosis, that is, fusion. Fibrin is removed during a second microsurgery under general anesthesia. This procedure helps prevent the formation of adhesions and stenosis on the vocal cords.
3 OPERATION
Next, on days 8-9 after the first operation, the final operation is performed under general anesthesia to remove fibrin. During the third surgical intervention, additional tissue treatment is performed with drugs that prevent tissue fusion. Laryngeal microsurgery is repeated using the “microflap” technique: suturing the vocal cords to prevent vocal cord adhesions and stenosis.
REPEATING THE CYCLE
In a number of serious cases of recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis, it is necessary to resort to repeating the entire cycle. It must be remembered that this disease is a manifestation of a virus that is in the human body. When the immune system is weakened, even after a full cycle of treatment, the body may malfunction and a relapse occurs again. Therefore, it is important after treatment to take seriously the restoration of immunity and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Contact the clinic
Treatment
Treatment of papilloma is complex; it includes not only drug therapy, but also vitamin supplementation. Traditional methods show effectiveness, but only if the inflammatory process has not yet started.
Sanitation of the oral cavity
Sanitation of the oral cavity is a mandatory stage in the treatment of papillomas.
Sanitation is a comprehensive measure aimed at removing concomitant diseases that affect the growth of the tumor or interfere with its treatment. It includes:
- treatment of inflammation;
- removal of plaque and tartar, treatment of caries and filling, installation of crowns, etc.;
- cleaning dentures;
- cleaning the braces (usually surgery, if necessary, is carried out after they are removed).
Sanitation of the oral cavity is necessary to reduce the risk of relapse. If they are not carried out, then the probability of re-growth increases by 2-3 times. After completing comprehensive oral therapy, the doctor prescribes special antibacterial tablets and rinsing with medical solutions for disinfection and healing.
Drug therapy
After sanitation, drug therapy is prescribed. Medications are used to boost weakened immunity. Panavir has proven itself, which must be used for two weeks. Also prescribed as therapy:
- Viferon (they need to lubricate the affected area, helps healing, has an antiseptic effect);
- Dimexide (gargle with it several times a day, avoid ingestion).
Likopid Isoprinosine tablets, Genferon suppositories, Allokin-Alpha solution are effective. The correct combination of medications is prescribed by a specialist after examining a specific case, identifying the cause and assessing the risks of relapse.
Traditional methods
You can alternate compresses with other treatment methods.
Alternative medicine methods have their place. They are not as effective as pharmaceutical drugs, but allergic reactions to them are extremely rare. There are such methods:
- crushed garlic mixed with Vaseline is applied to the affected area overnight;
- pickled lemon is fixed to the skin with a band-aid and waited for several hours;
- mashed potatoes with egg yolk are applied as a compress;
- lubricate the affected area with essential oils of juniper, orange, and tea tree.
Traditional methods are used for at least two weeks to achieve results. This makes it impossible to say that they are effective. To treat a viral disease, it is better to immediately consult a specialist.
Symptoms and signs of oral cancer
A developing tumor may cause one or more of the following symptoms:
- A non-healing ulcer or sore on the lip or mouth.
- White or red spots on the gums, tongue, tonsils, or lining of the mouth.
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing.
- Persistent pain in the mouth.
- Impaired jaw or tongue movement.
- Swelling or lumps on the lips, mouth, or cheek.
- Pain or discomfort in the throat, feeling of a “lump” stuck in it.
- Numbness of the tongue, lips, or other area of the mouth.
- Voice change.
- Growths in the neck or back of the throat.
- Earache.
- Weight loss.
Many of these symptoms can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, including other types of cancer. If at least one of them does not go away for more than 2 weeks, you should definitely seek medical help.
Pregnancy with papilloma virus
The papilloma virus passes from mother to fetus during childbirth in 98% of cases. The child passes through the birth canal, which is literally strewn with condylomas. As a result, the virus enters the fetus's mouth and eyes. For this reason, every woman who is planning a pregnancy should be pre-tested and, if necessary, treated for HPV and STDs. Only after finishing the therapy process can you start thinking about your future child.
If the disease was latent and was detected only during pregnancy, which often happens (the body’s defenses weaken during pregnancy), then you should immediately consult a doctor.
Laryngeal papillomatosis
You can also distinguish papillomatosis of the respiratory tract. With this disease, the tissue that lines the nasopharynx grows from the nose to the lungs. The larynx is also often affected. Respiratory tract papillomatosis is also a type of disease caused by the papilloma virus. In this case, formations are classified as benign. Local and ENT doctors cannot always identify this disease. More often they simply shrug their shoulders and prescribe rinses. In this regard, we recommend that you contact a private clinic.
What is the best way to treat?
A large number of papillomas certainly causes inconvenience and does not look aesthetically pleasing. However, this is not a reason to use old-fashioned methods for removal with thread, pliers or a blowtorch.
For single small (1x1 mm) formations, celandine juice
- a proven folk remedy.
When there are many papillomas or they are large, this method is not suitable
, as it can last for months and lead to severe inflammation.
Removal using radio wave surgery is much more convenient and effective
The operation does not require special preparation, is practically painless, and after it you can drive a car.
Once I had the opportunity to remove about 70 papillomas from one patient at once. It is difficult to convey all the joy of a person who got rid of them, whom they tormented for several years.
Removal of papillomas
Removal of papillomas is a method used in 80% of cases. The surgical intervention is painless, because before it the oral cavity is anesthetized. High accuracy is achieved through the use of the latest surgical methods. It is not always possible to get rid of a tumor in one visit; in this case, complex therapy will be required.
Removal methods:
- Removal with a scalpel. This method is old and is used if the patient has a limited financial budget and there are no other options for removal. The formations are cut off and there is a possible risk of scarring. It is prohibited to use it to remove papillomas on the lips.
- Laser. The growth is burned out layer by layer, while the remaining tissue remains undamaged. The method is modern and effective, no scar remains. Its only disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure.
- Medical loop. The papilloma is captured and gradually removed from the tissue. The method avoids re-infection and is characterized by rapid healing.
- Ultrasound. High-intensity ultrasound destroys infected tissue while sparing others. The method is effective and safe, but it costs a lot.
- Electrocoagulation. Removal occurs by microwave or electric current. Used primarily to work with formations under the tongue.
- Conchotom. Extracting the affected areas of the mucosa using biopsy forceps. The method is effective and safe, indicated for growths in the oral cavity, and not outside it.
- Radio waves. The impact of the waves is painless and safe for the patient. Histology confirms the benign nature of the neoplasm.
Is human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted disease?
HPV can be deciphered as a virus that causes a benign tumor of epithelial origin in the form of a papilla. Papilloma is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Unfortunately, today this concept has expanded significantly. If previously only a few, as it seemed then, “frightening” classical diseases of Venus were known, which in fact are easily treated and detected quickly (gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chancroid), today the list of STDs includes many dangerous, severe detectable, and sometimes difficult to treat and completely incurable (HIV) diseases. Moreover, their number is constantly growing.
Today, the list of “new” STDs includes mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis, ureaplasmosis, candidiasis, genital herpes and human papillomavirus. Growths from papillomavirus identified in the genital or perianal areas are called genital warts. In fact, both condyloma and papillomavirus are the same virus, just different strains (varieties).
Genital condylomas in the perineal area can appear either one at a time or as whole growths that look similar to cauliflower. In some cases, such formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and bleeding.