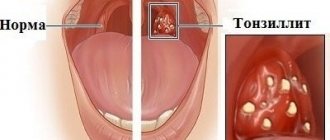
Tonsils
(
tonsillae
) - accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the thickness of the mucous membrane at the border of the nasal, oral cavities and pharynx. Depending on the location, there are palatine tonsils (tonsillae palatinae), pharyngeal tonsil (tonsilla pharyngea), lingual tonsil (tonsilla lingualis), tubal tonsils (tonsillae tubariae). They form the main part of the Pirogov-Waldeyer pharyngeal lymphoepithelial ring (Fig. 1). In addition to the tonsils, this ring includes accumulations of lymphadenoid tissue embedded in the mucous membrane of the outer parts of the posterior wall of the oropharynx, parallel to the velopharyngeal arches, the so-called. lateral ridges of the pharynx, as well as single follicles scattered in the mucous membrane of the pharynx (folliculi lymphatici pharyngei). The tonsils are part of a single lymphoepithelial apparatus that develops in the mucous membrane of the digestive, respiratory and genitourinary systems in the form of solitary lymphatic follicles (folliculi lymphatici solitarii) or group lymphatic follicles (folliculi lymphatici aggregati). During the process of phylogenesis, the accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the mucous membrane at the border of the pharynx and the oral and nasal cavities in the form of tonsils was first noted in mammals.
Embryology
Rice.
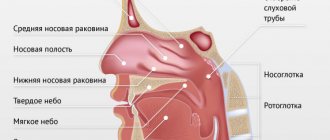
1. Schematic representation (sagittal section) of the nasal, oral cavities and pharynx: 1 - lingual tonsil; 2 - palatine tonsil; 3 - pharyngeal (nasopharyngeal) tonsil; 4 - tubal tonsil; 5 - scattered lymphatic follicles in the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall. Rice. 2. Schematic representation of the anatomical variants of the palatine tonsils (according to K. A. Orleans with some modifications): 1 - free tonsil protruding into the pharynx; 2 — the mouth of the accessory intrapalatal tonsil; 3 - additional intrapalatal tonsil; 4 - sine of Turtual; 5 - muscular wall of the tonsil fossa; 6 - tonsil capsule; 7 - triangular fold; 8 - tonsil, pinched in the palatine arches; 9 - upper corner of the tonsil fossa; 10 - large palatine lobule. The formation of the tonsils occurs during the prenatal period of development in the area of the head intestine. There is a certain sequence in their formation and development. First of all, the palatine, then the pharyngeal, lingual and tubal M. appears. The palatine M. are laid at the bottom of the second gill pouch at the end of the 2nd - beginning of the 3rd month in the form of a protrusion of the endoderm. The latter gives rise to the epithelial cover and crypt system of M. Lymphoid tissue of M develops from the surrounding mesenchyme. At the 8th month of intrauterine development of the fetus, lymphatic follicles of M. (folliculi lymphatici tonsillares) appear, and by the end of the 1st month of the child’s life, centers appear in them reproduction (centrum multiplicationis). Pharyngeal M. is formed in the 3rd-4th month in the form of 4-6 folds of the mucous membrane in the area of the pharyngeal vault. At the 6th month, lymph follicles appear for the first time, and at the 2nd - 3rd month after birth, reproductive centers appear. Lingual M. is formed as a paired formation in the 5th month in the form of longitudinal folds of the mucous membrane of the root of the tongue. At the 6th month, the folds fragment, at the 7th month, follicles appear, and at the 3rd - 4th month after birth, reproductive centers appear. Tubal M. are formed in the 8th month in the form of separate accumulations of lymphocytes around the pharyngeal opening of the auditory tube. By the birth of a child, follicles are formed, and in the first year of life, reproductive centers are formed.
FEATURES OF THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD
Despite the fact that tonsillectomy is one of the most common operations in modern otolaryngology, the patient’s condition must be monitored by qualified specialists in the postoperative period. The patient is transferred to the ward on a gurney or in a sitting position, depending on the type of anesthesia used. For quick recovery, it is recommended to use dry ice every two hours for 5-15 minutes. This prevents the appearance of swelling and inflammation.
Feeling is restored a few days after the operation. During the first day, you should not swallow saliva - you need to keep your mouth slightly open so that it flows by gravity. In the early postoperative period, you should not talk. If minor sore throat occurs, the doctor will prescribe a pain reliever. He also recommends the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which, in addition to the analgesic effect, prevent the development of an inflammatory reaction. In general, patients tolerate the operation easily and can return to their usual activities almost immediately.
During the first days after surgery, you can eat mostly soft, pureed foods. Avoid hot drinks. According to indications, specialists can prescribe medications to prevent bleeding. Antibacterial drugs are used to prevent the development of infectious complications.
For two weeks after surgery, physical activity is limited. It is forbidden to visit the bathhouse or actively engage in sports. You should also not actively gargle for the first days after tonsillectomy.
Anatomy
Palatal
The tonsil is a paired formation located in the fossa of the tonsils (fossae tonsillares) of the lateral walls of the pharynx between the palatoglossus arch (areus palatoglossus) and the velopharyngeal arch (areus palatopharyngeus). It has an oval shape, its long axis runs from top to bottom and somewhat from front to back. In a newborn, the size of the palatine m. in the vertical direction is 10 mm, in the transverse direction 9 mm, thickness 2.1 mm; in an adult, respectively, 15-30 mm, 15-20 mm, 12-20 mm. In the palatal M., two surfaces are distinguished: internal (free) and external, facing the wall of the pharynx. The inner surface is uneven, covered with a mucous membrane, has 8-20 irregularly shaped tonsillar dimples (fossulae tonsillares), which are the mouths of tonsillar crypts (cryptae tonsillares), which, branching, penetrate the thickness of the palatine membrane. The crypts increase the free surface area of each palatine membrane up to 300 cm2. When swallowing, the palatine membranes are slightly displaced, and their crypts are freed from their contents. The outer surface of the palatine membranes is covered with a capsule (capsula tonsillae) up to 1 mm thick; on it lies a layer of loose paratonsillar tissue, the edges go down to the root of the tongue, in front it communicates with the tissue of the palatoglossal arch, at the top - with the submucosa of the soft palate. In an adult, the distance to the internal carotid artery from the upper pole of the palatine M. is 28 mm, from the lower pole 11-17 mm, to the external carotid artery 41 mm and 23-39 mm, respectively. The upper corner of the M.'s fossa remains free and is called the supratonsillaris fossa. Sometimes there is an additional palatine M.—the palatine lobe of the palatine M., the edges of which can extend deep into the soft palate and not have a direct connection with the main palatine M. (Fig. 2). In these cases, it represents an additional intrapalatine M. (tonsilla intrapalatina accessoria), the edges usually contain a deep branched crypt - the sinus of Tourtuali, which plays a certain role in the pathology of the M.
Pharyngeal
M. (syn.: nasopharyngeal M., Lushka's tonsil, third M.) is located on the border of the upper and posterior walls of the pharynx (see), has the appearance of a round-shaped plate with 4-8 folds of the mucous membrane diverging on its surface, protruding into the cavity nasopharynx. The pharyngeal M. is well developed only in childhood; with the onset of puberty, its reverse development occurs.
lingual
M. (syn. fourth M.) is located in the region of the root of the tongue (see), occupying almost the entire surface of the root of the tongue. Its shape is often ovoid, the surface is uneven, and lingual follicles (folliculi linguales) are located on the mucous membrane, divided by grooves into a number of folds. M.'s crypts are shallow, at the bottom of many crypts the excretory ducts of the salivary glands open, the secretion of which helps to wash and cleanse the crypts. In a newborn, the lingual M. is well developed, its longitudinal size is 6 mm, transverse 9 mm. After 40 years, a gradual reduction of lingual M occurs.
Pipe
M. is a paired formation, which is an accumulation of lymphoid tissue in the thickness of the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx at the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube (see Auditory tube).
In a newborn, the tubal M. is well defined, approx. 7.5 mm, diameter approx. 3.5 mm. Tubal M. reaches its greatest development at 5-7 years of age; later it gradually atrophies and becomes almost invisible. Rice.
3. Schematic representation of the blood supply to the palatine tonsil: 1 - external carotid artery; 2 - maxillary artery; 3 - descending palatine artery; 4 - ascending pharyngeal artery; 5 - ascending palatine artery; 6 - facial artery; 7 - lingual artery; 8 - superior thyroid artery; 9 - common carotid artery; 10 - internal carotid artery; 11 - palatine tonsil. The blood supply to the tonsils of the lymphoepithelial pharyngeal ring, including the palatine M. (Fig. 3), is carried out by arterial branches (aa. tonsillares), extending directly from the external carotid artery or its branches: the ascending pharyngeal (a. pharyngea ascendens), lingual (a. lingualis), facial (a. facialis), descending palatine (a. palatina descendens). M.'s veins are formed in the parenchyma, accompany the arteries and flow into the pharyngeal venous plexus (plexus venosus pharyngeus), lingual vein (v. lingualis), and pterygoid venous plexus (plexus venosus pterygoideus). M. does not have afferent lymphatic vessels. The draining lymphatic vessels flow into the lymph nodes: parotid, retropharyngeal, lingual, submandibular. M.'s innervation is carried out by the branches of the V, IX, X pairs of cranial nerves and the cervical part of the sympathetic trunk. In the subepithelial layer of connective tissue septa, M.'s parenchyma, there are individual nerve cells, their clusters, pulpy and non-pulpate nerve fibers, various types of nerve endings, and extensive receptor fields. The blood supply and innervation of the muscle change with age.
Why do cysts appear on the tonsils?
Only a qualified specialist can indicate the exact cause of the appearance of a cyst on the tonsil, using examination data and a comprehensive examination. Chronic infectious and inflammatory processes in the oropharynx come first in this disease. If the patient suffers from diseases such as tonsillitis, sinusitis, laryngitis, in which there is pronounced swelling of the mucous membrane in the mouth and nose, then favorable conditions are created for tissue proliferation and the growth of pathological neoplasms.
But there are other reasons that lead to the growth of cysts on the tonsils:
- changes in hormonal levels;
- weakening of the body's defenses;
- bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- tonsil injuries;
- work in hazardous industries associated with inhalation of polluted air poisoned by chemical vapors;
- sluggish inflammatory process in the oropharynx;
- development of autoimmune pathologies;
- untreated tonsillitis.
Histology
Rice.
4. Diagram of the structure of the palatine tonsil: 1 - capsule; 2 - tonsil crossbars; 3 - lymphatic follicles of the tonsil; 4 - tonsil parenchyma; 5 - multi-row squamous epithelium of the pharynx surface of the tonsil, continuing into the crypts; 6—exit openings of tonsil crypts. M. consist of stroma and parenchyma (Fig. 4). The stroma forms the connective tissue framework of M., formed by collagen and elastic fibers. They form a capsule (shell) around the M.’s circumference, from which connective tissue crossbars (trabeculae) extend into the M.’s depth. In the thickness of the crossbars there are blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves of the M., and sometimes the secretory sections of small salivary glands. M.'s parenchyma is represented by lymphoid tissue (see), the cellular basis of the cut is lymphocytes, macrophages, and plasma cells. Elements of lymphoid tissue form in places round-shaped clusters—follicles, which are located parallel to the epithelium along the free surface of the tumor and along the crypts. The centers of the follicles can be light - the so-called. reproduction centers, or reactive centers. The free surface of the M. is covered with a mucous membrane with multi-row squamous non-keratinized epithelium. In the area of the crypts it is thinner and in places broken; the basement membrane is also fragmented, which contributes to better contact of the lymphoid tissue with the environment.
AT WHAT AGE IS SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CHRONIC TONSILLITIS MOST OFTEN PERFORMED?
The operation can be performed at any age, in accordance with the existing indications for surgery. Due to anatomical features, children are recommended to undergo tonsillotomy - partial removal (cutting) of the tonsils or conservative therapy. Adults undergo tonsillectomy - complete removal of hypertrophied tonsils. The minimally invasive nature of surgical treatment of tonsillitis allows for surgical intervention with minimal tissue trauma, without significant blood loss and with a short rehabilitation period.
Tonsillectomy is one of the most common operations in the modern practice of ENT specialists. Despite this, patients must be monitored in the early postoperative period so that qualified Clinic staff can monitor the patient’s health status and, in case of signs of deterioration or complications, provide the necessary medical care.
Physiology
Having a common structure with other lymphatic organs (see Lymphoid tissue), M. perform similar functions—hematopoietic (lymphocytopoiesis) and protective (barrier). The follicular apparatus, embedded in the mucous membranes, is a lymphoid barrier, biol, whose role is the neutralization of toxic substances and inf. agents that enter mucous membranes from the environment. In human M. there are both thymus-dependent and thymus-independent populations of lymphocytes (see), which carry out reactions of both cellular and humoral immunity (see). M. are a peripheral organ of immunity that has a certain uniqueness. Firstly, they have a lymphoepithelial structure, secondly, they are the entrance gates for microbial antigens and, thirdly, they lack lymphatic vessels. It is known that M. contain cells that produce antibodies of the IgE class, which are believed to perform a protective function. It has been shown that lymphocytes of M.'s lymphoid tissue produce interferon (see), which is a nonspecific factor of antiviral immunity.
FEATURES OF PREPARATION FOR TONSILLECTOMY
Before surgery, patients undergo a comprehensive examination. The list of studies includes:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for APTT, fibrinogen, PTI;
- Blood for RW, HIV, HBs Ag (hepatitis B), HCV (hepatitis C);
- glucose, total bilirubin, blood creatinine;
- fluorogram;
- ECG with interpretation.
5 days before surgery, specialists prescribe medications for patients undergoing surgical removal of the tonsils to reduce the risk of bleeding. Immediately on the day of surgery, you are prohibited from eating and drinking.
You must carefully follow your healthcare provider's recommendations. This will minimize the risk of complications, both during surgery and in the postoperative period.
If, during a comprehensive examination, specialized specialists identify somatic pathology, the operation may have to be postponed. The doctor will prescribe appropriate drug treatment, based on the results of which a decision will be made about the possibility of performing a tonsillectomy.
Research methods
Rice.
5. Examination of the tonsils by rotating them with a spatula: 1 - left palatine tonsil (the right one is symmetrical to it in the figure) with the open mouths of the lacunae from where their contents emerge; 2 - palatoglossal arches; 3 - spatulas. The tonsils can be examined during posterior rhinoscopy (see) - pharyngeal and tubal, during pharyngoscopy (see) - palatine, lingual, lateral ridges and lymphoid follicles (granules) of the posterior pharyngeal wall. The method of palpation and probing of lacunae is used. The palatal m. are examined by rotating or dislocating them using two spatulas, and the contents of the lacunae and its nature are determined. There is usually no content in the M. lacunae of a healthy person. The M.'s rotation is performed with a tonsillorotator or a wire spatula, which is pressed on the palatoglossus (anterior palatine) arch, which entails the rotation of the M. with the free surface forward. In this case, the mouths of the lacunae open and their contents are squeezed out - plugs, pus (Fig. 5).
Symptoms
How to independently recognize chronic tonsillitis? Symptoms and treatment in adults and children can only be correctly determined by an ENT doctor. Below are characteristic signs - if you find them in yourself, consult a doctor.
The disease is characterized by symptoms such as:
- Headache.
- Feeling of something foreign in the throat, as if something was stuck in the throat. In fact, this is nothing more than large accumulations of caseous masses, that is, plugs in the thickness of the palatine tonsils.
- Increased fatigue, weakness, decreased performance. All this is due to the so-called tonsillogenic intoxication, or in other words, intoxication syndrome.
- Aching pain in the joints and muscles (with severe illness).
- Aching pain in the heart, with interruptions in heart function - extrasystole (with severe illness).
- Pain in the lower back, in the kidney area (with severe disease).
- Bad mood, and in some cases increased body temperature, and for a long time.
- Persistent skin rashes, provided that there was no previous skin pathology.
All these symptoms appear due to the entry of waste products of microorganisms into the blood from the palatine tonsils, i.e. staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, poisoning the entire body.
Bad breath appears due to the accumulation of organic substances and the decomposition of bacterial infection in the lacunae (recesses of the tonsils) and crypts (their canals). Tonsils become a source of bacterial infection, which can spread throughout almost the entire body and cause inflammation of the joints, myocardium, kidneys, paranasal sinuses, prostatitis, cystitis, acne and other diseases.
If the tonsils do not cope with their function as an immune organ, then even slight overwork, stress, or mild hypothermia can significantly reduce the immune defense and open the way for microbes and exacerbation of the disease.
Pathology
Developmental anomalies
. Developmental anomalies include the palatine lobule and the accessory palatine M. Sometimes, instead of one palatine M, two M develop on each side. Additional lobules hanging on the stem have been described. As a rule, these anomalies do not require treatment.
Damage
— burns, wounds of M. — are rare in isolation; more often they are combined with internal and external injuries of the pharynx (see).
Foreign bodies
- most often fish bones, which can penetrate into the muscle tissue, causing pain when swallowing. Remove them with tweezers or special forceps. After removal, a disinfectant rinse and a gentle diet are recommended for one to two days (see Foreign bodies, pharynx).
Diseases
Rice.
6. Schematic representation of the first stage of the tonsillotomy operation: the hyperplastic area of the left palatine tonsil is captured by the tonsillotomy ring. Acute disease of palatine M.— acute
tonsillitis
, or tonsillitis
(see). Hron, inflammation of the palatine M.—tonsillitis (see). Hyperplasia of the palatine membranes occurs in children; there are no signs of inflammation. M. are only increased in size. If hyperplasia causes difficulty breathing or swallowing, children undergo surgery - tonsillotomy (Fig. 6), i.e. partial cutting off of the protruding part of the M. Before the operation, a full wedge examination is necessary.
The operation is low-painful, most often performed without anesthesia, on an outpatient basis, with a special instrument - a guillotine-shaped knife - tonsillotome, the size of which is selected according to the size of the removed muscle. Hyperplasia of the palatine muscles is in most cases accompanied by the proliferation of adenoid tissue of the nasopharynx, therefore tonsillotomy is often combined with adenotomy (see . Adenoids). Bleeding after tonsillotomy is usually minor and stops quickly. The child should remain under medical supervision for 2-3 hours. It is recommended to observe bed rest for 1-2 days, then semi-bed rest for 3-4 days. Food should be liquid and mushy, at room temperature.
Acute inflammation of the pharyngeal M., or acute adenoiditis
(see), observed mainly in children. In this case, the tubal M. may also be involved in the inflammatory process. Inflammation is catarrhal, follicular or fibrinous in nature. Due to the anatomical proximity of the mouth of the auditory tube, symptoms of tubo-otitis may occur (see).
Isolated disease of the lingual M. is much less common. It occurs in middle-aged and elderly people and may be accompanied by an abscess of the lingual M.; occurs with high fever, difficulty swallowing and speaking, and severe pain when protruding the tongue.
With angina of the lateral ridges of the pharynx, inflammation occurs in the lymphoid follicles scattered along the back wall and in the lateral lymphoid ridges (columns). Often a whitish dotted coating appears on individual follicles of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
A disease of the lymphoid tissue of the larynx is called laryngeal angina
; it is manifested by high fever, general malaise, sharp pain when swallowing food and palpating the larynx area. Plaques are often visible, and there may be swelling of the outer ring of the larynx (see Laryngitis).
In addition to the primary lesion of the tonsils, changes in the lymphoid tissue of the pharyngeal ring occur with blood diseases. With leukemia (see), infectious mononucleosis (see Infectious mononucleosis), lymphogranulomatosis (see), an increase in palatal M. can cause difficulty breathing and swallowing. Ulcerative changes in the palatine muscles, such as necrotizing tonsillitis, are also possible.
With syphilis, the palatine M. are affected in all stages of the disease. There are descriptions of hard chancroid M.: against a limited hyperemic background in the upper part of M. a hard infiltrate appears with painless erosion in the center, the edges soon turn into an ulcer with compacted edges and bottom; the lesion is unilateral, characterized by regional lymphadenitis (see). In stage II of syphilis, syphilitic tonsillitis occurs: round or oval plaques, separate and confluent, appear on the muscle, rising above the surface of the muscle, surrounded by a reddish rim, easily ulcerating; characterized by bilateral lesions; the entire M. is enlarged, dense, covered with plaque; Papules are found on the mucous membrane in the corners of the mouth, on the palatine arches, and along the edge of the tongue. In stage III, gumma can lead to the disintegration of M., which threatens bleeding from large vessels. Treatment - see Syphilis.
Primary M. tuberculosis is rare; its main symptom is difficulty swallowing and nasal breathing as a result of concomitant M. hyperplasia. Secondary M. damage can be observed in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Both forms can occur hidden, simulating a banal chronic condition, tonsillitis. Treatment - see Tuberculosis.
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC TONSILLITIS: WHY OPERATION?
Medical tactics for chronic tonsillitis are selected based on numerous diagnostic data and examinations. Specialists weigh the pros and cons, assess the risks of complications and make professional forecasts for the future.
In most cases, tonsillectomy is performed when a toxic-allergic form of chronic tonsillitis develops, which, unlike the simple form of the disease, occurs with severe symptoms of intoxication, immunosuppression and a high risk of developing infectious complications.
Radical removal of tonsils for chronic tonsillitis is absolutely justified: if conservative treatment of tonsillitis is ineffective, only surgery can get rid of the source of chronic infection in the pharynx and prevent the spread of infection.
Experts identify more than 100 concomitant diseases that occur with long-term tonsillitis: psoriasis, nephritis, eczema, prostatitis, scleroderma, lupus erythematosus, rheumatism and other pathologies. You should not postpone the operation if the specialist insists on it. The tonsils lose their main protective functions and turn into a dangerous source of infection.
There are certain indications for surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis, on the basis of which the doctor makes a decision on the need for surgery.