With gastroenterological diseases, stomach pain and belching of air are common. Pressing, incessant nausea and the release of gases accumulating in the gastrointestinal tract and esophagus are not only a sign of a serious illness, but also an unaesthetic symptom that causes inconvenience to the patient, to combat which it is necessary to establish the exact root cause of the disease.
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Even “advanced” ulcers or gastritis can be cured at home, without surgery or hospitals. Just read what Galina Savina says and read the recommendation.
Causes and symptoms
When a patient feels a dull pain in the abdomen after eating, gases arise and he constantly wants to burp, he thinks about the root causes of the unpleasant manifestations. Empty belching of air can be a symptom of an emerging or progressive gastrointestinal disease or occur for reasons that have no clinical manifestations and are related to a person’s daily lifestyle. So, the reason for belching may lie in the following:
Very important! Savina G.: “I can recommend only one remedy for the quick treatment of ulcers and gastritis” read more.
- frequent smoking;
- an excess in the diet of foods that provoke a lot of gastric gases - beans, sauerkraut, peas;
- drinking carbonated water and drinks;
- non-observance of an hour's pause between meals and exercise;
- disruption of the process of food absorption - swallowing air, not chewing food and swallowing large pieces.
When these causes are excluded and severe belching through the mouth is accompanied by other alarming symptoms, such as vomiting, excessive sweating, diarrhea, acute stomach pain, you should consult a doctor, since one of the serious diseases may develop, which can only be diagnosed by tests and a comprehensive gastroenterological examination .
Esophagitis of the esophagus
Constant belching of air is observed with chronic inflammation of the esophagus and is accompanied by a burning sensation in the pit of the stomach, which goes away after taking gastrointestinal preparations that envelop the mucous membrane. Both narrowing of the esophageal tube and erosion of the walls cause pain and inconvenience. The process creates a gas bubble that comes out of the mouth during yawning and chest movement. Endless dry belching in such cases is a reason to go to the hospital so that esophagitis does not cause complications.
THIS IS REALLY IMPORTANT! Right now you can find out a cheap way to get rid of stomach pain. FIND OUT >>
Gastric ulcer
The most dangerous disease that can lead to cancer and death. An adult suffering from an ulcer has a stomach ache and belches through the mouth already at the initial stage of the disease. With the chronic nature of the disease, the stomach seems to ache, the person regularly vomits, vomiting periodically occurs, and air belching is often accompanied by the release of acid.
Chronic pancreatitis
Frequent belching after eating and a burning sensation in the stomach are signs of pancreatic dysfunction. In case of acute pain, people call an ambulance, especially at night, since the aggravation of the disease occurs after a heavy feast and consumption of non-dietary foods, drinking coffee, alcohol and marinades. An air lump coming out of the mouth with pancreatitis is bitter.
Other reasons
Air in the stomach, which then regurgitates and torments the patient with hiccups, occurs with gastritis. The air lump comes with the smell of rotten food and is accompanied by heartburn, bloating, excessive salivation and flatulence. In the initial stages of the disease, treatment with diet is effective; acute stages require drug therapy.
Increased salivation: causes and treatment
Hypersalivation - what is it?
Why is there a lot of saliva in the mouth?
Salivation during sleep
Excessive salivation during pregnancy
Treatment of hypersalivation
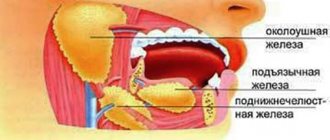
Saliva is not just a liquid secreted in the mouth. Saliva is involved in the digestion process and protects the body from bacteria. The process of salivation is not controlled by humans. Usually about 2 liters of saliva are produced per day. Under the influence of certain factors, its amount can greatly increase. In this article we will talk about the causes of increased salivation and how to treat it.
Preventive actions
To prevent the occurrence of the phenomenon in question, it is recommended:
- To ensure the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to drink a glass of clean water in the morning. This manipulation will speed up the functioning of the digestive system;
- do not drink liquid while eating;
- It is not recommended to abuse drinks with gases;
- you need to eat at the same time, dividing the diet into 6 times a day;
- It is not recommended to eat 2 times a day and in large portions;
- all foods are chewed thoroughly and slowly;
- The menu should not contain a lot of fat, spicy and salty foods.
Gastroenterologists say that a competent combination of foods will prevent discomfort in the organs of the digestive system.
For a competent combination of products and proper diet, it is recommended to consult a nutritionist.
Treatment
Information on how to reduce stomach acidity should be obtained from a gastroenterologist. Any options for self-medication at home using improvised means are not only ineffective, but can also lead to the development of complications. For symptoms of gastritis with high acidity, diet and treatment include exclusion from the diet of fried and fatty foods, smoked meats, fast food, alcohol, canned meat, fish and vegetables, spices, seasonings, and sauces. You should eat in small portions, 4-5 times a day. Dishes must be prepared mainly by steaming or boiling. In case of increased acidity of the stomach, diet No. 1 according to Pevzner is prescribed.
For symptoms of gastritis with low acidity, treatment and diet include recipes for dishes that stimulate the acid-forming function of the stomach.
To treat high stomach acidity, traditional medicine uses the following groups of pharmaceuticals:
- Antibacterial drugs that are effective for hyperacid gastritis caused by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
- Enveloping agents.
- Proton pump inhibitors.
- Antacids.
- H2 histamine blockers.
- Bismuth preparations.
To maintain normal gastric acidity, it is important to maintain a balance of normal gastric microflora. For this purpose, it is recommended to use metaprebiotics, which contain a natural nutrient substrate for gastric and intestinal bacteria. Metaprebiotic Stimbifid Plus helps not only restore the balance of normal gastric and intestinal microbiota, but also promotes the eradication (destruction) of Helicobacter pylori. Also, metaprebiotic components accelerate the process of restoration of the gastric epithelium.
Belching treatment
When you are tormented by night belching and want to quickly get rid of it, Almagel and Gaviscon products will come to the rescue. You can get rid of an unpleasant lump in the throat, which presses and provokes vomiting, by taking the digestive enzyme “Enzyme”, “Mezim”, “Movalis”. If gases often come out, you can cope with flatulence by using Motilium. Pharmaceutical preparations for the treatment of pancreatitis and ulcers are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
With such symptoms, it is better to eat steamed meat.
Pressive belching at night suggests treatment with diet. If you have heartburn, you can eat steamed vegetables, meat, and porridge. All dishes must be cooked in a steam bath, and the bread must be slightly dry before eating. If you cannot eliminate the symptom by regulating your diet, it is recommended to drink Omez before meals and enzymes to facilitate the digestion of food after a meal. A strict diet for belching in combination with medications gives good results.
Prevention
Proper diet and nutrition are the basis for successfully preventing heartburn and nausea. Additional recommendations:
- rejection of bad habits;
- correct work and rest schedule;
- weight loss;
- refusal of uncontrolled use of NSAIDs;
- wearing loose clothing without tight belts or corsets.
Timely treatment of diseases of the digestive system accompanied by heartburn, including recommendations for the use of Omez 10 mg, helps relieve heartburn.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, YOU MUST READ THE INSTRUCTIONS FOR MEDICAL USE OR CONSULT A DOCTOR.
Prevention of discomfort
Every meal should be taken while sitting
Each meal should be taken while sitting, without haste, in a calm environment. The pre-bedtime snack should be completed at least two hours before bedtime. It is advisable that this be a light dinner of a baked apple or an omelet, complemented by a mug of warm green tea.
After you manage to cope with the disorder, it is important to adhere to the right lifestyle - the stomach is very vulnerable, and problems tend to arise again. Reorganize your daily routine and do not abuse junk food and alcohol.
As a preventive measure, do not neglect walks in the fresh air and physical activity. Try to maintain a calm psycho-emotional state. Drink herbal infusions.
If you follow all the recommendations listed above, you can easily get rid of heaviness in the stomach and belching, and, in addition, maintain the resulting effect for many years to come.
Treatment of hypersalivation
There is no single treatment method for all cases. However, you can use methods to reduce the activity of the salivary glands - sometimes they are recommended by doctors as an addition to complex therapy.
- Reception of sorbents: activated carbon, polysorb, etc.
- Taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Exercise therapy, massage (most often prescribed for children).
- Botulinum toxin injections.
In rare exceptions, the salivary glands are partially removed, but the downside is that there is a risk of damaging the facial nerve.
Which doctors will help you cope with this disease? Dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.
DO YOU STILL THINK THAT IT IS HARD TO CURE YOUR STOMACH?
Judging by the fact that you are now reading these lines, victory in the fight against diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is not yet on your side.
Have you already thought about surgery? This is understandable, because the stomach is a very important organ, and its proper functioning is the key to health and well-being. Frequent abdominal pain, heartburn, bloating, belching, nausea, bowel dysfunction. All these symptoms are familiar to you firsthand.
But perhaps it would be more correct to treat not the effect, but the cause? We recommend reading the story of Galina Savina, how she cured her stomach. Read the article >>
What drinks can cause heaviness?
- Sweet soda, especially Coca-Cola, irritates the mucous membrane of the stomach, causing various disturbances in its functioning.
- Strong tea, coffee, kvass and beer greatly irritate the mucous membranes. This leads to various disturbances in the functioning of the stomach, most often to the appearance of heaviness.
- Many people experience milk intolerance as they age. Therefore, it is better to replace it with low-fat kefir or yogurt.
- Any liquid drunk immediately after a meal slows down the digestion of what you eat, as it dilutes the digestive juice and the food lingers in the stomach for a long time, causing a feeling of heaviness.
Causes of heartburn and nausea at the same time
Heartburn and nausea after eating can occur at the same time, and in some cases, nausea can begin after the burning sensation in the chest. Common causes of symptoms:
- binge eating;
- abuse of fatty, fried, difficult-to-digest foods;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- taking medications that relax the sphincter between the stomach and esophagus;
- consumption of products containing caffeine and cocoa beans;
- pregnancy, especially the last trimester;
- overweight;
- tight clothing that puts pressure on the stomach 5.
Causes of belching air and stomach pain
Belching along with painful sensations is not a separate disease, but signs of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. There is no point in taking measures and treating only these symptoms. You need to find the culprit of their occurrence and eliminate them; the signs will go away on their own. Irritation of the receptors responsible for the feeling of pain leads to unpleasant sensations. Let us note the main reasons why pain and belching appear together in healthy people:
- Eating fruit after meals. Fruits are healthy foods, but they contain organic acids that react with minerals found in other foods. This reaction is often the culprit of unpleasant sensations.
- Hot bath. The process of a relaxing, pleasant procedure immediately after eating can end unpleasantly. This is due to poor circulation. The blood concentrates in the extremities, decreases in the stomach area, resulting in a headache, stomach pain, and there is a risk of regurgitating the contents of the stomach.
- Sleep on a full stomach. Sleeping after eating disrupts proper digestion, resulting in heaviness and bloating in the stomach in the morning.
- Smoking.
Return to contents
general information
In 80% of cases, the cause of the development of the inflammatory process with high acidity of the stomach is the microorganism Helicobacter pylori, which disrupts the natural protective properties of the stomach and leads to damage to the epithelium of the organ. Gastritis with high acidity can develop in people regardless of age, including children.
Other factors predisposing to the development of this condition include:
- Regular exposure to stress on the body.
- Poor nutrition, predominance of fried and fatty foods in the diet, as well as deep-fried dishes.
- Abuse of so-called snacks.
- Long-term or uncontrolled use of drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Frequently eating food that is too hot or too cold. In addition, people with thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus and gout have a high predisposition to the development of hyperacid gastritis.
Why is high acidity dangerous?
Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, which is necessary to break down food components. To prevent the acidic environment from damaging the walls of the stomach, protective mucus is produced. With increased acidity of the stomach, destruction of the mucous protective layer is observed, followed by the formation of an inflammatory process, the formation of erosions and ulcers.
Clinical symptoms
Inflammatory damage to the organ with increased secretion of gastric juice often worsens during the off-season, in the autumn or spring months. Symptoms of high stomach acidity include:
- Drawing or cramping pain in the epigastric region, which often intensifies after eating. In the acute course of the inflammatory process, the pain may be accompanied by vomiting, which brings temporary relief.
- Heartburn, which is caused by acidic stomach contents refluxing into the esophagus.
- Belching sour.
- Bad breath.
- Stool disorders such as constipation or diarrhea.
Other symptoms of increased stomach acidity during gastritis include weakness, dizziness, increased sweating, excessive gas formation in the intestines (flatulence), increased salivation, increased or decreased appetite, and the appearance of a white or gray coating on the surface of the tongue. Reduced stomach acidity is accompanied by symptoms such as decreased appetite, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium, and rotten belching.
Drug therapy
There are a number of medications that are often used to treat episodes of poor digestion. These include Motilium.
The medication promotes rapid recovery of motor skills and relieves heaviness after eating.
With the help of this medicine it is possible to quickly minimize belching and fullness in the abdomen.
Periodic signs of dyspepsia are often provoked by stress, nervous shock, and errors in diet.
They are not a cause for particular concern as they often go away on their own.
If episodes of digestive disorders are observed frequently and are poorly relieved by Motilium, you should immediately be examined by a specialist.
Diseases of the stomach area
A healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet are the key to health and good mood.
Unpleasant sensations in the abdominal area can be caused by eating habits and certain habits. At the initial stage, they do not provoke the development of organic pathology and bring only some discomfort.
But when the body’s adaptive capabilities are exhausted, the tissues undergo changes and an inflammatory process begins in them. Abdominal pain and unpleasant belching can be the result of overeating or a late dinner, but if the factors that cause them act systematically, this can lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Why can't you use soda?
The most famous home remedy for eliminating a burning sensation behind the sternum is baking soda. Alkali neutralizes hydrochloric acid, thereby eliminating the unpleasant symptom. However, it has been proven that the use of this method of treatment only causes harm. In the process of neutralizing the acid, a large amount of carbon dioxide is released, which distends the stomach. This can cause damage to the mucous membrane, and in the presence of an ulcer, even bleeding5. In addition, the environment in the stomach must remain acidic. Therefore, after using soda, the compensatory mechanism for the production of hydrochloric acid starts almost immediately. The result may be even more severe discomfort in the stomach and esophagus5.
When is burping normal and when is it pathological?
Belching is the involuntary release of gas or food from the upper gastrointestinal tract. There are physiological and pathological causes of belching. It is considered normal if it occurs due to swallowing air while eating (which often occurs in an infant) or drinking soda.
Normally, the air comes out gradually through the mouth, but if the pressure in the stomach increases, the muscles push the air through the esophagus, and belching appears. If the air is odorless and the heaviness in the stomach goes away within half an hour, then this is not a sign of illness.
Involuntary swallowing of air occurs if there is no nasal breathing, for example, due to an allergic rhinitis or adenoids, or if a person swallows air while talking.
Belching can occur if a person eats quickly, chews food poorly, drinks liquid through a straw, and also if food is washed down with water (stomach juice is diluted, which slows down digestion). Air from the stomach or esophagus can also escape when consuming carbonated drinks or foods that increase gas formation.
Abdominal pain and belching can occur due to poor diet (overeating, eating too much fruit, vegetables, legumes). Eating dinner before bed can cause abdominal pain and belching in the morning.
Constant unpleasant belching can be provoked by pathological processes:
- disturbance of gastric or intestinal motility;
- changes in the concentration of hydrochloric acid in gastric juice;
- narrowing of the esophagus or deterioration of the sphincters;
- inflammation of the bile ducts or pancreas;
- neurotic disorders.
If food stagnates in the stomach and begins to decompose and ferment, then the gases have an unpleasant odor. Such belching is regarded as a sign of gastrointestinal disease. Air comes out more often after eating and is accompanied by other symptoms of indigestion. As a rule, a feeling of heaviness, bloating, constipation or diarrhea.
Although belching and hiccups are considered normal, they can occur with high frequency or even become constant, annoying and require medical attention. And patients with aerophagia should not undergo exploratory laparotomy. They require other treatment methods.
All about burping
Belching is an audible release of air from the esophagus into the pharynx. The medical term is erection. Almost 7% of the general population complain of excessive or unpleasant belching.
There are two types of it: the so-called gastric and supragastric . The first is the release of swallowed air that enters the esophagus during transient relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter (TELS). TRNPS is triggered by inflating the proximal stomach and allows air to be expelled from the stomach, thereby acting as a decompression mechanism for the organ and preventing large volumes of gas from passing through the pylorus into the intestine. Thus, TRNPS is sometimes called reflex belching.
Distension of the esophagus caused by refluxed air initiates reflexogenic relaxation of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), through which air can escape. Gastric belchings occur 25 to 30 times a day and are physiological. They are involuntary and completely controlled by reflexes.
The supragastric form is not a physiological reaction, therefore in all cases it is considered a pathology. Unlike gastric belching, such belching, a common cause of which is an anxiety disorder, is not a reflex and refers to a behavioral reaction. Contraction of the diaphragm creates negative pressure in the chest cavity and esophagus, subsequent relaxation of the IPS leads to an influx of air into the esophagus and is immediately pushed out by voluntary muscle tension.
Often patients seek help for very frequent episodes of belching.
They can occur directly during the examination with a frequency of up to 20 times per minute. Usually, if you are distracted by a conversation, the symptoms stop, then reappear. There are no episodes of belching during sleep.
Etiology
There are several important factors that influence the presence of gas in the gastrointestinal tract. These include the amount of air swallowed and the efficiency with which the gastrointestinal tract moves and expels air or gas. Excessive air entry into the stomach is associated with rapid swallowing of food and drinks, drinking through a straw, chewing gum, sucking hard candy, or wearing unstable dentures. People also take in more air when they are nervous. For some people, excessive burping is a learned behavior or habit.
Air that is swallowed and not expelled by belching passes through the gastrointestinal tract and exits through the anus. In normal people, about 50% of the gas expelled in this way is swallowed air. And this amount can increase significantly in those who ingest it exorbitantly.
Possible causes of gastric belching:
- breathing through the mouth;
- myocardial infarction (rare, but may cause belching with chest pain);
- emotional stress;
- drinking carbonated drinks;
- food intolerance;
- food allergies;
- lactose intolerance (lactase deficiency);
- reduced acidity of gastric juice (achlorhydria);
- diabetes mellitus (diabetic gastroparesis can cause frequent belching);
- occasional belching of offensive intestinal gas is a greater cause than swallowed air: fermentation in the intestines;
- gastroparesis (causes: diabetes type 1 or 2, anorexia nervosa, damage to nerves or muscles caused by surgery or injury, thyroid disease, pancreatitis, scleroderma);
- vagotomy;
- pyloric obstruction;
- peptic ulcer;
- intestinal tumor;
- nervous habit of swallowing air while eating or talking;
- gastrointestinal ulcers;
- gastritis;
- gallbladder diseases;
- pancreatic diseases;
- pregnancy;
- obesity;
- sliding hiatal hernia;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- celiac disease;
- Down syndrome associated with celiac disease.
A number of different medications can cause stomach belching or problems that cause it: drugs for type 2 diabetes (acarbose), laxatives (lactulose and sorbitol), pain relievers (naproxen, ibuprofen, aspirin). Excessive use of painkillers can cause gastritis and, consequently, belching.
Pathogenesis
Normally, air from the stomach enters the intestines. Belching occurs when air enters the esophagus and is pushed out through the mouth. As with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), this process requires the LES to be relaxed to regurgitate up into the esophagus and then audibly through the mouth.
Belching after eating, especially a large meal, can be normal and occur as a result of swallowing air. Relaxation of the LES is facilitated by food, primarily onions, tomatoes, fats, and alcohol.
Chronic belching does not lead to organic disorders. In most cases, swallowed air from the esophagus quickly flows back before reaching the stomach. This becomes a bad habit in some individuals. Magenblase syndrome, an incompletely understood disorder, causes severe bloating and tension in the abdomen from gas in the stomach after eating. These symptoms resolve after belching. Babies and children can swallow large amounts of air without realizing it.
Diagnostics
Belching itself is not cause for concern and does not indicate any serious illness. An examination may be indicated if the symptoms are very unpleasant or there are other associated ones - abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, gastrointestinal bleeding and sometimes heartburn.
Physical examination. It is necessary to make sure that air is regurgitated and belched again. Currently, there are several tests (other than history and physical examination) that are used to further evaluate regurgitation. In such cases, endoscopy may be useful if peptic ulcer disease or GERD is suspected.
Laboratory diagnostics. Low hemoglobin may indicate malabsorption of iron, folate, and vitamin B12. The albumin level provides evidence of hypoalbuminemia, suggesting malabsorption.
If it is necessary to exclude intestinal obstruction, an X-ray examination of the abdomen is performed. Sometimes lactose intolerance should be assessed. Tests are available to screen for celiac disease if other signs suggest the disorder.
Treatment
Patients with intense belching often suffer from decreased quality of life . Therefore, the symptoms must be taken into account and treatment carried out accordingly. However, other than a few anecdotal reports, there is still too little data on the treatment of patients with gastric regurgitation.
It is often recommended to make lifestyle changes, including avoiding fast eating and drinking, chewing gum, drinking carbonated drinks from a bottle, consuming chocolate, onions, hard candy, and alcohol. You should stop smoking.
Patients with GERD may experience a high frequency of gastric belching. However, in this category, supragastric disease was also observed. Patients with GERD swallowed air more often and then had more gastric burps than healthy people (Hemmink GJ et al., 2009). Acid suppressive therapy helps reduce the intensity of this process. This means that the unpleasant sensation of heartburn stimulates patients to take a large and frequent sip of saliva and, along with it, swallow more air. Belching symptoms respond to treatment with the TRNPS inhibitor baclofen (Cossentino MJ et al., 2013). Defoamers, in particular espumizan, do not help with gastric and supragastric belching.
Given that excessive supragastric regurgitation is a behavioral disorder, cognitive behavioral therapy appears to be a reasonable alternative approach (Chitkara DK et al., 2008). Observations support the effects of distraction and stimulation. A small study using baclofen, which reduces the incidence of TRNS, found that the drug reduced the number of supragastric belches (Blondeau K. et al., 2004). Successful treatment of excessive belching has been reported in several cases using hypnosis and biofeedback (Spiegel SB, 1996; Cigrang JA et al., 2006).
Inability to burp
The physiological significance of belching is illustrated by the example of those patients who have an acquired inability to do it. After anti-reflux surgery, a newly placed cuff around the LES prevents reflux by reducing the number of TRIPs and increasing sphincter pressure during relaxation (Bredenoord AJ et al, 2008). As a result, the number of gastric belches is significantly reduced, and in some patients it is not observed at all. Loss of the stomach's ability to ventilate can cause air to accumulate in the stomach and in the intestines, causing bloating and increased flatulence. These symptoms can be very severe and sometimes lead to a second surgery to restore normal anatomy.
Some, to reduce bloating symptoms after antireflux surgery, induce supragastric burping in a futile attempt to expel air. The fact that the patient is said to be able to regurgitate after antireflux surgery cannot be taken as an indication that the ventilatory capacity of the stomach is not impaired. After all, belching can also be caused by the supragastric mechanism. Its incidence has been shown to be lower after partial fundoplication (270 degrees Toupet) than after complete fundoplication (360 degrees Nissen) (Broeders JA et al., 2012).
Very rarely, inability to burp is observed in patients with achalasia. In this case, the neurons that control the motility of the smooth muscles of the esophagus are involved in the degenerative process. This typically results in a lack of peristalsis and an inability of the LES to relax. Air dilatation of the esophagus occurs and patients experience chest pain. Likewise, a high IPS threshold for relaxation can cause chest pain. It has been suggested that regurgitation disorders play a role in some patients with noncardiac chest pain (Gignoux C. et al., 1993).
Read the continuation of the material here.
Diagnostics
Multiple belchings accompanied by pain for a long time should be a cause for serious concern and a comprehensive examination. A clinical picture of blood, urine, a study of acidity levels, and an ultrasound of the abdominal organs allow the doctor to draw a conclusion about the causes of pain and belching. The most informative research method, which allows you to visually assess the degree of damage to the mucous membranes, is gastroscopy.
To complete the picture of the disease, fluoroscopic examination is sometimes prescribed.
Important! Belching and pain in the pit of the stomach may be signs of insufficiency of the cardiovascular system, cardiospasm of the esophagus, or aneurysm of the descending thoracic aorta.
Suspected cholecystitis is diagnosed using duodenal intubation, during which bile is collected. Microbiological analysis will reveal biliary tract infections and the presence of parasitic infestations.
Diseases that cause air to escape from the stomach
In some diseases, belching of air is the only symptom, such as in gastric neurosis (aerophagia). But more often it occurs against the background of gastrointestinal pathologies, and also appears reflexively in diseases of the liver and gall bladder.
Bitter belching occurs as a result of bile entering the stomach from the duodenum. The putrid smell of gas is felt if rotting and fermentation begins in the stomach. This happens if food stagnates due to poor gastrointestinal motility.
Sour belching is caused by an increased concentration of hydrochloric acid or fermentation, which occurs when there is a lack of acidic contents in the gastric juice. The release of gas with a sour odor often occurs when the gastric mucosa is inflamed due to an increased concentration of hydrochloric acid, as well as due to peptic ulcers.
In addition to belching, patients complain of severe stomach pain, heartburn that occurs after eating, and frequent constipation.
Flatulence, gas production and flatulence in a child, children
A significant amount of gas passes through the digestive tract of healthy people every day, and this is perceived as a natural process. The accumulation of a large amount of gases can be caused by aerophagia, the formation of a large amount of gases in the intestines due to dysbiosis, consumption of carbohydrates (cabbage, legumes), impaired absorption of gases in the intestines (for heart disease - consultation with a pediatric cardiologist, cirrhosis of the liver, etc.), incomplete or complete intestinal obstruction. The initial disorder that causes functional bloating and pain is a violation of intestinal motility, which leads to the patient feeling pain with a volume of intestinal gas that is easily tolerated by healthy people.
Increased gas formation in the intestines is observed after eating certain foods, such as cabbage, legumes, rye or bran bread, some cereals, in case of malabsorption of carbohydrates (lactose, sucrose), pathological bacterial colonization of the small intestine or infection with Lamblia intestinalis.
Analysis of stool for dysbacteriosis in children - Markushka clinic.
Flatulence (emission of gases) occurs with constipation, accompanied by putrefactive fermentation. Most often, gases are released during bowel movements. Conscious release of gases indicates that they are accumulating in large quantities in the colon.
Traditional methods
In alternative medicine, as in traditional medicine, treatment begins after an accurate diagnosis has been established.
Chronic gastritis and high acidity
Tea is brewed from mint, lemon balm, blackberry leaves and branches. Drink daily.
The collection of medicinal herbs helps remove acidity: flax seeds, fennel, linden blossom, mint. The collection is placed in a container and filled with water brought to boiling temperature. After cooling, the liquid is ready for use. Take 50 g twice a day. The course will end after symptoms decrease or disappear.
Increased acidity is removed with the help of: calamus root, flowers and rowan berries. Preparation of the decoction:
- 1 tbsp. ingredients, 2 cups cold water.
- Leave for an hour.
- Then put it on fire.
- Bring to a boil and cool.
- Take warm, 1 glass three times a day.
Peptic ulcer
The first aid that is always at hand is aloe. Unwatered for three weeks, no younger than 3 years old, wipe the leaves, put them in a dark place. After 5 days, the aloe is ground, honey and natural red wine are added. The resulting liquid is poured into a jar and placed in the kitchen cabinet. The potion is infused for 7 days.
September 18, 2022, 22:57 Article expert: Svetlana Aleksandrovna Nezvanova 0 21,908
Sudden pain in the stomach is a signal that there is a disruption in its functioning. The complications that arise bring discomfort to the person and disrupt the functioning of the entire body. What if the pain is accompanied by additional signs, for example, in the form of rumbling or belching? What does it mean? Symptoms of a complex disease or an ordinary situation?