Lips of the mouth
(
labia oris
; Greek
chelos
). The upper lip (labium sup.) and the lower lip (labium inf.) in the area of the corners of the mouth (angulus oris), connecting by commissures (commissura labiorum), form the oral fissure (rima oris). The Upper Lip is limited by the base of the nose, the oral fissure and the nasolabial grooves (sulcus nasolabialis), the lower Lip - by the oral fissure and the labiomental groove (sulcus mentolabialis).
During ontogenesis, the lips are formed from the jaw processes. The lower Lip is formed at the end of the first month of uterine development as a result of the fusion of the mandibular processes, the upper - at the end of the second month as a result of the fusion of the right and left maxillary processes with the median nasal process (see Face). Musculature in G. is found only in mammals. In humans, bundles of facial muscles are embedded in the thickness of the G., thanks to which the Crimea G. have great mobility and participate not only in the act of grasping and processing food, but also in the act of speech and facial expressions.
Functions of the labia
The labia are folds of skin located on either side of the vulva and surrounding the opening of the vagina.
The main function of the labia is to create a barrier. They protect the vagina from mechanical damage, provide comfortable penetration during sexual intercourse, retain moisture and help maintain normal bacterial flora.
The labia are divided into small and large:
- The labia majora (larger labia) are the outer labia. They consist mainly of fatty tissue and act as a shock-absorbing pad that protects against friction, for example, during sexual intercourse.
- Labia minora – internal. They are a fold of skin and can be compared to a curtain that blocks the access of bacteria, viruses and other agents hazardous to health.
These parts of the body are well innervated, so they also perform a sensory function and participate in a woman’s sexual pleasure.
Functions of the labia
Causes of lip cancer
Lip cancer develops for many reasons:
- From smoking;
- After a long stay in the sun;
- As a result of inflammatory processes of an infectious and non-infectious nature;
- Under the influence of high temperatures;
- In the presence of microtraumas;
- Due to prolonged exposure to chemicals.
Lip cancer often develops from smoking. Men get lip cancer much more often than women. Currently, the trend is changing, because many women suffer from tobacco addiction. Doctors believe that lip cancer develops due to smoking strong cigarettes for a long time.
The average smoker smokes at least ten cigarettes a day. In this case, the paper surface is constantly in contact with the lips. The skin here is especially delicate and sensitive. Microcracks appear on its surface. They are invisible to others and do not cause problems for the smoker. Damaged areas of the epithelium are affected by tobacco smoke. It contains a lot of harmful substances. Skin cells begin to degenerate.
The cause of mechanical trauma that causes lip cancer can be improperly made dentures, the habit of holding various objects with the lips (nails, the mouthpiece of a smoking pipe), or biting the lower lip. The mechanism of development of lip cancer is as follows: a long-term non-healing crack, wound, inflammation on the lip, papilloma develops into leukoplakia, Manganotti cheilitis, keratoacanthoma, warty form of dyskeratosis or other precancerous diseases. Against this background, lip cancer occurs.
Option 1. Labia too small
Such cases occur in several cases:
- in elderly patients, which is associated with changes in hormonal levels and general aging of the body;
- in women with a congenital or acquired (due to illness) tendency to tissue atrophy;
- The labia may be underdeveloped from birth.
It happens that the labia have become too small due to the fault of the surgeon, who severely trimmed them during labiaplasty.
When this reproductive organ is too small, the patient may feel pain during intercourse because there is not enough tissue to limit penetration too deep. This leads to injury and even pain in deeper organs.
In addition, if the labia are too small, the vagina is always open to microorganisms, which leads to inflammation of the female genital tract. The function of maintaining moisture is also impaired: the vagina quickly dries out, the mucous membrane ages prematurely, and muscles and other structures weaken.
One of the solutions to restore labia insufficiency is augmentation, which consists of filling the tissue with hyaluronic acid. After injection of hyaluronic acid, they increase in size, look more attractive and close the vagina as it should normally.
The second option for restoring the labia is autotransplantation of adipose tissue.
Unfortunately, these are not permanent procedures - after some time, the hyaluronic acid and fat are absorbed, so injections should be repeated from time to time.
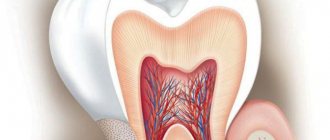
Structural features
The main and prominent part of the lips consists of muscle fibers, axillary connective tissue, collagen fibers, as well as fatty compounds, which are especially noted in the submucosal area. Their number determines the shape, contours, and plumpness, which can be corrected using special medical procedures. Structural changes in the musculocutaneous fold are noted up to 16 years of age. After 45 years, due to the deterioration of the regenerative abilities of tissues, the weakening of muscle fibers, the thinning of collagen compounds and other processes that accompany aging, the shape of the lips may change. If we consider the structure of human lips, we can distinguish three distinct zones:
- Skin.
- Transitional.
- Mucous.
Each part has certain structural differences and purposes.
Skin area
This part is not particularly different from the skin of the face. It also consists of the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat. There may be keratinized particles, and there may also be hair, fat or sebaceous glands.
Transition zone
This part is often called the red border, since it is the transition to the pink area that is considered its border. The transition zone is divided into an outer region and an inner one. The outer one has a characteristic pink color, the surface is smooth, and there are no sweat glands. The inner region originates from the place where the lips close and is sometimes called the villous region. It is distinguished by a pronounced pink-red color, since many blood vessels are located near the upper layer of the epithelium. Special papillae are distinguished, which are embedded in the epithelium, which is much thicker than in other zones. Also in this part the ducts of the salivary glands are formed.
The structure of the human lower lip, like the upper lip, involves an accumulation of nerve endings, especially in the transition zone, which explains the sensitivity of this part.
Mucosal zone
The structure is identical to the mucous membranes. The layers of the epithelium are not keratinized, there are relatively many of them. Salivary glands are formed, sebaceous and sweat glands are completely absent. The transition to the salivary gland section is carried out due to its own mucous plate, which also contains accumulations of blood vessels. Next come layers of muscle tissue, connective collagen fibers.
The mucous membrane passes into the gums and a frenulum is formed in the middle of both the upper and lower lips. They consist of elastic, collagen fibers and non-keratinizing epithelium.
Option 2. Labia too large
In the case of the labia majora, the consequences of dysfunction are similar:
- Excess tissue rubs, gets injured, and in some patients even forms folds where secretions accumulate, which are an excellent habitat for bacteria.
- Playing sports or any other serious physical exercise leads to microtraumas, wounds, tissue hypoxia and, as a result, susceptibility to various infections. Irritated tissue is easily permeable to microbes, which leads to diseases, papillary and even cancerous lesions.
- Another big problem for patients with long labia is difficulty during sexual intercourse, during which the lips are retracted deep into the vagina.
Such pathologies are a medical indication for reducing enlarged labia using labiaplasty. This operation involves giving the correct shape to the labia minora (labiominoroplasty) or labia majora (labiomyoroplasty).
Labiaplasty
Treatment of lip cancer
How to treat lip cancer? When treating the disease, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital take into account many different factors: the patient’s age, histological type of tumor, features of the spread of the tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic provide multidisciplinary treatment for lip cancer:
- Surgical interventions;
- Radiotherapy;
- Chemotherapy.
Regardless of the chosen technique, they affect the lesion or tumor, areas of regional metastasis. For grades I and II of lip cancer, radiation treatment is performed, which includes external radiotherapy and surgery.
Treatment in the initial stages
Squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip is a common complex tumor process. Its treatment consists of two stages: removal of the main focus and the fight against metastases that have spread to neighboring tissues and organs. Radiation treatment can suppress the development of a tumor focus. The radiologist selects the method of radiation therapy individually, depending on the size of the tumor, stage of the disease, and age of the patient.
Removal using the Krail method
In the initial stage of the tumor, surgeons perform a wedge-shaped excision of the entire thickness of the lip under local anesthesia. In order to remove a defect on the lip, plastic surgery is performed - skin flaps are transferred from the patient's cheek. Removal of the lesion is performed using the Krail technique. The operation is performed at the first and second stages of lip cancer, when the tumor has not spread to nearby tissues. Surgical excision of carcinoma makes sense in the absence of metastases.
The decision to remove a lymph node is made by an oncologist surgeon if the primary tumor process has already been cured or if the lymph node is removed along with the removal of the main lesion. In some cases, surgeons remove the primary cancerous tumor, the affected lymph nodes and the vessels that connect them. The scope of the operation is determined collectively by the clinic's oncologists.
Due to the fact that metastasis can occur in a cross way, the lymphatic apparatus of the suprahyoid region on the left and right is removed. If the oncologist sees that there are cancer metastases in certain lymph nodes, he decides to remove them, and those that are located along the lymph outflow.
Treatment tactics for lip cancer depend on the stage of the disease:
- Preventive surgery at stages I and II of lip cancer is carried out exclusively in cases where it is not possible to control the dynamics of the disease and there are unfavorable prognoses regarding the spread of cancer;
- At stage III, in the absence of metastases, treatment is carried out using a combined effect on the lesion and adjacent areas;
- In case of spread of cancer cells and the presence of single metastases in the lymph nodes, oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform combined treatment of lip cancer with subsequent surgery, plastic surgery and surgical correction of the lips;
- In stage IVC, palliative chemoradiotherapy is performed.
Candidates and doctors of medical sciences use innovative methods of treating lip cancer. The presence of modern equipment and competent medical personnel who are attentive to all the wishes of patients allows us to achieve good results in the treatment of lip cancer for many years. Lip cancer, treated in the early stages, is cured in 97-100% of cases. At stage III, 67-80% of patients can be cured. In the fourth stage of cancer and repeated relapses, complete recovery occurs in 55% of cases.
How to care for your labia?
When the labia are in good condition, normal hygiene procedures are sufficient. Good conditions for the functioning of this genital organ will be provided by: a daily shower, the use of special cosmetics for intimate hygiene and the choice of cotton underwear.
If the labia are deformed and enlarged, secretions can accumulate in the folds of the skin, which is an excellent breeding ground for various bacteria. In this case, an important task is careful care agreed with the gynecologist.
It is very important to properly moisturize delicate intimate areas. To do this, you should use preparations containing hyaluronic acid, which makes the skin smoother and more elastic, and reduces the friction of the lips against each other.
Moisturizing the intimate area
Proper care of the labia not only prevents bacteria and viruses from entering the reproductive system, but also makes the vulva healthy.
Diagnosis of a tumor by a doctor in a hospital
What does lip cancer look like? It could be a small ulcer or a widespread tumor. Doctors at the Oncology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital make a diagnosis of lip cancer based on the patient’s complaints, the results of an external examination and additional studies. The oncologist carefully examines and palpates the lips, cheeks, gums and regional lymph nodes. When examining the red border of the lips, skin and mucous membrane, use a magnifying glass.
How to identify lip cancer? Further examination is carried out using instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound examination;
- X-rays of the lower jaw;
- Panoramic tomography;
- Cytological examination of material obtained by taking fingerprint smears from the surface of the ulcer or histological examination of tissue obtained during a biopsy.
For lip cancer with lymphatic metastasis, a biopsy of the lymph nodes is performed. To exclude hematogenous metastases, chest X-ray and ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs are used. When the diagnosis of lip cancer is confirmed, an X-ray examination of the chest organs, general clinical and laboratory examination (electrocardiography, blood and urine tests) are performed.
A PET-CT study (positron emission computed tomography) is prescribed for the following purposes:
- Determining the stage of lip cancer;
- Assessment of response to treatment;
- Detection of disease relapse during the observation period.
PET-CT is an innovative method that combines the capabilities of computer technology and radiology. At the Yusupov Hospital, it is used not only to diagnose lip cancer, but also to monitor tumor development and evaluate the outcome of treatment. Thanks to PET-CT, radiologists have the opportunity to very accurately carry out radiation treatment, significantly reduce the irradiation area, and minimize the impact on healthy organs and tissues.
In many cases, the use of PET-CT excludes a number of additional studies in the future. This allows patients of the Yusupov Hospital to save time and money. The issue of the need to use this method is decided individually for a specific patient at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. A comprehensive examination of patients using the latest diagnostic equipment, the use of modern methods of performing laboratory tests using high-quality reagents allows oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital to obtain reliable results and provide adequate therapy for lip cancer at an early stage.
Advice from expert gynecological surgeon Ivanov A.V.
The labia can be affected by herpes, fungal diseases, HPV infection or even cancer. Therefore, when you feel itching, pain or burning in the vulva, you need to consult a gynecologist. You should also see a specialist if you notice any unusual tissue growth, ulceration, warts, nodules, or discoloration of the labia.
Regarding the size of the labia, modern plastic gynecology can solve almost any problem, so do not hesitate to contact our specialized Intimate Plastic Center in St. Petersburg with such questions.
You can see photos of labia disorders here ⇒.
Symptoms of lip cancer
There are local and general signs of lip cancer. Local symptoms of a malignant neoplasm can often be seen on the lower lip. When the pathological process is located on the mucous membrane of the lips, facing the vestibule of the mouth, the tumor has a pronounced malignancy. General signs of lip cancer can develop if the tumor is not detected in a timely manner and treated inadequately in the later stages of cancer.
First symptoms
The first signs of lip cancer usually go unnoticed. First, you can determine the enlargement of the mental lymph nodes. You can notice this by feeling the lower jaw. The next early sign of lip cancer is a swelling of a dense consistency. Itching occurs in it. This neoplasm is usually mistaken for a herpetic rash.
A small ulcer with a crust forms in the center of the swelling, which does not cause pain. If it is removed, the patient feels quite severe pain, and upon closer inspection, he may find a bleeding base, which is formed by tubercles.
Local signs of tumor
Symptoms of lip cancer are:
- Dyskeratosis of the lips;
- Papilloma;
- Erosion;
- Cheilitis.
In most cases, dyskateriosis looks like cracks and ulcers. The erosions are covered with a crust and resemble herpes in appearance, but, unlike it, they do not heal after a certain period of time. Some patients have no ulcers or erosions. Instead, a small compaction appears, which over time grows and becomes covered with a crust.
On the red border of the lower lip, away from the midline, a patch or formation may appear that protrudes above the surface. An erosion or ulcer with a granular surface and a roll-like edge forms in the center of the tumor. The formation has a dense consistency and gradually increases in size, eventually acquiring an irregular shape. Its boundaries are unclear.
Exophytic lip cancer predominantly develops from a warty form of productive diffuse dyskeratosis of papilloma. With exophytic growth, the tumor has a dense consistency, often covered with flat scales. Endophytic growth of a cancerous tumor is characterized by the formation of an ulcer with uneven, dense edges. It often appears against the background of destructive dyskeratosis, quickly infiltrates the soft tissues of the lip and is prone to metastasis.
Symptoms of the disease should be a signal to immediately contact oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital. Lip cancer, treatment of which is started on time, is completely cured in 90% of cases.
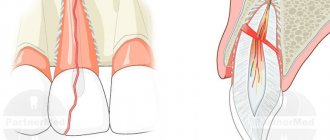
Vascular anatomy of the lips: which arteries supply blood to the lips
The lips receive most of their blood from the labial arteries. Thanks to their various branches, the labial arteries can effectively supply blood to the lips.
In addition to providing blood supply to the lips, the labial arteries provide adequate blood supply necessary for breathing, eating and facial activity.
The labial arteries are direct branches from the facial arteries .
Co-supply of the upper lip from the facial artery occurs in 97.3% of cases, from the artery arising from the transverse artery of the face in 1.8%, and from both at the same time in 0.9%.