Teething in an infant is a very exciting moment in the life of the baby and his parents. And although teething is a physiological process, almost all children experience discomfort and anxiety during this period. From the point of view of a scientific approach to this problem, the difficulty lies in the fact that with all the variety of teething symptoms from mild restlessness and moodiness, increased salivation to an increase in body temperature to high numbers and signs of impaired digestion, increased colic and diarrhea, there are no sufficient diagnostic criteria to connect all these numerous symptoms to the root cause. Nevertheless, many parents and some practicing pediatricians are still ready to blame the baby’s teething for almost all the troubles that befall them in the period from 5 - 6 months to one and a half - two years, when the teething process is mainly teeth should already be completed.
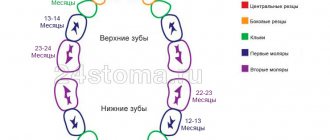
Most children begin teething between the ages of 4 and 7 months. As a rule, the eruption of each tooth lasts from 2 - 3 to 8 days. During this time, it is possible to increase body temperature to 37.4 - 38.0 degrees. At the same time, high temperature (from 38.0 and above) usually lasts no more than 2 days. Nasal discharge during the period when teeth are erupting is usually transparent, liquid, and should not contain pathological impurities: pus, greens, etc. Cough during teething is caused by saliva entering the nasopharynx and larynx area, which is released in large quantities. Cough due to teething does not require treatment. Regarding diarrhea, pediatricians sometimes differ in their opinions: some believe that diarrhea (loose stool) is not directly related to teething. And yet, studies have shown that from 10 to 30% of children have frequent and/or loose stools during teething. This is also explained by the large amount of saliva secreted, which enhances intestinal motility.
Teething or infectious disease
However, most modern pediatricians agree that such symptoms in an infant as: long-term, over 2-3 days diarrhea, cough, vomiting, fever (increase in body temperature above 38.5 degrees) are most often caused by infection, and not just teething teeth. Therefore, with any of the above symptoms, it is necessary to examine the child by a pediatrician, and only after other causes of increased body temperature have been excluded, efforts should be concentrated on helping the baby to reduce the discomfort from teething.
Maybe they don't exist?
All people have the beginnings of figure eights. But this does not mean at all that they will break through to the surface of the gums and there will be a full set of 32 permanent teeth on the dentition.
The structure of the modern human jaw makes the eruption of wisdom teeth increasingly difficult. Sometimes they simply do not have enough space on the jawbone, and they remain in the embryonic stage.
But there is also such a thing as an impacted wisdom tooth. This is a full-fledged molar, but it is completely or partially hidden in the jaw bone or gum.
Such teeth, despite the fact that they never erupted, are usually of completely normal size. In addition, they can get sick just like everyone else.
Read also: A wisdom tooth is cutting and it hurts, what to do?
The growth of wisdom teeth is very individual. Both the time of eruption of the “eights” and their location on the human jaw differ.
Teething: how to help your baby
This may require a fair amount of patience. During such a difficult period, you should take the baby in your arms more often, caress him, distract him from unpleasant sensations with toys, turn on pleasant, soothing music, and you can sing if natural abilities allow. A walk in the fresh air can also have a calming effect. Children who are breastfed, during teething, begin to cry more often and ask for the breast, and a loving mother needs to be patient, putting the baby to the breast every time, even if he grabs the nipple areola harder than usual during feeding. To satisfy the child’s need to chew something and hold something in his mouth, you can naturally use special rubber rings or toys, so-called teethers. You can offer your child dry food or baby cookies.
Currently, pharmaceutical companies offer a wide range of different products, primarily in the form of gels to “soothe the gums.” In general, most of these products contain painkillers such as lidocaine. You should not abuse these funds. They are not completely harmless; the anesthetics they contain can have an adverse effect on the child’s nervous and cardiovascular systems, and most importantly, they can cause serious allergic symptoms and contribute to the exacerbation of atopic dermatitis (diathesis) in children prone to allergies. In connection with the above, I can recommend, to reduce swelling and inflammation of the gums during teething, such special dental anti-inflammatory drugs for topical use as Cholisal gel, which can be applied to the baby’s gums 2-3 times a day, but must be rubbed in (not too much). of course) with light massaging movements over the entire surface of the gums, and not just putting it in the child’s mouth.
In addition, you can give a child suffering from teething special homeopathic drops, for example Dantinorm baby, according to the instructions for the drug. In any case, if the disturbing symptoms described above in this article appear, I advise you to play it safe once again and call a pediatrician to the home of a child with a high fever. A professional should give his diagnosis and recommendations.
At what age do wisdom teeth erupt?
Milk teeth are replaced by permanent teeth starting from the age of 6, this process ends around 12-13 years. The eruption of wisdom teeth most often occurs no earlier than 16-25 years of age. True, the literature describes cases where wisdom teeth erupted at the age of 40. But such cases are extremely rare.
Why did wisdom teeth get such a name?
Permanent teeth begin to erupt in a child at the age of 6-7 years, and the eruption of wisdom teeth occurs at the age of 16-25 years. It is by the age of 25 that the growth of all organs and systems of the human body, as well as their development, has completely ended, and then the process of aging of the body begins. Thus, the time when the eruption of the eighth teeth occurs can be considered the period of maturity of the organism, hence the last permanent eighth teeth got their name.
What you should not do if your wisdom tooth is sick:
- Under no circumstances should you apply any heat to your cheek (including heating pads), or rinse your mouth with warm water. As a result of any warming, the infection can spread even more, even suppuration of the bone tissue is possible.
- It is not recommended to put painkillers on the tooth area, because as a result, not only will the pain not be relieved, but an ulcer may form on the gum.
- Under no circumstances should you use advice given by friends and relatives. This or that remedy can help them, but the exact cause and diagnosis are unknown, as a result of which your wisdom tooth is swollen.
What to do if your gums are inflamed
Contact your dental surgeon immediately. Before you plan to do this, you can take an anesthetic (ketorol, analgin, etc.) orally. It is advisable to rinse the oral cavity with a cold solution, which is prepared at the rate of 1 teaspoon of soda and the same amount of salt per glass of water.
Treatment of such a pathology consists of incision (opening) of the mucous “hood”, further washing of the cavity and taking anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs. If a large amount of pus is removed during the autopsy, the patient must also take antibiotics. If the gums surrounding the wisdom tooth become inflamed again, then most often the dentist advises removing the wisdom tooth.
Caries
Carious lesions are another common problem that occurs during the eruption of wisdom teeth. The development of this pathology is due to the fact that the eighth teeth are located in a hard-to-reach place, which prevents good daily oral hygiene. Often, a wisdom tooth may erupt with initial signs of caries and damaged enamel. Due to the fact that such teeth are always pressed tightly against neighboring teeth, caries can quickly spread to them. In this case, after an examination, the dentist will decide whether the wisdom tooth can be treated or whether it is better to remove it.
The permanent crown did not appear
Long-term absence of permanent teeth can be caused by two reasons:
- Retention. It is characterized by slow eruption of the crown due to prolonged development of the rudiment or its incorrect position, for example, deep burial.
Retention can be either complete or partial. Partial is characterized by incomplete eruption, when the coronal part only appears slightly in the gum and stops growing.
These pathologies can be caused by certain factors:
Stimulation
In case of late tooth eruption, specialists prescribe special stimulating therapy. Standard stimulation therapy includes the following methods:
- Applying applications. To do this, use a ready-made 0.05% solution of humic acid obtained by isolating low-mineralized type sulfide silt mud.
The solution is prepared on the basis of isotonic sodium chloride. A tampon is soaked in the drug and applied to problem areas for an average of 5 minutes. The procedure is carried out for 15 days and no more.
This drug has a powerful biostimulating effect by improving tissue respiration, normalizing metabolic processes and sedimentation of minerals necessary for crown development.
In addition, the product leads to slight loosening of the bone area in the area where the rudiment is located, which facilitates its formation and eruption. Irritating removable dentures. It is a structure that looks like a bridge. But, unlike it, in an irritating prosthesis the main supporting part is located not on the adjacent teeth, but on the gum.
Due to constant pressure on the area of the jaw with an impacted rudiment, trophic processes are improved and its growth is stimulated. The period of wearing the prosthesis will depend on each specific case. Gum tissue massage. Aimed at regulating metabolic processes and saturating tissues with minerals. As a rule, massage is done 1-2 times a day until a positive result appears or for at least 8 months.
A set of exercises is selected by the doctor depending on the patient’s age and the area of the tooth. Physiotherapeutic procedures. The most effective in this case was electrophoresis performed using adrenaline or lidase. Both drugs have the same pronounced stimulating effect, but their therapeutic effects are completely different.
Read also: Number of roots and canals of teeth
Adrenaline is a hormonal drug whose action is aimed at stimulating the natural process of teething.
Unlike lidase, it gives a faster and more predictable result, but can cause a disorder in the hormonal balance of the child’s body, which will entail negative changes in terms of general health.
The main action of lidase is aimed at loosening the bone area in the area of the bud, which facilitates the process of its eruption.
This drug also has its disadvantages: such exposure can lead to disruption of the mineral balance of the dental tissue of the developing tooth and adjacent crowns. The drug Honsurid. Aimed at restoring the functions of the embryo and improving metabolism in bone and cartilage tissues. The drug is used externally, diluting it with novocaine or sodium chloride.
For a stimulating effect, the drug is used to treat the mucous membrane in the area of the supposed root of the problem area. The procedure can be carried out once every 2 days for 10 days.
In some cases, the course can be extended to 1 month.
Survey
Despite the existence of average periods for the eruption of permanent teeth, they are individual for each child.
A discrepancy of one or two years is quite acceptable.
But if eruption has not begun even 4 years after the loss of milk crowns, then this is a direct indication for a detailed examination. The following methods are used for this:
- visual examination – allows you to determine the general condition of the oral cavity;
- palpation and instrumental examination will show the degree of density of the gum tissue;
- intraoral targeted radiography. Performed to obtain accurate data on the position of the bud;
- orthopantomography – helps to see the condition of the embryo and its tissues;
- CT scan allows layer-by-layer examination of the tissues of the bud and the surrounding bone.
Diseases
During the examination, the following diseases are most often detected:
- rickets or rickets-like condition. It occurs due to a constant lack of bone-forming minerals due to a pathological condition. To resolve the problem, it is necessary to undergo long-term treatment with the inclusion of drugs with a high content of minerals and vitamins;
- pathologies of the endocrine system. Most often, the cause is hypothyroidism suffered in the first year of a child’s life. Treatment requires the use of hormonal drugs, both local and general;
- infectious diseases of a chronic type , for example, tonsillitis. As a rule, in the presence of such pathologies, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment aimed both at eliminating the disease itself and at increasing the immune functions of the body;
- acute respiratory diseases , which occurred at the beginning of the growth of permanent crowns. A problem of this nature should be addressed by a dentist together with a therapist.
Prevention of malocclusion
The timeliness of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones is important, since the correct development of the child’s bite depends on this. To ensure the normal formation of the dentition, it is necessary to follow a number of important rules:
- parents need to monitor the quality of their child’s oral hygiene , since children’s enamel is most susceptible to caries, and this can provoke premature loss of the crown;
- The child's diet should be as balanced as possible . It should not contain large quantities of foods containing fast carbohydrates. The menu should include foods rich in microelements and vitamins ;
- You should not avoid routine visits to the dentist. This will help prevent the development of dental pathologies and reduce the likelihood of retention;
- to take the child to an orthodontist or dental therapist as soon as possible .
Even more information about baby teeth in the video from Dr. Komarovsky:
What to do?
If a breast crown falls out, there is no need to immediately run to the dentist. In order to reduce the risk of infection in the wound and eliminate negative consequences, the following steps must be taken:
- Immediately after the prolapse, it is necessary to form a tampon from cotton wool or medical gauze and place it on top of the hole. The child should lightly press it with his teeth and fix it in this position for 15 minutes .
During this period, a blood clot is formed in the socket cavity, which performs protective functions. As the hole becomes overgrown, it will disintegrate on its own.
- During the day, you can irrigate the wound with antiseptic drugs .
- In order to relieve swelling, it is recommended to take baths with a solution prepared from ½ teaspoon of salt .
- Before eating, to minimize pain, it is recommended to treat the edges of the wound with lidocaine-based dental gel . For children, a special drug called calgel .
- You should not give your child food within 2 hours after a tooth falls out.
- On the first day, you should avoid eating foods at borderline temperatures, as well as foods high in acids.
Consequences of wisdom teeth removal
In almost all cases, removal of wisdom teeth is traumatic, which can result in slow healing and various complications. Pain after such a procedure may occur due to alveolitis, an inflammatory process in the socket. Normally, the hole is covered by a blood clot, which protects the wound from pathogenic microbes entering it. That is why it is strictly forbidden to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction! When a blood clot is washed out, an infection may develop or a dry socket may occur, which may require further surgery. In some cases, after removal of the “eight”, numbness of the tongue, chin or lip may occur in the first days. If this condition does not go away within a week, you need to consult a doctor again, who will prescribe the necessary treatment.
Is it normal for a baby tooth to have not fallen out yet, but the molar tooth is already growing?
It also happens that a child’s teeth begin to grow “in two rows.” Many parents find this funny and are in no hurry to take their baby to the doctor, waiting until the baby tooth falls out on its own. And this is an erroneous position, which will only add to bite problems in the future.
As a rule, the molar, which grows under a tightly seated deciduous tooth, finds its exit in the gum from the side of the tongue. Incorrect position disrupts the bite. And the longer competitors fight for one place, the more crooked the permanent tooth will grow.
“Such cases are due to the anatomical features of the child’s oral cavity,” notes Victoria Arutyunova. — The permanent tooth is already growing, but the root of the milk tooth has not yet resolved. In this situation, you need to help the child get rid of the tooth, since, as practice shows, it cannot fall out on its own.”
Do baby teeth need to be treated?
Caries is quite common in children at a very young age. To prevent caries, parents should pay special attention to their baby’s oral hygiene.
You need to treat caries in baby teeth! If caries is not treated, it can cause serious complications:
- early (unnatural) removal can lead to incorrect formation of a permanent tooth or to disruption of bite formation;
- violation of chewing function, which leads to the development of gastrointestinal pathologies;
- the development of pulpitis or periodontitis, which can provoke purulent inflammatory processes.
Why don't new teeth grow?
A situation may arise when the baby teeth have fallen out, all reasonable periods have already passed, but the permanent teeth still do not appear. There may be several explanations for this.
All of them fall into the category of pathologies that require specialist intervention
. An orthodontist deals with such problems. He is the one who knows how to correct any bite problems.
So, here are the two main reasons why a normal dentition does not form after the loss of temporary milk teeth.
This is, in essence,
a delay in eruption
. It can be complete or partial. If the crown part appears in the hole left after the baby tooth and the process stops, then they speak of partial retention.
If you can’t even see the crown, then the retention is complete. It can occur due to various reasons.
First of all, this is the early loss of a baby tooth
. That is, it fell out before the permanent one had time to fully form. This situation may arise due to the removal of milk, for example, by a doctor due to caries or accidental.
Drop Delay
can also cause retention, as well as incorrect or too deep location of the rudiment.
This is a more serious problem. Adentia in dentistry is the absence of teeth. This happens not only in old age, but also in young children.
One or more missing units in the bite – partial edentia. This may happen due to the fact that the embryo died before it had time to grow.
This developmental disorder is quite rare. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the death of the embryo occurs immediately after its formation - during intrauterine development.
For example, if a woman took strong medications during pregnancy around the end of the second - beginning of the third trimester. However, such an effect is rarely observed. In extremely rare cases, complete adentia occurs in children, when permanent teeth do not grow at all.
How long does it take for new ones to grow?
The first molars that a baby grows are “sixes.” They are not even associated with milk loss. However, the rest are already growing in those places that have become vacant.
The whole process begins around the age of six, and its completion is delayed until the age of 12–13. It is considered normal if this process began at age five and ended at age 14–15.
Small variations in the time of growth of new teeth, both in the direction of their decrease and increase, in most cases have no significance
. All children have different growth conditions, developmental characteristics, heredity, nutrition and a huge number of factors that affect how long permanent teeth will grow.
Why are we talking about such a long period - from 6 to 14 years? Because molars grow in the same sequence in which baby teeth fall out. But how long it takes for a tooth to grow after a baby tooth falls out is a completely different question.
On average, we can talk about a month - four weeks. It is after this amount of time that the “mouse” can bring the tooth back, updating it accordingly.
Read also: Sealing is
This period is also subject to change. The growth of the first permanent molars usually occurs most easily - central and lateral incisors, first molars, and so on. Their germination can last from just a few weeks to three to four.
However, those teeth that we used to call chewing teeth take longer to grow. Maybe up to a month and a half. Here it is also worth talking about the individual characteristics of the child’s development and the many additional factors that can affect this development.
Heredity, lack of nutrients, vitamins and minerals needed by the baby can increase these periods
. Therefore, the appearance of a gift tooth from a “mouse” can be delayed up to two months or even two and a half.
Of course, any deviations from the normal timing should be a signal to parents that they need to see a dentist. He will take an x-ray and find out the reason for the delay. However, in most cases this is a normal natural process that should not be interfered with.
What dentists say about this - watch the video:
So why do baby teeth fall out? We will answer this question in a separate publication.
This article will help you with choosing an electric brush for children's oral care.
When is it necessary to remove wisdom teeth?
Whether it is necessary to remove a wisdom tooth or not is the most common question that interests every person who is faced with the problematic eruption of “eights”. For wisdom tooth removal, as for any other surgical procedure, there are indications. Wisdom teeth are removed if:
- There are impacted “eights” - those that are incorrectly positioned in the jaw and cannot erupt, since they rest partially or completely on other teeth
- The “eight” has partially erupted, but there is pain and inflammation in the gums (recurrent pericoronitis).
- For pain along the trigeminal nerve.
- Presence of a mandibular cyst.
- Periodic pain in the area of the wisdom tooth, accompanied by headache, pain when swallowing or other painful conditions.
- Trauma to the oral mucosa as a result of improper tooth positioning.
How long do eights grow?
The process takes place individually. At what age a wisdom tooth can erupt depends on its readiness. By the age of 17, its main part (crown) is just beginning to form. The roots are still in progress. This will continue for about 3-4 years. In the range of up to 40 years, you can expect its appearance from the gums. For each person, this process occurs differently in terms of time and symptoms. The Guinness Book of Records records the latest case at 94 years. Some people experience a whole list of unpleasant symptoms with pain and fever, while for others everything happens quietly and calmly. At what age wisdom teeth erupt is a secondary matter. The speed of appearance is influenced by the size of the jaw. If there is not enough space, it will be difficult for the crown to come out of the gums.