Sweet taste in the mouth, causes, symptoms
A sweet taste in the mouth may indicate serious illness.
The human tongue is equipped with special receptors, thanks to which the taste of food and the sensation after it are felt. Why does it taste sweet?
Changes in any department lead to disruption of body functions and distortion of impulses sent to the brain.
They return to the receptor papillae on the tongue and completely change the sense of taste, so that sour and bitter tastes are perceived as sweet after food is eaten.
When absorbing food, the concentration of taste is high and its change is not observed.
General description of the anomaly
The sensation of sweetness, present in the oral cavity for a short time after eating desserts, is a natural, transient reaction of receptor zones that has no clinical significance. The need to visit a doctor is indicated only by phantageusia - the presence of the taste sensations in question in the absence of the influence of irritating substances on the analyzers (cells, their microvilli).
The described pathology can be permanent (protracted) or short-term. It is observed only in the morning or throughout the day, occurs in isolation or is accompanied by additional symptoms. Among the latest:
- bad breath;
- the appearance of dense gray deposits on the tongue;
- heaviness, discomfort in the stomach.
Shades of abnormal taste sensations vary from sweet and sour to cloying, milky and bittersweet.
Causes of sweet taste
A disorder in the digestive system can cause a sweet taste in the mouth.
The reasons for the change in taste in the mouth to a sweet taste are:
- Disorders of the digestive system. Occurs with gastritis and peptic ulcers, when there is an increased level of acidity. From the stomach, part of the processed food is thrown into the esophagus.
- Presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. This infection often affects the sinuses, causing congestion, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. Taste sensations are disturbed.
- Smoking. In the tongue receptors, with constant exposure to nicotine, the perception of taste changes.
- Poisoning with chemicals (pesticides).
- Pancreatitis. The development of pancreatitis is indicated by a persistent aftertaste in the morning and an unpleasant burning sensation in the stomach.
- Liver pathology.
- Impaired carbohydrate metabolism, overeating or eating a lot of sweets.
- A state of constant stress and tension. Inflammation of the facial or trigeminal nerve.
- Diabetes mellitus, in which a sweetish taste is formed in the mouth, additional symptoms appear: hunger, thirst.
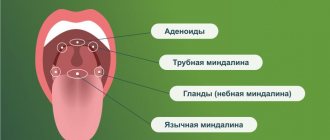
- Dental problems, diseases of the nasopharynx: pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis, caries, periodontal disease.
- When women become pregnant, functional changes occur throughout the body. Taste priorities also change.
- Respiratory tract infection.
Diagnostics
To determine the etiological factor of the sweet taste in the mouth, a consultation with a gastroenterologist is required, who, after an initial examination, can refer the person to other specialists. First, the doctor collects an anamnesis and examines the oral cavity in detail for purulent processes, then prescribes specific tests and instrumental methods. From a diagnostic point of view, the most important are:
- Blood tests
. In a biochemical study, attention is paid to glucose levels; even with a slight increase in sugar, an oral stress test is performed. To determine the cause of a sweetish taste in women, the concentration of estrogen and progesterone is assessed, and the level of hCG is measured. A clinical blood test reveals leukocytosis and increased ESR. - Gastroscopy
. If the unpleasant taste is accompanied by heartburn and chest pain, an endoscopic examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract is informative. The method is necessary to identify inflammatory changes in the mucous membrane, disorders of the contractile function of the lower esophageal sphincter. During endoscopy, a biopsy of pathologically changed areas is performed. - Sonography
. During a targeted ultrasound of the pancreas, the heterogeneity of the structure, the presence of hypoechoic areas, and space-occupying formations are determined. With pancreatitis, swelling and blurred contours of the organ are detected. Women are shown an ultrasound of the pelvic organs; transvaginal ultrasound is used for detailed visualization. - Neurological examination
. If the sweet taste is combined with paresthesia and swallowing disorders, damage to the central nervous system structures must be excluded. A standard examination includes checking pharyngeal and pupillary reflexes and assessing muscle strength and tone. To visualize the brain, an MRI or CT scan with contrast is performed. An EEG is sometimes recommended.
Possible complications
The taste of garlic in the mouth, which appears as a result of eating the plant or due to hormonal imbalance, does not require the use of medications and disappears on its own after 24-72 hours. Milk, lemon juice or parsley will help speed up the process of removing sulfurous substances from the body.
If the unpleasant taste is caused by the development of dental pathologies, diseases of the ENT organs or gastrointestinal tract pathologies, corrective treatment is required aimed at eliminating the disease and preventing further infection. If left untreated, the unpleasant condition will only worsen, leading to the destruction of tooth enamel, breathing or digestion problems.
The most dangerous cases are arsenic poisoning and selenium overdose, which can cause death. In this case, when a garlic taste appears, it is necessary to take emergency measures to prevent further toxic effects, as well as quickly cleanse the body.
The appearance of a garlic taste in the mouth is one of the common symptoms that often occurs during the season of respiratory infections and is associated with eating the vegetable. A garlic taste that disappears after careful oral hygiene or drinking milk can also be a symptom of hormonal dysfunction or heavy metal poisoning, as well as diagnose gastrointestinal problems that require medication and a special diet.
Taste of garlic in a child
The taste of garlic that appears in a child’s mouth can occur both after eating a vegetable and in the case of using medications containing garlic (choleretic drugs). In addition, a child’s garlic taste is one of the reasons for poor oral hygiene, which provokes the accumulation of bacteria or dental pathologies.
Children can also provoke a garlic taste:
- sore throat and condition of the tonsils;
- gas formation, stomach cramps;
- problems with urination;
- frequent stress.
If you visit the dentist and there are no oral problems, parents should make an appointment for the child to see a therapist to eliminate adenoid diseases, and also take a urine test.
Due to inflamed tonsils
If there is pathology of the tonsils, the baby will be prescribed conservative therapy or surgical removal of the inflamed cavities.
Treatment always begins with conservative therapy, including:
- washing the tonsils with infusion of chamomile or calendula, or saline solutions;
- the use of nasal drops with a drying and anti-inflammatory effect (solutions of protargol, collargol, albucid);
- taking vitamins C, D and ascorutin;
- prescription of physiotherapeutic treatment (UV irradiation of the nasopharynx, electrophoresis with drugs, laser therapy);
In the absence of positive results, as well as in the case of frequent (more than 4 times a year) respiratory diseases, surgical intervention is performed.
Due to problems with urination
To diagnose genitourinary pathologies, it is necessary to take a urine test, after which the doctor may prescribe an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, or an x-ray to clarify the diagnosis.
After the diagnosis is made, the following is prescribed:
- antibacterial therapy (Amoxicycline, Ceftrianson or Furazidine);
- ibuprofen;
- desensitizing agents (Loratadine);
- vitamin and mineral complexes.
Diagnosis and which doctor to contact?
It is worth noting! If a person experiences the taste of fish in his mouth and those around him smell it, then this becomes a big psychological problem.
To avoid it and understand the causes of this condition, you should seek help from a doctor.
Initially, you can contact your dentist to rule out problems with the oral cavity.
If everything is fine with this, then plan your next visit to a therapist .
The doctor will conduct a general examination and, if necessary, refer you to specialists.
Diagnostic procedures may include the following research techniques:
- Abdominal ultrasound to identify gastrointestinal diseases and sinus ultrasound to rule out problems in this area;
- taking scrapings from the mouth ;
- donating blood for analysis;
- checking sputum for the presence of fungal infection;
- X-ray of lung tissue, nasal septum;
- in extreme cases, a biopsy is performed;
- immunogram;
- CT and MRI.
After receiving all the test results, the general practitioner will be able to decide which specialist to refer the patient to.
Depending on in which organ the problem of fishy taste in the oral cavity lies, the attending physician is determined who can eliminate the disease.
Keep in mind! This could be an endocrinologist, dentist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, otolaryngologist and other specialized specialists.
Set my teeth on edge
Frequent heartburn and sour belching often accompany pregnancy: the growing uterus puts pressure on the diaphragm, intra-abdominal pressure increases. Those who eat a lot at night also often experience a sour taste in their mouth in the morning. But if these reasons have nothing to do with it, then it is better to deal with this symptom specifically. A persistent sour taste can occur:
Article on the topic
Diagnosis by a drop of blood. Siberian scientists identify potential diseases
for diseases of the digestive tract - often this is a sign of hyperacid gastritis, which is accompanied by increased stomach acidity, or gastroesophageal reflux, as well as gastric ulcer. If, in addition to a specific taste, a person is bothered by pain in the upper abdomen, nausea after eating, heartburn, sour belching, frequent diarrhea or constipation, weakness, it is worth visiting a gastroenterologist. And in order not to guess, you need to do a gastroscopy;
in case of problems with teeth - with caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, in addition to a sour taste in the mouth, there may be toothache, swelling and bleeding of the gums. Hurry to the dentist!
Causes of bitterness and nausea
Bitterness in the mouth and nausea often occur after eating
When considering the mechanism of bitterness and nausea, it is first worth paying attention to the functions of the liver.
The fact is that it is this organ that not only filters the substances entering the body for their further removal, but also synthesizes a considerable amount of organic materials that are necessary for the stable functioning of the body.
One of these, of course, is bile, which enters the gastrointestinal tract (hereinafter referred to as the GIT) and participates in the digestion process.
Bile acids perform a colossal range of functions - from breaking down fats to stimulating the work of enzymes, but they taste unpleasant and in large quantities are dangerous for the soft tissues of the digestive tract and nasopharynx.
To avoid bile from entering these cavities of the body, human nature requires the presence of a special sphincter, which limits the acidic environment of the stomach from more sensitive areas.
Disturbances in the functioning of this muscle, caused by gastrointestinal pathologies, invariably provoke the release of bile acids into the upper digestive tract and nasopharynx, which ultimately manifests itself in an unpleasant bitterness in the mouth.