Bad breath, which can become a constant companion of a person, can ruin relationships with others and reduce self-esteem. This condition is called halitosis, or halitosis. It is not an independent disease, but is one of the important symptoms of pathologies of the oral cavity and internal organs. You can drown out the stench with mints, spray or chewing gum, but this will not get rid of the problem. We need comprehensive diagnostic measures and subsequent elimination of the causes of halitosis.
Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis: symptoms
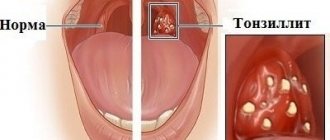
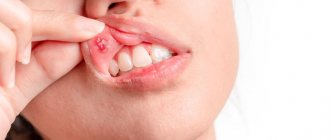
Often, for a long time, chronic tonsillitis occurs without symptoms or has scanty symptoms (in a simple form). There may be discomfort when swallowing food and liquids, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat, dry mouth, halitosis (bad odor) and tingling. Externally, the tonsils increase in size and there are signs of inflammation. The disease is characterized by exacerbations of sore throats up to three times a year, long periods of recovery, with general symptoms of asthenia and prolonged low-grade fever.
For the toxic-allergic form, more frequent exacerbations are typical, often with complications in the area of neighboring tissues (pharyngitis, peritonsillar abscesses), and the almost constant presence of asthenia and prolonged fever are typical.
The clinical picture of chronic tonsillitis during an exacerbation is as follows:
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- redness of the throat and tonsils;
- characteristic plaque;
- purulent discharge from the tonsils;
- bad breath;
- swelling of the nasopharynx;
- temperature increase;
- weakness;
- headache;
- fast fatiguability;
- arrhythmia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- dyspnea.
Ways to combat unpleasant odor
It is not always possible to independently guess that your breath smells bad. A person does not perceive an unpleasant aroma, so he can judge its appearance by indirect signs. If you have any suspicions, you can use the edge of a spoon to collect plaque from your tongue and smell it. The condition of the saliva is judged by licking the wrist and waiting for it to dry.
You can get rid of an unpleasant odor using traditional methods. At home, a decoction of dill is used to rinse the mouth. At home you can prepare an infusion of medicinal herbs with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects:
- chamomile;
- Oak bark;
- sage;
- mint;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort.
At home, a decoction is prepared from a mixture of several herbs to increase effectiveness. The infusion must be highly concentrated to suppress the growth of bacteria and cleanse the oral cavity.
If halitosis is associated with eating foul-smelling ingredients, parsley or celery root will help get rid of it. They block foul odors, and chewing the fibrous structure cleanses the teeth. Observance of a drinking regime relieves halitosis. Clean water cleanses the oral cavity and keeps saliva in a liquid state.
The reason why these methods do not help are pathologies of digestion and metabolism. You can get rid of them at home only under the guidance of a doctor.
Causes, main risk factors
Up to 30 different colonies of pathogenic microbes can be sown on the surface of the tonsils of patients suffering from chronic tonsillitis. But in crypts and lacunae staphylo- or streptococcus is usually determined. A key role in the pathogenesis of chronic tonsillitis is played by beta-hemolytic strains of streptococcus (type A). Other flora - gram-negative coccal, fungal, viral - have an impact on local immunity, they support inflammation.
There are a number of factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- decreased immunity;
- microtrauma of the tonsils;
- foci of inflammation in the mouth and in the head area (caries, sinusitis, adenoids, etc.);
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- allergy.
Viruses and bacteria that cause tonsillitis can come from the external environment.
What is the role of the palatine tonsils?
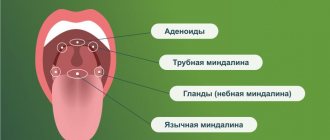
Tonsils are organs consisting of lymphoid tissue that are located in the nasopharynx and perform the function of immune defense. They got their name because of their external resemblance to an almond, which is why anatomists began to use the name “almond.”
Lymphoid tissue in the pharynx is present not only in the palatine tonsil, but also in other structures:
- lingual and nasopharyngeal tonsil;
- lymphoid foci of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
The lymphoid tissue of the pharynx is an important part of the immune system, since on its surface contact of the body’s immune cells with the environment occurs. The information received by the immune cells in the lymphoid structures of the pharynx is transmitted to the next level of immune organs (thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes) for the production of protective proteins (immunoglobulins). Subsequently, they neutralize pathogenic viruses, bacteria, fungi and protozoa that enter the body from the external environment.
With age, the role of the tonsils as immune organs is gradually lost. Lymphoid tissue is gradually replaced by connective tissue elements, so involution (reverse development) of organs begins. The nasopharyngeal tonsil is the first to undergo involution, later it spreads to the lingual and palatine tonsils. Therefore, in the elderly, the tonsillar tissue (tonsil) decreases to the size of a pea.
The palatine tonsil is the most complex in structure. It consists of a large number of channels - crypts (or lacunae). Some crypts look like a shallow, more or less straight tubule, others have greater depth, branch like a tree, and some crypts are interconnected. Often, where the crypt opens into the pharynx, there is a narrowing of the canal. This makes it difficult to clear it of its contents, against the background of which an inflammatory process develops.
The palatine tonsil is bounded by a capsule - a dense connective tissue membrane. Outside of it there is a layer of loose tissue - paratonsillar or peritonsillar tissue. With severe inflammation, the infection destroys the barrier of the capsule and goes beyond it, causing inflammation of this fiber. This condition is called paratonsillitis. It refers to a serious complication, which, if treated incorrectly or untimely, can have serious consequences, such as the development of a purulent focus in the soft tissues of the neck (peritonsillar abscess, phlegmon of the neck), sepsis, and damage to internal organs. Therefore, it is necessary to start treatment as early as possible.
Classification
Doctors distinguish various clinical forms of chronic tonsillitis, differing in clinical manifestations, severity of the condition and prognosis, risk of complications, as well as treatment tactics.
The simple form of chronic tonsillitis is characterized by a predominance of local symptoms. If general manifestations and lymphadenitis occur, this is referred to as a toxic-allergic form of tonsillitis. It comes in two versions:
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis 1st degree . Sore throats are typical for him, which can worsen after ARVI, combined with general symptoms.
Toxic-allergic chronic tonsillitis of the 2nd degree - the symptoms are more pronounced, associated with diseases that have common factors of etiology and pathogenesis.
According to the degree of compensation of the process, the disease is divided into two options:
- chronic tonsillitis, compensated form - the source of infection is in a dormant state, there are no reactions from the body, repeated sore throats do not occur; The function of the tonsils and general reactivity are not impaired.
- chronic tonsillitis is a decompensated form - relapses of sore throat occur, complications of the heart, damage to the paranasal sinuses, middle ear, and renal complications are possible.
According to pathomorphological criteria, the process is divided into the following options:
- lacunar tonsillitis with predominant damage to the area of the lacunae;
- parenchymal-lacunar, involving in addition to the lacunae also the area of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils themselves;
- phlegmonous - inflammation is predominantly localized in the area of lymphoid tissue;
- sclerotic with abundant growth of connective tissue fibers in the area of the tonsils and surrounding tissue.
Complications of chronic tonsillitis
Against the background of a chronic inflammatory process in the tonsil area, various complications are possible. Therefore, it is important to know why chronic tonsillitis is dangerous. Thus, the tonsils themselves, losing their function as a barrier to infection, become its breeding ground. Inside them are pathogens with the products of their metabolism. The infection can spread throughout organs and tissues, affecting the renal parenchyma, joint and heart tissue, and liver. In addition, tonsillitis adversely affects the functioning of the immune system and can be a provocateur of collagen diseases - lupus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, periarteritis. The skin and peripheral nerve fibers may also be affected. With prolonged intoxication against the background of the disease, damage to blood vessels (vasculitis) and platelets (purpura) is possible.
Reasons for the appearance of a purulent odor during inflammation of the tonsils
Why does my breath smell when I have tonsillitis? The tonsils, which have natural depressions or lacunae, absorb most of the pathogenic bacteria - pathogenic microorganisms, while retaining the remnants of their vital activity, decomposing pieces of food and particles of dead cells of the tissues of the oral cavity. This is exactly how unpleasant clots appear on the tonsils, causing over time the appearance of a purulent odor.
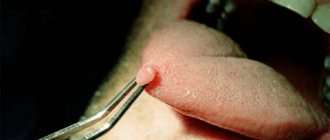
The inflammatory process can occur for various reasons (hypothermia; bacterial or viral infections; dental diseases and much more), but the consequence of this most often is the formation of purulent plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils . It is from them that the unpleasant odor of pus comes from the mouth. In advanced forms of the disease, these plugs turn into almond stones : they harden in the lacunae of the tonsils when calcium salts are deposited. Often patients can see them with their mouths wide open: white calcified deposits appear on the inflamed tonsils, which give off an unpleasant odor.
What do tonsil plugs and stones look like?
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis occurs on the basis of complaints, examination of the patient, and questioning of the patient. Objective signs, manifestations of chronic tonsillitis, and the general condition of the tonsils are important; the doctor determines the stages of the process and the form.
The following diagnostic procedures are also carried out:
- throat swab for flora;
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood test for antibodies to streptococcus.
This helps determine treatments for chronic tonsillitis.
Diagnosis of the disease
A diagnostic search for chronic tonsillitis is not only making a diagnosis, but also determining the form of the disease. Therefore, the examination is always comprehensive, which includes:
- Objective examination data (redness, swelling, injection of blood vessels on the tonsil mucosa, etc.);
- Survey – assessment of complaints, the history of their occurrence and other anamnestic information;
- Microbiological examination (seeding pathological secretions taken from lacunae on special media to determine the causative microbe, as well as its sensitivity to antimicrobial drugs);
- Laboratory tests (blood, urine);
- Instrumental examinations (ECG, ultrasound of the heart and lymph nodes).
Assessment of these parameters allows you to correctly determine the stage of the inflammatory process and optimally select treatment.
| Examination method | Signs | What does the examination give? |
| Collection of anamnesis and complaints | Pain and discomfort in the throat, sensation of a lump or foreign body, heart and joint pain, general weakness, malaise. Single or multiple exacerbations of tonsillitis throughout the year. | Allows you to suspect chronic tonsillitis and the stage of the process, and evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. |
| Pharyngoscopy | Pus or purulent plugs on the surface of the tonsils (pathological secretion fills the lacunae). Redness, infiltration and swelling of the arches of the palate, their cicatricial fusion with the tonsil. | Confirms the diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis, but does not allow assessing the stage of the process. Allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of conservative treatment. |
| Bacteriological examination | Identification of the microorganism and its sensitivity to antibacterial therapy. | Allows you to identify the causative microorganism and select the necessary treatment. Assess the effectiveness of conservative treatment. |
| Laboratory diagnostics | Clinical blood test, biochemical blood test (urea, creatinine, ALT, AST), C-reactive protein, ASLO, rheumatoid factor, IgE, total blood IgA. | Allows you to determine the activity of inflammation, identify the risk of development or the presence of concomitant diseases (rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, polyarthritis, infective endocarditis, etc.) Helps choose treatment tactics, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. |
| Functional diagnostics | ECG (electrocardiogram) Echo-CG (ultrasound of the heart) Ultrasound of the kidneys Ultrasound of the lymph nodes of the neck. | Helps determine the stage of chronic tonsillitis, identify the presence of associated diseases (rheumatism, glomerulonephritis, polyarthritis, infective endocarditis, etc.) Helps choose treatment tactics. |
Treatment methods in adults
In most cases, they resort to conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Source: Modern methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Eremina N.V., Shcherban K.Yu. Medical Council, 2022. p. 68-72:
- therapy for inflammation in the head and oral cavity;
- procedures that increase immunity (hardening, taking vitamins, physical education, etc.);
- hyposensitizing drugs (to suppress allergic reactions);
- immunomodulators (normalize the immune system);
- means of reflex action (acupuncture, manual therapy);
- washing the tonsils with antiseptics;
- administration of drugs to the tonsils.
The treatment plan is complemented by physical therapy for chronic tonsillitis.
A radical method of treating chronic tonsillitis is surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy). The operation is performed in cases where inflammation occurs more than five times a year and does not respond to complex conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Source: Choosing an antibiotic for exacerbation of tonsillitis. Karpishchenko S.A., Kolesnikova O.M. Medical Council, 2015. p. 40-43.
How to get rid of bad breath with tonsillitis?
Treatment of minor symptoms (such as unpleasant breathing) is unacceptable for tonsillitis, since inflammation of the tonsils and the chronic form of the disease can lead to very serious health problems: give complications to the heart, kidneys, thyroid gland, joints and blood vessels, and, of course, while a person is sick, the smell will not disappear, even if you try to mask it.
How to get rid of tonsillitis and bad breath? There are several ways to combat this disease.
Treatment with traditional methods
And although drug intervention for tonsillitis is called treatment, it is rather superficial in nature, since it cannot completely relieve the patient of the disease in a severe stage. It is important to understand that the methods presented below only inhibit the development of the disease, and also involve temporary elimination of symptoms , but cannot relieve the patient of the most important problem - the elimination of purulent stones and foci that cause an unpleasant odor.
- Local use of antiseptic drugs
To do this, you can rinse your mouth with Lugol, tincture of iodine, iodine glycerin, saline solution, decoctions of chamomile, linden, celandine or St. John's wort (you will need to infuse 2 teaspoons of the herb in 1 cup of boiling water for 30 minutes).
- Antibiotic therapy
The doctor prescribes a course of medication to combat tonsillitis, selecting the necessary antibiotic depending on the causative agent of the disease. The most common type of pharmacological drugs is protected penicillins.
- Physiotherapy
An ENT specialist can prescribe procedures that will help have a beneficial effect on inflamed tonsils: phonophoresis, ultraviolet light, diameter or laser.
- Antiseptic lavage of lacunae
A similar procedure temporarily saves you from bad breath: while rinsing the mouth, the grooves in the tonsils are washed with Miramistin, Furacilin or Chlorhexidine.
- Solving dental problems
Sometimes bad breath and sore throat, and then an inflammatory process that turns into tonsillitis, can be caused by diseases of the teeth or gums. Eliminating these problems will significantly alleviate the problem with bad breath, and also get rid of infectious foci that irritate the tonsils.
Important! Self-exposure to tonsil plugs and stones without the supervision of a medical professional can aggravate the situation . You should not touch the affected tissues with your fingers, ear sticks or other objects: there is a risk of introducing additional bacteria into the resulting wound, as well as damaging healthy tissues, which will only expand the affected area with tonsillitis.
Surgical intervention
Removing tonsils is a popular topic of discussion among various medical professionals, however, with advanced tonsillitis, doctors can resort to this method. The so-called tonsillectomy , that is, an operation to completely remove the tonsil, is now performed only in severe stages of tonsillitis with complications. Often, surgeons remove only the areas of the tonsils in the mouth that are most affected—this type of surgery is called a tonsillotomy . This procedure is considered the most gentle for the patient, since recovery after such an intervention occurs quite quickly, and the organ in the oral cavity partially continues to perform its protective function.
When is a tonsillectomy prescribed?
- in cases of frequent relapses of tonsillitis - from four times a year;
- in case of complications of the disease affecting other vital organs of the patient;
- when the process of decay moves from the tonsils to other areas of the oropharynx;
- in situations where traditional treatment for tonsillitis does not produce a positive effect.
Types of tonsillectomy:
- Classic way . Surgeons use special loops, a scalpel and scissors. This method of treating tonsillitis in comparison with modern procedures is considered less practical: it involves a high degree of trauma to the oral cavity and a long postoperative recovery period;
- Laser removal . This method of dealing with tonsillitis is considered more acceptable in our time, since it does not involve pain during the operation and a long recovery period after it, as well as swelling after completion of the procedure. The downside is the risk of burning healthy tissue in the mouth area;
- Ultrasonic scalpel . This method of combating tonsillitis provides for a quick recovery period after surgery.
- Surgitron (radio knife) . This method has its pros and cons: the intervention takes place without heating the tissues in the oral cavity, but anesthesia is required for its use.
Complete removal of tonsils helps completely eliminate the cause of bad breath. Whereas partial removal of the affected tissue can also relieve the patient from the source of the disease and bad breath with purulent notes, but at the same time preserve part of the organ.
Cryotherapy against purulent plugs
In case of chronic tonsillitis, there is another way to remove bad breath. One of the most popular types of tonsillotomy , that is, partial removal of the tonsils, is now considered cryotherapy . Cryosurgery in the fight against tonsillitis involves a destructive effect on the affected tissue using extremely low temperatures . After several procedures, foci of inflammation are destroyed and die.
Prevention of chronic tonsillitis in adults
Preventive measures to prevent chronic tonsillitis include:
- proper hygiene;
- hardening;
- balanced diet;
- maintaining cleanliness in the home and workplace, eliminating dust;
- timely treatment of inflammationSource: Treatment and prevention of chronic tonsillitis. Atagulova G. Zh. Medicine and ecology, 2012.
Chronic tonsillitis is a very common disease that causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient. But is it possible to cure chronic tonsillitis? If your tonsils often become inflamed, then do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor who will select the optimal treatment regimen for you and determine how to get rid of chronic tonsillitis. You can make an appointment with a medical specialist in St. Petersburg by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Article sources:
- Treatment and prevention of chronic tonsillitis. Atagulova G. Zh. Medicine and ecology, 2012
- Chronic tonsillitis in the practice of an otolaryngologist and cardiologist. Yalymova D.L., Kostyuk V.N., Vishnyakov V.V., Yalymov A.A., Shekhyan G.G., Zadionchenko V.S. Cardio Somatics, 2014. p. 60-65
- Choice of antibiotic for exacerbation of tonsillitis. Karpishchenko S.A., Kolesnikova O.M. Medical Council, 2015. p. 40-43
- Modern methods of treating chronic tonsillitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Eremina N.V., Shcherban K.Yu. Medical Council, 2022. p. 68-72
Cost of treatment
| Name | Cost, rub. | |
| 1 | Initial appointment with a doctor, doctor of medical sciences | 7500* |
| 2 | Procedures included as prescribed by a doctor: | |
| UZIS | 2700 | |
| Ozone ultraviolet sanitation | 450 | |
| Laser photoreactive therapy | 1800-2600 | |
| Application of a microcompress into the nasal cavity | 700 | |
| Application of gum-propolis suspension to mucous membranes | 600 | |
| 3 | Final examination by a doctor based on the results of treatment | 1000 |
* — When paying for the full course of treatment procedures, the cost of a doctor’s appointment is included in the amount of treatment. The course of treatment is prescribed by a doctor. The course duration is 7-12 sessions depending on the diagnosis.