Thrush is an inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system of a fungal nature. It most often occurs in women in the form of vaginal candidiasis. It manifests itself as cheesy or creamy white discharge from the vagina, burning, itching and redness in the genital area, pain during intimacy and during urination. Treatment includes local and systemic use of drugs with antimycotic effects, as well as correction of immunity.
Urogenital candidiasis is a common infectious disease. Thrush occurs mainly in women of reproductive age. In men who are sexual partners of such patients, candidiasis balanoposthitis may occur. A child becomes infected with a fungal infection from a sick mother during childbirth.
Causes
The disease is caused by microorganisms of the genus Candida.
They are part of the opportunistic microflora that constantly lives on the skin and mucous membranes of humans. However, with decreased immunity or hormonal imbalance, fungi begin to actively multiply, suppressing the growth of beneficial bacteria and causing an inflammatory response. The following factors can cause thrush:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- excess weight;
- diseases of the female reproductive system;
- disturbances in the state of the microflora of the mucous membrane of the external genital organs;
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, drugs with cytostatic effects, immunosuppressants;
- radiation and chemotherapy;
- use of tight clothing, underwear made of synthetic fabrics;
- rare change of sanitary pads;
- intrauterine contraception - vaginal diaphragms, douching, spermicides;
- use of intimate deodorants, scented pads and tampons.
An exacerbation of the disease often occurs on the eve of menstruation and after significant stress. Diet is also important - consuming large amounts of carbohydrates contributes to the development of fungal infections.
Classification
Vaginal candidiasis occurs in acute or chronic form.
In the latter case, the symptoms are less pronounced, but the disease has a long course and is more difficult to treat. Chronic thrush can be recurrent, with frequent exacerbations, and persistent, when episodes of deterioration are rare and associated solely with the provoking factor. The formulation of the diagnosis also specifies whether urogenital candidiasis is complicated or uncomplicated, depending on the number of exacerbations of the disease over 12 months and the severity of its manifestations. The congenital form of thrush is observed in children infected during childbirth from a sick mother. Candidiasis of newborns most often affects certain areas - eyes, mouth, respiratory tract, lungs, skin, but fungal sepsis cannot be excluded when a large amount of the pathogen enters the blood.
Symptoms
The acute form of vaginal candidiasis has a clear clinical picture.
A woman is worried about intense itching, burning in the genital area and near the anus, pain when urinating, during intimacy, discharge from the genital tract of a white or yellowish color with a cheesy consistency and a sour odor. The latter can be abundant or adherent in moderate quantities on the mucous membrane of the vulva, in the posterior and lateral vaults of the vagina. Also in the affected area there is redness, swelling of the tissues, and possible cracks in the skin and mucous membranes. With persistent thrush, the symptoms are less pronounced. There may only be itching and discharge in small quantities, appearing, for example, only on the eve of menstruation. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis may be accompanied by striking manifestations during exacerbations. They leave dryness, atrophy, and lichenification on the skin and mucous membranes.
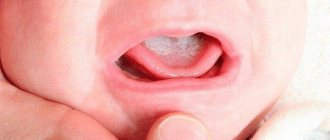
In newborns, thrush is often accompanied by damage to the oral cavity and tongue. A white coating appears on the mucous membrane; when you try to remove it, areas of redness and swelling are found underneath it. A child suffering from candidiasis from birth is capricious, and has sleep and appetite disturbances.
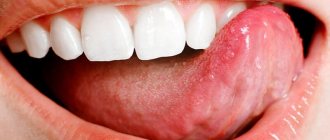
Thrush in men manifests itself in the form of candidal balanoposthitis and urethritis. The disease is accompanied by burning and itching, redness, and swelling in the area of the head of the penis. It may cause rashes, often covered with a white coating, and cracks. Just like in women, sexual intercourse and the process of urination become painful.
Causes of thrush in a newborn
There is only one reason that can provoke candidal stomatitis in babies in the first months of life - weak functioning of the immune system as a result of the influence of unfavorable factors.
Conventionally, unfavorable factors can be divided into two groups: internal, associated with the functioning of the body and the functioning of organs, and external.
Internal factors:
- deep prematurity (birth a month or more before the due date);
- low birth weight (less than 2500 g; and less than 1700 g for a child born during a multiple pregnancy);
- congenital defects and pathologies of the formation of internal organs;
- insufficient supply of nutrients and vitamins (occurs when the mother’s diet is poor, if the child is on breastfeeding);
- anemia (low hemoglobin levels as a result of iron deficiency);
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- rickets;
- history of infectious diseases.
External factors:
- Injury to the oral cavity . Abrasions and cracks in the oral mucosa are an excellent environment for fungi to settle and actively reproduce.
- Antibiotic therapy . It often happens that in the first days of a child’s life it is necessary to give him strong antibiotics (for example, when a child is born with pneumonia and is placed in the intensive care unit immediately after birth). Antibiotics of various groups have a detrimental effect not only on pathogenic bacteria, but also on beneficial microflora, destroying and destroying them. As a result, the newborn develops dysbiosis.
- Refusal of breastfeeding and transfer of the baby to artificial formula . Even the most expensive milk substitutes contain a lot of sugar, which is added to maximize the taste of the product. The acidity of the oral cavity increases and creates a breeding ground for fungal growth.
- Candidiasis in the mother in the last stages of pregnancy . If a woman does not have time to cure thrush before giving birth, the likelihood of infection of the child during passage through the birth canal becomes very high.
- Insufficient hygiene of the newborn. This includes any factors that can provoke the colonization of mucous membranes by harmful organisms: dirty rattles, unboiled nipples and bottles, poor skin care for the baby, etc.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist diagnoses and treats thrush in women. If candidal balanoposthitis appears, you should seek help from an andrologist. During the patient’s initial visit, the doctor clarifies the nature of the complaints, the duration and frequency of appearance of signs of thrush, and conducts an external examination of the genital organs. Next, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests:
- a smear from the mucous membrane of the genital organs followed by a microscopic examination of the biomaterial;
- cultural seeding to determine the species of the fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic drugs;
- detection of pathogen gene material by PCR.
In order to clarify the predisposing factors that contribute to decreased immunity and hormonal disorders, the following is carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of antibodies to HIV;
- blood test for the content of important microelements and vitamins;
- analysis of blood glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis, it is possible to conduct other tests, and if necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed - a therapist, gastroenterologist, dentist, immunologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist.
Treatment of thrush
The principles of treating thrush include both the elimination of provoking factors and the fight against the pathogen itself. In infants, the mother plays an important role in timely diagnosis, because the child is unable to formulate his complaints. Even with timely consultation with a doctor, treatment of children is complicated by the fact that not every drug can be used in infancy. Therefore, the mother’s efforts should be aimed at eliminating factors contributing to the development of thrush. This is the prevention of regurgitation, which is ensured by the correct feeding technique, in which air does not enter the child’s stomach, as well as by carrying the child “in a column” after swallowing air. Immediately after feeding, you should not change clothes or play with the baby - let him lie down for 2-3 minutes, this will also reduce the likelihood of regurgitation.
If the measures taken do not have an effect, then it is necessary to begin drug treatment. The most common method is to treat the child’s oral mucosa with a 10% soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of boiled water at room temperature). Use a sterile swab dipped in the solution to wipe the oral mucosa, not forgetting the space under the tongue, the inner surfaces of the cheeks and lips. Treatment is carried out every 2 hours, approximately 30 minutes before or after meals. Treatment usually lasts 5-10 days. The effectiveness of this simple method is based on changing the acid-base balance in the oral cavity - in an alkaline environment, the vital activity of the fungus is difficult.
In children older than six months, antifungal drugs can be used in addition to local treatment. Only a doctor can prescribe a drug and the timing of treatment; initiative here is unacceptable. You should not stop treatment on your own after the symptoms disappear - this may lead to relapse.
For children over 1 year of age, for local treatment, the doctor may prescribe nystatins, a solution of borax in glycerin, Candida solution, aqueous solutions of antibiotics, Canesten. Most often, treatment is carried out after eating and using the oral cavity 3 times a day for 10 days. These drugs are effective in mild cases, and in more advanced cases, Pimafucin, Lugol's solution, and Clotrimazole are used. (!) The described drugs have contraindications; consultation with a specialist is necessary to determine the age-specific dose and treatment period.
In addition to the means of official medicine and after consultation with a doctor, you can also use traditional methods. Honey (1:2 aqueous solution) is often used for external treatment; however, this healing product can cause allergic reactions in children. In this case, instead of honey, raspberry, carrot juices, decoctions of calendula and St. John's wort are used.
Treatment
Since fungi of the genus Candida belong to the opportunistic flora, treatment is required only in cases of vaginal candidiasis or balanoposthitis proven in laboratory studies, which have characteristic symptoms.
In case of uncomplicated course of the disease and early contact with a gynecologist, it is possible to prescribe only topical medications - vaginal suppositories and tablets for thrush, antifungal ointments, creams. In case of their ineffectiveness, as well as in case of chronic urogenital candidiasis, systemic antimycotics are prescribed - fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole.
Drug therapy for thrush during pregnancy is limited to topical antimycotic drugs for intravaginal administration. Children are prescribed systemic antifungal agents for thrush in a dosage adjusted based on body weight.
Local and general drugs are also used to treat balanoposthitis. To achieve greater effect from the use of ointments and creams, the head of the penis is first washed with a weak soda solution. If a man has a regular sexual partner, she also needs to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and, if necessary, a course of antifungal therapy, since infection with thrush is possible during intimate intimacy.
Stages of development of oral candidiasis
Photo: Depositphotos.com. Author: Mukhina1.
If a child has been diagnosed with thrush, it is worth immediately determining its stage:
- Easy. Small red pimples appear in the mouth, and after a few days the entire tongue is covered with a curd coating. At this stage, the disease does not bring much discomfort to the baby, so it is very important to detect and treat the fungal disease in time.
- Average. Plaque fills the entire space of the mucous membrane, erosions appear that bleed when cleaning the oral cavity. Candidiasis becomes sensitive for infants. The baby begins to experience discomfort and a burning sensation in the mouth, which can cause breast refusal.
- Heavy. The plaque spreads to the throat and lips. The disease is accompanied by enlarged lymph nodes, gastrointestinal dysbiosis, and elevated temperature. The child becomes capricious and lethargic. This is the most difficult and painful stage.
Prevention
Prevention of thrush consists of maintaining immunity, eliminating factors that provoke its decline or hormonal imbalance.
It is important to use antibiotics reasonably and only as prescribed by a doctor, and after completing the course of treatment with such drugs, restore the microflora with pro- and prebiotics. The following measures will also help to avoid the development of fungal infections:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely treatment of endocrine and urogenital pathologies;
- normalization of weight and nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives;
- having a permanent sexual partner;
- wearing underwear made from natural fabrics;
- refusal of scented personal hygiene products, intimate deodorants, and douches.
Treatment plan
How to treat vulvar candidiasis (thrush) in children of school age, and not only?
Basically, treatment involves eliminating the pathogen and stopping its reproduction, which will therefore eliminate the symptoms. Only a good specialist can treat the disease correctly and effectively, who can prescribe:
- antifungal drugs and antiseptics (topically);
- antibiotics;
- ointments and medicinal baths;
- therapy to restore and strengthen the immune system;
- therapy to restore the microflora of the reproductive system.
Which course of treatment will be chosen and prescribed depends on the specific case and the reasons that led to vulvovaginal candidiasis in a teenage girl and a smaller child.
Repeated appointment
At the follow-up appointment, the doctor assesses the child’s condition and checks how effectively the chosen regimen works. If no positive dynamics are observed, then repeated diagnostics and selection of new methods for treating thrush in the child are prescribed.
Control reception
The control reception is an important point. The doctor prescribes it to see how the child recovers after a full course of treatment, to see if there are any relapses or suspicions of them. It is also possible to prescribe physiotherapy and rehabilitation (for example, if a long course of antibiotics has been prescribed). A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled after 21–30 days or later.
Treatment result
The disease can be cured, but the timing of treatment is individual and depends on the stage and causes of thrush in young children or teenage girls. All details of treatment are discussed individually at a doctor’s appointment. If there is a suspicion that the parents are infected, then both parents are treated.
Prevention
Thrush in children is a fairly common occurrence, especially under “favorable” conditions for the disease. To protect the child, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- carry out proper personal hygiene of the child in accordance with age;
- wear the correct underwear;
- normalize nutrition (moderate or limited consumption of sweets, starchy foods and fast foods, more fruits, vegetables, etc.);
- Strengthen your immune system by taking vitamins and exercising.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene at home and in public places will also help avoid the occurrence of vulvar candidiasis and other unpleasant diseases in a teenage girl or young child.