Causes of geographic spots on the tongue
Geographic tongue is a disease manifested by dystrophic and inflammatory processes in the mucous membrane of the tongue.
The condition is characterized by alternating areas of peeling and thickening on the surface of the tongue. You should know why a child develops a geographic tongue and what parents need to do in this case. Causes of the disease:
- lack of B vitamins;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, gastroduodenitis, malabsorption syndrome, pancreatitis);
- endocrine diseases;
- autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis);
- severe forms of viral infection;
- exudative diathesis, colds;
- diseases of the oral cavity.
Blood diseases, nervous disorders and autonomic-endocrine disorders are also the causes of geographic spots on the tongue. In children, the disease is often a companion to helminthic infestation. Predisposing factors include heredity and diseases of the spleen.
Folk remedies
For the treatment of geographic tongue, traditional medicine has a large number of recipes that relieve burning and other unpleasant symptoms, and also help accelerate regenerative processes.
- Twice a day you need to rinse your mouth with a solution prepared from a glass of warm water, half a teaspoon of soda and a few drops of iodine. It is necessary to continue such procedures until the clinical manifestations of the disease completely disappear.
- A mixture of equal amounts of nettle, crushed oak bark and mint is infused in a thermos in a liter of hot water. The resulting warm infusion is used to rinse the mouth after each meal.
- Vegetable oil (natural olive, unrefined sunflower or any other) is sterilized in a bottle in a water bath for 30 minutes. After it cools down, rinse your mouth for 2-3 minutes. The procedure must be repeated regularly twice a day until the symptoms of the disease disappear.
- Prepare a decoction of sage (1 tablespoon of herb per 200 ml of water) and rinse the mouth with it before and after meals until complete healing.
Sometimes parents practice treating geographic language with spells. But such methods are questionable and most likely the effect of their use is explained by the spontaneous cure of the disease.
Although geographic tongue is not a serious illness, its symptoms cannot be neglected. If even the slightest signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to visit a doctor in order to identify its causes and prescribe the optimal treatment option.
Symptoms of the disease
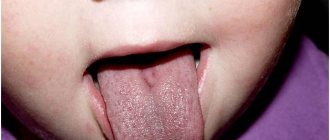
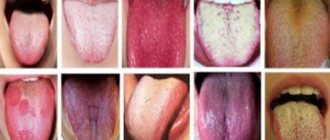
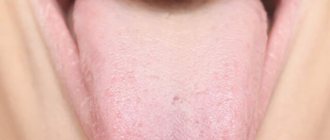
Symptoms most often appear on the back and side of the tongue. The disease is characterized by alternating areas of desquamation of the epithelium and thickening of the mucosa, resulting in whitish-gray and bright pink spots. In appearance they resemble a geographical map.
There are no obvious symptoms in this case. The condition is usually diagnosed when a patient is examined for another pathology. In rare cases (especially when eating spicy, hot and salty foods), the patient may complain of:
- change in tongue sensitivity;
- burning and tingling sensation;
- itching;
- discomfort while eating.
On our website Dobrobut.com you can make an appointment with a doctor and get answers to all your questions. If necessary, the specialist will prescribe additional diagnostics and a course of treatment after receiving the examination results.
Geographical language. What kind of disease is this and how to deal with it?
Geographic tongue (benign migratory glossitis) is an inflammatory disease that manifests itself as lesions on the back and sides of the tongue.
Typically, the affected tongue has a "bald" red area of varying sizes that is partially surrounded by an irregular white border.
The appearance of the affected part of the tongue is the result of the loss of finger-shaped projections (papillae) that cover the surface of the tongue. From time to time, similar lesions appear in other parts of the mouth - the palate, cheeks, under the tongue or on the gums. This is called geographic stomatitis or erythema migrans.
Geographic tongue can vary in color, shape and size - hence the name. Manifestations can persist for different periods of time - days, months and even years. They often disappear completely on their own. But they may appear again later.
What causes geographic language?
The causes of this disease are not fully known. Factors suspected include emotional stress, bad habits, allergies, diabetes and hormonal imbalances. An association between geographic tongue and psoriasis has been reported. However, none of these factors have been conclusively linked to geographic language.
Who gets geographic language?
Geographic tongue is a fairly common condition. Some reports in the medical literature indicate that geographic tongue affects women slightly more often than men. This can happen at any age, including in childhood. It is estimated that it may occur in 1-2.5% of the population.
Is it possible to get infected with it?
No, geographical language is not contagious. There is no evidence that the disease is transmitted in any way.
How is geographic tongue diagnosed?
Based on clinical examination and detailed history.
Are there any complications?
Geographic tongue is a disease that does not pose a threat to general health.
Does geographic tongue require treatment?
In most cases, there is no need to treat this condition.
Apart from appearance, geographic language in most cases does not manifest itself in any way. Sometimes it can cause unpleasant sensations: burning, tingling of the tongue, most often associated with eating spicy or sour foods.
If discomfort persists, your pediatrician may recommend anti-inflammatory medications (topical corticosteroids, such as triamcinolone in toothpaste applied several times a day as needed) or pain medications (local analgesics) applied directly to the affected areas. Antiseptics and anesthetics may also be effective.
Some authors have reported that the use of cyclosporine, topical and systemic antihistamines, and topical retinoids can sometimes produce beneficial results.
Can geographic tongue transform into cancer?
There are no documented cases of geographic tongue causing cancer.
Should you see a doctor if you suspect geographic tongue?
Geographic tongue is an uncomfortable condition but does not cause health problems. However, tongue damage can be a sign of other serious illnesses.
If you or your child has tongue lesions that do not go away within 10 days, be sure to contact your primary care physician/pediatrician or dentist.
Diagnosis and treatment of geographic tongue in an adult
Diagnosis of the disease in most cases does not cause difficulties. The diagnosis is made after a thorough examination and history. In some cases, consultation with a dentist and gastroenterologist will be required.
When making a diagnosis in adults, an extensive examination is necessary. When collecting anamnesis, the presence of chronic diseases and allergic manifestations, as well as the state of the immune system, is taken into account. Taking all this into account, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment for geographic tongue in an adult and monitor its implementation.
Diagnosis of geographic tongue
As mentioned above, the diagnosis of desquamative glossitis of the tongue is not difficult and may well be based on a visual examination of the oral mucosa. Diagnosis of desquamative glossitis is aimed at identifying the answer to the question - why the tongue may peel off, and is carried out in several ways:
The first thing that is necessary for a correct diagnosis of the pathology is an examination of the mucous membrane of the tongue to identify characteristic whitish spots and grooves, and a consultation with a dentist.- A very important place in the diagnosis of desquamative glossitis is occupied by interviewing the patient - his complaints of discomfort, itching and burning in the tongue area. Of course, when diagnosing the disease in young children, this point can be skipped.
- All diseases in the medical history of each individual person must be taken into account.
- If desquamative glossitis is suspected, general blood, stool and urine tests, as well as all other necessary laboratory tests, must be taken.
Treatment of pathology
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause. Geographic tongue is not an independent disease, but a condition that signals serious problems in the body.
Additional events:
- sanitation of the oral cavity;
- exclusion of salty, spicy and hot foods from the diet;
- alkaline rinses, local applications with anesthetic;
- prescription of antihistamines;
- prescription of multivitamin complexes.
If you strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis for the disease is favorable.
Traditional medicine recommends using oak bark decoction, calendula or chamomile decoction as rinses. You can also use propolis (applied to the affected areas), vegetable oil (oral baths) and honey.
Treatment
Most doctors (for example, Komarovsky) believe that geographic tongue does not require any specific therapy, especially if it does not cause any discomfort. The main point of the successful disappearance of the disease in this case is the elimination of the possible cause of its appearance.
But what to do if a child has complaints? In this case, treatment is carried out without surgery, aimed at restoring the epithelium on the mucous membrane of the tongue, eliminating pain and preventing inflammatory complications. All events are held at home.
The use of drugs with keratolytic and analgesic effects is indicated (Keratolin, oil solution of vitamins A and E). To speed up recovery processes, Solcoseryl ointment is prescribed. To prevent infection, rinse with antiseptic solutions (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin).
Complications and prevention
Geographic tongue is not an independent disease, but its appearance signals serious disturbances in the functioning of the body. The sooner you contact a specialist, the sooner adequate treatment will be prescribed. Timely therapy is a guarantee of a high-quality cure for the disease.
In childhood, complications are very rare.
Preventive actions. Fighting bad habits, taking vitamins in the spring and autumn, adequate treatment of gastrointestinal diseases and timely sanitation of the oral cavity will help avoid this condition.
Book a consultation with our specialists and find out how to treat geographic tongue disease.
Symptoms of the disease
The first symptom of the disease is the appearance of grayish spots on the mucous membrane of the tongue, which quickly increase in size. As they grow, the epithelium in the center of such formations sloughs off and the bright red surface of the papillae is exposed. The spots take on the appearance of rings or half rings. The tongue has a motley appearance, and the pattern on its surface resembles a geographical map (hence the name of the disease).
The duration of the disease varies among patients. After treatment, it may disappear forever, or it may become recurrent with periodic exacerbations.
90% of cases of the disease occur without any symptoms. Occasionally, a child may complain of a slight burning sensation or numbness in the tongue, increased sensitivity to sour foods. Only with the addition of a secondary infection may general symptoms appear: fever, pain in the mouth, weakness, malaise.
If geographic tongue brings discomfort and unpleasant sensations, and signs of infection appear, then an urgent consultation with a dentist is necessary.
Preventive measures
Diseases characterized by the formation of ulcers on the tongue can be avoided if preventive measures are taken in a timely manner:
- If, after the measures taken, ulcers appear on the tongue again, it is recommended to undergo a more thorough examination.
visit the dentist regularly;
- Brush your teeth and mouth twice a day with high-quality toothpaste;
- teach your child to rinse his mouth after every meal to remove small particles;
- strictly adhere to restrictions regarding the consumption of foods that cause an allergic reaction;
- develop a diet so that it contains 65-70% fresh vegetables and fruits;
- take vitamin complexes to maintain immunity;
- protect the child from stress.
If, after taking measures, ulcers appear on the tongue again, it is recommended to undergo a more thorough examination. This sign may indicate problems with the digestive system or other diseases.
Treatment methods
The tactics for treating ulcers on a child’s tongue depends on the type of disease and its course.
Aphthous stomatitis
The most common disease is aphthous stomatitis.
The following reasons can provoke its development:
- Sometimes the aphthous form of stomatitis in a child is often confused with the herpes virus
stress;
- genetic factor;
- lack of vitamins;
- allergy;
- folic acid deficiency.
Sometimes the aphthous form of stomatitis in a child is often confused with the herpes virus.
Mistakes can be avoided by carefully monitoring the development of the disease.
With stomatitis, at the initial stage, red dots form, after which white and gray bubbles with a red rim form in their place. Ulcers appear after the blisters burst.
To treat aphthous stomatitis, an integrated approach is used, including:
- systematic procedures for rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal plants (calendula, chamomile, tea tree, etc.) and solutions of potassium permanganate, lugol;
- local treatment of affected areas of the mucous membrane with pharmacological agents (for example, methyluracil ointment).
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the disease and the regularity of the procedures.
Herpetic stomatitis
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the degree of neglect of the disease.
Treatment of the disease in its advanced form is carried out in a pediatric hospital or infectious diseases department.
Mild cases of herpetic stomatitis are carried out on an outpatient basis, but the child is isolated from others due to the fact that he is a carrier of the virus.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the characteristics of the body and the degree of neglect of the disease.
Among the recommended drugs:
- antiviral (Acyclovir, Zovirax, Oxolinic ointment, etc.);
- antihistamines (Cetirizine, Loratadine, Fenistil);
- anti-inflammatory (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- wound healing (solutions of Trypsin or Chymotrypsin);
- antiseptic (Solutions of Chlorhexidine, Furacilin);
- immunostimulating (Imudon, echinacea extract, etc.).
In case of acute or recurrent stomatitis of the herpes form, physiotherapy or laser therapy procedures are also prescribed.
Thrush (candidiasis)
Starting at six months of age, doctors prescribe topical antifungals
Choosing a treatment method for babies is quite difficult, because babies cannot describe their symptomatic sensations.
The mother needs to closely monitor the child to understand the cause of thrush.
If this is regurgitation after eating, then it is worth reducing the diet or keeping the baby upright for 20 minutes every time after eating.
It is equally important to maintain hygiene and sanitary standards in your home.
The following methods are used to treat infants:
- treatment of the oral mucosa with a cotton swab dipped in soda solution (1 tsp per 200 ml of warm water);
- wiping the oral mucosa with gauze soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
It is advisable to carry out procedures at an early stage of the development of a fungal infection, then the chances of recovery double. Pediatricians rarely prescribe antifungal agents for infants.
Starting from six months of age, doctors prescribe topical antifungals. When the disease progresses to a severe form, an integrated approach is used, which combines internal and local drugs.
The following drugs are used to treat older children:
- Miramistin (ointment, solution);
- Nystatin (tablets);
- Diflucan (tablets);
- Clotrimazole (ointment, tablets), etc.
Allergy
Most often, the allergen is found in foods, hygiene products, and medications.
Red ulcers on a child’s tongue may appear as a result of the body’s reaction to an allergen (causative agent).
There is no point in treating the consequences; the main thing is to identify the product or substance that caused the formation of wounds on the tongue as quickly as possible.
Most often, the allergen is found in foods, hygiene products (you need to carefully study the composition), and medications.
Dental fillings, dentures, and braces can also provoke an allergic reaction.
Gastrointestinal problems
In infants, the digestive system is still at the stage of formation, so the gastrointestinal tract is very sensitive to many irritants.
Any failures provoke a violation of the absorption of nutrients into the blood, against which vitamin deficiency develops, spots and ulcers appear on the tongue.
Another reason for changes in microflora are antibiotics, so they are prescribed in combination with drugs containing beneficial bacteria.
The essence of treating ulcers comes down to eliminating problems in the gastrointestinal tract and treating the lesions with special local agents.
Tongue injuries
Scarlet ulcers can also appear on a child’s tongue as a result of injury:
- careless use of a toothbrush;
- biting the tongue with teeth;
- tissue injury from sharp edges of a damaged tooth or filling;
- due to the eruption of baby teeth;
- poor-quality installation of the prosthesis when correcting the bite, etc.
Treatment of wounds in such cases consists of eliminating the irritant and local treatment of the lesions with wound-healing agents.