Warts are classified as benign neoplasms.
They can appear on various parts of the skin and mucous membranes.
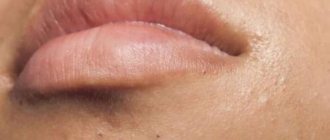
If a wart appears on the lip, it represents a cosmetic defect and can also cause discomfort to its owner, worsening the quality of life.
Forming on the lip, the tumor affects speech and interferes with eating.
A wart can cause pain, especially if it is localized on the mucous membrane inside the lip.
If measures are not taken to eliminate it, the growth may become injured, which will lead to a secondary infection.
Types of warts
A wart is a growth that rises above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane.
Its dimensions, as a rule, are no more than 1 centimeter in diameter.
The tumor can appear on any part of the body, including the face.
On the face, most often a wart forms on the lip, above or below the lip, on the buccal surface of the oral mucosa.
A warty growth can appear on both the upper and lower lips.
The following types of neoplasms are distinguished:
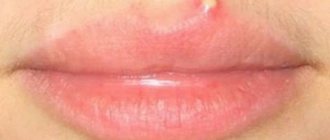
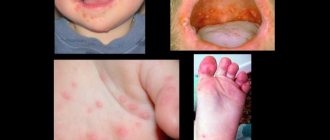
- Common (vulgar) warts. These are growths that have a dense structure, soft to the touch, flesh-colored or yellowish in color. New growths form on the red border of the lips. They are not painful, but tend to itch. Vulgar warts appear on the lips not only in adults, but also in children.
- Flat- shaped growths may appear on the outside of the lips or on the oral mucosa. Their surface is smooth, oval or round in shape. The color of the growth resembles the color of the skin and almost does not rise above it. The location is also the red border of the lips. Flat warts do not hurt, but they are very itchy.
- Hanging neoplasms are located on a thin stalk. At the beginning of development they resemble a bump. They have a brown, pinkish tint or close to the color of the skin.
- Filiform (acrochords). These are small growths that appear after 35 years, but can occur earlier.
- Genital warts . The localization of such growths is the mucous membrane. The new growths are elongated and arranged in groups, resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower inflorescences. The growths are prone to injury, which causes inflammation and bleeding.
The wart forms gradually and almost imperceptibly.
- At the beginning of development, a small compaction forms, which gradually increases.
- A white dot forms on the surface of the mucous membrane of the lip or in the mouth, which gradually turns into genital warts.
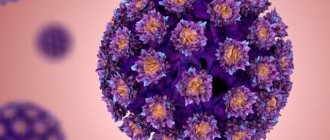
To date, approximately one hundred types of papillomavirus have been discovered.
Some types of growths have a benign course, while others are capable of malignancy.
They can provoke the development of cancer.
In addition to the types of growths listed above, there are also senile warts (keratoma, keratosis).
The difference between keratosis is that its appearance is not associated with papillomavirus, and keratoma does not provoke the formation of cancer.
In their development, senile warts go through several stages:
- ✓ brown spots appear, but the wart has not yet formed
- ✓ formation of papules and nodules
- ✓ appearance of keratoma - when you try to scrape off the scales, bleeding appears
- ✓ transition to the cutaneous horn, which is characterized by excessive growth and keratinization of the neoplasm
According to some experts, keratosis and senile warts belong to different diseases.
Treatment of papilloma on the lip
If you consult a specialist for help in a timely manner, papillomas on the inside of the lips can quickly be treated. The wounds begin to heal before our eyes. When treating a tumor, the main point is not to overdo it, since deep wounds can lead to the formation of scars that will never disappear from the face.
Official medicine offers several methods for removing growths.
- Cryodestruction. A procedure characterized by simplicity and high effectiveness. Involves freezing with liquid nitrogen. The growths fall off in about a week. After removal by cryodestruction there are no scars left on the surface of the skin. Small wounds heal within a week. The technique is effective in the fight against small papillomas. Larger tumors must be removed using other methods.
- Thermocoagulation. Provides for burning out growths using electric current. The technique is painful and requires the use of painkillers. Burning the wounds too deeply can cause the appearance of keloid scars, which will ruin the appearance.
- Treatment with keratolytics. Elimination of the deficiency is carried out by exposing the neoplasm to a chemical substance that can dissolve keratin, which is abundant in the keratinized layer of papilloma. The method is effective for removing small growths. If the doctor decides to treat the child in this way. The drug is applied with caution. Upon completion of the procedure, the growth is sealed with a plaster to prevent it from getting on the mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth.
- Surgical intervention. It is used in serious cases when HPV begins to manifest itself in the form of large warts. After removal, a scar remains. In order to reduce it, the use of hormonal ointments is recommended.
Attention! How to get rid of a benign formation, and what method a specialist decides on based on a visual examination and laboratory test data.
Treatment with traditional methods is welcome when the treatment is agreed upon by the supervising physician. Some of the methods given below allow you to achieve high results in getting rid of papillomas in adults and children.
- A solution of vinegar with iodine.
If a papilloma appears on the lip, take sterile cotton wool, roll it into a small ball and soak it in 9% vinegar or iodine. Apply the ball to the problem area and cover with a band-aid. The number of procedures performed is 2-3 per day. The technique is highly effective, but is not suitable for everyone, since it involves staying at home.
- Celandine juice with fruits and berries.
Cut off the stem of the celandine during the flowering period and lubricate the resulting wart with the yellow juice released from it. Similar manipulations are carried out with sour berries. Naturalness and low toxicity make it possible to treat HPV in a child. During the first day after lubricating the growth, the papilloma becomes slightly inflamed, darkens and dries out.
- Tying with thread or hair.
An old grandmother's method that allows you to get rid of club-shaped growths of various sizes. For bandaging you will need a natural thin thread or hair. Wrap the pre-prepared hair around the stem of the wart, almost at the root, and tie it in a knot. Don't be afraid to put pressure on your leg. This will only be beneficial. After about a couple of days, the papilloma will fall off. The wound that appears after the growth must be lubricated with celandine or iodine for 2 weeks.
These folk remedies in the fight against papillomavirus are safe, provided that the treatment process is agreed upon with the doctor and the patient has been diagnosed.
Papillomavirus can appear not only on the outside of the lip, but also on the inside. The following neoplasms in the lip area are distinguished:
- papilloma on the mucous membrane of the lip;
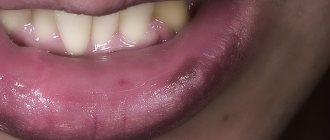
To distinguish mucosal papilloma from other diseases, you need to know that the average diameter of a papilloma is 1 cm, the surface of the neoplasm is rough to the touch and resembles cauliflower. The growth on the mucous membrane of the lip has a wider stalk, the color is close to pinkish-flesh, and the patient feels pain when palpated. The neoplasm can be seen with the naked eye.
- papilloma on the lower part of the lip;
The presence of a growth on the lower part of the lip can ruin a person’s aesthetic appearance. Refusal of treatment leads to the growth of growths and the formation of nests. Timely treatment can correct the deficiency without surgery.
- papilloma on the inside;
It is characterized by a high degree of pain, since there is a high risk of injury to the teeth during eating. Diagnosing HPV on the inside of the lip requires emergency intervention from a specialist. Otherwise, there is a high risk of the tumor degenerating into a malignant tumor.
- papilloma in the mouth;
The diameter of the neoplasms is no larger than a centimeter. They have a tuberous-nodular surface and a thin stalk. Capable of growing families. It can be visually diagnosed by its shape, which resembles a cockscomb or cauliflower. The color is close to the oral mucosa. The consistency of the neoplasms is characterized by high levels of firmness and elasticity. Soft to the touch. Medical intervention is mandatory because the risk of injury is high.
- papilloma on the upper lip;
The neoplasm can be confused with a wart or herpes virus. It has a small shape, the color is closer to flesh-colored. Timely treatment and removal allows you to maintain the same appearance and smoothly remove the tumor.
- papilloma above the lip;
The shape resembles a blister or wart. Capable of increasing in size, multiplying and being reborn. Causes disgust in patients and others. For small papillomas, drug removal of the growth is possible.
If you notice small papillomas on your lips, you should not ignore their appearance. It is better to contact a specialist once again and refute the diagnosis than to observe this defect for a long period.
The difference between a wart and keratoses and cancer
Keratosis may be similar in appearance to melanoma (a type of skin cancer).
Melanoma can begin as a warty growth or as a seborrheic keratosis.
A dermatologist can distinguish them from cancer.
To exclude an oncological process, a biopsy is performed.
The peculiarity of seborrheic keratosis is that the formation is waxy, flat, and there is no pain when touched or at rest.
With cancer, a growth similar to a keratosis may change shape or color.
In this case, you will need to consult a specialist.
We care about your health
What is papilloma?
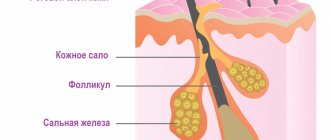
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm of stratified squamous or transitional epithelium. In ICD-10, the disease corresponds to code B 97.7. Macroscopically (visually) it is defined as an overgrowth of the papillary type (cauliflower/cockscomb). On the external genitalia they usually have the appearance of a wide formation on a thin stalk, most often the color of the surrounding tissues. Much attention has been paid to this problem because the formations can become malignant (malignant), plus they are perceived as a cosmetic defect.
Why do papillomas occur?
The etiological factor of the disease is the human papillomavirus (HPV), in contrast to condylomas, which are caused by other causative factors. Localization of the process on the genitals is due to sexual transmission; infection in the home is less common. Warts can be found on the labia, clitoris, frenulum, vagina, uterus, etc. Microtraumatization of the skin and mucous membranes during sexual intercourse facilitates the easy penetration of HPV into the blood, from there it spreads throughout the body and, most often, does not manifest itself for a long time, persisting in the body. When provoking factors occur (stress, hormonal imbalance, smoking, alcohol intoxication), leading to a decrease in immunity, a clinical picture of a viral infection develops - skin formations.
Why should this disease be treated?
A woman with an active infection is a source of infection for her loved ones. The main danger for the infected person is that if the disease is left untreated, the growths can transform into a malignant tumor of the genital organs. Papillomas of high, medium, and low risk of malignancy are distinguished, which depends on the location of formation and the HPV strain. In addition, there is a high probability of damage to formations and the development of bleeding, as well as infection of the wound. Another complication of the process is the spread of the virus to surrounding tissues with the development of large foci of infection.
How to treat papillomas on the labia?
Therapy implies, as with any systemic disease, drug treatment, which should not be neglected. They use immunostimulants (Cycloferon), antiviral drugs (Acyclovir) orally, and virucidal ointments (Panavir, Zovirax, etc.) are prescribed locally. Currently, gynecologists use 5 main methods of surgical removal of papillomas:
- Papillomectomy is an operation to excise a tumor with a scalpel. Local anesthesia is required. After the procedure, a skin defect may remain;
- cryodestruction - “freezing out” with liquid nitrogen. After exposure, the formation is rejected due to malnutrition. A long recovery period is often required. Can also lead to a cosmetic defect;
- laser removal - destruction by a high-temperature light beam. A highly effective method, however, it requires large financial costs;
- electrocoagulation - exposure to electric current. Rarely used;
- radio wave excision using the Surgitron apparatus. The method allows you to achieve good results, but is not always available in regular clinics.
How to treat papillomas during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, pronounced hormonal changes occur in the female body, the functioning of all systems changes, and, most importantly, the immune system. This explains the appearance of papillomas in women during this period. However, if monitored by a doctor, there is no great danger in them. If they are small and do not cause discomfort, you can simply observe them in dynamics. If the tumor is large, it can be excised surgically or frozen. Exposure to laser, electric current, and, especially, radio waves is undesirable due to the danger to the fetus. The addition of itching should be considered as a poor prognostic sign, since it may be a symptom of tumor malignancy. Such a papilloma should be removed.
Causes of warts
The appearance of warts is caused by infection with papillomavirus or HPV.
Since the skin on the lips is quite thin, it is therefore easily permeable to viruses.
It should be noted that signs of infection with the human papillomavirus do not always occur.
The better the immune system, the less likely it is that symptoms of the disease will appear.
And yet, most of the world's population is infected with HPV.
The incubation period for the development of the disease can be several months or years.
As soon as the immune system fails, the first signs of infection appear.
Activation of the virus is accompanied by the formation of warts.
As a rule, growths appear on the area of the skin or mucous membrane where the pathogen entered the body.
Infection can occur both through sexual contact and through household contact.
Can the virus be transmitted by kissing on the lips?
The most common cases of infection are:
- intrauterine infection of the fetus if a pregnant woman is infected with papillomavirus
- shaking hands or kissing an infected person (if there are wounds or abrasions, the risk of infection increases)
- the use of personal items of an infected person (toothbrush, dishes, lipstick) is unlikely, since the pathogen is not stable in the environment
- sex accompanied by oral sex
- visiting common areas (swimming pool, sauna, shower)
People at risk are those who:
- patients with diabetes mellitus or other pathology of the endocrine system
- suffer from obesity and metabolic disorders
- taking antibiotics for a long time
- have chronic diseases
- suffer from increased sweating, especially on the feet, as this is where plantar warts often form
A malfunction of the immune system can occur for the following reasons:
- If there is a deficiency of essential substances in the body
- After suffering stress or physical exhaustion
- In case of hormone imbalance: during puberty, during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause, during treatment with hormonal drugs
- In case of chronic lack of sleep and overwork
- Due to a recent infectious disease
- If a person abuses smoking and alcoholic beverages
Reasons for appearance
A papilloma on the lip is a benign growth caused by the activity of the human papillomavirus (HPV). About 80% of the entire population of the planet is a carrier of a pathogenic infection, and not everyone has external manifestations. A viral agent can be asymptomatic in the body and manifest itself only in a situation where there has been a sharp decrease in immune defense . Thus, the main reason for the unpleasant phenomenon is the activity of the virus, which can get inside in several ways:
- through a kiss in case of contact of mucous membranes and the presence of microtraumas,
- when sharing personal hygiene items (relevant in rare cases, since the pathogen does not live long outside the body),
- through oral sex,
- in a child, papillomas on the lips can only occur through contact with a carrier (transmission rarely occurs during pregnancy),
- Growths in the lip area can appear in a person who bites his nails and sucks his fingers, having formations on the skin of his hands.
Immediately after infection, symptoms do not appear, even if a person has reduced immunity - the virus must remain in the body for at least a month to develop. Factors that create conditions for the formation of external manifestations of papillomavirus and reduce the level of natural protection are:
Diagnosis of warts
The main diagnostic method is to examine the patient's face for the presence of warts on the lips and oral mucosa.
To confirm or refute the presence of HPV, it is enough to take tests:
- ✓ Blood tests for antibodies
- ✓ To conduct a histological examination (biopsy), a small part of the tumor is taken for analysis
- ✓ The PCR technique allows you to detect the genetic material of a pathogen with one hundred percent probability
Before getting rid of the growth, you should visit an oncologist.
A specialist will use dermatoscopy to determine the condition of the wart to rule out signs of malignancy.
Clinical manifestations of warts on the lip
A wart on the lip does not appear the next day after the papilloma virus enters the body.
The incubation period can last from six months to several years.
This often occurs when the immune system malfunctions.
Having penetrated the skin or mucous membrane, the virus integrates its genetic material into human cells and thus begins to multiply.
As a result, characteristic neoplasms appear at the site of virus introduction.
The pathogen provokes warty growths, disrupting the processes of keratinization of the skin.
Oncogenic strains of papillomavirus change the genetic apparatus of cells in such a way that a malignant formation is formed.
Human papillomavirus in women
HPV, or human papillomavirus, is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections. To date, more than 150 types of HPV have been described, of which about 40 types can infect the genital mucosa.
Human papillomavirus causes a number of gynecological diseases
: anogenital condylomas, chronic cervicitis, dysplasia of the vulva, vagina, cervix. In addition, it has been established that HPV infection causes the development of cervical cancer and can contribute to the development of vulvar and vaginal cancer.
However, the presence of human papillomavirus does not always lead to the development of these diseases,
The state of the body's defenses, the presence of concomitant gynecological and somatic diseases, the level of viral load and the type of papillomavirus are of great importance.
Based on their ability to cause malignant diseases, all types of HPV are divided into groups:
- low risk
(types 6, 11, 40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81, CP6108); - potentially high risk
(types 26, 53, 66); - high risk
(types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, 73, 82).
HPV is transmitted primarily through sexual contact.
At the same time, using a condom reduces,
but does not eliminate, the risk of contracting this infection.
A vertical route of transmission of human papillomavirus infection (from mother to newborn) is possible. It has been established that HPV can also be transmitted through contact (most often through contact of the genitals with the biological fluids of a sick person).
During preventive gynecological examinations, a specific analysis for HPV is not performed. The doctor may suspect the presence of this infection based on the results of an oncocytological examination. And then to identify HPV, it is recommended to conduct a special examination using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This study determines the presence of papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk and determines their type.
HPV testing is recommended for all women
especially in the presence of cervical erosion, cervicitis, anogenital condylomas, papillomas with changes in the oncocytological smear, with a change of sexual partner, specific itching of the external genitalia and the exclusion of candidiasis and sexually transmitted infections.
There is an opinion that HPV infection cannot be cured and, accordingly, there is no point in carrying out therapy. It's a delusion. Completely eliminate the virus from the body
we can at the stage of virus carriage (before the introduction of HPV into cells). But even if there is an integrated form of HPV (HPV has managed to invade the cells), treatment should be carried out, as this will reduce the viral load and reduce the risk of developing dysplasia and cervical cancer.
If HPV is present, treatment of human papillomavirus infection is carried out together with a sexual partner,
despite the fact that for men this infection does not pose such a serious risk as for women. This reduces the likelihood of reinfection and ensures the success of treatment.
Therapy for HPV infection is long-term and consists of several stages:
- complex antiviral, immunomodulatory treatment;
- surgical treatment - removal of tissues affected by the virus (radio wave therapy is optimal);
- If a young girl or woman is not sexually active and has genital HPV, vaccination is recommended before the first sexual debut. In the United States, adolescents aged 11-13 years are vaccinated.
The earlier the disease is detected, the more effective any treatment measures will be. Dear women, take care of your health, be attentive to yourself!
Is it necessary to remove a wart on the lip?
Removal of the tumor is carried out if there are indications for this.
The growths sometimes disappear spontaneously.
Therefore, if the wart is small and does not cause much concern, then there is no need for removal.
The decision to excise the growth must be made by a specialist.
If a wart causes discomfort in the form of itching, burning, pain, grows, becomes inflamed, or changes in appearance.
If it has increased in size, changed shape and color, or is bleeding, then it must be removed by resorting to excision by one of the methods.
Removing a tumor at home is not safe.
As a result of incorrect actions:
- It may not be possible to remove the wart completely, which will cause its reappearance
- the risk of injury to healthy tissues that surround the growth increases
- scars and cicatrices may form
Wart treatment
Treatment of any growth on the lips begins with a medical examination and determining whether the growth is malignant.
Next, the doctor selects a method of therapy.
In case of a malignant form, the patient is referred to an oncologist, who will decide how to treat the patient.
Treatment of the disease is complex.
Treatment consists of the main stages: removal of the growth and drug therapy.
Removal of the tumor can be done in one of the following ways:
- ✓ Using pharmaceutical products
- ✓ In a medical institution where modern excision techniques will be used
- ✓ Folk remedies. The use of alternative medicine methods must be agreed with a doctor
Diagnostics
A neoplasm on the lip, called papilloma, usually has a regular shape, a yellow-white tint (brown when keratinized), and is pedunculated. Both individual capsules and groups of growths can appear. The maximum size of the formation is about a centimeter. Constant trauma to the teeth when the process is localized on the inside of the lip causes pain.
Having noticed a neoplasm, you need to contact a dermatologist to make a clear diagnosis. After an external examination and dermatoscopy, the doctor will prescribe a number of studies:
- blood test to detect papillomavirus in the body,
- biopsy of the formation (to determine whether it is benign or malignant).
Pharmacy products for removing warts
You can buy medications at the pharmacy that will help you deal with warts at home.
Among them:
- Super clean . The product is an alkaline solution that has a chemical effect on the growth, causing cauterization.
- Cryopharma, Wartner . These agents cause cryodestruction of the wart; as a result of cold exposure, the neoplasm is frozen.
- Solcoderm . A drug containing acids that have a cauterizing and mummifying effect on pathological tissues.
- Immunomodulators – Viferon, Oxolinic ointment will help increase immunity and the body’s fight against the virus.
- Antiviral agents – Isoprinosine, Interferon.
The use of cauterizing agents on the lips and face is extremely undesirable; application of these agents to the oral mucosa is especially dangerous.
Treatment
The growth of tissue in the lip area is not only an aesthetically unpleasant situation, but also potentially dangerous. Injury to the growth can lead to its excessive growth, and there is also a risk of malignancy of the process. For this reason, it is necessary to promptly treat papillomas.
Medications
Treatment requires an integrated approach, so drugs from various groups can be prescribed:
- Immunomodulators (the activation of the virus is based on a decrease in the body’s defense, so first of all it is necessary to restore it). This category includes the drugs “Genferon”, “Immunomax”, “Cycloferon”, etc.
- The use of antiviral agents (Isoprinosine, Interferon, Panavir) to suppress the pathogen (orally or locally). Local exposure involves administration directly to the sites of tissue proliferation.
- Taking vitamin complexes to strengthen the body.
- Prescription of agents for destruction of formation (Solcoderm, Condilin).
- If the process is complicated by a bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy is indicated.
Wart removal in the clinic
The clinic uses modern hardware techniques to excise growths:
- Laser therapy . The method allows you to quickly and without blood remove the growth. There is no discomfort during the procedure, as pain relief is performed. During one session, you can get rid of several tumors in a very short time. The method is suitable not only for adults, but also for children. The likelihood of relapse is minimized. Skin defects in the form of scars after laser use are very rare.
- Radio wave therapy . The technique is considered the safest. When excising a wart using a radio wave, there is no contact with the skin. It is not always possible to completely remove the growth. The procedure leaves no traces of impact.
- Electrocoagulation . The procedure requires anesthesia. Using an electrode to which a high-frequency electric current is applied, the wart is burned out, followed by cutting off the growth with a special metal loop. Scarring may appear after removal.
- Cryodestruction . Liquid nitrogen is used and the wart is treated until it turns white. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, the growth tissues die. There is no need for anesthesia for the manipulation. The disadvantage of the technique is the lack of control over the depth of nitrogen exposure. For this reason, frequent relapses occur.
- Surgical. Removal is done using a scalpel. The disadvantage of the procedure is the formation of a scar, so this technique is used only for certain indications (in case of malignancy of the process and large size of the wart).