Echo of childhood
Milk teeth are something from the realm of a carefree and touching childhood, most of us are sure. It is not for nothing that the Scottish writer James Barrie, in the fairy tale about Peter Pan - a boy who did not want to grow up and remained forever young - specifically mentions that “his mouth was full of pearly milk teeth. None have fallen out yet.” Replacing baby teeth with permanent ones is the same step into adulthood as first grade and first grade.
The change of teeth begins at the age of 5–6 and usually ends by the age of 14–16. Moreover, according to the observations of doctors, children are currently replacing their baby teeth with permanent ones at a younger age than several decades ago. But sometimes baby teeth persist into adulthood. People encounter similar cases at 20, 30, and even 50 years old! Why does this happen and what should be done in this case?
When does teeth change?
In order to monitor the order of changing teeth and be able to identify pathology if necessary, you should remember the time frame:
- Children's incisors change at the age of 6-8 years.
- Fangs fall out and new ones appear at 9-12 years of age.
- Molars begin to change at 9-10, and can change up to 12 years.
- Large molars erupt from the age of 6 to 11-13 years, and the last ones (“eights”, so-called “wisdom teeth”) can appear at 20-30 years.
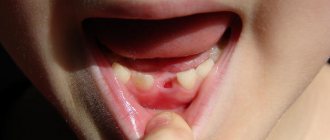
And if you notice a change in incisors and fangs immediately - the child is happy to show everyone his charming toothless smile, then with molars everything is not so simple.
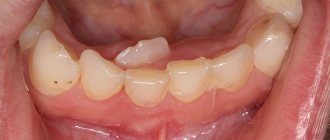
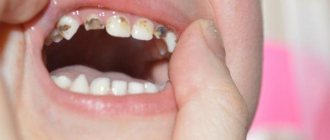
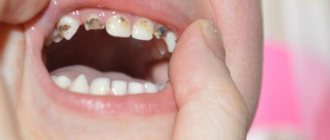
How to distinguish a permanent molar from a baby tooth
You can distinguish between temporary and permanent teeth, first of all, by color. Milk enamel is white and even has a bluish tint.
These are the teeth that are called snow-white. But the permanent ones are always a little darker and have more of a yellowish or grayish tint.
Also, temporary teeth are smaller, and permanent teeth
are larger
; molars and premolars have a large chewing surface and several large tubercles on it. The teeth give the impression of being impressive and strong.
The formula of the dentition in children whose teeth have already been replaced will be similar to that of an adult - 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 8 molars. That is, on one side of the jaw there will be 2 small molars and 2 large molars. To understand this formula and learn to distinguish a permanent molar from a baby tooth, we recommend comparing them in the photo.
Why didn't my baby tooth fall out?
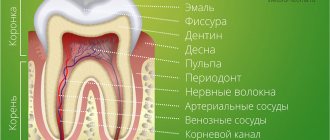
The structure of temporary and permanent teeth has certain differences. Dairy teeth have the same shape as molars, but they are smaller in size, their roots are much shorter, and they grow in the amount of only 20 pieces versus 32 permanent ones, including wisdom teeth. The service life of “children’s” teeth is also short: their roots begin to dissolve (dentists say “resorb”) approximately 2 to 3 years after they are fully formed. The process begins from the area where the crowns of the permanent teeth growing underneath touch them.
However, it happens that the rudiments of molars do not form for some reason. In this case, the roots of the milk teeth most often dissolve under the influence of the rudiments of adjacent permanent teeth. But sometimes this does not happen, and then “children’s” teeth are preserved in adults - doctors call them persistent, from the Latin persistere - to remain, to remain.
The reasons for the absence of permanent tooth buds can be different. Sometimes these are hereditary characteristics, metabolic disorders or disorders of the endocrine glands, trauma and osteomyelitis of the jaws. Chronic and acute inflammatory processes in baby teeth, in particular, periodontitis that is not cured in a timely manner, can also lead to damage and death of the rudiments of permanent teeth.
It also happens that the rudiments of permanent teeth, although they are formed, lie very deep, without touching the roots of milk teeth. This may be caused by insufficient space or misalignment of the permanent tooth. In these cases, milk teeth can remain in an adult.
Rehabilitation after removal of baby teeth
The hole heals completely in 7-9 days. If the dentist did everything correctly, there are no complications after the operation. Sometimes on the first day there may be bleeding from the wound, slight swelling and inflammation of the operated area. Normally, unpleasant symptoms disappear after 1-2 days; if they persist longer, consult a doctor.
During the postoperative period, parents need to monitor the child so that he does not injure the socket or wash out the clot. You cannot rinse your mouth, heat your cheek, sunbathe, take a bath, play sports or play outdoor games. Avoid drinking carbonated drinks, hot and sweet foods.
What to do if an adult’s baby teeth don’t fall out?
Of course, baby teeth often cause problems in adults. Firstly, they are designed to have a short lifespan, and therefore their resistance to caries is much lower than that of permanent teeth. Secondly, baby teeth that do not fall out in time can interfere with the growth of permanent teeth and lead to their incorrect location. However, this does not mean that a baby tooth found in an adult must necessarily be removed. It all depends on each specific case. Most often, doctors recommend keeping well-preserved baby teeth in adults - let them last as long as they can. After all, the permanent ones may never emerge in their place.
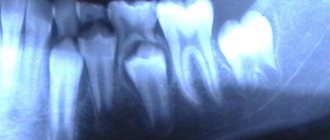
In any case, the question of the fate of a baby tooth in an adult is decided only after an x-ray is taken. This will help to find out whether there are rudiments of an unerupted permanent tooth, as well as whether the roots of the baby tooth are being reabsorbed. If there are no rudiments and the roots of the baby tooth have not resolved, while the baby tooth is motionless and looks quite aesthetically pleasing, then it is not worth removing it. The same applies to cases when the permanent tooth, judging by the x-ray, is in such a position that it is impossible for it to erupt even after the removal of the milk tooth.
What is caries and where does it come from?
Caries is an infection that develops as a result of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms in the mouth. How can pathogenic microorganisms enter a child's mouth? This happens through saliva:
- when taking a temperature test by a parent
- when kissing parents who have pockets of caries in their mouths;
- if you eat food with one spoon;
- if the child suffers from “nasal breathing” and during sleep he breathes through his mouth.
At night, the child’s mouth dries out and there is no saliva, which has protective properties and slows down the development of caries.
If a child drinks compotes and other sweet drinks at night, the risk of developing caries increases due to the presence in the oral cavity of a favorable environment for cariogenic microorganisms.
Milk teeth are similar in structure to permanent teeth, and they also contain a nervous system. If caries affects the nerve, the tooth hurts greatly, pulpitis, periodontitis and other “adult” problems develop in it.
Is it possible to grow a baby tooth on an adult?
If the baby tooth is mobile or does not suit you from an aesthetic point of view, you still need to start with an x-ray examination. If the x-ray reveals that there are no permanent tooth buds, and the roots of the baby tooth have resolved, while the baby tooth has mobility of 3–4 degrees (that is, the tooth is very mobile), then it should be removed and further decide what type Prosthetics are more suitable for you to replace the loss.
If you are not satisfied with the appearance of the tooth, it is necessary, again using an x-ray, to determine the condition of the rudiments of the permanent tooth and the roots of the baby tooth. Further decisions will depend on each specific case, including the age of the patient and the place in the dentition of the baby tooth. If there are no rudiments and the roots of the baby tooth have not resolved, then you can install a veneer on it or carry out a tooth restoration, which will make it invisible in the dentition. And for those who want to completely transform their hair, we can recommend getting lumineers.
If there are rudiments of a permanent tooth, in this case it is worth assessing how much time they need before erupting and making a decision about removing the baby tooth and “pulling out” the permanent one.
Although milk teeth in adults are an anomaly, this is not a reason to necessarily part with them - they can serve you well for many years to come. However, it is possible that this “greetings from childhood” prevents the permanent tooth from growing. So, if you suddenly have a baby tooth, be sure to take an x-ray and consult a specialist.
Tell us about removal from your experience
scare and turn the child against the doctor.
Not the best solution is a video with a story about how a child’s baby tooth is removed. What to do?
A good option is an adaptation technique. Doctors at the Azabuka children's dental clinic will tell you about the upcoming meeting with a dental surgeon in such a way that the child will confidently go to the appointment and allow the tooth to be pulled out without any whims in the chair. The center’s staff knows many psychological communication techniques and, through games, relieves children’s fears and objections.
Is extraction required?
Only a doctor can answer this question, and always on the basis of an x-ray.
It is recommended to leave well-preserved temporary elements with a normally formed rudiment - in this case, replacement will occur later and the services of a prosthetist may not be needed in old age.
If the position of the permanent tooth in the jaw is incorrect, and it will not be able to erupt when the temporary unit is removed (if it is in good condition and there is no process of root resorption), then doctors also advise leaving it.
The doctor makes a different decision in the following cases:
- the baby tooth is mobile (3-4 degrees of mobility);
- small size and aesthetically unpleasant appearance (in the absence of the rudiment of a permanent unit);
- there is not enough space for the correct arrangement of adjacent teeth (if there is no rudiment or if it is too deep);
- the permanent element is sufficiently developed for eruption, but is hampered by the temporary unit;
- the temporary element is damaged and can cause inflammation, injuries to the jaw and oral cavity.
Aesthetics and size alone cannot serve as an indication for removal, but are taken into account for further prosthetics , since simple removal can provoke movement of the entire row and further orthodontic problems.
Teeth crowding - symptoms and treatment
Dental crowding is a developmental pathology, which is characterized by a lack of jaw space for the correct, from a physiological point of view, arrangement of teeth on the jaws. The main manifestation of the anomaly is the incorrect angle of rotation of certain teeth relative to the rest and/or “piling up” of teeth on top of each other, as well as their eruption outside the dental arch.
In the 1980s, the term “clustered teeth syndrome” (TDS) was introduced to describe the anomaly, which defines crowding of the front teeth, which prevents satisfactory oral hygiene [1].
SRD affects 70% of the world's adult population. The anomaly occupies a leading place in the structure of all dental pathologies. The syndrome can manifest itself both during the development of baby teeth and during the eruption of permanent teeth. In the first case, the prevalence is 34%, and in the second - 68% [2][3].
As a person gets older, the degree of crowding of teeth may increase, as changes occur in periodontal tissues: the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth becomes less stable [4]. According to studies, the older the age group of patients, the higher the percentage of people who need orthodontic treatment [5][6][7]. Thus, we can talk about the pattern of distribution of the anomaly by age and the absence of a pattern of distribution depending on gender.
The main reasons for the development of SRD include:
- Quick replacement of baby teeth with molars (up to 6-7 years). The jaw bones do not have time to develop, so there is not enough space for the teeth. However, there is no data on why some children change teeth earlier. This is an individual feature that is caused by abnormalities in the growth and formation of teeth.
- Bad infantile habits, such as thumb sucking or pacifier sucking. As a result, the risk of malocclusion and abnormal tooth growth increases.
- Congenital malocclusions. Changing the size of the jaw (less often the shape) negatively affects the location of molars, premolars, canines and incisors.
- Unfinished development of the alveolar process and the basal part of the jaw.
- Macrodentia, which implies an excessive increase in the size of one or all teeth.
- Narrowing of dental arches due to soft tissue dysfunction. The causes of dysfunction can be hormonal disorders, previous injuries, metabolic disorders, heredity and predisposition, and malocclusion.
- The appearance of third molars - “wisdom teeth”. This reason is typical for people of mature age, when the dentition is already formed and there is no room for “eights” [8].
- Supernumerary teeth - the presence of additional (extra) teeth.
Factors of SRD include: dysfunction of lip closure, abnormality of the frenulum of the tongue, infantile swallowing, mouth breathing [9]. Prolonged mouth breathing in childhood leads to deformation of the facial skeleton: the lateral parts of the upper jaw come closer together, as a result of which the upper jaw develops incorrectly; the hard palate becomes higher and narrower. As a result, the upper dentition becomes significantly narrower. Similar changes subsequently occur in the lower jaw. All this leads to overcrowding.
Norms and anomalies during shifts
Normally, during the formation of the rudiments of permanent units, temporary elements are subject to displacement. As the child grows, the primordium begins to grow and its crown touches the milk root. At this point the replacement process begins.
As a result of displacement, the root begins to dissolve and dissolve. This continues until the temporary unit has something to hold on to, then it becomes loose under mechanical stress and falls out, making room for the permanent unit to erupt.
Replacement begins at 5-8 years and usually continues until 12-14.
Absence of rudiments of permanent teeth and premature loss of milk units are considered abnormal. If the replacement rudiment has not formed, then the temporary element remains and is called “persistent” (persistere - to remain, lat.).
The root of a temporary tooth sometimes begins to dissolve earlier than expected under the influence of the crown of the adjacent element. In this case, the replacement occurs much later or, in the absence of a rudiment, it may remain in its place for a long time.
What to do with them
How to solve the problems that have arisen? This is decided by the dentist on a case-by-case basis.
- Often, a milk unit that has been well preserved is left, and it serves for a certain time. After all, a permanent unit may not grow in its place.
- An accurate diagnosis can be made after monitoring the x-ray. It shows whether there are undetected sprouts, and whether the root of the milk organ is resolving.
- If there is no permanent rudiment, and the roots of the temporary fixed unit do not change and the crown looks good, then tooth extraction is not prescribed.
- The same is done when the picture shows that the permanent unit will not erupt even after the elimination of the temporary tooth.
And one more thing: baby teeth are left if they do not interfere with other permanent units. But when baby teeth have not fallen out, but they are loose, create problems for the patient and do not look aesthetically pleasing, a decision may be made to remove them. The lost organ is replaced by prosthetics. A damaged unit that is not loose can be revived with lumineers or veneers, giving it the appearance of a permanent tooth
Reasons for deviations
Reasons for the absence of the process of changing bone organs in the jaw row:
- heredity;
- maxillary osteomyelitis;
- mechanical injuries of the jaw in childhood;
- metabolic disorders (in particular calcium deficiency);
- glandular pathologies;
- acute and chronic inflammation (periodontitis);
- unfavorable factors during the mother’s pregnancy (the fetus may not develop the rudiments of permanent teeth or the formation process will begin much later than usual).
If there are rudiments of permanent units, problems may also arise:
- the germ is too deep (the crown does not touch the root of the temporary tooth and replacement does not begin);
- incorrect position or direction of growth of constant units.
In all these cases, an adult may have many or one milk tooth left.
Signs of the development of Costen's syndrome and orthopedic treatment used in modern dentistry.
In this article we will discuss whether malocclusion can develop due to a pacifier.
Follow the link https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/chelyustey/krivaya-ne-prigovor.html to find out which doctor you should contact if your jaw is crooked.
This Personal Data Privacy Policy (hereinafter referred to as the Privacy Policy) applies to all information that (hereinafter referred to as the company), whose website is located on the domain name linedent.ru, can receive about the User while using the website, programs and products of the company.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
1.1. The following terms are used in this Privacy Policy: 1.1.2. “Personal data” - any information relating to a directly or indirectly identified or identifiable individual (subject of personal data). 1.1.3. “Processing of personal data” - any action (operation) or set of actions (operations) performed using automation tools or without the use of such means with personal data, including collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, clarification (updating, changing), extraction, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of personal data. 1.1.4. “Confidentiality of personal data” is a mandatory requirement to not allow their dissemination without the consent of the subject of personal data or the presence of another legal basis. 1.1.5. “Site User (hereinafter referred to as the User)” is a person who has access to the Site via the Internet.
GENERAL PROVISIONS
2.1. Processing and ensuring the security of Data is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Law, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, by-laws, and other federal laws of the Russian Federation defining cases and features of Data processing. 2.2. The User’s use of the website linedent.ru means acceptance of this Privacy Policy and the terms of processing of the User’s personal data. 2.3. In case of disagreement with the terms of the Privacy Policy, the User must stop using the site linedent.ru 2.4. This Privacy Policy applies only to the website linedent.ru The Company does not control and is not responsible for third party websites that the User can access via links available on its website. 2.5. The site administration does not verify the accuracy of the personal data provided by the site user.
SUBJECT OF THE PRIVACY POLICY
3.1. This Privacy Policy establishes the obligations of the Site Administration to non-disclose and ensure a regime for protecting the confidentiality of personal data that the User provides at the request of the Site Administration when registering on the site or when placing an order for the purchase of Services. 3.2. Personal data permitted for processing under this Privacy Policy is provided by the User by filling out the registration form on the Website linedent.ru and includes the following information:
3.2.1. last name, first name, patronymic of the User; 3.2.2. User's contact phone number; 3.2.3. email address (e-mail). 3.3. The Company protects Data that is automatically transmitted during viewing of advertising blocks and when visiting pages on which the system’s statistical script (“pixel”) is installed:
IP address; information from cookies; information about the browser (or other program that accesses advertising); access time; address of the page on which the advertising unit is located; referrer (address of the previous page).
3.3.1. Disabling cookies may result in the inability to access parts of the site that require authorization. 3.3.2. The company collects statistics about the IP addresses of its visitors. This information is used to identify and resolve technical problems. 3.4. Any other personal information not specified above is subject to secure storage and non-distribution, except for the cases provided for in paragraphs. 5.2. and 5.3. of this Privacy Policy.
PURPOSES OF COLLECTING USER'S PERSONAL INFORMATION
4.1. The Site Administration may use the User’s personal data for the following purposes: 4.1.1. Identification of the User registered on the website for placing an order and (or) concluding an Agreement. 4.1.2. Providing the User with access to personalized resources of the Site. 4.1.3. Establishing feedback with the User, including sending notifications, requests regarding the use of the Site, provision of services, processing requests and applications from the User. 4.1.4. Determining the location of the User to ensure security and prevent fraud. 4.1.5. Confirmation of the accuracy and completeness of personal data provided by the User. 4.1.6. Creating an account if the User has agreed to create an account. 4.1.7. Providing the User with effective customer and technical support if problems arise with the use of the Site. 4.1.8. Providing the User with his consent, information about prices, newsletters and other information. 4.1.9. Carrying out advertising activities with the consent of the User. 4.1.10. Providing the User with access to partner sites or services in order to receive products, updates and services.
METHODS AND TERMS OF PROCESSING PERSONAL INFORMATION
5.1. The processing of the User's personal data is carried out without a time limit, in any legal way, including in personal data information systems using automation tools or without the use of such tools. 5.2. The User agrees that the Site Administration has the right to transfer personal data to third parties, in particular, courier services, postal organizations, telecommunication operators, solely for the purpose of fulfilling the User’s order. 5.3. The User’s personal data may be transferred to authorized government bodies of the Russian Federation only on the grounds and in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. 5.4. In case of loss or disclosure of personal data, the Site Administration informs the User about the loss or disclosure of personal data. 5.5. The site administration takes the necessary organizational and technical measures to protect the User’s personal information from unauthorized or accidental access, destruction, modification, blocking, copying, distribution, as well as from other unlawful actions of third parties. 5.6. The site administration, together with the User, takes all necessary measures to prevent losses or other negative consequences caused by the loss or disclosure of the User’s personal data. 5.7. The site administration warns in advance about a change of site owners so that the User can delete his account and his personal data.
OBLIGATIONS OF THE PARTIES
6.1. The user is obliged to: 6.1.1. Provide information about personal data necessary to use the Site. 6.1.2. Update, supplement the provided information about personal data if this information changes. 6.2. The site administration is obliged to: 6.2.1. Use the information received solely for the purposes specified in clause 4 of this Privacy Policy. 6.2.2. Ensure that confidential information is kept secret, not disclosed without the prior written permission of the User, and also not sell, exchange, publish, or disclose in other possible ways the transferred personal data of the User, with the exception of paragraphs. 5.2. and 5.3. of this Privacy Policy. 6.2.3. Take precautions to protect the confidentiality of the User's personal data in accordance with the procedure usually used to protect this type of information in existing business transactions. 6.2.4. Block personal data relating to the relevant User from the moment of application or request from the User or his legal representative or the authorized body for the protection of the rights of personal data subjects for the period of verification, in the event of detection of unreliable personal data or unlawful actions.
ADDITIONAL TERMS
7.1. The site administration has the right to make changes to this Privacy Policy without the consent of the User. 7.2. The new Privacy Policy comes into force from the moment it is posted on the Site, unless otherwise provided by the new edition of the Privacy Policy. 7.3. Any suggestions or questions regarding this Privacy Policy should be reported to 7.4. The current Privacy Policy is located on the page at