The period when a baby's baby teeth erupt is both exciting and difficult for both the child and his parents. Children are often capricious during this period, sleep poorly, cry, and all because the appearance of their first teeth is accompanied by unpleasant sensations. Since the child himself cannot tell his parents about his problem and always reacts the same way to any type of discomfort, it is difficult for mom and dad to differentiate the signs of teething under the child’s behavior.
In this article, especially for young parents, we have collected as much useful information as possible about the eruption of baby and permanent teeth in children, so that you understand what is happening and how to act in this situation to help the baby.
When and what teeth do children erupt?
In fact, the rudiments of baby teeth are formed in children even during the period of embryonic development, and at the moment when they begin to grow and erupt, the rudiments of permanent teeth are already being prepared in the child’s jaw to replace them.
If we talk about the “gold standard”, then the teething scheme looks like this:
- 6-8 months – two central lower incisors.
- At approximately 8 months, the upper central incisors also appear.
- At 8-12 months, the upper lateral incisors appear.
- Around the same time (10-12 months), the lower lateral incisors erupt.
- At 14-20 months, the first chewing teeth appear on the lower and upper jaws (one on each side - 4 in total).
- At 1.5-2 years, the first canines erupt in the upper and lower dentition.
- At the age of 2-3 years, the following chewing teeth appear.
Despite the specified timing, each baby has his own individual teething order. So, some babies show their first teeth at 4.5 months, while others are “delayed” and, on the contrary, grow a little later than the established age. Such features depend on many factors, including gender (usually girls take the lead in teething).
What are the complications, and when to see a doctor?
| Symptom | Teeth are being cut, there is no need to go to the pediatrician | The disease develops, contact your pediatrician |
| Cough | A coughing attack begins due to excess salivation. The cough is wet and infrequent. | The cough gets worse, does not go away, does not allow the baby to sleep, and prevents him from eating. Doesn't stop for more than 2 days. Breathe heavily. |
| Nasal discharge | Nasal discharge is transparent and watery and disappears by the 4th day. | The runny nose does not go away for the 4th day. Lots of yellow or green discharge. |
| Heat | The temperature does not exceed 38 °C and lasts no more than 2-3 days. Rapidly decreases under the influence of antipyretics. | Fever above 38.5 °C for more than 2 days. Signs of a cold appear (severe cough and runny nose). |
| Loose stools | Lasts less than 72 hours. | Lasts more than 72 hours. |
| Changes in the oral cavity | The gums become swollen and red. | The oral mucosa is covered with white plaque or ulcers. |
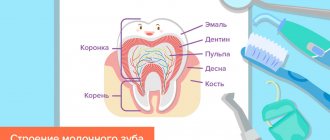
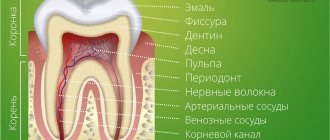
Formation of milk bite
The process of building a human bite has 5 stages, and all of them occur in childhood.
Each of the five stages is important for the final formation of the entire dental system and dental occlusion:
The first stage is from birth to 6 months (before the appearance of the first teeth).
The second stage is the period of eruption of all baby teeth in a child (6 months - 3 years).
The third stage is the period of jaw growth, preparation for the natural change of milk teeth to permanent ones (3-6 years).
The fourth stage is the time of active growth of the jaws and the eruption of permanent teeth (6-12 years).
The fifth stage is 12-15 years old, when the child’s baby teeth have already changed and all teeth are permanent.
Correct formation of the primary dentition is one of the main conditions for the development of a correct permanent dentition in a child.
Causes of delayed eruption of permanent teeth –
If for baby teeth delayed eruption is considered to be a delay of only 2-3 months, then for permanent teeth this figure is already 2-4 years. Among the main reasons for the delay in the eruption of permanent teeth, it is particularly worth highlighting the preceding inflammatory processes in the area of the roots of primary teeth, as well as the early removal of primary molars.
1) Violation of local conditions for teething:
- underdevelopment of the upper and lower jaws,
- lack of space in the dentition,
- premature removal of primary molars,
- incorrect position of the tooth germ,
- tooth germ injury,
- inflammation in the bone tissue of the jaws, for example, with purulent periodontitis of baby teeth.
2) Common causes of delayed eruption of permanent teeth:
- rickets or congenital syphilis,
- exudative diathesis,
- various chronic intoxications,
- metabolic disorders,
- disturbances of reflex-trophic processes,
- hormonal imbalances (for example, hypothyroidism, hypofunction of the thymus or adrenal glands).
Which permanent teeth are more likely to experience delayed eruption?
- one of the canines of the upper jaw (MF) – occurs in 43.64% of children,
- two HF fangs at once – in 25.65%,
- second premolar of the mandible (MF) – in 12.84%,
- two HF canines and LF second premolars at once – in 10.34%,
- both second premolars LF – in 5.11%,
- both lateral incisors HF – in 2.61%.
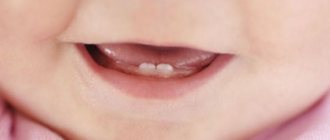
Symptoms of baby teeth erupting
Each baby reacts individually to the eruption of baby teeth, however, there are characteristic symptoms by which parents can understand that this is happening:
- heavy salivation;
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- itching
Severe itching and sometimes even painful sensations make the child capricious. He becomes restless, which disrupts his sleep. To somehow relieve the itching, children put toys in their mouths and intensively rub their gums. Children often refuse to eat or eat with less appetite. What does the gum look like when teeth come in? Changes in the condition of the gums are one of the criteria by which parents can differentiate teething. The gums in this place look inflamed - they turn red, swell, and immediately at the site of tooth eruption they become white.
However, the biggest concerns about the child’s condition are cough, runny nose, and fever during teething. Indeed, the appearance of baby teeth in its symptoms can resemble colds, and it is difficult for parents without experience to understand whether the baby is sick or is just teething.
First of all, you need to understand that both fever and cough during teething in children are acceptable reactions. Cough, hoarseness, and runny nose are most often the result of excessive salivation. For the same reason, during teething, babies develop a rash on the chin and around the mouth.
Another frequently asked question from parents is what kind of stool can a child have when teething? During a particularly acute period of teething, babies may have weak stools, which is associated with general irritation of the nervous system and has nothing to do with eating disorders.
However, it must be taken into account that when babies are teething, they are more susceptible than usual to various infections. If unpleasant symptoms (fever, diarrhea, cough) do not go away on their own after 2-3 days, the child should be examined by a doctor.
How long does teething take for babies?
With normal development and growth, baby teeth erupt within a few days (2-8 days), and the most unpleasant symptoms usually appear within about 2 days.
The period of formation of the primary occlusion ends at 2-3 years, and at this moment the baby has 20 primary teeth.
Problems and complications when the first teeth appear
Sore gums, fever, poor appetite and indigestion are, although unpleasant, acceptable symptoms during the eruption of baby teeth.
In some cases, children experience complications:
- long delay - can be either a genetic feature or pathological adentia (if the child has not formed the rudiments of teeth);
- formation of a hematoma (cyst) - in this case, the gum above the growing tooth acquires a dark purple tint, then a lump or hematoma appears in this place, which may be due to both difficult eruption (the tooth cannot cope with the mucous membrane) and other reasons;
- violation of the order of teething;
- aphthous stomatitis - rashes on the mucous membrane in the form of purulent ulcers;
- enamel hypoplasia – occurs in babies under 10 months of age;
- malocclusion - improper closure of teeth, crowding, possible problems with the eruption of permanent teeth in the future.
If your baby experiences “difficult eruption” of primary teeth or you encounter the listed complications, you should definitely consult a pediatrician. If the formation of a primary occlusion is clearly incorrect, consult an orthodontist.
Norm or pathology
Can teeth be cut at 3 months? The earliest age for the eruption of the first elements is considered to be three months of age. Dentists consider it normal for the first teeth to appear at 3 months of age. If the incisors appear earlier than the expected period, then the child should be shown to a therapist. The early appearance of elements on the surface of the gums may signal hormonal disruptions occurring in the body.
The appearance of baby teeth on the surface is accompanied by a number of distinctive symptoms:
- Pain in the gums. Because of this, the child puts fists and foreign objects into his mouth. At this moment, it is important for adults to ensure that there are no small toys or objects near the child that could get into the respiratory tract.
- Deterioration of the oral cavity. The gums swell and redden, becoming more sensitive to external irritants. In some cases, due to teething, the child may experience slight redness of the throat.
- Irritability and increased tearfulness of the baby. The symptom is associated with constant pain in the area of the eruption of the element. At this moment, children become more active and faster.
- Disorders of the digestive tract, manifested by loose stools, regurgitation, and rare bouts of vomiting.
- Temperature increase. The symptom is due to the fact that when teething, the newborn’s body is vulnerable to bacterial and viral pathogens.
What to do when teething: advice for young parents
Now that you know what is happening to your child, you can draw up a rough action plan aimed at making the process of the appearance of the first teeth as easy as possible for the baby.
Tips for moms and dads:
- 1
Stay calm. It’s not easy for a child anyway, and your anxiety and irritation will only negatively affect the baby’s well-being. - 2
Surround your baby with love and tenderness. Remember that small children feel calm and safe only in the arms of loving parents.
- 3
Provide your baby with special gum toys that will help relieve itching and make teething easier.
- 4
Turn on the increased antibacterial protection mode (frequent ventilation, sterilization of toys, pacifiers, etc.), since during this period the child can easily catch an infection.
If your baby's gums are bothering you a lot, you can use a special teething gel. This product has a mild anesthetic effect, relieves itching and pain. Regarding the choice of gel, it is better to consult your pediatrician. He will tell you which drug is suitable for your baby’s age and has a safe composition.
What to do when the temperature rises? Doctors recommend avoiding the use of antipyretic drugs, as the body fights infections by raising the temperature. If hyperthermia is very high, you should consult a pediatrician, he will recommend what medications and in what dosage can be given to the baby. Under no circumstances use folk remedies or medications without first consulting a doctor!
Alarming symptoms
Many signs of teething are harmless and go away on their own once the incisor comes to the surface. However, some signs may indicate the addition of bacterial or viral diseases against a background of weakened immunity.
Reviews of Dentokind for teething up to one year
Normal signs of the condition include:
- Profuse salivation. The symptom is observed in almost all children under three months. It does not require treatment for the child.
- Skin irritation near the chin. The symptom is caused by increased salivation during teething. It is enough to use an emollient cream every day at night to eliminate skin redness.
- The child's desire to breastfeed frequently. During feeding, the baby scratches its gums on the mother's nipple.
The list of alarming symptoms of teething includes:
- refusal to eat (more than 3-4 feedings);
- persistent diarrhea (may indicate an incipient intestinal infection);
- constant crying of the child.
Small bruises (hematomas) may appear in the eruption area. They dissolve quite quickly if you apply a compress to the problem area.
Formation of permanent bite
The development of permanent teeth is a long and complex process. The formation of permanent teeth begins at approximately 3 years of age, when the child’s primary bite is already fully formed.
Preparations for their eruption are ongoing, but changes occur gradually, so most often we don’t even notice them. Meanwhile, the child:
- jaws grow and expand;
- the distance between baby teeth increases (this is important, since permanent teeth are larger and by the time they erupt there should be enough space for them in the dentition).
Timing of eruption of permanent teeth in children
The order of growth of permanent teeth in children is mainly hereditary. In approximately 50% of cases, the molars (sixes) grow first. Second molars appear at 7-8 years of age. Around the same time, the incisors are replaced.
The first permanent tooth appears in children at 6 years of age, and the complete formation of the permanent dentition of the lower and upper jaw is completed at 12-13 years of age. After this, the roots of permanent teeth continue to form and this process ends by the age of 15.
Teething symptoms
Unlike baby teeth, permanent teeth in children erupt almost always painlessly and with virtually no symptoms.
In rare cases, during the teething period the child’s well-being may deteriorate:
- the child gets tired quickly;
- drowsiness appears;
- gums become inflamed;
- salivation increases, a runny nose appears;
- The gums itch where the tooth grows, and when chewing, painful sensations appear.
Problematic eruption of permanent teeth in children
Problems that may arise during the eruption of permanent (molar) teeth:
- 1
Growth retardation – after a baby tooth falls out, the permanent one is in no hurry to appear for 6 months or longer.
- 2
Bite pathology. It may be associated with premature eruption of permanent teeth (if the baby teeth have not yet fallen out), or lack of space on the jaw for normal tooth growth.
- 3
Hyperdentia - permanent teeth grow second row behind the milk teeth. The reason is the strong fixation of the temporary tooth in the socket, as a result of which the permanent tooth “chooses” a more convenient direction for growth.
- 4
Caries and its complications.
Signs of teething
You can understand that the first molar will soon come out by the following signs - the gums begin to swell and hurt greatly, which is accompanied by increased salivation. In this case, a similar picture can begin several months before the actual appearance of the teeth themselves. Sleep becomes restless, the child is capricious, due to severe discomfort, children refuse some meals, and an irresistible urge to put various objects in their mouth appears.
Once teething enters the active stage, you will notice a thin white line on the gum or a whitish protrusion. If you lightly tap the exposed teeth with a teaspoon, you will hear a slight clicking sound, some parents do this, but if you decide to do this test, do it very carefully.
How to correctly distinguish between symptoms
Some signs characteristic of the onset of the appearance of molars in children often overlap with the symptoms of infectious diseases. Therefore, if you have any doubts about this, it is better to seek advice from a specialist.
Pay attention to the temperature - it can rise to 38.5–39 degrees and stay for two days, this is normal. Paracetamol in small quantities is suitable for knocking it down, but if after this period the indicators do not decrease, you should not hesitate to go to the doctor.
Watery diarrhea also often occurs due to excessive salivation; normally, this repeats up to 2-3 times a day. If this period is exceeded and blood inclusions appear, there is already a reason to make an appointment with a specialist.
Regarding the runny nose, clear discharge that lasts 3-4 days does not cause concern; it is enough for parents to clear the sinuses of it in a timely manner.
If this period is exceeded, and the snot becomes whitish or greenish, do not hesitate to go to the doctor. The same applies to a cough, if it lasts more than two days and is accompanied by sputum, consultation is needed.
How to help your child: recommendations from Amel Dental doctors
To cope with the discomfort caused by the eruption of permanent teeth, it is enough to massage the child’s gums. If your gums are inflamed, a teething gel will help relieve the inflammation (your dentist will help you choose the right one).
What to do if complications develop?
- 1
Bite problems in children are easier to eliminate than in adults, so if there are defects, you should consult an orthodontist.
- 2
Caries requires immediate treatment, otherwise there is a chance that the child will lose a tooth in childhood.
- 3
If dental growth is delayed, you should immediately see a doctor. One of the main reasons for delayed eruption of permanent teeth in children is immune disorders.
What can be done to help a child with severe itching and pain?
- Carry your baby in your arms more often, play with him and distract him.
- Give chilled water in a bottle, cool fruit puree or kefir. The main thing is that the liquid is not too cold, otherwise the baby will catch a cold.
- Massage the gums with a special silicone brush (see picture above) or you can gently use your clean finger.
- Buy your baby a teether and let's chew.
Such devices are made from plastic, rubber, silicone, wood, or a combination of different materials. The surface of the toys should be elastic and uneven to make it easier for the child to scratch the gums. A cooled teether relieves itching better, so it can be placed in the refrigerator to cool for 10-15 minutes. But don't chill it in the freezer!
- Do not use gum gels with lidocaine and benzocaine.
The child has a lot of saliva in the mouth, so gels are not effective during this period. The child swallows most of the gel.
How to keep children's primary and permanent teeth healthy?
Both baby and molar teeth of a child require careful care. The health of future permanent teeth depends on how healthy the child's baby teeth were. The main concern of parents is quality care, timely treatment and preservation of baby teeth until the time comes for their natural replacement with permanent ones.
What should you do for this?
- Carefully monitor the condition of your baby’s teeth and regularly take him for examinations to the dentist in order to diagnose caries in time.
Prevention of caries is one of the main conditions for the health of a child’s future permanent teeth. You can protect your teeth by ensuring regular high-quality oral hygiene. One of the most effective measures to prevent caries in children is the dental procedure of sealing the fissures of baby teeth.
- Treat caries in a timely manner.
Unfortunately, temporary teeth have very thin enamel and not a very dense structure, so when affected by a carious infection, they are quickly destroyed. With timely diagnosis, caries is treated quickly and without complications - in dentistry, baby teeth are filled with safe materials. Thanks to modern materials and technologies in dentistry, it is even possible to restore baby teeth with severe destruction. In some cases, if the baby tooth could not be saved, and there is still a lot of time left before the permanent teeth erupt, prosthetics of temporary teeth is used.
- Take care of proper nutrition.
Food is an important source of useful vitamins and microelements, so it is important that the child’s diet is varied and balanced.
Both baby and molar teeth of a child require careful care. The habit of brushing teeth and observing the rules of oral hygiene is formed in children from the appearance of their first teeth. Maintaining the health of children's teeth requires very little time and effort, but all this effort will help your child keep his teeth healthy for a long time!
What should you not do when your baby is teething?
- Strongly touch the child’s gums with your fingers, press on them and pick them out. This can increase pain or cause infection.
- Conduct vaccination, because immune system is weakened during this period .
- Without supervision, allow your child to chew any hard foods that could cause choking.
- Give homeopathic remedies. Not only will they not help the child, but they can cause serious harm.
The eruption of baby teeth is not a problem, but a natural process for a child’s body. But if you are not sure about something, do not hesitate to ask specialists. If you have any questions, write to us on Instagram.
How to care for children's teeth -
Oral hygiene should begin even before the first teeth erupt. Typically, infants' gums are cleaned twice a day. It is done either using a special fabric fingertip, or a clean bandage wrapped around the finger and moistened with boiled water. When teeth erupt, special hygiene products are needed (special toothbrushes, as well as toothpastes or tooth foams).
Remember that the enamel of children's teeth is more porous and rough, because... it contains few microelements (compared to already mature mineralized enamel in adults). Consequently, in the absence of proper hygiene and diet, there is a very high risk of developing multiple early dental caries. We hope that our article on the topic: Timing and order of teething in children was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal 20 years of experience as a dentist, 3. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (EU), 4. National Library of Medicine (USA), 5. “Pediatric therapeutic dentistry. National leadership" (Leontyev).
Possible complications
"Surprises"
The problems that nature presents when infants have their first teeth do not end with the listed troubles. Sometimes other complications are possible:
- Formation of hematomas.
A bluish-colored bubble swells on the gum. Most often it resolves over time, but sometimes if the blister is too large, surgery is required. The doctor makes a small incision on the gum to remove the bloody fluid.
- The appearance of vomiting.
This may be caused by excessive salivation. However, if vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea and fever, these may be signs of rotavirus, so it is necessary to urgently show the child to the pediatrician.
- Cough reflex.
With normal teething it does not happen. The cause of the cough may be excessive saliva secretion, which causes the baby to choke.
If a runny nose appears, take your child to the doctor
- teething probably coincided with a cold.
Important:
If your baby is experiencing fever, diarrhea and vomiting during teething, take this seriously. The cause of their appearance cannot be teething. It is urgent to call a pediatrician, since the baby’s body is at risk of intoxication due to a developing infection.
Teething symptoms
There is an opinion that the appearance of the first teeth is accompanied by the development of a whole complex of pathological processes (fever, the appearance of a rash, abnormal stool, vomiting, convulsions, etc.). In fact, the formation of a temporary bite is a natural process that is not characterized by the symptoms described above. Pathologies detected during the teething period are most often manifestations of infectious diseases or a consequence of changes in diet.
In particular, factors that can lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms include:
- introduction of artificial complementary foods;
- hypovitaminosis;
- acute viral infections;
- stomatitis;
- tonsillitis;
- runny nose;
- otitis;
- vaccination, etc.
The true symptoms of teething are:
- hyperemia and gradual swelling of the gums;
- the appearance of a small bluish hematoma on the gum tissue;
- slight bleeding from the gums;
- wet cough;
- mild itching caused by mechanical irritation of sensitive nerve fibers in the gum tissue;
- increased salivation;
- various somnological disorders;
- sharp deterioration in appetite;
- tearfulness, capriciousness.
Folk remedies
Medicines are effective for teething, but what should you give a child when teeth are cutting and you don’t want to use synthetic drugs? Home methods are auxiliary because they cannot always completely eliminate pain. However, for some children, these options are the most preferable and really help cope with pain. Doctors sometimes advise using:
- Compresses with chamomile. It is necessary to moisten a bandage or cotton pad in chamomile infusion and then apply it to the painful cheek. To relieve inflammation and swelling, dentists recommend giving several teaspoons of herbal tea.
- Honey. If the baby is not prone to allergic reactions, you can lubricate the inflamed mucous membranes with a honey substance. You should rub the substance in carefully, otherwise the baby will simply swallow it, and all manipulations will be useless.
- Soda solution. It is recommended to dissolve 1 tsp. soda in a glass of clean warm boiled water, dip a gauze cloth and wipe the gums. This product helps not only relieve pain, but also disinfect the surface.
Before using traditional methods, you must always consult a doctor, even if the herbal substances used are considered completely safe. Sign up for a consultation at the dental office, our specialists will recommend effective formulations that will not harm the little patient.