It is believed that periodontal inflammation develops with the participation of periodontopathogenic microorganisms, the action of which manifests itself when the balance between the protective forces of the human body, organs and tissues of the oral cavity and bacterial infection is disturbed [11, 19]. Of all the branches of periodontology, practitioners are certainly most interested in the issues of adequate and effective drug treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases.
Unfortunately, in the treatment of periodontal diseases there is no multidisciplinary approach, and internists are rarely involved in the treatment process. Usually, so-called monotherapy is carried out, in which a specialist of one profile is involved - usually a dentist-therapist. With the so-called complex treatment, all stages are carried out in random order, in the absence of an algorithm for complex therapy, without clear preliminary planning and subsequent objective assessment of the effectiveness of each stage, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient, without a medical examination program and supportive therapy [1, 21].
The purpose of this message is to inform dentists specializing in periodontology, interns, clinical residents, senior dental students about the main directions of drug therapy for inflammatory periodontal diseases, which are most widely used today in Russia.
Based on our own experience and data from domestic literature, we can propose the following course of action for the dentist.
The authors have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of the information presented, including drug dosages. Aware of our responsibility associated with the preparation of the publication, and taking into account the constant changes occurring in medical science, we recommend that the dosage of medications be updated according to the appropriate instructions.
What is a dental cyst?
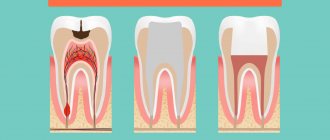
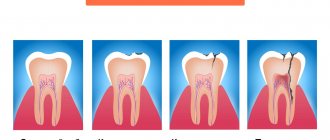
Tooth cyst - what is it? An odontogenic cyst is a pathological neoplasm that occurs in the upper part of the tooth root. The internal cavity of the cyst is filled with liquid or mushy purulent contents; it is enveloped by a dense layer of epithelium.
The size of the cyst starts from a few millimeters, with rapid development reaching several centimeters in circumference. Most often, the pathological process affects the upper jaw, since the roots of its teeth have a more porous structure.
In order to understand what a dental cyst is and how to treat it, you need to know why such a phenomenon occurs. The formation of cysts occurs as a result of inflammation, thus the body restricts healthy tissue from the affected areas, clogging them along with bacteria into bubbles.
Treatment of gums with injections and medications
In some cases, injections of various medications may be required. Antibacterial medications are prescribed strictly individually. In any case, the clinic doctor will not ignore his patient’s dental problem. As evidenced by reviews of our clinic in Moscow, we are always ready to help!
Restoration of teeth and gum tissue in our clinic includes the use of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs. The action of therapy is aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation and stopping the disease. Powerful antiseptics Actovegin and Solcoseryl are used, which have an epithelializing effect. In acute cases, physiotherapy is prescribed.
Vacuum and finger massages are also used as an additional method of therapy. Such measures allow blood to circulate better in the affected areas and trigger the necessary recovery processes.
Important!
Regular dental hygiene should be performed to prevent the formation of mineral deposits and the development of disease.
Causes
There are several reasons why a dental cyst develops. The main reason is the activity of pathogenic microorganisms in a closed dental space; the following risk factors contribute to this:
- severe pathology, lack of timely treatment and incorrect treatment of dental diseases - caries, periodontitis, pulpitis;
- infectious complications after tooth filling, implantation procedures - in such cases, the doctor removes not only the cyst, but also the crown or implant, this avoids relapse;
- complications during teething, especially when wisdom teeth erupt - dental tissues injure the gums, bacteria get into microcracks,
- microorganisms also enter wounds that form due to mechanical damage to teeth;
- Nasopharyngeal diseases – infections in the nose and throat can spread to the oral cavity.
To provide adequate treatment, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the development of a dental cyst; based on it, the dentist will prescribe suitable therapy. So, in cases of injury, treatment consists of removing the cyst and tissue regeneration, but if the cyst is a complication of another disease, then in addition to removing the vesicle, the patient will be prescribed treatment for the underlying disease.
Laser gum treatment
Elimination of periodontal problems in our clinic is also carried out using laser equipment. The method allows you to deeply disinfect all gum tissue and the oral cavity. The laser has a powerful regenerating effect. Its use is safe and appropriate for periodontitis. The procedure has fewer contraindications and is accessible to most of our patients. After the procedure, rehabilitation is faster and easier. Laser restoration of teeth and gum tissue is an innovative method that is widely used in Europe.
Therapy is carried out in a course prescribed by the doctor. Already after the first procedure, partial restoration of tissue cells occurs. The laser provides non-contact, minimally invasive dental care and positive results. The technology allows a specialist to eliminate all problems with the disease, as well as eliminate stomatitis and gingivitis. Our specialists are fluent in new technologies and methods for eliminating dental problems.
Complex treatment has a more positive result. The use of antibacterial medications, laser exposure, and surgical curettage make it possible to forget about the disease. Statistics show that complex therapeutic methods are 65% more effective than monotherapy.
Types of dental cysts
Tooth cysts have different classifications, each of which is formed according to certain characteristic parameters of the pathology.
According to the nature of the disease, they are distinguished:
- residual cysts – occur after tooth resection (removal) surgery; this is the most common type of cyst;
- retromolar – formed during severe eruption of wisdom teeth;
- radicular - cysts are located on or near the tooth root;
- follicular – at the heart of such cysts is the germ of a permanent tooth; follicular neoplasms arise as a result of poor quality care of baby teeth.
Classification of neoplasms according to their origin:
- odontogenic – arise as a result of the transition of the inflammatory process from other dental diseases;
- non-odontogenic - the causes of the development of such cysts include problems not related to the teeth and oral cavity.
Locations of cystic formation:
- anterior teeth;
- teeth that are adjacent to the nasal sinuses with their roots;
- wisdom teeth.
Gum treatment: price
The cost of the service is formed from various aspects. It is affected by:
· stage of the disease;
· extent of damage;
· cost of medicines;
· volume of work of a doctor.
Our price is not overpriced and is formed quite transparently. If you live in the capital, then gum treatment in Moscow will cost you inexpensively in a clinic that provides a similar service.
Treatment of gums in dentistry requires careful and long-term therapy. An experienced doctor will examine the oral cavity, identify problems in the gums and teeth and begin the necessary treatment. The price of treatment is also influenced by the cost of injections. How much the patient will spend depends on the characteristics of the disease.
You can find out the cost of our dental services in advance from the administrator or by calling the specified phone number.
Symptoms
The danger of a dental cyst lies in the fact that signs of pathology appear only when the neoplasm reaches a relatively large size. In the early stages, small cysts do not manifest themselves in any way, meanwhile the infectious process covers an increasingly larger area of healthy tissue. In the initial development of pathology, cysts are discovered by chance during routine examinations or treatment of other diseases.
The duration of the formation of a dental cyst takes only 1-2 days; as it develops, the following symptoms may occur:
- unpleasant and even painful sensations in the tooth, which intensify when chewing solid food;
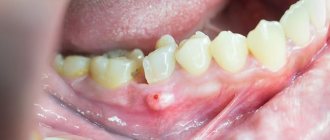
- protrusion of the gum of a tooth, in the area of the root of which a cyst forms, the growth of the gum becomes larger over time, redness is observed;
- the formation of a fistula in the area above the root of the tooth, the release of serous or purulent accumulations from it;
- general weakness and malaise;
- increase in body temperature.
Note! When a dental cyst occurs, the symptoms are not immediately visible; they appear in the later stages of development. The pain when a tumor appears is aching in nature, but it is less pronounced than the pain caused by caries and pulpitis.
If a clinical picture occurs and you suspect a pathological process, be sure to consult a doctor. Under no circumstances should you resort to self-treatment - the dental cyst must be removed. In addition, taking the wrong medications can worsen the patient’s overall well-being.
Sometimes there is no pain in the oral cavity; instead, the basis of the clinical picture is intense headaches. The cause of this phenomenon may be a cystic formation in the maxillary sinus.
Types of pain relief
Dentists, as a rule, provide drug local anesthesia, which involves injecting the drug into the tissue in the treatment area. The effect of the product lasts for a certain time required by the specialist to perform the treatment procedure. After a short period of time, the drug is eliminated from the body, and tissue sensitivity is restored.
Treatment under general anesthesia is rarely performed. It is often used in complex jaw surgery operations.
Local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is almost always performed during dental treatment. It causes less stress to the body, so it is used even for children. A few years ago, only injections of Novocaine and Lidocaine were used. However, today different substances and their forms are used for pain relief.
- Application anesthesia
Anesthesia provides a superficial decrease in sensitivity. A special spray, gel or ointment is applied to the causative area of the oral cavity. A common substance is a solution of Lidocaine, produced in the form of an aerosol. This type of sensitivity reduction is indicated for manipulations with a minor degree of intervention, for example, when removing stone or preparing the dentition for prosthetics.
The concentrated drug penetrates the tissue by 2-3 mm and blocks nerve endings. The effect is noticeable within a few minutes and lasts half an hour to an hour. The anesthetic is not absorbed into the circulatory system, therefore the method is considered the safest. Other disadvantages of topical anesthesia include the insignificant depth of anesthesia and the short duration of its action.
- Infiltration anesthesia
Such anesthesia makes it possible to reduce the sensitivity of one element of the dentition or a small area of periodontal tissue. Such anesthesia is recommended for depulpation or when treating teeth severely damaged by caries.
The drug is injected into the root apex area. The substance does not allow the passage of a pain impulse in the area of the nerve branch. The method is recommended for the treatment of upper teeth, since the bone skeleton of the upper jaw is thinner and allows easy access to the nerves. The disadvantages of the method include the need to use a significant amount of anesthetic if it is necessary to anesthetize a large area. There is also a high risk of soft tissue deformation (swelling) at the injection site, which may interfere with the effective implementation of the procedure.
- Conduction anesthesia
This anesthesia is used to anesthetize several dental elements located in a row “in the neighborhood.” This method of reducing sensitivity is used during tooth extraction, puncture of inflammation, acute periodontitis and when installing a drainage system in a purulent focus. A properly selected anesthetic temporarily reduces the sensitivity of an entire nerve branch. The disadvantage of the technique is the high risk of injury to the nerve and vascular network. Manipulations require specialist skills.
- Intraligament method
When treating children's teeth, an intraligamentous method of pain relief is used. The substance is injected into the periodontal zone, near the alveoli and tooth root. With this method, the mucous membrane does not lose sensitivity, so the risk of the baby biting the mucous membrane and lips is reduced.
- Intraosseous anesthesia
This type of sensitivity reduction is indicated when tooth extraction is necessary. The substance is injected into the gum, reducing the sensitivity of the target tooth and gum area. Pain relief occurs very quickly, but the effect does not last long.
- Trunk anesthesia
With this type of anesthesia, the trigeminal nerve and its branches at the base of the skull are blocked. This radical method is used for extensive operations in dentistry and jaw surgery. The duration of anesthesia is increased due to the vasoconstrictor. Trunk anesthesia affects both jaws. The patient is constantly monitored.
When is pain relief not performed?
Before using this or that drug, the dentist finds out whether the patient has mental illnesses or allergic reactions. Drug pain relief is not used if:
- allergy;
- cardiac ailments;
- diabetes;
Important: Drug pain relief is administered to pregnant women and nursing mothers with extreme caution.
In some cases, when anesthesia is contraindicated, drugs are used in dentistry to relieve the patient of anxiety. Sedatives reduce fear, are not hypnotics, and give good results. They are prescribed by the dentist depending on the need.
What drugs are used in dentistry for pain relief?
Novocaine and Lidocaine have already been mentioned. In modern practice they are used less and less. Experts prefer modern anesthetics: Articaine, Ultracaine, Scandonest, Septonest.
Anesthesia drugs in dentistry are prepared in capsules, which are placed in the body of a syringe with a thin needle.
What complications can arise when using painkillers in dentistry?
Common side effects when using anesthesia include:
- allergic reactions due to individual intolerance to the drug;
- poisoning (when using an overdose);
- nerve injury from a needle (in case of violation of the local anesthesia protocol).
The following manifestations and conditions may also be observed after an injection:
- swelling and hematomas due to damage to the blood branch;
- infection of tissues at the site of drug administration due to the doctor’s violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis;
- trismus due to nerve damage;
- biting soft tissues due to loss of sensitivity after administration of the drug.
How to prepare for anesthesia?
It is recommended to refrain from drinking alcohol two to three days before the procedure, as ethyl alcohol reduces the effect of the drugs. If you're nervous about your upcoming dental visit, take a sedative at night. Dental treatment is not carried out against the background of colds.
General anesthesia
Anesthesia is a complete (temporary) loss of sensitivity in a patient, which is accompanied by impaired consciousness of varying degrees. This method of pain relief is rarely used in dentistry.
The indication for general anesthesia is one of the following conditions:
- intolerance to local anesthetic drugs;
- mental conditions and disorders;
- pathological fears of dental procedures.
Before visiting a dentist, if procedures are to be performed under local anesthesia, the patient is required to undergo a medical examination:
- ECG and consultation with a cardiologist;
- laboratory blood tests;
- consultation with a therapist.
Before visiting the dentist's office, you should avoid drinking alcohol. Eating on the eve of the visit and in the morning is contraindicated. General anesthesia is carried out only by an anesthesiologist in the presence of a resuscitator.
Consequences
Without adequate treatment, the dental cyst continues to grow and develop; in advanced stages, large neoplasms destroy the bone tissue of the skull, as a result it is replaced by connective tissue formations, which leads to the development of the following complications:
- dissolution of the jaw bone, which depends on the growth of the cyst;
- the formation of pus in the cyst, further purulent inflammation can lead to the development of an abscess;
- inflammatory process of lymph nodes located near the source of infection;
- development of osteomyelitis or periostitis;
- development of chronic sinusitis when the cyst grows in the maxillary sinus;
- pathological fracture of the jaw bones when the cyst reaches a large size;
- development of phlegmon due to a long-term purulent inflammatory process in the cyst;
- sepsis – blood poisoning;
- degeneration of a cyst into a malignant tumor without timely treatment.
Many patients are interested in why a dental cyst appears in the maxillary sinus, how dangerous it is and its symptoms. The formation of a cyst of this type occurs as a result of untreated inflammation of the tooth root in the upper jaw. A granuloma forms at the root of the tooth, which increases in size and becomes a peri-radicular cyst, then takes a position in the maxillary sinus. The volume of such a cyst can reach 9-12 cubic centimeters.
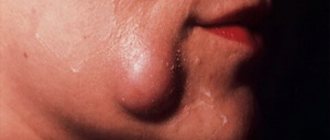
The symptomatic picture includes painful sensations, the nature of which is similar to trigeminal neuralgia, pain in the occipital, temporal and parietal regions of the head. Externally, a dental cyst can be identified by the asymmetry of the face. Tooth cyst - photo shows a cyst in the maxillary sinus.
What symptoms require gum treatment?
Therapeutic methods for eliminating periodontitis boil down to eliminating the inflammatory process in the gingival tissues and are aimed at preventing tooth extraction procedures. Treatment should begin if:
· there is bleeding;
· unpleasant odor from the mouth;
tissue swelling;
· or loose teeth.
A qualified dentist at our clinic competently determines the treatment method and selects the drug on an individual basis.
Inflammation of the tissue around the teeth is accompanied by pain, discomfort in the oral cavity, and the presence of tartar.
Regular hygienic brushing of teeth and getting rid of tartar will help to avoid the disease.
When affected, frequent bleeding and high sensitivity are observed. The teeth begin to loosen. Periodontitis destroys the supporting apparatus of the tooth. The ligament loses its functions, its cells are destroyed. Food debris accumulates in the gum tissue, which promotes the deposition of mineral particles. Sometimes even pus is found under the gum. Often the patient suffers from complications - the disease develops further, inflammation progresses, and the temperature rises.
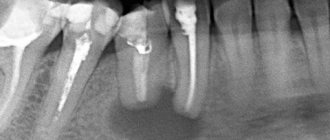
Diagnosis of tooth root cyst
To make a diagnosis and carry out appropriate treatment, the dentist collects and analyzes the medical history. During the initial diagnosis, many patients report the fact of endodontic treatment performed to eliminate periodontitis or pulpitis. Some patients indicate an exacerbation of the disease after intraoral dissection.
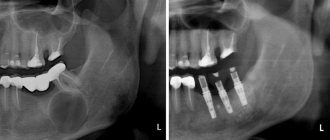
Radiography is used as the main diagnostic method. Below is a photo and x-ray of a dental cyst.
To obtain an x-ray, several methods are used, the first method is based on contact intraoral x-ray, the advantages of this technique:
- determining the degree of destruction of the jaw bones;
- assessment of the condition of the tooth root and tooth canal;
- assessment of the quality of canal filling;
- identifying the presence of perforations and fragments of instruments and materials in the tooth canal;
- determination of the relationship between the cyst and the roots located near the teeth.
The second method of performing radiography is an orthopantogram; the procedure is a panoramic photograph of both jaws and the maxillary sinuses of the upper jaw.
Another method of the procedure is a survey X-ray in the nasomental projection; the X-ray covers the bones of the skull from the nose to the chin; using the image, the doctor assesses the condition of the maxillary sinuses and detects cysts that have grown into the nasal cavity.
In addition to radiography, to detect a tumor, the patient may be prescribed an electroodontic diagnostic procedure. This technique helps to assess the degree of such an indicator as the electrical excitability of the teeth that are located next to the cystic tooth. If the value exceeds 60 microamps, the dentist prescribes endodontic treatment to the patient.
For diagnostic purposes, histological and cytological studies are used to determine whether the neoplasm is benign or malignant.
Diagnosing a dental cyst is not difficult, but only qualified dentists can carry it out in a hospital setting; under no circumstances try to independently determine the presence of a cyst and do not take therapeutic measures; strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Surgical methods for treating periodontitis
In our clinic, if necessary, various surgical methods are used, and the price for gum treatment is acceptable for all patients. The disease can be eliminated using advanced techniques:
· opening of an abscess during periodontal disease;
· closed curettage of periodontal pocket;
· increase in attached gum tissue;
· splinting of teeth;
· use of fiberglass to strengthen teeth.
Treatment of gums with surgical methods helps strengthen teeth and prevent their destruction and loss. Periodontal disease can be eliminated if you contact a periodontist at our clinic in a timely manner.
Treatment
Treatment of dental cysts is carried out through surgery, laser treatment and conservative therapy. The latter has a positive effect only in the initial stages of the disease; overgrown cysts must be removed.
Surgery
To eliminate the pathology, it is not necessary to remove the entire tooth; only the tooth root on which the cyst is located is subject to resection. After removing the affected area, the dentist seals the remaining root, treats the surgical canal through which he removed the bladder with its contents, and stitches it up.
After a few days, the doctor removes the stitches and monitors the wound healing process. It is important to make sure that there are no cyst particles left in the dental canal; to achieve this goal, repeat radiography is performed.
Note! Sometimes it is impossible to remove the root along with the cyst; in these cases, the doctor completely removes the tooth. Indications for complete tooth resection are a difficult-to-reach location of the cyst and a severe course of the disease.
After surgical removal of a cyst, the patient must regularly visit the dentist and follow the recommendations prescribed by the doctor.
Conservative therapy
Tooth cyst - treatment of the disease with conservative methods is possible only in the early stages of its development. In order to eliminate the tumor, the patient is prescribed injections and rinses.
During therapeutic treatment, the dentist opens the dental canal, which leads to a cystic neoplasm, and pumps out exudate from it. The doctor does not fill the canal for ten days; during this period, the patient uses antiseptic solutions and tinctures to rinse the mouth.
Upon completion of the treatment course, the dentist treats the dental canal with medications and then fills the tooth.
Laser removal
Laser treatment is a modern method of treating dental cysts. When performing the method, the doctor opens the dental canal and uses laser irradiation to treat the area where the cystic tumor is located. The laser destroys not only the epithelium of the cyst, but also hundreds of thousands of bacteria that are inside the bladder.
The advantages of laser removal are rapid tissue healing and no risk of secondary infection in the oral cavity and dental canal.
Treatment with antibiotics
In some cases, dental cysts are treated with antibiotics. Taking antibacterial drugs is an auxiliary measure to destroy an expanded infection or the main method of treatment if a dental cyst develops against the background of a primary infectious disease.
Antibacterial drugs can only be prescribed by the attending physician; the following drugs are most often used:
- amoxicillin – has a high antibacterial effect, greatly facilitates the treatment of cysts with other methods;
- Cifroploxacin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that actively destroys bacteria and relieves inflammation;
- tetracycline - this drug is prescribed more often than others, it actively relieves the inflammatory process, pain syndrome, and facilitates other methods of treating dental cysts.
Sometimes a doctor can prescribe topical antibacterial agents to a patient, but taking such medications is not always advisable - local drugs - antibiotics are quite difficult to distribute evenly over the diseased area.
Note! Antibacterial drugs are potent drugs that also affect beneficial bacteria in the body. You can take such medications only as prescribed by a doctor, without increasing the number of doses or dosage.
Treatment at home
Treatment of dental cysts at home is possible only as an auxiliary therapy. A cyst should not be confused with a granuloma; the latter can resolve on its own, but the cystic formation must be radically removed. Home treatment is not used to remove the cyst, but to eliminate the inflammatory process and destroy harmful bacteria.
The main goal of therapy at home is to provide an antiseptic effect. Propolis tincture, calendula tincture, eucalyptus tincture have an antiseptic effect. Tinctures are used as follows: a small amount of medicine is applied to a cotton swab and applied to the affected area, held for 5-10 minutes.
Medicines with an antiseptic effect can be used before surgery to remove a cyst and after tooth root removal. The antiseptic effect allows these medications to be used in the treatment of caries and other infectious diseases of the oral cavity.
Prevention
It is always easier and faster to prevent any disease than to cure it, so one should not forget about simple preventive rules that will help avoid the development of a dental cyst. The basic rules for preventing dental cysts are based on compliance with the rules of oral care.
How to prevent the formation of pathology:
- do not trigger the course of dental diseases such as caries, periodontitis, pulpitis; if infections occur, consult a doctor immediately;
- Brush your teeth daily and prevent the appearance of plaque, which can later transform into tartar;
- monitor the condition of the teeth and oral cavity after operations and mechanical injuries;
- visit your dentist regularly;
- monitor the condition of filled teeth and dental implants;
Patients who have had their teeth filled or have dental crowns or implants placed are advised to periodically have dental x-rays taken. This will allow timely detection of pathological changes and increase the chances of successful recovery without serious consequences.
Note! All diseases must be treated in a timely manner; inflammatory processes reduce immunity, as a result of which infections move freely from one organ to another; in addition, secondary infections can be added to already developed pathologies. It is important to monitor your health and strengthen local and general immunity.
To strengthen your immune system, strengthen your body, include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet, play sports and walk outdoors more often. It is more difficult for any infection to get into a hardened body than into a weakened body.
What are the dangers of taking medications on your own?
The need for antibiotic therapy is determined by the nature of the disease and the body’s response to it. Selectivity in its appointment is explained by two reasons.
- Antibiotics affect all types of microflora, both harmful and beneficial, which in some cases can lead to problems with the mucous membranes of other organs and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- When exposed to them, bacteria begin to mutate, forming resistance to drugs of a certain type. For this reason, first-generation drugs, such as penicillin, have already ceased to act on pathogens. Scientists have proposed new developments, but if used thoughtlessly, without following the rules of therapy, history may repeat itself.
In addition, each of the drugs has its own side effects - from nausea and itching to anaphylactic shock. Their manifestations may require immediate medical attention.
Therefore, dentists prescribe a course of antibiotics only in cases where the likelihood of complications of the disease exceeds the risks of taking the drug. At the same time, they consciously approach the choice of medication and its dosage, as well as the duration of the course. Let's look at what can lead to self-prescription of an antibiotic for tooth root inflammation.
What causes gingivitis?
The disease occurs due to local and general factors:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Taking specific medications (for example, bismuth preparations)
- Chemical or thermal effects
- Hypovitaminosis
- Bad habits
- Infectious processes in the body
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Caries and its complications
- Decreased immunity
- Errors in dental treatment
- Malocclusions
- Radiation damage
The main cause of gingivitis in adults and children is the accumulation of dental plaque with its hardening into tartar. Leftover food, being an excellent breeding ground for bacteria, breaks down and causes an unpleasant odor. Microbial plaque contributes to gum injury, the impact of decay products of pathogenic microflora on the gums and impaired microcirculation.
Why do you need treatment with the Vector device?
Effective treatment of periodontal diseases is carried out only by a complex of therapeutic measures. Cure is impossible without eliminating the cause of the problem, that is, without removing tartar and plaque from the entire surface of the dental elements. One of the most effective methods of cleansing is treating teeth with the Vector device. The principle of the method is to target plaque and stones with ultrasound and a liquid containing tiny abrasive particles (about 10 micrometers in size). The doctor carefully inserts the device’s nozzle into the gum pocket and millimeter by millimeter treats the surface of the roots.
Hardware treatment of gums with the Vector device is a non-contact removal of soft and hard supragingival and subgingival deposits using a special device produced by the German company Dürr Dental. Its action is based on the effect of ultrasound on pathogenic deposits, which are then washed away with a directed flow of a suspension containing an abrasive (hydroxylapatite and calcium phosphate). As a result, tartar is removed and the surface of the roots is polished at the same time. The innovative features of the Vector device are the vertical direction of the movements of the working nozzle, which ensures the accuracy of the impact, as well as the ability to regulate the amplitude of the radiation. "Vector" is used for the prevention and treatment of gingivitis and periodontitis.
Specialist recommendation: to avoid relapse of the disease, hardware therapy should be repeated regularly. The frequency of visits to the clinic will be recommended by your attending physician, depending on the conditions of your clinical case.
Symptoms of gingivitis in adults
To properly treat the pathology, you need to know that the symptoms of gingivitis and treatment are closely interrelated. What helps with the catarrhal form may not be sufficient with the necrotic form. What to do if you are in doubt about what kind of gingivitis you have? Photos from the collections will help in a rough assessment, and then you should go straight to the periodontist’s office.
Common signs of gingivitis:
- Bright red tint of gums (due to dilated capillaries)
- Swelling of the papillae (due to exudation processes)
- Unpleasant odor (halitosis)
- Bleeding (increased vascular permeability)
- Pain when eating (nerve endings are compressed due to swelling)
- Dense plaque and tartar
Important! Chronic gingivitis often occurs together with general pathology. Usually this is an ulcerative lesion of the gastrointestinal tract or HIV infection.