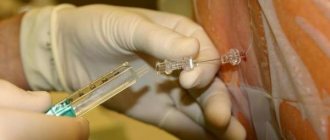
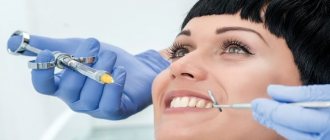
Anesthesia without adrenaline has been used in dentistry for quite a long time; it allows painless treatment even for those patients who have contraindications to common means of local anesthesia. Typically, drugs that do not contain adrenaline are used in cases where it is necessary to treat teeth in patients with high blood pressure, heart disease, and pregnant or breastfeeding women.
What is Articaine and what is its composition?
Articaine is an amide anesthetic intended for local, infiltrative or conductive anesthesia for both simple and complex dental procedures. A local anesthetic blocks the generation and conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold of electrical excitation in the nerve, slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and decreasing the rate of rise of the action potential.
The uniqueness of Articaine as a member of the amide family is that it contains an ester group and a thiophene instead of a benzene ring. The thiophene ring increases the lipid solubility of articaine, facilitating more efficient diffusion of the anesthetic across the lipid membrane of nerve cells into surrounding tissues. Articaine is widely used in dentistry due to its safety during short procedures that require rapid onset of anesthesia.
The onset of action of the drug Articaine is:
- from 1.5 to 1.8 min. with infiltration of the upper jaw;
- from 1.5 to 3.6 min. with block anesthesia of the lower jaw.
Articaine pulp anesthesia lasts from 30 to 120 minutes. Anesthesia of soft tissues with the drug lasts ~ 2.25 hours for infiltration of the upper jaw, 4 hours for blockade of the lower jaw.
The drug is produced in the form of an injection solution - a transparent, colorless or yellowish liquid. For retail sale to pharmacy chains, Articaine is supplied in ampoules made of colorless chemically pure glass, enclosed in blister packs and/or cardboard packs.
Composition of articaine in dentistry:
- active agent - articaine hydrochloride;
- Excipients: sodium chloride (to make the solution isotonic) and distilled water.
1 ml of solution contains 40 mg of active agent.
In odonto-dental anesthesia, articaine is used alone or in combination with epinephrine (adrenaline). Epinephrine, diluted to 1:100,000 or 1:200,000 and added to the solution, slows down the passage of articaine into the general bloodstream and thus ensures long-term maintenance of the concentration of the active substance in the tissues, allowing a small hemorrhagic surgical field to be obtained.
It is possible to replace Articaine with synonyms with the same active substance, such as:
- Artikain-Binergy;
- Ultracaine;
- Artikain-DF;
- Articaine with Epinephrine.
The decision to use analogues is made by the attending physician, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
What to do if you are afraid of anesthesia -
Indeed, an anesthetic injection can be painful. The pain will depend both on the patient’s pain sensitivity threshold and on the doctor’s anesthesia technique. According to the rules, a solution of one anesthetic carpule (1.7 ml) is excreted into the tissue within 40-45 seconds. If the doctor saves time, then it is logical that rapid administration of the solution will cause pain.
To reduce the discomfort from an anesthetic injection, you can ask the doctor to first use a gel or spray with lidocaine to conduct topical anesthesia at the site of the future injection. You can also ask your doctor to administer the anesthetic slowly.
Drugs to relieve fear and anxiety – There are also drugs that can reduce fear and anxiety before an upcoming trip to the dentist. At the same time, there are drugs with a sedative effect such as (Persen forte), and there are drugs only for relieving anxiety, for example, Afobazol. The latter does not have a sedative effect, and it makes sense to start taking it only 10 days before going to the dentist, because... the drug has a cumulative effect (24stoma.ru).
In a number of large clinics, as a premedication, you can also be given an intramuscular injection of diphenhydramine 30 minutes before the start of treatment. You can also use tinctures of valerian, motherwort, Corvalol, valocardine. However, it is also advisable to take these drugs in a course (at least a few days before visiting the doctor), because they also have a cumulative effect. But you need to take into account that these drugs also have a hypnotic effect, which is not very good for motorists and working people.
Manufacturers Articaine
On the Russian pharmaceutical market, the anesthetic Articaine and its analogues are represented by domestic and foreign manufacturers. You can buy articaine in St. Petersburg and Moscow using the link.
The products of the following enterprises are most in demand:
- JSC "Biokhimik" (Russia);
- CJSC "Binergy" (Russia);
- LABORATORY INIBSA, SA (Spain);
- Welfarm LLC (Russia);
- Armavir biofactory FKP (Russia);
- Borisov Medical Preparations Plant (Republic of Belarus);
- Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH (Germany).
Preparations based on articaine, created at different enterprises, may have certain differences due to production technology, quantitative and qualitative composition of excipients, but at the same time retain the main direction of action of the active substance.
How to improve the quality of pain relief?
A patient who is indicated for anesthesia without adrenaline in dentistry can make sure that the effect of the painkiller lasts longer and is of better quality. To do this, he only needs to follow a few general recommendations:
- Before visiting a doctor, if there is strong anxiety and fear of treatment, it is better to take a sedative, preferably based on herbs (for example, about 30 drops of valerian root tincture).
- The day before visiting the dentist, you should not drink alcohol, since alcohol in the blood weakens the effect of the anesthetic.
- If you are taking any medications or have any allergic reactions, you should inform your dentist at the treatment planning stage.
- It is better not to visit a doctor if you feel unwell or during menstruation.
Articaine: side effects
Such qualities of Artican as low fat solubility, high% binding to blood proteins, low half-life ensure low toxicity of the drug. However, depending on the general condition, age, individual reactions of the patient and his existing systemic diseases, side effects may be observed during anesthesia with the drug, such as:
- disturbance or confusion;
- vertigo;
- headache;
- nausea;
- dyspnea;
- decreased blood pressure;
- diplopia;
- muscle tremors;
- allergic and local reactions, manifested in symptoms of urticaria, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, skin hyperemia, swelling and inflammation at the injection site.
Articaine should be used with caution during dental procedures in patients with impaired cardiovascular function, vascular diseases, liver and kidney failure.
Articaine (ultracaine) is a local anesthetic of the amide type of a series of thiophenes. Allergy to this drug is rare and can manifest itself in the form of skin rash, itching around the injection site, rhinitis, and in severe cases, angioedema and anaphylactic shock. Determination of specific immunoglobulin E for a given allergen in increased quantities indicates the presence of sensitization of the body to it.
A drug allergy is a specific reaction of the immune system to drugs.
Drug allergies can occur as a complication during the treatment of the underlying disease or as a result of prolonged contact with medications (by doctors, healthcare workers, pharmacists). The main reasons for the development of allergies to drugs are hereditary factors, the presence of other types of allergies, long-term use of drugs, simultaneous use of a large number of different drugs, overdose (in this case we are talking about a pseudo-allergic reaction). An allergic reaction can be provoked by any medications, but the most common allergens are antibiotics, local anesthetics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. This type of allergy is characterized by the following symptoms: redness of the skin, itching, various types of skin rashes, year-round conjunctivitis. Allergic reactions to medications develop from a few seconds to several hours and can cause an attack of bronchial asthma, urticaria, Quincke's edema, allergic rhinitis or anaphylactic shock. If you have an allergy to a certain medicine, it should be taken into account that it can also occur when using medicines with a similar composition.
The study is carried out only for type 1 allergic reactions. A negative test result cannot guarantee that you will not have another type of allergic reaction.
Synonyms Russian
Specific immunoglobulins of class E to articaine (ultracaine).
English synonyms
Allergen c68 – Articaine/Ultracaine; IgE.
Research method
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Units
IU/ml (international unit per milliliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
Articaine is the international name for an amide-type local anesthetic, widely distributed under the following trade names: Ultracaine, Ultracaine D-S, Ultracaine D-S forte, Alfacain, Ubistezin, Primacaine.
The drug is used for infiltration and conduction anesthesia, most often in dental practice. The anesthetic enters the nerve fiber cells, where it blocks the entry of sodium ions, thereby temporarily stopping the conduction of the nerve impulse. Articaine is a local anesthetic with a fairly strong anesthetic effect; the effect occurs almost immediately after administration and lasts up to several hours.
One of the side effects of using articaine is the development of an allergic reaction in sensitized individuals, which occurs quite rarely, but can lead to serious consequences. The reaction develops as an immediate type of hypersensitivity - within a few minutes or hours. As a rule, a mild form of allergy occurs with the appearance of hyperemia or urticaria, itching at the injection site, and allergic dermatitis. In more severe cases, allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis, and bronchial asthma develop. The most severe manifestations are angioedema (Quincke's edema) and anaphylactic shock, involving the vital cardiovascular and respiratory systems in the process, which requires urgent medical intervention.
What is the research used for?
- Diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to articaine/ultracaine;
- differential diagnosis of the causes of allergic reactions in children and adults during the use of local anesthetics.
When is the study scheduled?
- When planning local anesthesia with articaine/ultracaine in patients with suspected allergies to local anesthetics;
- when examining children and adults with urticaria, itching, allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis, bronchial asthma, angioedema, anaphylactic shock after the use of local anesthetics.
What do the results mean?
Reference values: 0.00 - 0.35 IU/ml.
Reasons for the positive result:
- immediate hypersensitivity to articaine/ultracaine.
Reasons for negative results:
- lack of IgE sensitization to this allergen;
- long-term restriction or exclusion of contact with the allergen.
- successful implementation of ASIT.
Articaine during pregnancy in dentistry
Articaine is usually well tolerated at all stages of pregnancy. There is no data on the long-term effects of the drug on the neurophysiology of the newborn. Also, no teratogenic damage was observed after use of the drug in the first trimester.
There are no data from clinical studies of the penetration of Articaine into breast milk. To minimize possible risk to the baby, breastfeeding mothers may choose to express milk for approximately 4 hours after the injection. After which breastfeeding can be resumed.
Instructions for use
To exclude or minimize intravascular administration of Articaine, an aspiration test is required before using the drug. An accurate and slow technique for injecting the drug is required with control of the pressure on the syringe plunger depending on the sensitization of the tissue.
The instructions for use in dentistry recommend using Articaine in a dosage corresponding to the nature of the manipulation:
- 1.7 ml of solution per tooth for uncomplicated extraction of the upper jaw tooth;
- 0.1 ml for anesthetizing incisions when creating a palatal depot and suturing;
- 0.5-1.7 ml per tooth for grinding teeth for crowns and in case of cavity preparation.
After each injection of Articaine, careful and constant monitoring of vital signs of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems (adequacy of ventilation) and the patient’s state of consciousness should be carried out.
using Articaine in dentistry for infiltration anesthesia during extirpation of mandibular premolars.
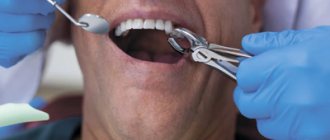
Possible complications after tooth extraction
After simple extraction of any tooth, complications occur quite rarely, provided that the doctor’s recommendations are followed.
The main thing is that the patient needs to remember that if the blood clot remains in the socket until healing, then infection and suppuration of the wound will not occur, and within two weeks a healthy gum mucosa will appear at the site of the clot. In case of loss of a blood clot, the unprotected wound surface of the socket is exposed to pathogenic microflora of the oral cavity; the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria provokes the development of an inflammatory process - alveolitis.
Infection of the alveolar socket is the most common complication after tooth extraction. In this case, the infection penetrates and affects the soft tissues surrounding the tooth. If an infectious infection of the hole is accompanied by the presence of throbbing pain and suppuration, this signals the development of an abscess. When alveolitis is advanced, there is a danger of the inflammatory process spreading to the jaw bone - the development of osteomyelitis.
Complex (traumatic) tooth extraction has more prerequisites for the development of inflammatory complications. If after removal there remains a piece of tooth infected with caries, curettage of the hole and extraction of the tooth fragment will be required.
Also, after a complex removal, there is a possibility of delayed bleeding, several hours after the operation. The causes of such bleeding can be high blood pressure, severe stress, the body's reaction to certain medications, excessive rinsing and irritation of the wound with hot food.
In rare cases, the nerve trunks of the lower jaw may be damaged during surgery. Simple or complex tooth extraction is an unpleasant operation, but there is no point in postponing a visit to the doctor if the tooth causes discomfort and pain, most likely its removal is only a matter of time. Modern ultrasonic removal of teeth on the upper or lower jaw will save you from unwanted consequences and many troubles associated with the onset of complications after surgery.
Incorrect position of the wisdom tooth in the row
When a wisdom tooth takes an incorrect position during growth or is partially erupted, pericoronitis (inflammation of the tissues around the tooth) often develops, this is due to the fact that part of the tooth remains in the gum, and the formed periodontal pocket covering the tooth is difficult to clean from food debris , which accumulate and create an environment favorable for the development of pathogenic microflora.
A common disease of wisdom teeth is caries, since food particles remain in the interdental space with the adjacent tooth due to difficult access for cleaning, and plaque forms on the teeth. In this case, carious destruction spreads to the adjacent second molar.
Doctors recommend removing wisdom teeth if they have partially erupted or are incorrectly positioned in the dentition as early as possible, before complications occur and before their roots are fully formed.
Removal of impacted wisdom tooth
Defects in the development of third molars are caused by injury and destruction of the wisdom tooth itself and, if it puts pressure on the adjacent tooth, it damages the roots and surrounding tissues. This situation is observed due to improper growth, damage by caries, often inaccessible to treatment, surfaces of the wisdom tooth with the formation of a focus of infectious inflammation. These complications diagnosed by a doctor are absolute indications for tooth extraction.
This includes the removal of an impacted (unerupted) figure eight, when the tooth failed to erupt and remained embedded in the gum or bone.
Immersion may be tissue if the tooth has passed through the bone but is unable to penetrate the gum tissue, or bone if the tooth remains completely in the jawbone.
Follicular cyst of wisdom tooth
The formation of a follicular cyst can be asymptomatic, but the appearance of pain and high temperature already signals its active development and the presence of an inflammatory process. An increase in the size of a follicular cyst is dangerous due to the thinning of the jawbone tissue due to its replacement with a new growth.
Also, impacted and semi-impacted (partially erupted) figure eights are indicated for removal, since remaining covered by a large layer of dense mucous membrane, they put pressure on the surrounding soft tissues.
Prolonged injury to the mucous membrane from the inside contributes to the formation of pathogenic microflora. The appearance of redness, pain, and swelling indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process, pericoronitis.
Simple tooth extraction
Simple tooth extraction, including wisdom teeth, is in most cases permissible in the upper jaw, which has a looser and softer structure and allows the tooth to be successfully grasped with forceps. If the tooth has fused roots and can be rocked, then its removal will not be difficult.
Simple removal of a wisdom tooth in the upper jaw can be done with little resistance.
Complex tooth extraction
The anatomy of the lower jaw itself prevents not only the eruption of third molars without complications, but also complicates the process of wisdom tooth extraction.
Difficult tooth extraction from below is due to the fact that the mandibular bone has a denser and stronger structure, and the roots of such teeth in the lower jaw are often curved and may have several processes, which complicates their smooth removal.
Bent or damaged roots of the eighth tooth below or above and its incorrect location, including complete or partial immersion in bone tissue, create a serious obstacle to its extraction. This situation is non-standard and requires labor-intensive efforts to remove wisdom teeth in difficult conditions. To provide quick access to the area where the tooth is located, the surgeon cuts the gum and periosteum.
During such an operation, it is possible to drill out a certain amount of bone covering the tooth or extract the problematic tooth in parts.
Ultrasound removal of wisdom teeth
At the Apex-D Dental Implantation Clinic, wisdom teeth are removed using an ultrasonic instrument.
Ultrasound surgery allows the removal of wisdom teeth, especially in complex cases, in the most atraumatic way.
The use of ultrasound in dental surgery makes it possible to perform surgery in extremely hard-to-reach places, minimize trauma to the soft and bone tissues surrounding the tooth, reduce the likelihood of complications after surgery and speed up the healing of the wound surface of the socket after tooth extraction.
Questions and answers on this topic: Tooth extraction, wisdom teeth removal
You can make an appointment at Apex-D Dentistry by calling the administrator at +7 and +7, or filling out an electronic form (the administrator will contact you at the specified phone number and agree on the date and time of the appointment).
Articaine in pediatric dentistry
The pharmacodynamics of local anesthetics in children is comparable to that in adults. In pediatric dental practice, extreme caution must be exercised when using amide local anesthetics as lower intrinsic clearance or decreased serum protein binding may easily lead to an increased risk of toxic reactions. The route of administration is one of the main safety factors when using local anesthetics in neonates and children.
Anesthesia in dentistry with the drug Articaine , carried out using intraosseous injection, is effective in achieving deep anesthesia of teeth affected by MIG with hypersensitivity associated with chronic inflammation of the pulp in children.
In pediatric dentistry, it is recommended to use Articaine 2% due to the lower Cmax and shorter half-life of the drug.
Why is adrenaline needed in anesthesia?
Adrenaline is a vasoconstrictor - a substance that narrows blood vessels. Therefore, on the one hand, its presence in the drug provides a longer-lasting analgesic effect, and on the other hand, it reduces the risk of bleeding during dental procedures (for example, during tooth extraction).
Given this, dentists always warn patients that anesthesia without epinephrine in dentistry has a shorter lasting effect and is not suitable for long procedures. In cases where the patient is indicated for pain relief using non-adrenaline anesthetics, treatment must be carried out very quickly or divided into stages so that the doctor has the opportunity to provide anesthesia before each subsequent stage of manipulation.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Reviews from dentists about the drug Articaine
Most practicing dentists consider Articaine to be the best representative of local anesthetics due to its high effectiveness. At the same time, when using the medication, there is a low incidence of allergic reactions, the possibility of safe use in pregnant women, and the absence of addiction. The only small drawback of Articaine, according to experts, is the inability to prescribe it to children under 4 years of age. In all other cases, Articaine is rightly called one of the drugs of choice.
This information is intended for medical professionals and specialists.
Cost of anesthetics and anesthesia
The cost of one carpule of anesthetic is approximately 10-20 UAH. Carrying out one anesthesia in a dental clinic will cost an average of 130 UAH.
What to do if you are afraid of anesthesia
Many people are afraid of injections, because each person has their own pain sensitivity threshold. During anesthesia, the pain from the injection may depend on the professionalism of the doctor, the anesthesia technique, and also on the speed of administration of the anesthetic. An experienced doctor does not save time and administers painkillers for at least 40 seconds. Immediately before the injection, you can ask the doctor to treat the area of the upcoming injection with an anesthetic spray (for example, Lidocaine spray).