Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity has its own microflora and its own specific diseases arise. Let's talk about one of them - fibrous epulis of the gums: what kind of disease it is, what are the causes of its occurrence, how is the treatment carried out.
What it is
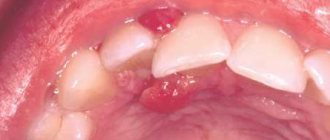
Epulis is a tumor-like neoplasm that develops on the alveolar process of the jaw. It also has other names - epulid, supragingival, giant cell granuloma. More often it is localized in the area of incisors, canines and small molars of the upper jaw, less often the tumor is detected in the lower jaw. The growth has a round or irregular shape and a wide stalk; the size of the formation varies from 3 mm to 5 cm.
Despite the fact that such a tumor looks frightening, it practically does not cause concern to the patient, unlike, for example, a burn, with the exception of a violation of aesthetics and the sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity. Large tumors may cause difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
If epulis is accompanied by bleeding, infection may occur, which will lead to complications.
The disease mainly affects adults, but the neoplasm can also appear in children; in the latter, it occurs during teething. Studies have shown that women are more susceptible to developing epulis than men.
Dentists' recommendations
Epulis is a gum tumor that poses a great danger to the health of teeth and the entire body. Treatment of the pathology is complex and lengthy, but even with high-quality treatment, the risk of relapse cannot be ruled out.
It is not always possible to prevent the occurrence of epulis on the gums of a child or an adult, but with timely consultation with a specialist, complications, complex treatment, long recovery and aesthetic defects that remain after surgery can be avoided.
The best prevention is to visit the dentist every 6 months. If you are concerned about discomfort and a feeling of rubbing of the mucous membranes or gums, you should immediately consult a dentist, without waiting for a tumor or other pathologies to occur.
Varieties of epulis
Conventionally, there are 3 types of epulis:
- Fibrous. The neoplasm is dense, the basis is coarse fibrous tissue. Characterized by slow growth. There is no pain or bleeding.
- Angiomatous. The tumor contains a large number of blood vessels and is localized mainly in the lateral parts of the jaw. With this form of the disease, bleeding is observed even with slight pressure, for example, with a toothbrush or food. When pressed, the tumor is painless and has a soft consistency.
- Giant cell. The tumor can reach large sizes, displacing teeth that are located in the epulis growth zone. The mucous membrane of the epulis is bluish-red in color. On palpation, the neoplasm is painless, but may bleed moderately if injured.
Depending on the nature of the process, epulis can be benign or malignant. In the first case, the neoplasm is characterized by slow development and, as mentioned above, in most cases does not cause pain. The tumor size in this case rarely exceeds 10–20 mm. When the process becomes malignant, rapid tissue growth is observed. In this case, the process is often accompanied by pain, bleeding gums and affects the root canals of neighboring teeth.
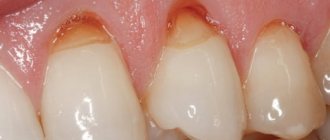
Bleeding gums when brushing teeth
Sometimes blood spots on the brush are perceived as a sign of inflammation, but this is not always the case. Often, the reason is trivial - incorrectly selected bristles or too zealous hygiene. To reduce the risk of injury, dentists remind you of the rules for brushing your teeth:
- Movements of the bristles along the vestibular side should not be from side to side, but up and down, as if sweeping away remnants of food and plaque.
- Medium hardness is optimal, but if you have pathological sensitivity, it is better to buy soft ones (Soft) and even ultra-soft ones (Ultra Soft).
- If the brush is positioned slightly at an angle to the teeth, the chance of better cleaning of gaps increases.
- It is advisable to move along the gum line in a circular motion - additional massage stimulates blood circulation.
- You should spend 40 seconds to a minute cleaning your tongue. Much more bacteria accumulates on its surface than on enamel, but many people ignore this fact.
- If you have an irrigator at home, it is recommended to put periodontal attachments on it at least once a week and clean out the gum pockets. Make sure that the water supply is turned on at minimum power at this moment, otherwise there is a risk of tissue rupture.
- For those who wear braces and other devices, it is better not to skimp on special brushes. A large amount of plaque accumulates under the ligatures and the corrective arch, which must be removed daily.
- It is necessary to change the brush every 2 months, and if you are prone to inflammation - monthly.
Diagnosis and treatment of epulis
Diagnosis of epulis comes down to collecting complaints, clinical examination, radiography and histological examination of the material.
The primary task in making such a diagnosis is to eliminate the provoking factor: professional cleaning of dental plaque, treatment of caries and its complications, replacement or correction of orthopedic structures according to indications. In fibromatous and angiomatous forms, dynamic observation is indicated, since after sanitation of the oral cavity and elimination of the causes of the disease, the tumor may decrease in size until it disappears completely.
Treatment of epulis is carried out surgically. The growth on the gum under local anesthesia or general anesthesia is excised with a scalpel or laser within the healthy tissue along with the periosteum. The second method is preferable, since the laser simultaneously coagulates the vessels and stops bleeding. With giant cell epulis, the area of bone tissue involved in the process is also removed. To do this, use a bur or cutter. The wound is closed with gauze with an iodoform mixture or a formed mucoperiosteal flap. If necessary, the material is sent for histological examination.
Intact teeth in the area of tumor localization must be removed with a high degree of mobility and severe exposure of the roots. If the bone lesion is extensive or epulis recurs, partial resection of the alveolar part along with the teeth is performed.
To speed up the healing of a fresh wound, the doctor prescribes compresses with medicinal ointments and rinses to the patient.
Symptoms of the problem
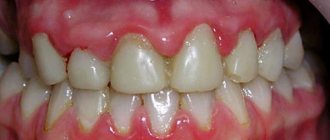
You should consider the main diseases that cause redness of the gums and their distinctive signs:
Causes of gum inflammation
- Gingivitis. The disease is associated with damage to the tissue near the tooth by harmful agents. The main cause of the problem is improper oral care. Untreated gingivitis is complicated by periodontitis or periodontal disease, and tooth loss. The main signs are pain when eating and brushing teeth, bad breath, and fever.
- Periodontitis. In pathology, the soft tissues around the tooth are affected. The disease is acute with pronounced symptoms, as well as changes in pain intensity. The pathological process develops within 7-14 days. If not treated in a timely manner, periodontitis can lead to heart attack, stroke, loss of dentition, and intoxication of the body.
- Periodontal disease. During the disease, the tissues surrounding the teeth also become inflamed. A distinctive feature of the pathology is sluggish development. The problem occurs with hidden symptoms for several years, but ultimately leads to the loss of units. The main signs of periodontal disease: unsteadiness of elements, red growths on the gums, divergence of teeth in different directions. Untimely treatment of periodontal disease can lead to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract due to inadequate chewing of food.
Preventive actions
Monitoring the condition of the teeth and oral cavity will reduce the likelihood of tumors.
- Timely sanitation of the oral cavity. Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination and professional hygiene twice a year will prevent the growth of caries, the appearance of defects in fillings and the formation of tartar, leading to gum injury and the appearance of epulis.
- Prevention of gum injury. If systematic injury to soft tissue occurs as a result of poorly fitted orthopedic or orthodontic structures, consult your doctor about this problem. He will adjust the crowns or dentures.
If these preventive measures are followed, the prognosis is favorable and epulis does not recur.
We hope that our article about epulis will be for informational purposes only. And if you want to soothe your gums, make them strong and strong, try the unique two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE.
This is the only rinse with a combination of chlorhexidine + benzydamine for the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases. The product has a combined effect: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic. Instant anesthetic effect allows you to quickly reduce pain.
Emergency help for inflammation
What to do if your gums hurt? First aid to relieve symptoms is provided at home. It is recommended to regularly (once every 2 hours) rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions - furatsilin, baking soda, chlorhexidine.
To treat redness of the gums, ointments with an antiseptic and hemostatic effect are used.
The basic rule of emergency care is the exclusion of radical methods of treatment: such therapy leads to serious consequences. To stop the proliferation of pathogenic flora, herbal tinctures sold in pharmacies without a prescription are suitable - Givalex, Stomatodin, Mevalex. The products are used according to the instructions for use.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Principles of treating gum disease
The treatment regimen is developed by the doctor depending on the type of pathology that is accompanied by redness of the gums. Each dental disease requires an individual approach.
Gingivitis
The problem is characterized by inflammation of the periodontal papillae and the appearance of small pimples in this area. Treatment of the problem begins with the removal of hard and soft deposits from the surface of the enamel. After this, local anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs are prescribed. The prognosis for recovery from gingivitis is usually favorable.
Periodontitis
The disease is considered a more serious form of gum tissue damage. If left untreated, the periodontal papillae atrophy, and balls filled with pus form in the periodontal pockets. Treatment of the disease is carried out in stages: taking or injecting antibiotics into the gums; splinting of moving elements of a row; surgical formation of atrophied areas of the gums.
Inflammation of the gums requires immediate treatment, since if the pathological process is complicated, periodontal disease or complete loss of the dentition may develop. There are many ways to combat the problem at home. Therapy includes the use of pharmacological drugs and traditional medicine. Mild forms of inflammation can easily be eliminated in a few weeks if all the rules outlined by the dentist are followed.
Causes of gum swelling
Physiological
Normal gums are pink, painless and of normal size. But sometimes they swell for natural reasons:
- during teething - in children and adults (wisdom teeth);
- after tooth extraction—slight swelling and redness of the gums is observed for up to 3 days;
- after injury - damage to the soft tissues of the gums leads to their swelling for some time while integrity is restored;
- during pregnancy - under the influence of hormones and due to the redistribution of blood in the body, gums may swell in women carrying a child;
- injury from dental structures - veneers, braces and fillings, if installed incorrectly, come into contact with gum tissue, causing damage to them.
There is no need to panic if the gums of a child aged 1 to 7 years are swollen. At this time, baby or permanent teeth erupt, which may cause swelling and redness in this area. Sometimes small balls appear - cysts. They are safe and in most cases go away on their own over time. If the cyst interferes with tooth eruption, it is surgically removed in dentistry in 1 session. The procedure is performed under anesthesia and does not cause any discomfort.
Pathological
In most cases, gum swelling occurs due to inflammation. Pathological reasons:
- periodontitis - local inflammation above or below the tooth;
- periodontitis - inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- gingivitis - inflammation of the gums;
- periodontal abscess - suppuration localized at the edge of the tooth;
- stomatitis - ulcers that appear on the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- secondary infection against the background of immunodeficiency - with HIV or hepatitis, even opportunistic microorganisms can cause oral diseases;
- atypical sore throat - spreads to the gums, the main symptom is that it is painful for a person to swallow;
- Vitamin deficiency C - a lack of vitamin affects the gum tissues, causing them to swell.
Swelling of the gums due to an allergic reaction is also considered pathological. It can develop from an injection of an analgesic during dental treatment or from any irritant to which a person is sensitive.
Swelling of the gums with acute pain
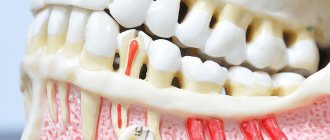
When the gums are not only swollen, but also very painful, this may be a symptom of a serious pathology of the oral cavity. Most often, such complaints are accompanied by periodontitis. This is an inflammation of the soft tissues that support the tooth. Other symptoms of periodontitis include:
- increased body temperature;
- suppuration in the area of swelling;
- lack of temperature sensitivity of the tooth, as well as a reaction to sweets.
If swelling in the gums is accompanied by fever, it may be periodontitis. This is due to the fact that the factors in the development of pathology are most often related to infection.
Causes of periodontitis:
- transition of the inflammatory process from the throat or sinuses to the gums;
- penetration of microbes through the dental canal into the periodontium;
- advanced caries;
- poor-quality dental treatment, due to which irritating substances entered the periodontium;
- trauma to the periodontium or the tooth located next to it.
In rare cases, periodontitis develops as a consequence of an immunological reaction, that is, an allergy.