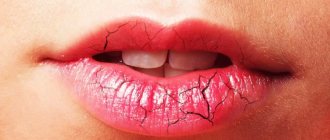
Many people are familiar with the expression “ cold lips . It is usually used when a bubble with transparent contents forms in the lip area, which subsequently bursts and the affected area becomes covered with a crust. Cold sores are an infectious disease caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 or 2. The source of infection can be infected people, both with and without pronounced signs of herpes. Cold sores on the lips are not limited to the presence of the virus only in this area. In patients the herpes virus is detected in such body fluids as blood (including menstrual fluid), urine, discharge from the nose and tear ducts, vaginal secretions, amniotic fluid and sperm. How the virus is transmitted and how to treat herpes is discussed in this article.
How does herpes infection occur?
As mentioned above, colds on the lips are caused by two types of viruses - herpes virus type 1 and herpes virus type 2 . Infection with herpes virus type 1 mainly occurs in childhood and adolescence. The main routes of transmission of infection are contact (for example, through personal objects) and airborne droplets (by inhaling the virus, kissing). However, infection can also occur through oral-genital contact. Infection with herpes virus type 2 occurs through direct sexual contact and is therefore more common among young people and adults. Transmission of pathogens of both types 1 and 2 can occur from mother to fetus (transplacentally), and also in isolated cases through infected blood products (parenterally). It is worth noting that the risk of infection increases significantly if an infected person has herpetic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes.
Prevention
For those infected with herpesvirus type 1, it is generally almost impossible to completely avoid the appearance of cold sores on the lips. You can only reduce the risks of its occurrence due to reactivation of the virus. To do this, first of all, you should use the usual methods of maintaining immunity (a healthy lifestyle, a nutritious and varied diet, a minimum of stress, etc.). However, herpes on the lips can also occur unexpectedly, for no apparent reason.
Particular attention should be paid to prevention for infants and young children, since primary infection can have serious consequences due to imperfect immune defense. It is believed that it is most important to avoid too early infection with herpes viruses (which is almost inevitable later), for example, transmission of the virus from a nursing mother. If signs of a herpetic lesion appear in the mother or surrounding people, precautions should be taken: no close contact with a small child, stricter personal hygiene.
Request a consultation
Forms of herpetic infection
There are several forms of herpes infection. The bullous form of herpes is characterized by the appearance of blisters that can reach the size of a plum. The abortive form occurs without the formation of a blistering rash, and at the site of the lesion there is swelling and small cone-shaped elevations above the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. The most severe forms of herpes are ulcerative, ulcerative-necrotic and gangrenous. They are characterized by the appearance of vesicles with hemorrhagic contents, the appearance of long-term non-healing deep ulcers that leave scars. The development of the gangrenous form occurs in people weakened by any diseases, as well as in elderly patients with gastric ulcers, diabetes mellitus and other concomitant pathologies.
- Stress or emotional distress;
- Various somatic diseases, in particular colds, flu, diabetes, HIV;
- Poisoning or intoxication;
- Drinking alcohol, caffeine and smoking;
- Excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- Hypothermia or overheating;
- The arrival of menstruation;
- Overwork and exhaustion;
- Inadequate nutrition (diet) or stomach upset;
- Other factors individual to each person.
After activation, the virus travels along nerves from the trigeminal ganglion back to the skin.
It is important to know that the trigeminal plexus gives off branches that innervate the lips, oral mucosa, gums, skin on the earlobe and part of the cheek. Lesions on the skin will be located in accordance with the exiting nerves. As the virus travels through a nerve, it causes inflammation of the nerve tissue, which causes pain along the nerve fiber. In its development, herpes on the lips goes through stage IV:
Stage I of herpes - tingling. This is when most people feel like they are getting sick. Before a cold sore appears on the lips, the skin in the corners of the mouth or the inner surface of the lips, or on the tongue, or even all over the face begins to itch. In the place where a relapse of herpes will soon develop, harbingers of the disease appear: pain, tingling, tingling, itching. The skin over the site of future relapse turns red. The development of herpes can be prevented if acyclovir-based drugs are used at this stage. If you are experiencing severe itching, you can take an aspirin or paracetamol tablet.
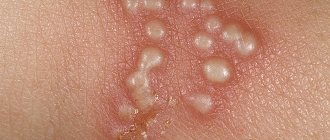
Stage II of herpes - the stage of inflammation, begins with a small painful vesicle, which gradually increases in size. The bubble is tense and filled with a clear liquid, which later becomes cloudy.
Stage III of herpes is the ulceration stage. The bubble bursts and a colorless liquid oozes out, filled with billions of viral particles. An ulcer forms in its place. At this moment, the sick person is very contagious, as he releases a huge amount of viral particles into the environment. Due to the pain and sores on the face, this stage is the most annoying for a person.
Stage IV of herpes - scab formation. A crust forms over the ulcers, and if damaged, it can cause pain and bleeding.
Herpes rashes are most often located on the red border of the lips, but can also be on the nose, on the cheeks, in the ears, on the forehead, in the oral cavity: on the gums, the inner surface of the lips and cheeks.
Strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. “Colds” on the lips are contagious! Always wash your hands with soap and water before and after touching cold sores, including after applying antiviral cream.
Don't touch your eyes! (especially women while applying makeup). Do not use saliva to wet contact lenses. Despite the itching and pain, you should not touch the rash, kiss, especially with children, use someone else's lipstick or borrow your own, or smoke one cigarette with a friend. Do not attempt to remove blisters or scabs to avoid spreading the infection to other parts of the body or causing a bacterial infection.
Avoid oral sex! Oral sex during a “cold” on the lips of an “active” partner can cause genital herpes in a partner passively participating in oral sex. In this case, herpes from the lips of the “active” partner can be transferred to the genitals of the partner receiving caresses.
If you have a cold on your lips, use individual dishes or a towel, and do not drink from someone else’s glasses.
Provocateurs of herpes infection
Colds on the lips rarely have an acute form; a chronic course of the disease is much more common. According to WHO, approximately 70% of people around the world are infected with the herpes simplex virus and about 10-20% of patients experience various symptoms of herpes infection. Exacerbations of chronic herpes occur for a number of reasons. The main factors that lead to relapse are emotional and physical stress, hypothermia, sexual intercourse, menstruation in women, concomitant diseases (ARVI, including influenza), ultraviolet radiation and others.
Symptoms of herpes on the lips
Quite often, the first symptoms of herpes on the lips are almost unnoticeable - mild irritation of the affected areas, their increased sensitivity. Subsequently, visible symptoms appear: inflamed and painful blisters, possible purulent plaque on the mucous membranes of the lips, and in some cases, inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Primary infection with the virus usually occurs with mild or moderate damage. Reactivation of the virus leads to more pronounced symptoms of herpes on the lips, but in some cases there are practically no external symptoms. The intervals between repeated outbreaks can be very varied, and are mainly associated with the frequency of provoking factors. Mild forms of this disease pass quite quickly, but when they become severe, they require specific treatment, since complications are possible.
Why is the herpes virus dangerous?
The herpes simplex virus affects many organs and systems. Herpetic blisters can appear on the mucous membranes of the vagina, cervix, urethra, mouth and skin, and with an extensive process they can appear in the liver and brain. Herpes can cause dysfunction of both the autonomic and central nervous systems. In addition, the herpes virus is associated with cancer, unfavorable pregnancy, childbirth, as well as pathologies in the fetus and newborns. According to the World Health Organization, the mortality rate from severe forms of the herpes simplex virus is 15.8% compared to other viral infections and ranks second after deaths from influenza (35.8%). In our country, the number of patients diagnosed with herpes infection every year exceeds 2.5 million. Patients with chronic herpetic lesions of the skin and genitals make up more than 10% of the total population of Russia.
Is it possible to permanently get rid of the herpes virus in the body?
It is impossible to get rid of the herpes virus forever. It penetrates the body and remains with the patient for the rest of his life. The virus lives in nerve cells and the spinal cord, but may not cause any disorders or complications in life.
One way or another, 90 percent of the entire population of the planet are carriers of the herpes virus. At the moment, there are a large number of drugs that can stop the DNA of the virus.
But at the same time, a remedy that allows you to get rid of herpes forever has not yet been invented.
Treatment of herpes
The herpes virus enters the body through the mucous membranes and settles in the nerve ganglia for life. Therefore, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogen. However, with proper therapy, it is possible to reduce the intensity of the rash, significantly reduce the duration of the prodromal period and reduce the frequency of exacerbations. Treatment of herpes at home includes antiviral therapy using antiherpetic drugs. But since colds on the lips are accompanied by immunodeficiency, the treatment regimen also includes immunomodulatory agents, for example, interferon preparations or its inducers. In the combined treatment of herpes, the drug Viferon can be used, which resists viruses and corrects protective functions. Using the drug in a treatment regimen allows you to quickly relieve the symptoms of herpes and prolong remission. In addition, the good tolerability of the drug makes it possible to use it in children and pregnant women.
Based on materials:
1. Malinovskaya V.V., Delenyan N.V. et al. "Viferon". Guide for doctors. M. 2004. 6. Malinovskaya V.V., Uchaikin “Viferon (suppositories and gel) in the complex therapy of herpes virus infections”, A.A. Haldin, D.V. Baskakova, A.N. Vasiliev. 2. “Algorithm for the treatment of exacerbations and secondary prevention of herpes simplex with Viferon”, A. A. Khaldin, I. V. Polesko. 3. “Algorithm for the treatment of exacerbations and secondary prevention of herpes simplex with Viferon”, Haldin A.A., Polesko I.V.
Loading...
Take other surveys
Diagnosis of the disease
Herpetic blisters look so characteristic that they cannot be confused with the morphological signs of other diseases - neither with an abscess, nor with specific ulcerations, nor with an allergic rash. In the vast majority of cases, the diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical manifestations.
A blood test for antibodies to the herpes simplex virus is an indirect method of identifying the pathogen in the body. It can be used if the body’s reactivity (the intensity of the response to external harmful agents) is low, and the infiltrate does not develop into characteristic blisters, which raises the question among clinicians: is it herpes?
Herpes simplex, which is manifested purely by a rash on the face, should be distinguished from herpes type 6, which is characterized not only by a rash, but also by a sharp increase in temperature.
Prevention methods
What is herpes - it is a viral disease. It is transmitted by using other people's things, kissing, and unprotected contact. Preventive measures are aimed at preventing infection with the virus:
- Wash dishes thoroughly after other people.
- Do not take other people's towels, combs, toothbrushes and other personal hygiene items.
- Women should not use other people's lipsticks, glosses, or balms.
- Avoid touching your face and groin area with unwashed hands.
- Damage to the skin must be treated with disinfectants.
- Take vitamins regularly to strengthen your immune system.
- Avoid unprotected sexual contact with strangers.
When in contact with people who have visible symptoms of herpes, the risk of becoming infected is higher. But even if a person is a hidden carrier of the infection, he can become infected. Therefore, you need to follow the rules of personal hygiene.
Advantages of "Polyclinic +1"
- The consultation is conducted by experienced dermatologists and venereologists.
- Receive test results and make a diagnosis within 1 day.
- Official license to provide paid medical services.
- Possibility to take tests and undergo treatment anonymously.
- Convenient location in the center of Moscow, 5 minutes from Novokuznetskaya and Tretyakovskaya metro stations.
- Doctors are available daily from 9:00 to 21:00, including on weekends.
- Free parking is available for visitors (notify the administrator in advance).
conclusions
Only an experienced doctor can select an effective treatment regimen for herpesvirus. When deciding how to treat herpes on your own, you risk not getting the desired result, and sometimes even causing complications. Make an appointment with a doctor at the phone number indicated on the page to get rid of unpleasant symptoms and forget about relapses.
The article was checked for compliance with medical standards by a leading specialist at the Polyclinic+1 clinic, a dermatovenerologist, urologist, and mycologist.
Malashenko Vladimir Alexandrovich
Classification of herpes viruses
Researchers have identified 8 strains of herpesvirus that can infect humans:
- First. Causes inflammation of the lips and mouth (labial herpes). In rare cases, it can cause genital rashes.
- Second. Affects the genitals and groin area. Causes genital or vaginal herpes. Less commonly, it is the causative agent of oral herpes.
- Third. Causes chickenpox and shingles.
- Fourth. Known as Epstein-Barr virus. Causes mononucleosis, lymphomas and carcinomas.
- Fifth. Cytomegalovirus. Causes mononucleosis, hepatitis, herpetic retinitis.
- Sixth and seventh. Roseoloviruses. They cause roseola, exanthema. May be one of the causes of chronic fatigue.
- Eighth. Causes lymphoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, Castleman's disease.
The causative agent of herpes simplex is herpesvirus type I or II. There is a misconception that the disease cannot be cured. In fact, herpes is curable. Although modern medicine cannot completely remove the virus from the body, it is possible to suppress its vital activity so much that it stops causing inconvenience.
Treatment methods
There is no single way to quickly cure the virus: herpes occurs differently in different people. The treatment method depends on the strain, location of the affected area and other factors. At Polyclinic +1, doctors select a suitable herpes treatment regimen for each patient. Comprehensive treatment of infection with drugs prescribed by a doctor gives quick results.
Creams and ointments
The most popular drug is Acyclovir. It is available in the form of a cream or ointment with an active ingredient content of 5%: Acyclovir-Sandoz, Zovirax, Acyclovir-hexal. For treatment, it is better to use creams rather than ointments. Creams are better absorbed into the affected areas. The drugs must be applied to the affected area five times a day for seven days.
Despite its prevalence, acyclovir is considered an obsolete drug. It copes poorly with relapses of the disease, eliminates symptoms, but does not suppress the virus inside the body. In 30% of patients, treatment with acyclovir does not produce results.
A more modern drug is penciclovir. Fenistil Pentsivir is manufactured on its basis. This cream contains propylene glycol + cetomacrogol. They accelerate the penetration of the active substance into the skin. Only 0.2% of strains are resistant to Fenistil Penciclovir. The reproduction of the herpes virus stops on the second day after applying the cream, making the healing process faster. But the drug has a drawback: it is not suitable for children under twelve years of age.
Pills
When a treatment regimen for herpes in adults is drawn up, drugs can be prescribed in tablet form. The use of potent tablets is permitted for the treatment of adolescents over twelve years of age. When treating young children, parents should use the Viferon ointments and suppositories listed above.
The action of acyclovir in tablets is similar to the action of the ointment of the same name. The tableted drug is inexpensive and available in almost every pharmacy. It is approved for use in the treatment of children under twelve years of age.
Valaciclovir is used to synthesize acyclovir. It is contained in the drug Valtrex. When the tablet enters the body, valacyclovir is converted to acyclovir. This technique increases the concentration of the drug in the body. The effect of taking valacyclovir can be compared with intravenous administration of acyclovir. It is suitable for people with normal immunity.
Famciclovir is the most effective medicine for herpes. After administration, famciclovir is almost completely absorbed and quickly turns into active penciclovir, which allows you to get rid of symptoms and suppress the activity of the herpes virus. Famciclovir is contained in the drugs Famvir and Favirox. A single dose of three tablets is allowed to quickly stop inflammation. Famciclovir is suitable for adults with weak immune systems.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes help eliminate the symptoms of the disease, but do not fight the herpes virus as the cause. Here are examples of common recipes:
- Apply lemon balm essential oil to the affected area every two hours.
- Lubricate the area of inflammation with Kalanchoe juice three times a day.
- The affected area can be lubricated with crushed garlic cloves three times a day. If garlic causes a burning sensation, you should choose a different recipe.
- A mixture of bee honey and apple cider vinegar, taken in a ratio of 1 to 1, can be applied to the inflamed area. Treat the skin three times a day.
We do not recommend treatment solely according to traditional recipes. To eliminate symptoms and suppress the activity of the herpes virus, use medications prescribed by an experienced doctor.
Causes of viral and bacterial runny nose
Rhinitis is most often caused by viral and bacterial infections that cause respiratory diseases.
The vast majority of rhinitis, about 90% of the total, are viral in nature. The causative agents of colds are different types of influenza and parainfluenza viruses, adeno- and rhinoviruses.
Viruses are quite active during the cold season - autumn and winter. However, you can “catch” the infection in a situation where there is a carrier nearby, since it is transmitted by airborne droplets. The development of a viral runny nose is facilitated by reduced immunity.
The cause of a bacterial runny nose is the activation of opportunistic microflora, which, when multiplied, causes inflammation of the nasal mucosa. The causative agents of the pathology can be staphylococci and streptococci, pneumococci and other microbes.
In this case, the impetus for the development of bacterial rhinitis is also in most cases a viral infection. The virus penetrates cells and causes a pathological process, against the background of which immunity decreases and the body becomes more vulnerable to pathogenic microbes. In some cases, a bacterial infection is primary, and rhinitis occurs without the participation of viruses.
The development of bacterial rhinitis is promoted by:
- chronic respiratory diseases;
- congenital or acquired anomalies of the structure of the nose;
- severe systemic diseases;
- smoking, working in unfavorable working conditions (dust, chemical fumes).