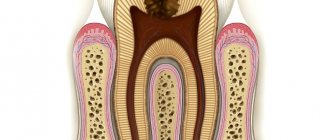
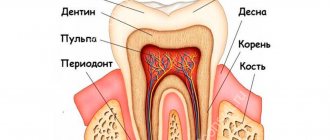
The treatment tactics for caries depend on the cause of the pathological process and its neglect. This is the most common dental disease, characterized by gradual tooth decay. The pathology goes through several successive stages; at first, the patient may not feel anything; in complex cases, complete loss of dental units is possible.
It is not difficult to detect the disease, because most of the symptoms are quite obvious. However, it is better to prevent the occurrence of carious lesions by following preventive recommendations, and then a snow-white smile will delight you for many years.
Caries - what is it?
More than 95% of the inhabitants of our planet face the disease. Thus, it can be called the most common dental problem. At the very beginning, the pathological process affects only the enamel, and in the absence of therapy it penetrates into the deep hard layers. Then the soft tissues with nerve fibers and blood vessels become inflamed.
The disease is insidious because in the earliest stages it does not manifest itself in any way, and the patient begins to sound the alarm only when acute pain and a large hole appear that cannot be eliminated by conservative methods.
How many teeth with caries can be cured at one time?
The decision is made by the attending physician after a thorough examination. Factors such as the complexity and technical features of the procedure, the patient’s health status, and the presence of allergic manifestations are taken into account here. In some cases, it is prohibited to treat even two teeth at the same time.
Previously, dentists used the rule “One appointment, one tooth treated.” Today there are no such restrictions, but only a few teeth with caries can be treated at a time. Other diseases require more attention from a doctor.
Causes of caries development
Oral disease develops under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms that multiply in a favorable environment. Dentists are of the opinion that the disease occurs due to changes in the acid-base balance on tooth surfaces. Fermentation of carbohydrates caused by pathogenic bacteria releases destructive amounts of organic acids.
The main factors that contribute to the formation of carious cavities:
- improper hygiene care;
- eating problems;
- systemic chronic or acute diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reduced concentration of vitamins and minerals in the body;
- hereditary predisposition, etc.
Bacterial plaque and tartar
Streptococci are microorganisms that live in organic acids, leading to the destruction of enamel and dentin. During brushing, soft structures are easily removed, but hardened structures cannot be removed. They also contain pathogens that cause destructive phenomena.
Poor nutrition
Every person knows from an early age that you can’t eat a lot of sweets. However, adults often ignore this rule and consume large amounts of carbohydrates, sugar, baked goods, and starchy foods. The enamel layer becomes thinner and more susceptible to external factors. Bacteria multiply better in a carbohydrate environment.
Decreased salivation
During the day, a person secretes about 2 liters of saliva. The secretion washes away food debris from dental surfaces and protects them from the negative effects of pathogenic microflora. If the salivary glands do not function well enough, a lot of food particles settle on the crowns, which the microbes feed on.
Violation of the mineral composition of enamel
This factor is directly related to diet. Demineralization is observed with a meager, monotonous menu, lack of calcium, phosphorus and fluorine. Seeds, cottage cheese, cheese, red beans, and buckwheat are rich in such microelements.
Genetic predisposition also influences mineralization. This means that the disease can be inherited from parents and other relatives.
The problem occurs in pregnant women at different gestational stages. The fetus takes all the useful minerals, and the expectant mother experiences a lack of them. Subsequent intervention is complicated by the inability to use anesthesia.
What is the difference between caries and pulpitis?
Caries and pulpitis are the most common dental diseases. They are very similar to each other, but there are also differences. The main difference is the depth to which inflammation has developed in the tooth tissues.
Caries appears at the initial stage of tooth damage. A small stain or darkening appears on the surface. This is called the first manifestation of caries. Subsequently, inflammation develops and moves deeper into the tooth. Caries that has reached the nerve is called pulpitis. Pulpitis already affects the nerve, and not just the tooth tissue. Pulpitis is characterized by severe pain, and caries can be accompanied by a painful reaction to sweets and cold foods.
Stages of cervical caries and its clinical manifestations
The stages of cervical caries are the same as those of other types in terms of localization. Each has its own symptoms, by which the dentist can determine it:
- At the spot stage, a white chalky spot appears in the cervical area, the surface of which is initially smooth, but gradually becomes rough, which indicates that the enamel is beginning to deteriorate. At the same time, the spot itself becomes more noticeable and stands out against the background of unaffected areas. There are usually no clinical manifestations at this stage;
- At the stage of superficial caries, the spot darkens, the enamel continues to deteriorate, and the patient experiences short-term pain in response to exposure to temperature (hot or cold food) or chemical (sweet, sour food) stimuli. As soon as the influence of the latter is eliminated, the pain symptoms also go away;
- The middle stage manifests itself as the formation of a carious cavity deep into the tooth. Food particles get stuck in it, causing pain. Sometimes they occur during conversation or oral hygiene activities;
- At the stage of deep cervical caries, serious destruction of dental tissues and pain symptoms are observed in response to exposure to irritants. If treatment is not started promptly, the process will spread to the dental cement and reach the pulp. Thus, pulpitis will begin, which will manifest itself in severe pain.
At later stages of development, when pathological processes involve the deep layers of dentin and cement, the cavity becomes even deeper. Dead tissue, pieces of food and pathogenic microflora get into it. Failure to adequately treat cervical dental caries at this stage will lead to serious complications in the form of pulpitis and periodontitis. The latter consists of inflammation of the connective tissue around the tooth root and its apex. Ignoring this problem will cause the development of a jaw cyst, abscess or fistula, as well as a very high risk of losing a tooth.
Is it necessary to treat caries on baby teeth?
This question plagues many parents, but it is important to listen to experts. It is imperative to treat baby teeth at the first signs of pathology. The condition of baby teeth affects the formation of the jaw and the growth of permanent teeth. If baby teeth fall out prematurely, the molars will grow crooked.
Damaged teeth in the oral cavity will lead to the appearance of chronic infectious diseases, as well as serious allergies. This can be avoided if you monitor the condition of your child's teeth.
Classification of dental disease
Depending on the depth of the lesion, there are the following types of disease:
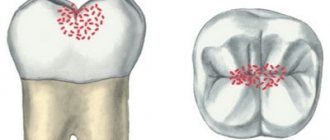
- Spot. At this stage, a light or dark spot appears on the surface of the enamel, while its structure remains unchanged. It occurs due to demineralization of the enamel. During this period, treatment is the simplest, fastest and most painless.
- Surface. To understand how initial superficial caries in adults is treated, you need to understand its essence. At this stage, destruction occurs within the enamel layer and does not affect the dentin. The patient may experience pain when eating cold, hot and sweet foods. To combat the disease, the stain is polished, after which the tooth is remineralized.
- Average. This type of disease affects the surface layer of dentin. A person may experience constant aching or intermittent pain. Do you want to know how to treat average caries in the video? To heal, the damaged part of the tooth is removed and a filling is installed in its place.
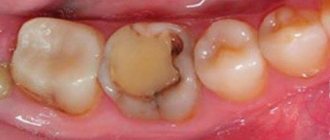
- Deep. In this case, tissue damage is most severe. Interested in the question of how to treat deep advanced caries? To successfully get rid of such a complex disease, you need to completely remove the damaged area of the tooth by installing a filling. Untimely treatment can lead to serious complications associated with pulp inflammation.
To see how dental caries is treated and photos of the stages of the disease, it is enough to study the principles that modern dental clinics follow. The algorithm and complexity of the procedures performed depend on how advanced the problem you have is.
According to Black's classification, there are the following types of caries:
- Fissure. Do you doubt whether fissure caries should be treated? This type of disease is characterized by the occurrence of damage that occurs in the fissures - the natural recesses of the tooth. Timely consultation with a doctor will help prevent the further development of this pathological process.
- Approximal. The disease affects the contact surfaces of the canines, incisors and molars.
If you want to know how to treat decay on your front teeth while maintaining their integrity and attractiveness, seek help from an experienced dentist.
- Cervical. The process affects the base of the teeth near the gums. Would you like to know how root and cervical caries on the front teeth are treated? An experienced dentist decides how to treat caries near the gums. To restore the original functions of the cervix and its aesthetic appearance, the help of a professional doctor is necessary.
How is caries treated without drilling?
Many adults are even more afraid of dentists than children, and prefer to treat dental caries using non-invasive methods, without the use of dental burs. Conservative treatment without drilling teeth can be carried out using several methods.
The first option is remineralization. When caries just begins to affect the tooth enamel, a small white spot forms on it. This is the focus of demineralization - the zone in which the loss of mineral components of the enamel began. If you notice a change in enamel color in time and contact your dentist, your doctor may prescribe remineralization therapy to restore mineral balance. The dentist treats the patient’s teeth with special fluoride and calcium-containing preparations, makes medicinal applications, or prescribes home use of medications with a similar effect. Deep fluoridation is considered the most effective method of remineralization therapy.
How is caries treated using the ICON method?
When dental caries in adults is in the staining stage, it can be treated with a non-invasive infiltration method. This technology allows you to stop the spread of carious lesions deep into the tooth without the use of a drill.
Caries is treated according to the following scheme:
- The dentist removes plaque and other deposits from the surface of the tooth enamel.
- A special etching gel with hydrochloric acid is applied to the affected area.
- Within two minutes the surface layer is removed;
- After two minutes, the gel is washed off with an air-water jet, the surface is dried and washed with an ethanol solution to remove residual moisture from the porous areas of the tooth. At the final stage, the tooth is covered with a composite material that seals the pores of the tooth enamel.
The main advantages of the method: it is possible to treat both caries of permanent teeth and baby teeth for children.
The treatment is absolutely painless, so no anesthesia is needed. Healthy areas of dental tissue are preserved during treatment. You can quickly and easily treat carious lesions on several teeth in one visit. The procedure takes no more than 15 minutes.
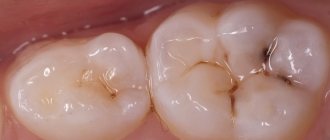
Average caries
If the pathological process has reached this stage, it is already difficult for a person to ignore its symptoms. A carious tooth reacts more often and more sharply to cold and hot, and may hurt when in contact with sweet foods and drinks. But, as soon as the irritant disappears, the pain goes away quite quickly.
Visual symptoms also change. The carious spot darkens. A small cavity may also form on it. If a cavity has formed on the front wall of the tooth, you can see it; if on the back, you can feel it with your tongue. Food debris gets clogged into the cavity, and this provokes a new sign of caries - an unpleasant odor in the mouth and “stuffy” breath.
Treatment of caries at this stage is more complex and often requires pain relief, since the pathological process has affected the internal tissues of the tooth. The doctor uses a drill to remove all affected dentin and fill the cavity with filling material.
Middle caries is the last stage at which pathology can be eliminated without serious long-term therapy. If you do not see a doctor, tooth decay will continue and move to the next stage - deep caries.
Is it necessary to treat caries at the initial stage if the tooth does not hurt?
It is necessary to treat caries, since the process of disease development has already begun.
As long as the destruction has not affected the pulp (tissue complex), you can quickly cope with the treatment and relieve the patient from unpleasant sensations and significantly save the family budget, since treating pulpitis is much more expensive. Treatment of a tooth that has only been affected by caries will take 10-15 years minutes and will cost 3-5 times less in a paid clinic than working on a tooth with pulpitis or other complex disease. To install a filling in a complex case, you will need to visit the clinic at least 2-3 times.
Tooth decay is contagious - fact or fiction?
Some scientists consider caries to be a contagious disease, since its occurrence and development is caused by pathogenic microbes. The microorganisms themselves are transmitted by contact, which means that caries is theoretically a contagious disease.
Other experts point out that each person has his own pathogenic microflora in his mouth, but it does not always cause caries. The disease appears as a result of poor hygienic care, as well as as a result of exposure to a number of other factors. It turns out that caries is not a contagious pathology, despite the existing theoretical calculations.
How long does it take to treat caries?
Very often you can hear the question: “how long will the treatment take?” It is difficult to give a definite answer, because a huge number of factors influence the duration of treatment.
So what can affect treatment time?
Let's sort it out in order.
The first step is pain relief . Anesthesia for the treatment of teeth in the upper jaw occurs quickly and quite well, it takes about
5 minutes (application anesthesia, the so-called “jam”, occurs within 1-2 minutes, then direct infiltration anesthesia, in which the administration of the anesthetic takes 1 minute and waits for the onset of the anesthesia effect for about 2-3 minutes).
And when treating lower jaw teeth, difficulties with pain relief may arise, which is due to anatomical features.
Often, infiltration anesthesia alone is not enough, and it is necessary to resort to conduction anesthesia.
Its effect develops on average within 5-7 minutes, but there are cases (rather rarely) when you have to wait up to 30 minutes. This depends on the individual characteristics of the patient.
Degree of mouth opening and access to tooth.
This is the next factor that influences the duration of treatment. There are a number of patients with limited mouth opening and pathology of the temporomandibular joint. Also, molars (the very last teeth) have a complex arrangement. All of this can increase the time required for treatment.
The fundamental factor is the degree of tooth decay .
This refers to the depth of the carious process (caries can be superficial, medium and deep), as well as the number of affected tooth walls.
The deeper the cavity, the longer it takes to remove the entire carious process and preserve the tooth tissue as much as possible.
If the contact surfaces are affected or, for example, caries is located under the gum, this also increases the duration of treatment, since it is necessary to install a matrix system and restore the physiological contact point.
The time of preparation of the carious cavity and its restoration depend on these factors. Preparation time can take from 5 to 20 minutes, and the restoration itself can take from 10-40 minutes.
Creating a high-quality restoration takes a sufficient amount of time, which is associated with performing certain manipulations:
- high-quality insulation (use of rubber dam),
- use of optics (microscope or binoculars),
- installation of a matrix system and its adaptation to recreate a dense physiological contact point;
- stage of conditioning with a special gel to create micro-spaces,
- compliance with the technique of introducing the adhesive system (adhesive is a kind of “glue” that firmly connects the filling material to the tooth tissues),
- layer-by-layer application of filling material, its adaptation and polymerization, formation of anatomical formations (tubercles, fissures),
- polishing the restoration.
Compliance with all stages affects the quality and service life of the restoration.
To summarize, we can say that on average, caries treatment time can take from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
At Belaya Medvetsa, we pay great attention to the quality of the treatment, which requires a certain time to perform all the necessary manipulations according to the treatment protocol, and as a result, obtain a functional restoration that will repeat the anatomical shape of a natural tooth.
And finally, let's look at a few clinical cases.
Clinical case 1:
Objectively: on the chewing surface of the 17th tooth there is a carious cavity of medium depth.
The treatment of this tooth took 30 minutes.
Clinical case 2:
Objectively: on the chewing surface of the 36th tooth there is a filling with a defect in the marginal fit, on the contact surfaces there are carious cavities of medium depth. There is also a carious cavity on the distal surface of the 35th tooth.
In this case, the treatment time was 1.5 hours.
Methods for diagnosing caries
In order to develop a program for the correct treatment of a patient with caries, it is very important for the doctor to make a correct diagnosis and find out what caused the damage to the tooth tissue.
The work uses two main methods:
- Visual inspection. The doctor uses a special instrument to check the condition of the tooth and whether there are signs of damage. A detailed examination helps to understand which tooth is affected, even if there are no clear external signs.
- Radiography. X-rays in our clinic are performed using high-quality modern equipment. This allows you to get a clear picture of the condition of the deep parts of the tooth, its roots. In this way, it is possible to understand exactly how severe the lesion has developed.
Also, at the first appointment, the doctor collects a general picture of the person’s condition and finds out what the cause of the disease may be. A good dentist always tries to eliminate not only the tissue damage itself, but also the factors leading to its appearance.
How does caries develop and what are the consequences?
Conventionally, there are 3 stages of caries:
1
2
3
- Superficial caries (or spot caries)
- Average caries, when tooth decay is only at the enamel level
- Deep caries, when a cavity forms in dentin
If caries has reached the pulp (the soft tissue of the tooth with blood vessels and nerves), then doctors call it pulpitis. Typically, pulpitis is accompanied by severe and persistent pain, which even prevents sleep.
If pulpitis is not cured, a complication will appear, inflammation of the jaw bone tissue or, in medical terms, periodontitis.
- Caries
- Pulpitis
- Periodontitis
Caries is a source of infection in the oral cavity. It not only imperceptibly deteriorates teeth, but also undermines a person’s overall health.
At the initial stage, caries can be easily, completely and inexpensively cured. By postponing a trip to the dentist, a person does not save, but on the contrary, significantly (manifold!) increases the cost of his treatment.
If at the initial stage treatment would cost up to 2,500 rubles, then treatment of pulpitis of one tooth may require about 15,000 rubles. Most often, the costs are more modest, but if you delay going to consultation and treatment, the situation will only get worse.
Caries leads to tooth loss. Even the absence of one tooth brings a lot of inconvenience (it is inconvenient to eat, aesthetics suffer, asymmetry occurs on the face, other teeth are displaced).
And the loss of several is a tragedy for the body. Dozens of people who have experienced this themselves contact us every month. They come to get implants to restore comfort and eat, smile and live with pleasure again. Implantation is a high-tech treatment that requires expensive materials, equipment and enormous doctor qualifications. Therefore, a new artificial tooth costs 60,000-100,000 thousand. It’s not cheap, but those who have experienced a life full of restrictions and inconveniences due to the absence of a tooth(s) already understand the value and know that it’s worth it.