Curettage is a dental procedure in which the doctor cleans periodontal pockets of subgingival dental plaque and irreversibly changed (granulation) tissues, which has a beneficial effect on strengthening teeth. Closed surgery is indicated for pocket depths up to 3 mm (mild stage of periodontitis) and takes place without compromising the integrity of the gum tissue. Open curettage is a full-fledged surgical operation that involves exfoliation of part of the mucous membrane and is performed for early and severe periodontitis, when there is already damage to the bone tissue.
- Peculiarities
- Indications
- Operation
- Recommendations
- Our advantages
- On a note
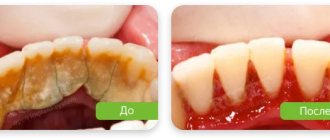
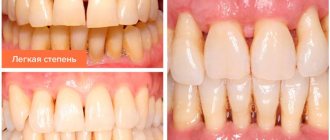
- Photos before and after
Curettage is a procedure for removing subgingival dental deposits and irreversibly changed (granulation) tissues from periodontal pockets in order to strengthen teeth. Periodontium refers to the gum tissue surrounding the teeth. If plaque is not removed in a timely manner, it mineralizes and turns into tartar, which is deposited both above and below the gum, pushing the gum tissue away from the neck and root of the tooth. If an infection gets into the resulting voids (pockets) (and it certainly does, because the oral cavity has ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora - warm, humid, there is a large amount of dietary fiber), then the periodontal tissues become inflamed and are subsequently destroyed, contributing to the deepening of the gap between tooth root and gum tissue.
The wider and deeper the periodontal pocket, the more severe periodontitis occurs, and the more uncomfortable a person feels. So, he begins to be bothered by bad breath, which persists even after thoroughly brushing his teeth and using breath freshening compounds. In addition, the gums become red, swollen and begin to bleed. Eventually, the teeth become mobile, the spaces between them widen, and pus begins to leak from the periodontal pockets. The entire body as a whole suffers from the inflammatory process - a person develops lymphadenitis and signs of intoxication appear. A gum pocket filled with infection is a serious pathology that, if left untreated, becomes chronic and eventually spreads to the jaw bone, which can lead to complete loss of teeth. Fortunately, such methods of treating periodontitis as curettage and splinting, masterfully performed by dentists at the St. Petersburg Grandmed Clinic, can significantly improve periodontal health and strengthen teeth.
What is curettage
Normally, between the gum and the cervical area of each tooth there is a dentogingival junction that protects the tissues from the spread of pathological processes, microorganisms, and food particles. In the absence of adequate treatment for gum inflammation, destructive processes and local disruption of microcirculation lead to the destruction of the dentogingival junction, a periodontal pocket is formed - the space between the tooth root and the connective tissue of the gums, where a favorable environment is created for the active activity of pathogenic bacteria.
Thus, gingivitis, which most often manifests itself as bleeding and swelling of the gums, develops into a more serious dental pathology - periodontitis, the treatment of which is no longer possible without surgical interventions. The causes of the occurrence and spread of the inflammatory process may be poor hygiene, constant trauma to the teeth, and some somatic diseases.
Curettage is a procedure for cleaning the cavity between the gum and tooth root. Only after treating the root part of the tooth with careful removal of all pathological contents (granulations, plaque, stone), it is possible to create conditions for successful healing of the lesion and restore the dentogingival junction. Curettage of the periodontal pocket is the basis of periodontitis therapy, which is confirmed by positive reviews from doctors about the procedure. The method of curettage is selected by a specialist depending on the severity of periodontitis, the main criterion of which is the depth of the periodontal pocket.
Prices for laser sterilization
Prices for laser treatment of periodontitis in Moscow depend on the degree of gum damage, the number of periodontal canals treated, and the number of procedures. The cost of processing one channel starts from 500 rubles. The sooner you contact our dental clinic, the lower the final cost of treatment will be.
In our clinic you can receive a full range of dental services. Modern technologies, good equipment and qualified doctors allow us to provide effective care to patients even with serious problems. Come to us at the first symptoms and you can maintain the health and integrity of your teeth.
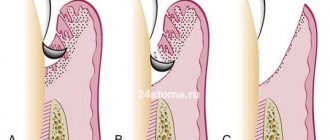
Closed curettage of periodontal pocket
Closed curettage is a treatment technique performed in cases of mild or moderate pathology. Its peculiarity is that pockets are cleaned without incisions or gum detachment. After diagnosis, during which dental X-rays are necessarily studied and the depth of each pathological pocket is measured using periodontal instruments, local anesthesia is performed. The patient rinses the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution, and after complete anesthesia of the gums in the corresponding area, the doctor sequentially cleans each side of the tooth. Closed curettage of periodontal pockets is performed using a set of special hand instruments - scalers, curettes. The specialist inserts the instrument to the depth of the pocket and, using lever-like scraping movements, cleans the surface of the root and gums, as well as the bottom of the formation. Thus, the following are removed from the pathological pocket:
- hard subgingival calculus;
- granulations that have grown in the pocket;
- soft coating.
After basic cleaning with a periodontal bur, the accessible part of the tooth root is polished to prevent the accumulation of plaque on it and improve the conditions for restoring the periodontal attachment. The cleaned area is washed with an antiseptic. In one session, closed curettage can be performed in the area of 5-6 teeth.
Flap surgery on gums
Flap surgery on the gums in dentistry allows you to:
- remove granulations from under the gums;
- clean out subgingival deposits;
- eliminate periodontal pockets;
- stimulate the restoration of bone tissue by adding a synthetic analogue.
It is worth noting that all of the listed goals of periodontal flap surgery completely coincide with the goals of open curettage.
But still, there is one significant difference between these methods. It lies in the fact that patchwork surgery on the gum involves making an incision 1-1.5 mm from the edge of the gum. This strip of gum is completely cut out due to the fact that it loses its ability to adhere tightly to the surface of the teeth. The last stage of this operation is the tension of the flaps of the gum mucosa to the dental necks. Due to this, the periodontist prevents the possibility of “recession” of the gums.
Flap operations can be relevant both in the presence of generalized periodontitis and in cases where the surgeon is faced with the task of preventing receding gums and exposing the roots.
In order to become more familiar with the advantages and disadvantages of the presented methods, it is necessary to carefully study the reviews of patients who have experience in performing the listed operations.
Open curettage
The open curettage technique is more complex and requires making incisions in the gums. Thanks to gum detachment, deeper access is provided, and the doctor performs manipulations in the periodontal pocket with a wide view of the entire pathological focus. This allows the use of the open method in the treatment of moderate periodontitis, when the depth of the pathological pocket can reach 5 mm.
The operation is carried out as follows:
- After rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic and anesthesia, the dentist makes an incision at the tops of the gum papillae and peels away the tissue to expose the tooth roots for the duration of the procedure.
- With periodontal instruments, all surfaces are cleaned of necrotic tissue and plaque, vascular and epithelial formations are scraped out, and the bottom of the pocket is processed.
- Root polishing is carried out.
- The surgical field is washed with antiseptics, the gums are returned to their original position, and sutures are applied. If necessary, hemostatic sponges are used.
- The operation is completed by applying a bandage with therapeutic components to the treated area, designed to protect against oral fluid and injury.
During normal healing, the sutures are removed on average after 10 days. A course of local and general treatment with medications is prescribed. The patient takes a selected antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs. At home, baths and rinses are performed, and dental ointments are used. After thorough cleansing of pathological formations, drug therapy helps reduce signs of inflammation, eliminate pathogenic microflora, and promote tissue regeneration.
Advantages of curettage over therapeutic techniques
When the depth of periodontal pockets is 3 mm or more, bone tissue is replaced by granulation tissue, and this process cannot be reversed either by anti-inflammatory therapy or by removing dental plaque. Only scraping of pathologically altered tissues, that is, curettage will really improve the health of the gums; moreover, during the procedure, all subgingival deposits of tartar and pathogenic microflora accumulated in the periodontal pocket are removed. Moreover, this is not done “by eye”, for example, as when removing with ultrasound during professional cleaning, but in full.
Curettage can be closed or open. Closed surgery is indicated for pocket depths up to 3 mm (mild stage of periodontitis) and takes place without compromising the integrity of the gum tissue. The walls of the tooth, the adjacent soft tissues and the bottom of the pocket are treated with a curette, the cavity freed from stone and granulations is washed with a disinfectant solution, after which a bandage is applied to the wound. Open curettage with detachment of part of the mucosa is done for moderate and severe stages of periodontitis, which are characterized by damage to bone tissue.
Laser curettage
Dental pockets can be cleaned using a laser device. Instead of curettes and scalers, manipulations in the periodontal pocket are carried out using a diode or erbium laser beam. The procedure is prescribed for mild periodontitis. Using a dental laser attachment, the doctor inserts a beam into the space between the gum and the surface of the tooth root. When a laser acts on pathological growths (granulation tissue), they coagulate - destruction under the influence of high temperature and evaporation. An important feature of the technique is the absence of bleeding during curettage of periodontal pockets with a laser, which is due to the instant cauterizing effect of the beam.
To better eliminate pathogenic flora, the laser method is combined with photodynamic therapy. To do this, before the procedure, the gums and pocket area are treated with a preparation based on chlorophyll, a plant pigment. Its molecules accumulate in periodontal cells affected by microorganisms and form photosensitizer compounds. Half an hour after applying the pigment, the doctor acts on the colored tissue with a visible spectrum laser, which activates the resulting photosensitizers. The compounds destroy bacterial cells and elements affected by them, actively releasing oxygen. Since the chlorophyll in the drug has a selective effect, the laser does not affect healthy tissue. According to patient reviews, the procedure is almost painless; a tingling sensation may be felt.
Advantages of the laser method:
- low risk of gum injury;
- fast healing;
- no bleeding.
Laser cleaning is the method of choice for a group of patients who have contraindications to standard curettage methods - patients with diabetes mellitus, serious cardiovascular diseases, and bleeding disorders.
How is closed curettage performed?
The purpose of the operation is to remove granulations from periodontal pockets, as well as those subgingival dental deposits that could not be removed using an ultrasonic scaler.
Disadvantages of the technique: curettage is carried out blindly, there is no visual overview of the surface of the roots, periodontal pockets - because of which granulations and dental deposits partially remain in their places. Scheme of closed curettage –
Closed curettage of periodontal pockets is performed under local anesthesia. Curettage of the gums with sharp curettes is accompanied by bleeding, which further complicates visual control. At the end of the operation, the wound surface is treated with antiseptics, and a protective gum bandage is applied for several days. In Fig. 7 you can see the instruments used to perform closed curettage. Laser surgery is also an option (see video below).
Closed curettage can be more or less effective only with shallow periodontal pockets (no more than 3-4 mm), i.e. with the mildest degree of periodontitis. For moderate and severe periodontitis, closed curettage (by reducing the volume of granulations) can only temporarily improve the condition of the gums, but this improvement will only be short-term, and periodontitis will definitely progress further. In some cases, closed curettage is performed as a preparatory step before open curettage or flap surgery.
The closed curettage technique is popular in dental clinics that do not have an experienced periodontist surgeon, and therefore the operation is performed by an ordinary general dentist (periodontist). These specialists have neither the skills nor experience in performing complex surgical interventions in the oral cavity, which include open curettage and flap operations. Therefore, the worst thing that can happen to you in this situation is that you will undergo a closed curettage (although with your pocket depth, more radical techniques have long been indicated for you).
In this case, the following consequences are possible - 1) you will get a short-term, but still improvement, 2) you will not get any results from the treatment in principle, 3) closed curettage can provoke an exacerbation of periodontitis, in which case you will get suppuration from the periodontal pockets and acceleration of inflammatory bone resorption.
Closed curettage using curettes and laser –
Video 1 shows scraping of granulations from a periodontal pocket in the area of only one tooth. As you can see, this use of curettes is quite traumatic and is accompanied by bleeding. In video 2, periodontal pockets are treated using a laser. In most cases, this will also be accompanied by slight bleeding (especially if the gums are loose and inflamed).
Deep curettage
Severe periodontitis is a serious pathology, accompanied by the presence of periodontal pockets deeper than 5 mm, in which bone pockets often appear. With such signs, more extensive interventions are indicated to cleanse subgingival deposits, especially if the lesion has spread to a large number of teeth. The large depth of the gaps between the gums and the tooth root requires visual control to completely remove the pathological contents, so a radical operation is performed with peeling off a flap of tissue in the area of half or the entire jaw to the depth of the lesion.
After exposing the roots, they undergo deep treatment: removal of epithelial growths, any deposits, affected cement, as well as altered bone tissue. The treated area is washed with antiseptics and stitches are applied. In the presence of severe bone loss, osteoplastic materials are used to promote regeneration. Healing of oral tissue continues for a month.
Causes, features and consequences of periodontitis
If a person does not pay sufficient attention to oral hygiene, plaque and hard deposits can form on the teeth - these are obvious factors in the development of periodontitis. Inflammation of the gums begins, and at first this manifests itself through their bleeding, and later the mobility of the teeth occurs, they can move, and pus can come out from under the gums.
Thus, the initially soft dental plaque, due to mineralization, becomes tartar, the microorganisms of which produce toxins. These toxins stimulate an inflammatory process in the gums, which results in various adverse effects.
Firstly, the bone tissue around the tooth begins to gradually dissolve. It doesn’t just disappear; in its place, another tissue appears—granulation tissue—containing many microbes that also dissolve the bone. Thus, bone tissue atrophy occurs many times faster. Secondly, periodontal pockets are formed. Inflammation causes destruction of the attachment of the tooth to the bone (the so-called periodontium). With the help of periodontium, the tooth is securely attached to the bone tissue with microbonds.
As for the periodontal pocket, it is an area where bone tissue is destroyed, and the cavity itself is filled with pus, granular tissue and dental plaque. Popularly, a periodontal pocket is also called a gingival or dental pocket. Such a disease can be detected in a patient using x-rays or by probing.
If, as a result of an examination, deep gum pockets (from 3-4 mm) are discovered in a person, then no therapy or antibiotics can help in this case, since the destruction process becomes irreversible.
There are several reasons for this.
- Not even the most highly qualified specialist can give a 100% guarantee that with the introduction of an ultrasonic tip under the gum, all subgingival deposits will be removed. This happens due to the fact that the doctor cannot see what exactly is happening in the gum pockets. Therefore, in almost all cases, a lot of destructive deposits remain there.
- Moreover, such a procedure is very expensive and painstaking, takes a lot of time, effort and money, and there is no guarantee of a complete cure.
- Even if we assume that subgingival deposits have been completely removed from the pocket, periodontitis will still progress, since there are all conditions for the favorable development of infection.
The only way out that can guarantee improvement is surgical intervention. Only it can completely remove all deposits, granulation tissue and periodontal pockets.
Types of surgical treatment of periodontitis
There are three main methods of surgery for this disease: open and closed curettage of gum pockets and flap surgery. Let's look at the features of each method in more detail.
Vacuum curettage
Vacuum curettage is a combined method; its technique is similar to the closed method of curettage of periodontal pockets, but together with standard curettes, hollow nozzles connected to a vacuum apparatus are used. Using a compressor, a vacuum is created in the device’s container, capable of sucking out mucus, deposits, and granulations from the space between the root and the gum. To improve visual control, the vacuum method can be performed in conjunction with gingivotomy (dissection of the gums).
Stages of the vacuum method:
- injection pain relief;
- scraping out accessible deposits from the tooth root with curettes;
- scraping granulations from the gums;
- bottom treatment with a vacuum nozzle;
- washing the cleaned area with antiseptics;
- applying a protective bandage for two days.
The vacuum method can be used in the area of 2-4 teeth in one session. As a result of the procedure, congestion is reduced, lymph and blood circulation is normalized. During the action of vacuum, microhematomas are formed, which help accelerate regeneration processes and, as a result, more rapid restoration of the periodontal junction.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
What does closed curettage provide:
- The cause of the occurrence and development of inflammation (stone, granulation, plaque) is eliminated
- Reduces inflammation and swelling of gums
- Reduces sensitivity of teeth and gums
- The connection between the teeth and the periodontium improves (the instability of dental units decreases)
Advantages of the closed access method:
- No surgical incisions
- Efficiency of processing (about an hour for all teeth)
- Fast patient recovery
Flaws:
- Lack of visual control
- Possibility of cleaning only shallow pockets (up to 4 mm)
Indications and contraindications for surgery
Curettage is indicated for:
- mild (closed method) and moderate periodontitis (open method);
- some forms of gingivitis, accompanied by abundant subgingival deposits;
- absence of bone pockets.
Since curettage is a type of surgical intervention, it has a number of restrictions on its use in patients with severe systemic diseases, as well as under some unfavorable conditions that prevent operations in the oral cavity.
Contraindications related to the condition of local tissues include:
- discharge of pus from the gums;
- severe gum atrophy, thinning or changes in the walls;
- high tooth mobility;
- infectious lesion of the mucous membrane.
Contraindications related to general condition:
- bleeding disorders, diabetes mellitus (laser technology is recommended instead of standard technology);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the stage of decompensation;
- mental illnesses in which the patient is not able to adequately perceive the doctor’s manipulations during the procedure;
- feverish condition.
When visiting dentistry, before the procedure, diagnostic measures are required to select the optimal therapy and exclude contraindications to this treatment. Before carrying out a specific method of curettage of a periodontal pocket, a specialist will explain in detail what kind of cleaning method this is and give professional recommendations for the postoperative period.
The effectiveness of open curettage and flap surgery
The main advantage of these techniques is the fact that only they allow the complete removal of periodontal pockets. In addition, these operations help reduce bone tissue atrophy. Due to this, the problem of tooth mobility can be partially eliminated.
That is why, for the effective treatment of periodontitis, only these surgical methods can be recommended. Thanks to these methods, the patient will be able to do without false teeth and dentures for a long time.
To complete the picture, it is worth talking about the disadvantages of these methods. The first disadvantage is that these operations can only be entrusted to qualified periodontal surgeons. Unfortunately, such specialists do not work in all dental clinics.
Another disadvantage is the cost of these procedures. Carrying out these operations requires payment for the services of not only the surgeon, but also his assistant. In addition, these operations require the use of expensive materials (monofilament, synthetic fabric, etc.).
The relative disadvantages of the listed procedures include the fact that there is a risk of gingival recession (exposure of the gum roots). The extent of this problem depends on the extent of bone atrophy.
Do not forget that within a few months after the operation, the gingival papillae become flattened. Therefore, they are not able to fill the entire interdental space. Therefore, cavities between teeth are not eliminated immediately.
The last disadvantage of these techniques is their duration. The periodontist spends about two hours working with one area (7-8 teeth).
Dental care after curettage
The duration of recovery and the nature of recommendations during the recovery period depend on the chosen method of intervention.
The healing process when using the closed curettage technique for periodontal pockets takes about a week. Immediately after the operation, the pockets are filled with a blood clot, the presence of which is very important for normal tissue repair, so rinsing it out is prohibited. Brushing your teeth is not recommended for 2-3 days; a brush with soft bristles is used throughout the entire treatment period. Hot, irritating and solid foods should be avoided. At home, oral baths are made with solutions of antiseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Immediately after open curettage, an ice pack is applied to the treated gum area. Drinking is allowed after 2-3 hours; to maintain the integrity of the protective bandage, it is recommended to use a straw. You will have to wait 6-8 hours to eat. In the first 2-3 weeks, increased sensitivity to temperature stimuli may occur. Brushing your teeth should be done with brushes with super-soft bristles, eating soft foods and taking baths with medications selected by your doctor. If you have a bad habit, smoking is prohibited for 8-9 weeks; during this period, physical activity and visiting a bathhouse or sauna are also not recommended.
Performing any curettage method requires the dentist to have excellent manual skills, attentiveness and careful attitude towards the gum tissue. At the Academy Dent clinic in Moscow, the procedure is performed by a specialist with many years of clinical experience in periodontology. Comprehensive equipment with advanced equipment allows the use of only modern operating techniques, and an individual approach at each stage of therapy and diagnosis makes treatment comfortable and painless for the patient.