Types, quality and conditions of medical care
Types of medical care
As part of the Territorial Program for Free Medical Care, the following types of medical care are provided free of charge to persons insured in Moscow:
- Primary health care, including primary pre-medical care, primary medical care and primary specialized care;
Primary health care is the basis of the medical care system and includes activities for the prevention, diagnosis, treatment of diseases and conditions, medical rehabilitation, monitoring the course of pregnancy, promoting a healthy lifestyle and sanitary and hygienic education of the population. Primary health care is provided free of charge in outpatient and day hospital settings in planned and emergency forms. Primary pre-hospital health care is provided by paramedics, midwives and other medical workers with secondary medical education. Primary medical care is provided by general practitioners, local physicians, pediatricians, local pediatricians and general practitioners (family doctors). Primary specialized health care is provided by medical specialists, including medical specialists from medical organizations providing specialized, including high-tech, medical care.
- Specialized, including high-tech, medical care;
Specialized medical care is provided free of charge in inpatient settings and in a day hospital by medical specialists and includes the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions (including during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period), which require the use of special methods and complex medical technologies, and also includes medical rehabilitation. High-tech medical care is part of specialized medical care and includes the use of new complex and (or) unique treatment methods, as well as resource-intensive treatment methods with scientifically proven effectiveness, including cellular technologies, robotic technology, information technology and genetic engineering methods developed based on the achievements of medical science and related branches of science and technology.
- Ambulance, including specialized emergency medical care;
Ambulance, including specialized ambulance, medical care is provided to citizens in an emergency or emergency form in case of diseases, accidents, injuries, poisoning and other conditions that require urgent medical intervention outside a medical organization (at the place where the ambulance team is called, including specialized ambulance, medical care, as well as in a vehicle using medical equipment - during medical evacuation). Ambulance, including specialized emergency medical care, is also provided on an outpatient and inpatient basis by mobile emergency advisory ambulance teams, including specialized emergency medical care, if it is impossible to provide this type of medical care in the appropriate medical organization. When providing emergency, including emergency specialized medical care, if necessary, medical evacuation is carried out, which is the transportation of citizens in order to save lives and preserve health (including persons undergoing treatment in medical organizations that do not have the ability to provide the necessary medical care). assistance for life-threatening conditions, women during pregnancy, childbirth, the postpartum period and newborns, persons injured as a result of road accidents, emergencies and natural disasters). Ambulance, including specialized emergency medical care, is provided free of charge by medical organizations of the state healthcare system of the city of Moscow, as well as by other medical organizations participating in the implementation of the Territorial program in terms of providing this type of medical care. Medical evacuation is carried out by mobile ambulance teams, including specialized emergency medical care, carrying out medical care measures during transportation, including the use of medical equipment.
- Palliative care provided by medical organizations;
Palliative care in outpatient and inpatient settings is provided by medical professionals trained to provide such care, and is a set of medical interventions aimed at relieving pain and alleviating other severe manifestations of the disease in order to improve the quality of life of terminally ill citizens. Palliative medical care for residents of the city of Moscow is provided free of charge by the State Budgetary Institution of Healthcare of the City of Moscow "Moscow Multidisciplinary Center for Palliative Care of the Department of Health of the City of Moscow", departments (rooms) of palliative treatment of medical organizations of the state healthcare system of the city of Moscow, including in nursing beds, as well as visiting patronage services.
- Medical rehabilitation.
Medical rehabilitation as a necessary stage of treatment is provided free of charge in an outpatient setting, a day hospital and inpatient settings and includes the complex use of natural healing factors, drug, non-drug therapy and other methods aimed at the full or partial restoration of impaired and (or) compensation for lost functions affected organ or system of the body, maintaining the functions of the body in the process of completing an acutely developed pathological process in the body, as well as prevention, early diagnosis and correction of possible dysfunctions of damaged organs or systems of the body, preventing and reducing the degree of possible disability, improving the quality of life, maintaining working capacity the patient and his social integration into society.
Forms of medical care
The Territorial Program provides medical care in the following forms:
- Emergency - medical care provided for sudden acute diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases, conditions that pose a threat to the patient’s life;
- Emergency - medical care provided for sudden acute diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases, conditions without obvious signs of a threat to the patient’s life;
- Planned - medical care provided during preventive measures, for diseases and conditions that are not accompanied by a threat to the patient’s life, do not require an urgent or urgent form of medical care, the delay of which for a certain time will not entail a deterioration in the patient’s condition, a threat to his life and health.
Conditions for providing medical care
The Territorial Program provides medical care in the following conditions:
- Outside a medical organization (at the place where the mobile ambulance team is called, including specialized emergency medical care, as well as in a vehicle during medical evacuation);
- In an outpatient setting, including at home when calling a medical professional;
- In a day hospital setting (medical observation and treatment are provided during the day, but round-the-clock medical observation and treatment is not required);
- In an inpatient setting (24-hour medical supervision and treatment is provided).
Waiting times for medical care
- Inpatient emergency medical care is provided immediately;
- The waiting period for specialized medical care (with the exception of high-tech) in a hospital setting in a planned form (planned hospitalization) is no more than 14 working days from the date the attending physician issues a referral for hospitalization of the patient;
- The waiting period for specialized medical care for a patient with an oncological disease (a condition that has signs of an oncological disease), with the exception of high-tech, in connection with the presence of the specified disease (condition) in a hospital setting in a planned form, is no more than 7 working days from the date of histological verification of the tumor or from the date of diagnosis of an oncological disease (a condition that has signs of an oncological disease). Planned hospitalization is provided if there is a referral for hospitalization of the patient;
- Medical care for emergency indications in an outpatient setting is provided by local therapists, general practitioners (family doctors), local pediatricians, obstetricians and gynecologists and is carried out on the day of the patient’s application;
- The waiting period for emergency primary health care is no more than two hours from the moment the patient contacts;
- The provision of primary health care in a planned form is carried out by prior registration of patients, including in electronic form. The waiting period for an appointment with local therapists, general practitioners (family doctors), and local pediatricians should not exceed 24 hours from the moment the patient applies;
- The waiting period for an appointment with specialist doctors when providing primary specialized health care in a planned manner is no more than 10 calendar days from the date of the patient’s application;
- The waiting period for an appointment (consultation) with medical specialists in case of suspected cancer is no more than three working days from the date the patient contacts the medical organization;
- The waiting period for diagnostic instrumental studies (x-ray studies, including mammography, functional diagnostics, ultrasound) and laboratory tests when providing primary health care in a planned manner is no more than 10 calendar days from the date of appointment of the study;
- The waiting period for computed tomography (including single-photon emission computed tomography), magnetic resonance imaging and angiography when providing primary health care in a routine manner (with the exception of studies for suspected cancer) is no more than 14 working days from the date of appointment of the study;
- The time it takes emergency medical teams to reach a patient when providing emergency medical care should not exceed 20 minutes from the moment the emergency medical team is called to provide such medical care;
- The waiting period for diagnostic instrumental and laboratory tests in case of suspected cancer is no more than 7 working days from the date of appointment of the study;
- The period for establishing dispensary observation by an oncologist for a patient with diagnosed cancer is no more than three working days from the date of his diagnosis of cancer;
- Waiting periods for the provision of high-tech medical care in a hospital setting in a planned form are established by the federal executive body that carries out the functions of developing and implementing state policy and legal regulation in the field of healthcare. In medical organizations that provide specialized, including high-tech, medical care in inpatient settings, a “waiting list” is maintained for the provision of specialized medical care in a planned form and citizens are informed in an accessible form, including using the information and telecommunications network Internet, about waiting periods for the provision of specialized, including high-tech, medical care, taking into account the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation on personal data.
Features of providing medical care
- In order to provide medical care to a patient undergoing treatment in an inpatient setting, if he needs diagnostic tests and it is not possible for them to be carried out by a medical organization providing medical care in an inpatient setting, free transport services are provided with simultaneous accompaniment of the patient by an employee of the medical organization;
- One of the parents, another family member or other legal representative is given the right to free joint stay with the child in a medical organization when providing medical care in an inpatient setting during the entire period of treatment, regardless of the child’s age. When staying together in a medical organization of the state healthcare system of the city of Moscow or a medical organization participating in the implementation of the Territorial Compulsory Medical Insurance Program, in an inpatient setting with a child until he reaches the age of four years, and with a child older than this age - if there are medical indications, a fee for creating conditions of stay in stationary conditions, including for the provision of a bed and food, there is no charge from these persons;
- When providing medical care in a hospital setting for medical and (or) epidemiological reasons, patients are accommodated in small wards (boxes) free of charge;
- When providing medical care to citizens entitled to receive state social assistance, the organization of drug provision for which is provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, and to certain categories of citizens entitled to receive social support measures in accordance with the legal acts of the city of Moscow, provision of drugs and medical products is carried out , as well as specialized medical nutrition products for disabled children in the manner prescribed by Appendix 3 to the Territorial Program;
- When providing, within the framework of the Territorial program of primary health care in a day hospital and in an emergency form, specialized, including high-tech, medical care, emergency, including emergency specialized, medical care, palliative medical care in inpatient conditions, free provision is provided citizens with medicinal products for medical use included in the list of vital and essential medicinal products for medical use approved by order of the Government of the Russian Federation for the corresponding year, and medical devices included in the list of medical devices implanted into the human body during the provision of medical care approved by the Government of the Russian Federation within the framework of the program of state guarantees of free medical care to citizens, in accordance with the standards of medical care in the manner provided for in Appendix 3 to the Territorial Program;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program, certain categories of citizens are provided, in the manner prescribed by Appendix 8 to the Territorial Program, with emergency medical care in medical organizations of the state health care system of the city of Moscow;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program, when providing specialized, including high-tech, medical care, donor blood and (or) its components are provided in the manner prescribed by Appendix 3 to the Territorial Program;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program, dispensary observation is carried out, which is a necessary examination of persons suffering from chronic diseases, functional disorders, and other conditions, carried out at certain intervals, for the purpose of timely detection, prevention of complications, exacerbation of diseases, other conditions, their prevention and implementation of medical rehabilitation of these persons The procedure for conducting dispensary observation and the list of studies included in it are approved by the Moscow Department of Health in accordance with the procedure and list approved by the federal executive body exercising the functions of developing and implementing state policy and legal regulation in the field of healthcare;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program for the provision of primary specialized health care, patients who apply to medical organizations (structural units) participating in the implementation of the Territorial Program and do not provide relevant medical services are routed by referring them to other medical organizations (structural units) participating in implementation of the Territorial program to receive such medical services. To receive medical care, citizens have the right to choose a doctor, including a general practitioner (family doctor) and an attending physician (subject to the doctor’s consent), as well as to choose a medical organization in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program, medical care is provided during official physical education, sports and mass sports and entertainment events held on the basis of legal acts of the city of Moscow, during official mass events held in accordance with Federal Law of June 19, 2004 No. 54- Federal Law “On meetings, rallies, demonstrations, processions and picketing”, as well as within the framework of ensuring the safety of life in the city of Moscow at the request of the Main Directorate of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation for Moscow, the Main Directorate of the Ministry of the Russian Federation for Civil Defense, Emergency Situations and liquidation of consequences of natural disasters in the city of Moscow, the Office of the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation in the city of Moscow and the Moscow region, the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation. Preventive medical examinations (examinations) of minors in order to obtain permission to engage in physical education and sports;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program, medical examination of athletes - members of sports teams of the city of Moscow is provided;
- Within the framework of the Territorial Program, orphans and children without parental care are provided with medical care of all types, including specialized, including high-tech, medical care, as well as medical rehabilitation, if they are diagnosed with diseases. At the same time, hospitalization of orphans and children left without parental care under the age of 15 years staying in inpatient institutions (in organizations for orphans and children without parental care, social service organizations) (if there are medical indications until they reach age 18 years), to provide them with medical care in a hospital setting, accompanied by employees of these organizations.
Quality of medical care
The care provided to the insured must be of adequate quality, therefore, the tasks of insurance company experts and freelance medical care quality experts include studying cases of medical care, identifying medical errors, finding out the causes of these errors, and recommendations for their prevention. For failure to fulfill obligations to provide the insured with medical care of appropriate quality and guaranteed volume, financial sanctions are applied to medical organizations. Special control is subject to cases when complaints are received from the insured about the availability and quality of medical care in a medical organization, deaths, including maternal and infant mortality, complications of diseases, and nosocomial infections.
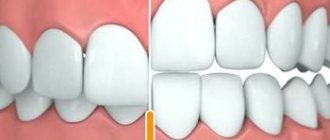
Cons of depulpation
Today it is known that unnecessarily depulpation can cause much more harm than good:
- After depulpation, the tooth becomes fragile and decays much faster
- During depulpation, the nerve may not be completely removed
- The dental canal may not be properly cleaned or filled.
- During treatment, gums may be injured
That is, a “dead” tooth will never be better than an ordinary healthy tooth that has not been opened. A crown can prolong its life for some time, but the risk of complications after depulpation and rapid tooth destruction is no less than if it were kept intact. That is why many professional dentists prefer to examine the tooth as thoroughly as possible and prepare it for prosthetics, but do not open it or remove the pulp.
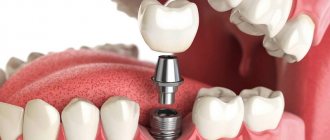
Home assistance for people with limited mobility
The provision of dental care at home is carried out within the framework of the order of the Moscow Department of Health dated July 7, 2009 No. 783 “On improving the provision of dental care to disabled people with severe disabilities.” Dental clinics have teams to provide therapeutic and orthopedic care to bedridden patients. To provide medical care at home, a preliminary examination by a local physician is required, followed by the issuance of a report on the general state of health and the possibility of providing assistance at home. Comprehensive dental care at home for disabled people with severe disabilities is provided in accordance with the list of dental services:
- Examination of the oral cavity.
- Determination of the state of oral hygiene with indication of dental plaque (hygiene index).
- Determination of the condition of periodontal tissues and oral mucosa.
- Manual removal of dental plaque and recommendations for brushing teeth.
- Carrying out atraumatic treatment of dental caries using glass ionomer cements for filling.
- Treatment of hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues.
- Treatment of pulpitis, periodontitis and periodontal diseases.
- Grinding of teeth.
- Taking impressions to make partial or complete removable dentures
- Correction of prostheses
- Removing crowns
- Prosthetic repair
- Surgical dental care is provided only in outpatient or inpatient settings upon referral from the dental clinic to which the patient is assigned.
Information updated 03/17/2021