A deep bite is a functional disorder in which the upper incisors overlap the lower ones by at least 1/3 of the crown surface when the dentitions are closed. The disease can cause teeth to become loose and fall out at a relatively early age.
What to do if a deep bite develops in adults? How to eliminate a functional disorder? You can get answers to these and other questions by carefully studying the article.
The essence of the application
With an anatomically correct bite, the upper front incisors protrude anteriorly in relation to the lower elements and overlap them by a third. Each chewing unit interacts with two antagonists. The mounds of elements overlap each other.
Several methods are available for correcting pathological occlusion, in particular the installation of permanent crowns.
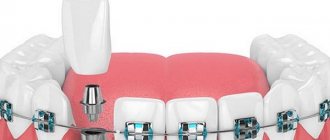
An artificial crown is a prosthesis that is applied to the prepared surface of a damaged element protruding above the gum tissue.
The purpose of prosthetics is to restore the correct shape, eliminate crowding and speech or chewing defects, and restore the aesthetics of teeth.
Comprehensive treatment plan
- Neuromuscular bite adjustment, teeth alignment using braces and creating space for implant prosthetics, osteopathic correction.
- Implantation to restore a missing tooth.
- Treatment and preparation of teeth for prosthetics.
- Complete dental prosthetics: crowns for chewing teeth, crowns for implants, veneers for front teeth.
For personal reasons, the patient refused to install veneers on her front teeth. Since the front teeth are the least affected by bruxism, their prosthetics are recommended, and the exclusion of this step does not affect the overall result. It was decided to use prosthetic teeth only in the lateral areas.
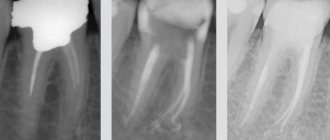
The patient agreed with the plan presented. For accurate calculations, in-depth diagnostics are required (photometry, photographs, CT, TRG in lateral projection, casts). The orthodontist combined the diagnostic data obtained, made the necessary calculations and began treatment.
The initial state:
Computed tomography for diagnosing the condition of the TMJ:
Indications and contraindications
Installation of crowns for bite correction is advisable if the patient has certain pathologies:
- Reduced or enlarged elements.
- The presence of defects on the surface of the teeth (chips, damage).
- Curvature or rotation of clinical crowns.
- Increased interdental spaces.
- The top of the unit is completely or partially destroyed.
- Implantation of an implant instead of a removed element.
- Unit divergence.
Covering with crowns does not correct every malocclusion. To eliminate some defects, it is necessary to use other methods that do not require grinding of the support unit.
Prosthetics cannot correct pronounced defects in which the shape and position of the clinical crown and root are disrupted. In such situations, alternative correction methods are used.
It is prohibited to use crowns if the wall thickness of the element is insufficient due to the risk of thermal burn of the pulp.
Veneers and inlays - modern types of dental prosthetics
A partial alternative to orthodontic structures can be elements made from high-tech ceramics, which allow:
- restore the integrity and functionality of the tooth;
- change its shape or “turn” around its axis;
- eliminate chips on its surface;
- visually reduce the large gap between the front teeth;
- restore the dentition when one or two teeth are lost (adhesive prosthetics).
The cost of microprosthetics is quite affordable, considering that along with the rapid restoration of the aesthetics of the dentition, the chewing ability of the teeth is also restored. Modern technologies make it possible to produce ceramic inlays and veneers that are indistinguishable in color and shape from the patient’s healthy teeth. Microprostheses are made by a dental technician using an individual impression, so they fit tightly to the surface of the teeth and have a long service life. It is also important that when microprosthetics is applied to a tooth, its healthy neighbors are not subjected to treatment and do not experience additional stress.
Quick appointment Free consultation
Material
The service life and characteristics of the product depend on the material of manufacture. Zirconium oxide structures are characterized by increased strength. Even titanium is inferior to this material in terms of strength.
Products are created from stainless steel, metal alloys, plastics, dental ceramics and combinations of materials.
Steel
Durable, technologically advanced and cheap material. Dental sockets are manufactured by stamping in laboratories or factories. The steel cap is open-forged to a configuration that matches the shape of the unit being restored. A coating of titanium nitride and a layer of ceramic or plastic is applied on top.
Due to low aesthetics, crowns are used on chewing elements.
Metal alloys
Combinations of cobalt, silver, titanium and gold are used. Products from refractory compositions are made by stamping, and from low-melting ones, casting and stamping technologies are used.
Prostheses made of noble metals are characterized by high biocompatibility with body tissues and long-lasting use.
Metal ceramics
A layer of ceramic is applied to the metal base, and the structure is fired in a kiln. The products combine the strength of metal and the aesthetics of ceramic composition.
Ceramics
Metal-free products are made from ceramics. They are highly aesthetic. Almost invisible in the oral cavity. Models made from durable types of dental ceramics are made using sintering, casting or sawing technology.
Metal-plastic
Models consisting of a metal base and a plastic layer. They are distinguished by functionality and aesthetics.
Stages of prosthetics
The procedure requires several visits to the dentist. Initially, the patient is examined, interviewed and examined. The doctor develops a treatment plan. The unit is then prepared. The dentist removes a layer of enamel from the tooth equal to the thickness of the crown wall. Local anesthesia is performed.
An impression of the dentition is taken and sent to a dental laboratory. The dental technician chooses the production technology depending on the type of prosthetic structure.
After making the prosthesis, the doctor fits the structure. Then grinding and polishing is carried out.
The prosthesis is fixed with cement. The stump and surface are first degreased and disinfected. At the last stage, the dentist removes excess cement.
Features of care
Crowns do not require special care. It is enough to observe daily oral hygiene and a gentle diet. It is recommended to get rid of the habit of smoking cigarettes.
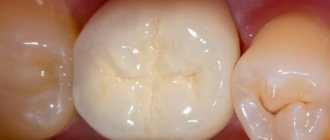
Ceramic inlay - microinsert that replaces a filling
As you know, before filling a tooth affected by caries, the doctor first excises its non-viable tissue. Therefore, in case of secondary caries, when the filling has to be re-placed, due to the significant size of the cavity, the tooth is already practically destroyed. The patient is recommended to undergo depulpation and cover it with a crown.
Recurrence of caries occurs due to the lack of proper sealing between the walls of the tooth and the composite filling, which decreases in volume during polymerization. The ceramic inlay is free of this drawback; it is manufactured individually with high precision and therefore fits tightly to the tooth. The ceramic material of the inlay does not shrink and does not change color or shape during use.
Microprosthetics with inlays is performed on teeth whose defects make up up to 30% of the volume of their coronal part, and allows you to create exact copies of teeth with the correct shape of the chewing surface.
In what cases is tooth lengthening necessary?
Indications for lengthening the crown of a tooth are aesthetic, functional (or retention) and restorative (restorative). The first group includes patients who want to increase the length of their teeth due to their cosmetic imperfections, which include an inharmonious relationship between the gums and teeth: when smiling, too much gum is exposed, and the teeth appear small, this is the so-called gummy smile.
In the realities of modern life, the number of patients with pathological tooth wear, which is provoked by constant stress or formed as a result of some bad habits, has increased significantly. In order to return teeth to their original appearance and size, and also to stop the progression of the process, surgical lengthening of the crowns of the teeth and optimal orthopedic correction are often necessary. In patients with complete destruction of the tooth crown, surgical lengthening makes it possible to create the effect of enveloping the hard tissues of the tooth or the so-called ferrule effect to fully distribute the chewing load and prevent fracture of the tooth root, as well as decementing of the orthopedic structure. This group is very significant from the total number of patients.
Therapeutic or orthopedic restoration, for example, of a chipped part of the crown of a front tooth, is actually also an extension of the clinical crown of this tooth due to the free space between the antagonist teeth. This is the last category of indications for lengthening the crown of a tooth, when, for example, due to a filling or ceramic veneer, the height of the tooth is essentially increased or restored.
Methods for correcting bite
There are five main ways to correct the bite, each of which corresponds to the conditions of the structural features of the jaws and the state of the patient’s dentition.
- The path of a set of regular exercises. During exercise, the load falls on the masticatory and facial muscles. Exercises contribute to the prevention, easy correction and correction of malocclusion. They also improve diction, form the correct position of the jaws and develop muscle memory of the correct movement; With all the advantages of this method of bite correction, there are also disadvantages - this process is quite lengthy and requires a lot of time, effort and perseverance from a person.
- Way of using orthodontic appliances . Trainers, plates, mouth guards and braces are used for this purpose. They allow you to correct your bite at any age using physical influence. One of the most effective methods of occlusion correction, the downside is some ease of use, and there are also restrictions on use in case of serious occlusion deformities.
- Path of surgery . Surgical correction is applied only to adult patients. The advantage is that it is possible to correct even the most complex malocclusion, the negative side is that surgical intervention is always a risk in itself.
- Complex method . The method combines the use of orthodontic and surgical intervention; This method is good for drastic actions in terms of bite correction.
- Orthopedic correction (prosthetics). This includes replacing an extracted tooth with a prosthesis, installing veneers and crowns. The method allows you to correct your bite in the shortest possible time.
The most drastic solution for correcting the bite is correction through the installation of crowns. This procedure is recommended by dentists when the dentition contains teeth whose size does not correspond to physiological harmony, as well as when some of them have large chips or are rotated relative to their own axis. Experts recommend this same method of correction in case of large interdental spaces.
Other methods of bite restoration
Modern dentistry offers a large arsenal of techniques for correcting bites. Experienced orthodontists use different designs depending on the complexity of each specific situation and the wishes of the patient. Let's look at the most popular orthodontic structures below.
Braces
The most common non-removable structures, made from a variety of materials to suit any budget (metal, plastic, ceramics, etc.) guarantee the achievement of the desired treatment results in the shortest possible time with a lower risk of relapse. Equally effective in both simple and very complex cases.
The only drawback is the visibility of braces when communicating with others, as well as the presence of slight discomfort when wearing them.
Aligners or aligners
These structures are removable, so more patients prefer their installation. They are made from hypoallergenic plastic or silicone, they are completely transparent and do not affect their appearance in any way.
Trainers
Another removable design that allows you to cope with minor bite pathologies. It is especially effective in childhood, when the jaw bones are not yet fully strengthened and formed. If there is one drawback, you cannot talk, eat or drink while wearing it.
Operation
Preference for this method is given only in the most complex and advanced cases, when no other method of bite correction can guarantee the desired effect. After surgery, braces or wearing removable structures may also be prescribed.
previous post
Photos of bite correction before and after
next entry
Why is it important not to delay starting treatment?
If the patient does not have a tooth in the upper jaw, then the lower antagonist teeth may begin to move upward. If there is no tooth in the lower jaw, then the upper teeth, which are located above this defect, can also move down. And jaw blocking can occur when a displaced tooth prevents chewing correctly, which sometimes causes dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. It happens that after the removal of the sixth and seventh teeth, the eighth teeth, wisdom teeth, erupt, then the orthodontist will have to make a decision about their removal or preservation.
Surgical lengthening of the coronal part of the tooth
Lengthening the tooth crown can be carried out using several techniques: surgical, orthodontic, orthopedic and therapeutic. The idea of lengthening is to increase the visible, that is, protruding above the gum, part of the tooth and/or restoration. Surgical lengthening of the crown of a tooth is performed on teeth with significant destruction of hard tissue, as well as when it is necessary to change the contour and position of the gums, for example, in people with a gummy smile. Many doctors mistakenly understand that the surgical lengthening method is only the excision of part of the gum - gingivectomy, but this technique is used only in cases of impaired passive teething, when there is no apical displacement of the gum and there is an excess of it on the tooth. Only in this case it is possible to remove part of the excess gingival margin without damaging the periodontium of the tooth. With thoughtless excision of the gingival margin and subsequent prosthetics of a given volume of the clinical crown of the tooth, a violation of the “biological width” - the zone of dentogingival attachment - occurs, which can lead to severe periodontal inflammation in this area and even tooth loss.
With the classical method of surgical lengthening, an important anatomical formation is excised - the periodontal groove, which provides protective, hygienic and immunological functions. After which it may be incompletely restored, followed by scarring and disruption of the original functions. To minimize this risk, a modernized technique of surgical tooth lengthening is used without excision of the natural gingival margin. At the moment, it is the safest and most effective way to make beautiful teeth of the desired length.
Diagnostics
Any treatment at Dial-Dent begins with a comprehensive diagnosis. This is an important stage, as it makes it possible to correctly draw up a treatment plan. This means 100% compliance with the timeframe and cost stated before treatment. Comprehensive diagnostics, including photographing the patient’s teeth, face and posture, taking impressions, making and analyzing plaster models of the jaws, OPTG and TRG images in the lateral projection, consultations with an orthopedist, orthodontist, neuromuscular dentist, osteopath, and psychologist, lasted two weeks. The cost of diagnostics was 20 thousand rubles. The main conclusion made by doctors after diagnosis is that orthodontic treatment and bite correction can be carried out without surgical intervention! The position of the lower jaw will be changed, but not surgically, but through a functional restructuring of the temporomandibular joints. Such treatment will give a stable result, the restructuring will take place gradually, the posture will have time to adapt to the new position of the lower jaw, in which an osteopath will provide indispensable assistance. The patient will avoid all risks of surgery.
Diagnosis by orthodontist O.A. Baranova: crowding of the frontal group of teeth of the lower dentition, rotation of tooth 3.3, oral position of tooth 3.4, narrowing and lengthening of the upper dentition, narrowing and shortening of the lower dentition, deep distal bite (skeletal form of the anomaly).
A neuromuscular dentist performed a diagnosis of muscle function and movement of the lower jaw.
Myography at rest before treatment. The functioning of the masticatory and sublingual muscles is impaired and there is an imbalance.
Load myography before treatment. Chronic fatigue of the masticatory muscles is observed.
Axiography of the movement of the lower jaw before treatment. The movement graph indicates a strong displacement of the lower jaw back, displacement of the disc of the temporomandibular joints. Rotation of the C1–C3 vertebrae (the first three cervical vertebrae) was diagnosed. The functioning of such organs and parts of the body as the inner and outer ear, brain, eyes, visual, auditory, facial nerves, temporal joints, and teeth depends on the correct position of these vertebrae. Symptoms of displacement of the first cervical vertebrae: headaches, high blood pressure, pain in the temporal joints, eye diseases, hearing loss, neuritis.
Using special equipment, the physiological position of the lower jaw was determined. This position will be fixed with special overlays on the teeth (orthotic). A non-removable orthotic installed on the teeth will help the muscles rebuild their work and secure the correct trajectory of movement of the lower jaw, in which there is no overload in the temporal joints.