Teeth are important organs that provide several human needs at once: an aesthetic effect and calmness of the nervous system, chewing food and the proper functioning of the digestive system, the formation of a bite, and therefore correct speech. At the same time, they are very delicate, and this is fraught with serious health problems for a person. If many often encounter painful caries, cysts in the gums, and destruction of the crown, then the situation when such a terrible disease as tooth cancer develops turns out to be very unexpected. If only because many people cannot even think about this type of oncology. The director of the dental studio Fedor Zakharov told AiF.ru about how tooth cancer can be hidden behind a harmless wound on the gum or a lump on the lip .
Question and answer Which brush is better: with natural bristles or synthetic?
What is the essence of the problem
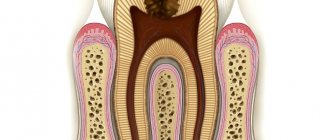
The term “dental cancer” is used in everyday life, but it is not entirely correct. Yes, tumors can develop from tooth tissue: odontoma, cementoma, etc. But these are benign formations. Malignant is adamantinoma, which develops from tooth enamel, but is extremely rare and not fully understood. Most often the problem occurs in the lower jaw. Adamantinoma, in cases where it has been discovered, affects people at a fairly young age: 18-26 years. It is located in the area of the outer chewing teeth and in the corner of the mandibular bone. It can be of two types: dense and cystic. The first is a formation with a large number of cavities. The second is a formation filled with a brown mass.
The process resembles a cystic lesion of the cavity. As the tumor grows, the bone structures begin to thicken, which later combine into one bulge.
What can provoke such a terrible disease? These can be the most trivial reasons: chronic injuries to the mucous membrane, exposure to ionizing radiation, bad habits (smoking, chewing nasvay), occupational hazards (working in hot shops or dusty rooms), unhealthy diet (excessive consumption of spicy, pungent foods). In addition, there is a risk of developing jaw cancer in cancer patients with tumors of the kidneys, stomach, and lungs. In this case, they will talk about secondary oncology.
Drink milk and chew apples. How to eat for healthy teeth Read more
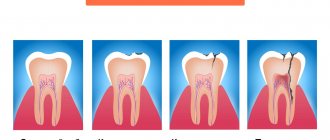
Tooth cyst
A dental cyst is a formation resembling a capsule, localized in the area of the apex of the root canal of a problem tooth, in the bone tissue of the jaw. Standard sizes
neoplasms -
from 0.5 to 2 cm
. Contents: serous exudate. The shell consists of connective tissue.
Causes of cysts:
- Dental or somatic diseases (for example, sinusitis, sinusitis).
- Chronic periodontitis - the root membrane and peri-root tissue become inflamed.
- Consequence of traumatic injuries.
Types of cysts
Dentists distinguish several types of such neoplasms. A cyst happens:
- Radicular
, located next to the root of the tooth. In the vast majority of cases, this is a consequence of inflammatory processes (for example, periodontitis). - Follicular
, adjacent to the crown. Formed when a formed but not yet erupting tooth bud becomes infected. - Paradental
. It is typical for heavy growth of the eighth molars - the tissues become inflamed, the process is difficult. - Teething
. Occurs during the period of change from primary teeth to permanent ones. - Retention cysts
are formed as a result of the outflow of secretions in the salivary glands. Typical localization is the sublingual area, mucous membranes of the cheeks, lips, and bottom of the tongue. - A keratocyst
occurs during pathological primary development of the unit. - Residual
- a consequence of complex or poor-quality tooth extraction.
Symptoms
The initial stages of cyst formation are asymptomatic. The first signs appear when the cyst has already reached a fairly large size - 0.5 cm or more. The capsule puts pressure on the tissue, and vague sensations begin, causing discomfort.
An increase in formation leads to painful sensations that do not go away after taking analgesics. When intensive formation of pus occurs in the capsule, the pain intensifies and swelling appears. Sometimes the temperature rises. Symptoms of a mature cyst are a fistula in the gum, gumboil.
Treatment of cysts
Dentists try to save the tooth, so they choose gentle techniques in each case. Deleting a unit is possible only in advanced or exceptional cases.
Therapeutic methods:
- Antiseptic treatment. In case of a cyst or granuloma, purulent exudate is pumped out of the cavity and disinfectant and anti-inflammatory drugs are administered.
- Using a laser. The beam not only removes the formation, but also has a disinfecting effect on the tissue.
Surgical methods
applicable if the cyst is located in a dangerous place, or its size is quite large (more than 2 cm, usually 3-4 centimeters). The surgeon opens the cyst, removes the pus, injects an antiseptic, and sutures it. Less commonly, the front part of the capsule or the neoplasm with the root of the tooth or its fragment is removed.
Dangerous symptoms
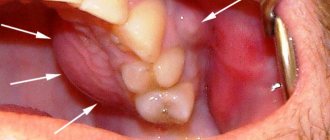
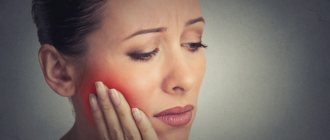
It is clear that diagnosing dental cancer is not so easy. It is worth being wary in cases where there is the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers on the oral mucosa, deformations that are sometimes already noticeable to the eye, pain in untreated and intact teeth, when sensitivity changes. These are alarm bells that need to be responded to urgently and immediately run to the dentist. The earlier a tumor is detected, the greater the chance of minimizing losses.
It is also worth considering such an important sign as bleeding gums. If in a normal state, in order for blood to flow, you need to damage the gum, then in the case of cancer, light pressure will be enough. Also, swelling of the gums and increased body temperature may appear in parallel.
Oral tumors: detection and treatment
REASONS FOR THE APPEARANCE
Tumors are divided into two groups: epithelial and nonepithelial.
The most common tumors are those that develop from glandular, flat, and tooth-forming epithelial tissue. Depending on their location, tumors of the gums, tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, hard and soft palate, as well as the salivary gland in the sublingual area are distinguished.
The causes of benign tumors of the oral mucosa are not entirely clear. Based on experience and observations, doctors give the following recommendations to minimize risks:
- Monitor the condition of chronic ulcers and cracks formed due to poor-quality dentures and crowns or injury to soft tissues from chipped teeth.
- Avoid using tobacco in any form. Its long-term use can lead to consequences in the form of a tumor.
- Avoid eating too hot foods, spices, alcohol and foods high in acids. This will prevent burns and irritation of the mucous membrane.
A timely visit to a specialist when the first symptoms are detected can save you from cancer: a dangerous disease that is difficult to treat.
TYPES OF NEW FORMATIONS
Neoplasms arise in various types of tissues of the oral cavity: connective tissues, bones, nerves and muscles. Some tumors cause irritation and discomfort. It is possible to notice them on your own, but often they are discovered only by a specialist during an examination. Benign tumors are divided into several types:
Epithelial:
Papillomas. They consist of stratified squamous epithelial cells localized on the tongue, lips, soft or hard palate. Papillomas resemble a protrusion on the mucous membrane with a smooth surface or papillary growths. Usually papillomas are single, but multiple ones are also found. Over time, they become overgrown with keratinized epithelium and become whitish and rough.
Nevi. In rare cases, they occur in the mouth. They are convex with varying degrees of pigmentation: from pink to brown. Some nevi can transform into melanoma.
Glands of Serres. They are located in the area of the alveolar process, resemble hemispherical dense formations of light yellow color, and can be multiple.
Connective tissue:
Fibroids. Often found in the tongue area, on the palate and lower lip. These are oval or round formations that are difficult to notice: their color blends with the mucous membrane.
Myomas. Usually develop from muscle tissue. Observed in the thickness of the tongue in the form of nodular formations.
Myxomas. They have a lumpy, rounded or papillary surface. Localized in the area of the hard palate and alveolar process.
Epulis. They arise on the gum, growing from its deep layers, as well as from the periosteum and periodontal tissues.
Pyogenic granuloma. It develops from the connective tissue elements of the oral cavity and from the mucous membrane after injury. It grows quickly, has a burgundy color, and bleeds when touched.
Neuromas. They are the result of the proliferation of Schwann sheath cells of nerve fibers. One of the few formations that causes discomfort upon palpation.
Vascular:
Hemangiomas. They are among the most common. They are divided into capillary, cavernous, capillary-cavernous and mixed. They turn pale or shrink in size when touched and may bleed.
Lymphangiomas. Appear due to disorders of embryogenesis of the lymphatic system. Often discovered in infancy. Visually they resemble swelling in the oral cavity, limited or diffuse. Prone to inflammation after injury to the mucous membrane or exacerbation of a chronic inflammatory disease of the nasopharynx.
At the first alarming signs, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis and identification of neoplasms.
Tumor in the oral cavity: symptoms
The cause of the appearance of benign neoplasms in the oral cavity can be disturbances in the acid-base balance, neglect of hygiene, mechanical damage and bad habits. These risk factors are a serious reason to see a doctor for an examination.
There are several striking symptoms of the presence of a tumor:
- Discomfort when talking and eating.
- Unpleasant or painful sensations of a constant nature.
- Feeling of the presence of a foreign body.
Tumors do not cause any problems with your health, but you should not ignore the symptoms. Systematic irritation of the affected area can contribute to the degeneration of a neoplasm into a malignant one.
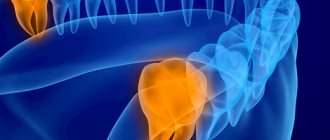
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
Oral tumors may be discovered by a dentist during an examination or treatment. Determining the depth of their germination is possible using ultrasound. X-ray examination is necessary to assess the condition of bone tissue. For gum fibromatosis, an orthopantomogram is performed to identify areas of destruction of the alveolar process.
Depending on the type of tumor, the following types of surgical treatment are used:
- Laser removal.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction.
- Surgical excision.
- Sclerotherapy.
There are diffuse tumors. They tend to grow rapidly and penetrate into the deep layers of the mucosa. Their removal is carried out in several stages. Fibromatous growths are excised along with the periosteum. Areas of affected bone tissue are treated with a milling cutter and also removed by coagulation (cauterization).
Vascular tumors are sclerosed by introducing special solutions into the tumor vessels. Active substances damage the walls of blood vessels, causing further scarring.
A tumor is a formation consisting of cells that have lost the ability to grow under controlled conditions. A separate branch of medicine—oncology—is devoted to neoplasms. This science studies the development, diagnosis and treatment of both benign and malignant tumors. A dentist can refer you to an oncologist to make an accurate diagnosis.
Extrodent specialists have a common goal: to preserve the health of patients in all available ways. This is possible thanks to high-quality technical equipment and the professionalism of the clinic’s doctors. Complex clinical cases are their area of interest and competence, so the result of their work is always successful.
We will take care of your health and give you a full life!
Treatment
Tooth cancer requires surgery. And often, after tumor removal, reconstructive bone surgery may be required. Naturally, auxiliary types of therapy will also be determined if necessary: chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc.
What happens to your teeth if you don't brush them? Infographics Read more
Problem statistics
Tooth cancer, like any other type of oncology, is dangerous due to its active development. And here the rule also applies: the earlier it is detected, the greater the chances of recovery. According to statistics, tooth cancer cured at stages 1-2 gives an 80% chance of five-year survival, at stage 3 the prognosis is 40%, at stage 4 - less than 15%. It is important to understand that the jaw is located close to the brain, and oncology is a metastatic disease. Therefore, you should not play Russian roulette; it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
At the same time, no one has canceled prevention: even if nothing bothers you, you should visit the dentist once every six months. This will allow you to identify any pathologies at an early stage. After all, prevention is easier than cure.