From this article you will learn:
- why is my cheek swollen after removal,
- How long does swelling of the cheek or gum last?
- What does the temperature say after tooth extraction?
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
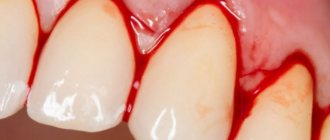
If your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction, this in most cases is an unfavorable symptom of the development of inflammation, for example, this may indicate the development of alveolitis (suppuration of a blood clot in the socket of the extracted tooth). Swelling of the cheek can also be caused by the formation of a hematoma along the transitional fold, the formation of a purulent abscess on the gum in the area of the extracted tooth, and other reasons.
However, in some cases, swelling after tooth extraction may be natural, without requiring a second visit to the doctor. As you probably know, swelling of the soft tissues after an injury or surgery is the norm, and therefore it is logical after a complex tooth extraction (for example, when the extraction was carried out with an incision in the gums and sawing out the roots of the tooth with a drill).
Swelling of the cheek after wisdom tooth removal –
Moreover, some patients complain only that their gums are swollen after tooth extraction, and they do not have visible swelling of the cheek. The appearance of swelling of the gums has the same reasons (as with swelling of the cheeks), it’s just that there are features of the course of the inflammatory process - depending on the location of the inflammatory focus. For example, if the inflammatory focus is located closer to the transitional fold (i.e., the place where the mucous membrane of the gums enters the cheek), then this is more likely to lead to swelling of the soft tissues of the face.
Below we will examine in detail the cases - when the appearance of edema is quite natural and does not pose a danger, as well as situations in which you urgently need to contact a dental surgeon for a re-examination.
Why did gumboil appear after dental treatment?
Swelling of the gums indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process, which caused the complication. If painful sensations are observed against the background of the tumor, the main reasons for this may be:
- Periodontal inflammation. The tumor is observed on both cheeks, but pronounced swelling occurs only on the infected side.
- Neglected teeth, improper placement of fillings. Before swelling occurs, pain occurs. After 2-3 days, a flux with pus may form.
- Incorrect development of wisdom teeth. A hood forms from the mucous membrane, in which food particles accumulate and become inflamed.
- Removal of a tooth. Due to mechanical damage to the tissue, swelling can be considered normal.
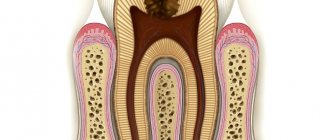
- Cyst. The inflammatory process lasts for 1.5-2 years and injures the periosteum. The pathology occurs against a background of severe pain.
Attention! Swelling of the cheek after dental treatment can develop due to infection in the socket, which not only causes discomfort and swelling, but can also lead to more serious consequences.
If there is no pain during swelling, the reasons for this are as follows:
- allergic reaction to anesthesia, dental materials (swelling sometimes affects the entire face);
- removal of the nerve: part of the nerve may remain in the canals; after installation of the filling, flux appears;
- dissection of the gums, extracted tooth (in these cases, swelling is normal);
- infectious inflammation of the lymph in children, accompanied by aches and fever;
- neurological diseases accompanied by swelling, congestion in the ears, sore throat, weakness.
Important! In the case of severe pathologies of internal organs, the drainage of fluid is often disrupted; as a result, it accumulates in the nose, cheeks, neck, cheekbones and near the eyes.
Clinical picture
A clear sign of gumboil is a lump on the gum with purulent contents. Before its formation, the disease makes itself felt by throbbing pain in the tooth. Symptoms of the pathology are also:
- swelling and redness of the gums,
- swelling of the cheek or lip,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
- pain when opening the mouth and swallowing,
- discomfort when pressing on a tooth,
- increase in body temperature,
- excessive weakness
- decreased appetite.
If you detect at least one of the listed signs of flux, you should contact the dentist. You should not warm the sore spot with a warm compress, take antibiotics without a doctor’s prescription, or open an abscess at home.
What does flux look like?
It is of infectious origin, the process occurs against the background of inflammation of the body of the jaw or in the periosteum. Flux is formed not only after dental surgery, but also after furunculosis or tonsillitis. If the cheek and gums are swollen, there is throbbing or mild pain, in advanced stages pus may appear and the temperature may rise. On the upper jaw, the flux covers the lip, cheek, gum and nasolabial area. In addition to the face, the infection often spreads to the neck.
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. After using topical medications, you should not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours.
When to see a doctor
Often this symptom tells us that not everything in our body is as good as we would like. Make an appointment with your doctor if:
- you have swelling, but no toothache. Usually this phenomenon occurs after pulpitis, when the doctor has not completely cleaned the canals. Due to the fact that the nerves are no longer there, there simply cannot be pain. The cheeks and gums, which are very swollen and painful, will tell you about the problem;
- Clinical signs include shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. This may indicate the presence of allergies in the body;
- intense pain in the socket area. Symptoms should, at least gradually, subside;
- fever, which is accompanied by general malaise. This may indicate the presence of intoxication in the body;
- strong odor from the mouth. Most likely you will need to clean the hole from the accumulation of pus;
- pain when swallowing, jaw movements began to bring discomfort;
- swelling occurred three days after the intervention, which is often observed with alveolitis.
You shouldn’t deal with complications on your own and put off visiting a doctor, especially if your condition is getting worse every day.
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Anesthesia makes tooth extraction easier. But, if after treatment of a tooth your cheek is swollen, you should find out the origin of the pathology. You may need treatment for your gums. Discomfort appears in many patients after depulpation. Pain and swelling on the inside of the cheek can be observed from 2 hours to 7 days. If discomfort intensifies or occurs 2 days after surgery, you should immediately consult a dentist.
If, after removing the nerve, in addition to painful sensations, the gums become inflamed, purulent discharge appears, and the temperature rises, you should visit a dentist. He will find out why the cheek is swollen and how to remove the gumboil.
Attention! You cannot take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs before consulting a doctor; this will complicate the diagnosis, which will not allow you to prescribe adequate treatment.
Remedies for eliminating swelling after tooth extraction
The factors that determine how long it takes for swelling to subside after tooth extraction (over time) include the quality of the rehabilitation period. To avoid infection, the doctor washes the hole with antiseptic solutions, and in case of a more extensive intervention, administers antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Oxamp, Ofloxacin and others). Antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are often prescribed in the following days. If the patient has a weakened immune system, it is recommended to take vitamins. If, a few days after removal, negative symptoms increase, there is no need to self-medicate and drink handfuls of painkillers: they will not eliminate the problem and can negatively affect your health. After the extraction procedure, the patient must be aware and follow a number of necessary measures that will help to recover faster and avoid complications.
- Remove the tampon no earlier than half an hour after tooth extraction.
- You can eat warm and soft food only after 3-4 hours. You should not chew on the side where the surgery was performed.
- It is not recommended to eat solid, as well as too hot and cold foods for 10-12 days after tooth extraction.
- Hygiene must be very careful, especially in the first days. You should not brush the area around the operation so as not to destroy the blood clot. You also need to be careful when rinsing.
- Quit alcohol and tobacco (preferably for the entire period of rehabilitation).
- You need to avoid physical activity for at least a week and avoid visiting the sauna and swimming pool.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Yaroslav Ikonnikov
What to do if swelling appears after treatment at the dentist
If after tooth extraction your cheek is swollen from the tooth, there is no need to worry - this is a normal reaction. You can take a pain reliever that your dentist recommends. When a pathological condition is accompanied by pain and weakness, the temperature should be measured.
Edema does not always indicate a complication; it is worth distinguishing a simple reaction of the body from a pathological condition. Don't worry if:
- the flux disappears 3 days after surgery;
- the swelling is not pronounced and does not increase in size;
- no temperature or it does not exceed 37.5 degrees;
- the pain is aching, slight, gradually goes away, eliminated with analgesics;
- in the hole there is a bloody dense clot, which is covered with fibrous tissue within 2-3 days.
On a note! Do not apply hot lotions to the injured area, release pus yourself, or massage the gums. This will provoke further development of the infection, which will lead to serious consequences.
The following symptoms indicate complications:
- the flux grows;
- there is severe pain that cannot be relieved with analgesics;
- tension together with surgery;
- temperature over 37.5-37.6 degrees;
- it hurts to swallow, speak, open your mouth;
- there is no blood clot in the hole or it is covered with a green, gray or yellow coating;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- itching, hyperemia, shortness of breath - indicate an allergic reaction.
Attention! If you have any of the symptoms, you should consult your doctor. Such signs indicate infection. If an operation was performed, the treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon or an endodontist if the root canals were cleaned.
Swelling that is not dangerous
For each patient, tooth extraction is a serious surgical action aimed at healing through injury. When a tooth is extracted, blood vessels rupture and gum tissue is damaged. The longer and more difficult the surgery, the longer the damaged tissue will remain swollen and painful.
Important! Even uncomplicated extraction of a single-rooted tooth leads to swelling, which naturally subsides when impaired blood circulation returns to normal. Physiological tumor of the gingival tissue after extraction is not a complication and does not pose a threat to the patient’s health.
When edema develops, it is important to understand whether the situation is within normal limits or requires medical intervention
Gum swelling is not dangerous in the following cases:
- general condition, despite the presence of a tumor, is satisfactory;
- the temperature is normal or slightly increased only on the day of removal;
- the tumor is localized in one place and does not spread to facial tissues;
- the pain is present, but is fading and lasts no more than five days;
- immediately after the operation, the cheek swells, but no increase in pain is observed, and the swelling subsides within a few hours;
- facial skin or oral mucous membranes are of normal color, without redness;
- there is no tissue decay, there is no unpleasant odor from the gums, and there is no unpleasant taste in the mouth.
As for postoperative pain, it is always present in the background. Simple removal is accompanied by aching pain for three to four days. A difficult one can cause pain for a week.
Pain after tooth extraction is common
The main evidence that everything is normal is a gradual decrease in swelling and pain. If everything happens this way, you don’t need to do anything about the swelling, just watch it. You can take painkillers for pain.
When does swelling of the cheek go away?
How long the swelling lasts after tooth treatment depends on the degree of damage. Swelling causes injury to tissues, ligaments, and blood vessels during surgery or root removal. After such an intervention, swelling is normal. It can last from 2 hours and last for 7 days or the first day after surgery. There are no painful sensations.
Swelling after surgery on a wisdom tooth can last 4 days longer and persists for 11 days. If the surgery was serious, a bruise may form on the cheek. Pronounced swelling, increasing every day, pain is a reason to urgently consult a dentist.
In what cases can swelling of the cheek be normal?
Please note that swelling of the cheek may appear not only immediately after tooth extraction (or the next morning), but only a few days later. The last scenario will definitely indicate the development of inflammation. Therefore, the norm may be the occurrence of swelling of the cheek or gums - in the first hours after removal, or the next morning. When it might be normal:
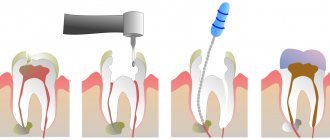
- After a complex tooth extraction – in this case, tooth extraction is often accompanied by incisions in the gums, cutting out bone tissue with a drill, and dislocation of tooth roots with special elevators. All this leads to significant trauma to bone tissue, as well as soft gum tissue. And therefore, it is quite natural that after a complex extraction you may experience swelling, and this happens especially often when it comes to the complex removal of wisdom teeth.
What does a complex wisdom tooth extraction look like?Moreover, if your cheek is swollen after the removal of the 8th tooth, then the appearance of swelling of the surrounding soft tissues can gradually lead not only to facial asymmetry, but also to temporary difficulty opening the mouth, as well as painful swallowing. Therefore, according to the rules, after a complex tooth extraction, the doctor is always obliged to schedule the patient for a second examination (the very next day) so as not to miss the development of inflammatory complications.
- After the removal of wisdom teeth , swelling can appear not only after a complex wisdom tooth removal, but also if the removal of the 8th tooth was relatively simple. The fact is that with a small length of the body of the lower jaw, with a small size of the upper jaw, the wisdom teeth may be partially located in the depths of the soft tissues (moving soft tissues of the oral cavity). Such a tooth can be removed easily, but with such localization of 8 teeth, swelling of the soft tissues can easily occur.
- When a tooth was removed due to inflammation - if the tooth was removed due to purulent inflammation (i.e. at the time of removal you could have symptoms such as swelling of the gums, pain when biting the tooth, the presence of a fistula on the gum with purulent discharge).
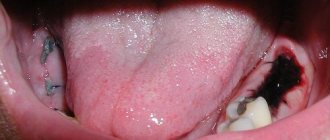
According to the rules, in this case, after removal, the doctor must wash the wound with an antiseptic, put medicine (Alvogel) into the hole of the extracted tooth, and also prescribe antibiotics to prevent suppuration of the blood clot in the hole. The development of soft tissue edema in this case is due to the fact that any surgical operation on inflamed tissues always leads to more pronounced edema. Those. in this case, swelling will not necessarily indicate the development of a complication. But on the other hand (even with prophylactic antibiotics) increasing swelling of the cheek may also indicate a complication that requires a visit to the doctor. - If you have had a gum incision made – if the tooth was removed due to pain and inflammation, then an inflammatory infiltrate (slight swelling) could be present on the gum or in the area of the transitional fold. Making an incision in this case has the purpose of 1) releasing pus if a purulent abscess has already formed, 2) preventing the formation of an abscess after tooth extraction. An incision is made in the center of the infiltrate; usually a thin rubber drainage is inserted inside it.
Making an incision in the area of the transitional fold (i.e., where the gum meets the cheek) can always lead to the appearance or increase of existing swelling of the cheek. According to the rules, if a doctor opens an abscess along a transitional fold, the patient should always be scheduled for a re-examination the next day. If the infiltrate was opened, but no pus was obtained, then in the absence of complaints from the patient, the latter is sometimes recommended to independently remove the drainage from the wound after a few days (24stoma.ru).Opening an abscess along the transitional fold -
- Complaints that the cheek is swollen after tooth extraction occur very often in certain groups of patients. For example, hypertensive patients, as well as people with a significant amount of subcutaneous fat on the face, are predisposed to the appearance of edema after tooth extraction. In these patients, swelling of the cheek may appear after a simple simple removal.
What symptoms in this case will indicate the absence of inflammatory complications -
As we said above: swelling after tooth extraction usually appears either within a few hours after the intervention, or the next morning. Accordingly, only over the next day will it be possible to draw timid conclusions about whether there is a reason to worry or whether you need to urgently run to the doctor for a second examination. Let's look at the signs that indicate that the development of edema does not require urgent intervention -
- The swelling that appears is not too pronounced and does not tend to increase. The latter means that the swelling that occurs the next morning after tooth extraction should not increase further in the evening. But if the swelling tends to further increase, this is a bad prognastic sign. Also not a very good sign is hardening of soft tissues, i.e. Normally, edematous tissue should be soft, but if tissue compaction (infiltrate) appears in the center of the edema, then this is a sign of suppuration.
- If you do not have a fever, especially an increasing one - if you did not have an elevated temperature at the time of tooth extraction, then normally it should not be elevated the day after the extraction.
At the same time, a slight temperature of up to 37.5 in the evening on the day of removal (after a complex removal or removal due to inflammation) is considered normal. If you had a high temperature before removal, then from the next day it should begin to decrease progressively. If an elevated temperature after tooth extraction appears only the next day or even later, this most likely indicates the development of complications and requires immediate consultation with a doctor.
- If you do not have severe pain, especially increasing pain, after a simple removal you may feel pain for only 1 day, after a complex removal it is normal for only a few days. The appearance of severe pain and prolonged pain for 4-7 days only indicate that the removal is excessively traumatic, and this is a question for the doctor’s skills. In any case, normally the pain should progressively decrease every day, but if the pain does not decrease or occurs, this is a symptom of the development of complications.
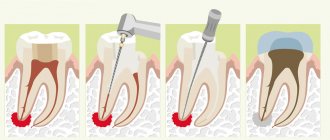
- The hole must be closed with a dense blood clot - after removal, the hole is filled with blood, which immediately coagulates, forming a blood clot in the hole of the extracted tooth. In some cases, the clot may not form, or it may fall out due to the patient rinsing the mouth too much. The absence of a blood clot in the socket will inevitably lead to the development of alveolitis (inflammation of the socket of an extracted tooth).
A fresh clot normally has a dark burgundy color, but after some time a whitish or grayish-yellow fibrinous coating will appear on its surface (this is normal and does not indicate inflammation). The clot should be dense, without an unpleasant odor. Pay attention to how the blood clot should look on the day of removal and a few days after (Fig. 6-7).What should a blood clot normally look like?
After tooth extraction, the cheek is swollen: what to do in this way, let's summarize... if the resulting swelling of the cheek is 1) soft to the touch and does not tend to increase and harden, 2) if there is no temperature, difficulty opening the mouth and painful swallowing, 3) if the hole is closed by a dense blood clot, 3) if there is no severe or constant aching pain in the area of the socket of the extracted tooth, then, in principle, we do not see any indication for an urgent visit to the dentist for a second examination.
How long does swelling last after tooth extraction?
There is no average answer to this question, because... much depends on the degree of trauma of the removal and the characteristics of the body. In some patients, swelling of the cheek may last only a few days, while in others it can last for a week. The problem here is that after a traumatic extraction (especially with cutting out the roots with a drill), very often a sluggish inflammation can occur in the socket of the extracted tooth for a very long time.
In this case, there may be only slight discomfort or no pain at all, but the swelling in this case can last quite a long time. Therefore, after a complex extraction, it is always worth going to the doctor for a second examination to see if the socket of the extracted tooth and the blood clot in it are normal. By the way, you can also make the swelling go away faster.
How to relieve swelling after tooth extraction -
So, if the appearance of edema is associated with traumatic removal or making an incision along the transitional fold, we can significantly increase the rate of its reduction. This can be done at home using compresses with a dimexide solution (diluted 1:4 or 1:5, i.e. to obtain a 20 or 25% concentration). Dimexide is diluted with lukewarm boiled water.
A gauze bandage is soaked in the diluted solution and applied to the site of swelling for 20 minutes. A layer of cling film is placed over the gauze bandage, and then secured to the head with a bandage. The procedure can be done 1-2 times a day, the duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. An important point - in this case, you cannot place a thick cloth or towel on top of the cling film (this is usually done to make a thermal compress). If there is inflammation, a heat compress can be harmful.
How to treat gumboil on the cheek
Once a tumor develops, antibiotics are often indispensable. The dentist selects them taking into account the stage of the pathology and the characteristics of the body. Antibiotic therapy should be completed to the end, otherwise further treatment will be greatly complicated.
If surgery is required, all activities are carried out in a dental clinic. For any complication, the patient is given local or general anesthesia. The gum is incised and the accumulated pus is completely pumped out. A drainage is placed to quickly remove fluid. The patient is prescribed antibiotics to allow the soft tissues to recover faster. In case of severe damage, the gum is sutured. In the absence of complications, this is not required.
How to remove swelling from the gums through surgery:
- In case of complicated flux, urgent hospitalization in a dental clinic and an operation performed by a dental surgeon are necessary.
- If an inflammatory process is diagnosed due to dental problems, endodontic therapy (cleaning and filling the canals) or root removal will be required.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed to treat infection in many situations. In case of serious complications, combination drugs are used to treat severe swelling, selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogens.
- Surgical treatment - incision of the abscess (on the face and oral cavity - the incision is made in both areas), removal of purulent discharge, treatment with disinfectants, installation of drainage. In severe cases, general anesthesia is used.
- Additional therapy - analgesics to eliminate discomfort, antipyretic drugs, large amounts of fluid (if necessary, fluid is introduced into the body by infusion during hospitalization).
Chronic pathology often occurs without pronounced symptoms, pus appears gradually. In this situation, the dentist uses a therapeutic approach, both surgical and conservative. Surgery can be replaced with herbs or antibiotics, or used as an additional treatment after consultation with a specialist.
Swelling of the cheek does not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
A tumor after depulpation is normal and does not require serious treatment. When the gumboil gradually grows, pain is observed against this background, and the help of a dentist is required. In case of serious complications, surgical intervention while taking antibiotics is indicated. The doctor's consultation
When the tumor is predetermined
Everyone knows that you need to go to the dentist when a tooth just begins to bother you. But in real life this does not always happen. The result is tooth extraction as a last resort. And since treatment cannot be carried out, it means that there are serious problems in the oral cavity. Even when absolutely healthy tissues are damaged, for example by a cut or an injection, they swell. Moreover, a tumor occurs if the extracted tooth was adjacent to infections of the oral cavity or there are other dental problems.
Swelling after tooth extraction is inevitable if there are infectious processes in the oral cavity
By the way. The duration and intensity of swelling after extraction directly depends on factors such as the qualifications of the dental surgeon, the choice of anesthesia method, types of anesthesia, the complexity of the surgical operation, and the quality of the antiseptic used.
Table. Causes of soft tissue tumors
| Reason for swelling | Description |
| Alveolitis | A disease in which the socket of an extracted tooth becomes inflamed due to infection. It is not necessary that microbes are introduced into the socket due to non-compliance with the operation protocol (although such cases have occurred). Alveolitis after extraction often occurs against the background of existing inflammatory processes, the most common of which are periodontitis and stomatitis. After removal, the infection will spread and develop with renewed vigor. In addition to the inevitable swelling, the patient will feel severe pain and a bad smell will come from the mouth. |
| Difficult removal with incision of gum tissue | To remove a problematic tooth during an active purulent process, you must first release the pus. To free the gum tissue from the pus sac and remove the abscess, it is necessary to cut the gum. Only after this can the surgeon remove the tooth cleanly, along with the roots. Of course, additional trauma to the gum in the form of a cut increases the swelling that forms after extraction. |
| Traumatic extraction | Occurs when a dystopic (improperly located, growing at an angle, protruding from the dentition) tooth is subject to removal. To remove such a tooth, which is practically healthy, firmly embedded in the gingival tissue, and is subject to extraction only due to its dangerous location for other teeth or mucous membranes, significant efforts will be required. The gums swell very much when such a tooth is literally “torn out” from the jaw. |
| Deep extraction | Typically, it is subjected to rear molars, or simply teeth that have not fully erupted (impacted) for various reasons. After this procedure, severe postoperative swelling is inevitable. |
| Presence of chronic diseases not related to dentistry | Swelling may be increased if there are health conditions such as diabetes or hypertension, blood and vascular diseases, or low immunity. In this case, the extraction is always more difficult and is accompanied by painful swelling of the tissue. |