Self-help: ways to stop bleeding
When blood bleeds for a long time after the removal of a wisdom tooth, it brings discomfort on a physical and emotional level. If you can't get to the dentist, use gauze swabs. Fold a small piece of bandage into several layers, apply it to the hole and bite firmly. Keep for 20 minutes. To disinfect, you can soak a swab in hydrogen peroxide. Bleeding after wisdom tooth removal can be stopped by this method both day and night. Another option is to use ice. Apply to your cheek and apply for 5 minutes with short pauses. If the patient has a history of hypertension, a high blood pressure pill should be taken.
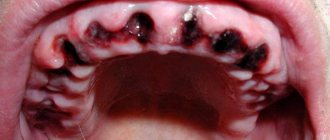
The main causes of bleeding gums
There may be several reasons - from gum disease to an incorrectly selected brush and stones on the teeth.
- A common cause of bleeding from the gums when brushing teeth is a common disease in children and adults - periodontal disease. Dental bacteria infect the oral cavity and then penetrate into the periodontal pockets. The gums in the affected area may be sore and swollen, and blood may appear when brushing your teeth. Treatment of periodontal disease will help you get rid of this problem.
- Another fairly common reason why gums bleed and become inflamed is the formation of stones on the teeth and under the gums due to poor oral hygiene. You need to clean plaque at least once a year, this is done by your dentist.
- Pregnancy and the resulting hormonal changes cause gum pain and bleeding.
- A hard brush is a common cause of bleeding when brushing your teeth. The best option is a brush with soft bristles or medium-hard bristles.
- Infectious diseases of the throat and nose can also cause the gums to become swollen, painful, and bleeding.
- Avitaminosis. Due to a lack of vitamins and microelements, not only the body as a whole suffers, but also the oral cavity.
- In fairly rare cases, bleeding can be caused by smoking.
Causes of bleeding
The following factors can cause bleeding:
- mechanical damage to blood vessels;
- neoplasm or inflammatory process in the walls of blood vessels;
- deterioration of the integrity of blood vessels due to infection, lack of vitamins or poisoning of the body.
Remember that timely assistance with bleeding can save the victim’s life!
1 Help with bleeding. Types of bleeding
2 Help with bleeding. Types of bleeding
3 Help with bleeding. Types of bleeding
Symptoms of bleeding
The main symptom is the appearance of blood from the nasal sinuses, its flow outward and inward (through the nasopharynx). Bleeding may also be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increased heart rate;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- nausea;
- general weakness;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- feeling of fullness in the ears;
- paleness of the skin of the face and hands.
Bleeding can be either light or heavy. Depending on the volume of blood lost, there are 3 degrees of severity:
- light – up to 500 ml;
- average – 500-1400 ml;
- heavy – more than 1400 ml.
Treating bleeding gums at home
In addition to pharmaceutical gels and rinses, folk remedies can also be used to treat gums. Herbal infusions are best suited for this:
- a spoonful of sage flowers in a glass of boiling water;
- a teaspoon of calendula flowers per 200 ml of water (leave for half an hour);
- boil two tablespoons of oak bark in 500 ml of water and let stand for 10 minutes;
- boil a decoction of 2 tablespoons of yarrow and 0.5 liters of water for 15 minutes;
- Infuse 200 ml of boiling water with 1 tablespoon of chamomile flowers.
It is recommended to rinse your mouth 3 to 6 times a day after meals.
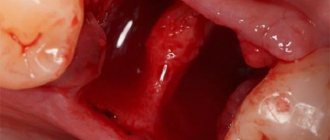
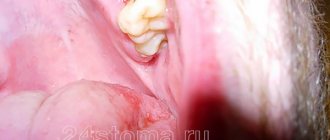
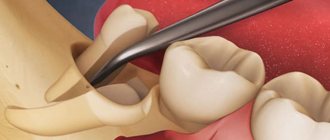
How to stop bleeding after tooth extraction
Bleeding after tooth extraction is a natural process, a consequence of surgical intervention. During the operation, the tissues that hold the tooth in the row are damaged. Accordingly, inevitable bleeding occurs. In this material we will tell you in detail how to distinguish normality from pathology, how to properly stop bleeding after tooth extraction, and what kind of help should a doctor provide?
Is bleeding after tooth extraction normal?
After removing a tooth from the socket, blood begins to flow immediately, and the doctor takes measures to weaken the flow. For example, the dentist applies a sterile swab, previously soaked in a special liquid. However, after some time (after 2-3 hours or the next day), the wound may bleed again, catching the patient by surprise on the way home or already at home. The professional must inform the person about this and give some instructions so that the patient can react correctly.
Bleeding after tooth extraction occurs due to the following reasons:
- the dentist damaged a large vessel - often this problem occurs after a complex tooth “comes out” and during an incision in the gum;
- the patient has increased blood pressure - as a result, the vessels do not close, bleeding is activated;
- poor blood clotting – often found in patients suffering from leukemia or hepatitis;
- the patient is taking anticoagulant drugs;
- if there was an infection that provoked inflammation.
Bleeding after tooth extraction is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- headache and dizziness are observed;
- a person's temperature rises;
- there is weakness, faintness;
- the socket swells;
- blood oozes so much that the patient spits out clots every two to three minutes;
- the person feels severe pain in the surgical area;
- the pain radiates to the temples, neck, ear.
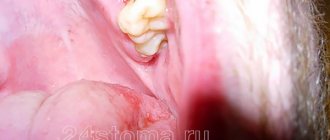
How long does it usually take to bleed after tooth extraction?
It is normal if blood oozes from the wound for about a day. Sometimes it takes two days to stop completely, which is also within normal limits. If a patient has had a wisdom tooth or a “complicated” tooth removed, blood may ooze for about 3 days - this will also be considered normal. If the bleeding bothers you for several days, or the symptoms listed above are observed, you should urgently consult a dentist. It is also an alarming symptom if a blood clot does not form in the socket.
Bleeding after tooth extraction - what can the patient do?
- Take painkillers that were previously selected and recommended by the dentist.
It is strictly prohibited to independently choose medications to relieve pain and stop bleeding.
- Apply a cold bandage or object to your cheek. After holding the cold object for 3 minutes, you can take a break. In one session, you can perform three alternating applications.
Placing ice or cold objects into the hole from which the tooth was removed is strictly prohibited. This can trigger the development of infection and inflammation.
- Apply a gauze swab previously soaked in hydrogen peroxide.
The tampon must be clean and sterile (!) to avoid infection of the wound.
- Take medications to lower blood pressure. As a rule, they are recommended for people suffering from hypertension.
Selecting and prescribing blood pressure medications on your own is strictly prohibited!
Attention! Self-medication can lead to deterioration of health. All medications and other measures to stop bleeding after tooth extraction should be recommended by an experienced dentist.
Professional medical help: how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction?
- The doctor examines the patient and determines the nature of the bleeding - natural or pathological. If necessary, refers the person to x-rays and ultrasound of the tooth;
- the doctor cleans the wound and then dries it.
- The doctor prescribes medications: painkillers, antiseptics, possibly antibiotics.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures are performed if necessary.
- If there are appropriate medical conditions, additional stitches are placed on the wound.
What to do if the bleeding does not stop after tooth extraction? No need to self-medicate! It is imperative to contact a dentist, who will rule out pathological processes or, if they exist, provide emergency assistance. Dentists at Zuub.rf accept patients with acute pain, if there is bleeding after tooth extraction and the person’s condition does not allow them to lead a normal lifestyle.
If you have the symptoms described in this article, be sure to make an appointment at our clinic.
Don't self-medicate! Even the smallest problem, if not treated correctly, can significantly complicate your life.
By contacting us, you can be sure that:
- Get high-quality and free consultation .
- You will receive the best prices for treatment and the opportunity to receive a special promotional price.
- Only modern equipment and materials will be used.
- You will be treated by professional doctors with many years of experience.
- We offer treatment on credit or in installments. There is also the possibility of obtaining a tax deduction.
- We work seven days a week and without a lunch break, from 9 a.m. to 10 p.m.
+7
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor can determine the cause of the problem based on the diagnostic results. This includes examination and x-rays. The dentist evaluates the condition of the prosthesis, gum tissue and root system of the tooth, excluding cysts, granulomas and fistulas.
If bleeding gums are associated with an incorrectly selected crown or a violation of its installation technique, removal of the prosthesis and re-prosthetics are indicated. For gum diseases, conservative treatment with the use of antifungal, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs is possible.
Symptoms accompanying gum disease
Pathologies that cause blood from the mouth may be accompanied by a number of other unpleasant symptoms:
- swelling of the gums;
- pain when pressing or eating solid foods (sometimes the pain is quite severe);
- itching and discomfort in the gum tissue;
- bad breath;
- tooth mobility (with advanced dental diseases).
Even if nothing bothers you throughout the day, and blood appears only when brushing your teeth, this may indicate a problem.
Emergency care for arterial bleeding
Remember that in case of arterial bleeding you cannot hesitate!
Quickly assess the situation and proceed to provide assistance. First of all, pinch the artery with your finger:
If bleeding is in the face area, press your finger on the corner of the lower jaw.
If bleeding is from the head area, then press your finger on the temporal bone in front of the ear.
If bleeding is in the area of the shoulder joint, then press the subclavian artery to the rib.
If bleeding is in the area of the hand, then press the brachial artery to the bone from the side of the shoulder.
If there is bleeding in the thigh area, then you need to press your fist on the frontal bone in the groin area.
Next you need to apply a tourniquet. To temporarily stop arterial bleeding, an Esmarch tourniquet or improvised rubber material is used. Rules for applying a tourniquet:
- Raise, if possible, the victim's arm/leg - this will lead to the outflow of venous blood from the limb;
- Place the tourniquet over the victim’s clothing or a piece of fabric: this is necessary so as not to injure the person’s skin.
- The first 2 turns need to be made the tightest, the crosshair is applied on the back side of the artery. Make sure that the bleeding from the wound has stopped and the skin below the tourniquet has turned pale.
- The victim should be immediately sent to the hospital or call an ambulance.
If you do not achieve complete disappearance of the pulse on the radial artery, then within 10-15 minutes the hand will swell and turn blue. Then the tourniquet can be removed only if the arm is amputated. Record the time of application of the tourniquet. The maximum permissible time in summer is 90 minutes, in winter – 60 minutes, otherwise tissue necrosis occurs.
Every 30-40 minutes, regardless of the time of year, you should remove the tourniquet for 20-30 seconds (until the skin below its application turns pink). This is done so that blood can enter the damaged limb to supply it with oxygen and remove metabolic products.
Then the tourniquet should be applied again below or above its previous location. You can do this for several hours.
First aid for venous bleeding
With venous bleeding, a stream of blood comes to the surface at high speed so that it does not allow a blood clot to form and stop the bleeding.
As a result, a person may lose a large amount of blood.
Algorithm for providing assistance:
- Raise the injured limb upward;
- Cover the wound with a bandage or clean cloth folded several times;
- Cover the wound tightly with a bandage.
In case of severe venous bleeding, a tourniquet is applied and then cold is applied to the wound. Next, go to the hospital for help.
Prevention
To avoid gum bleeding when brushing your teeth, dentists recommend following these rules:
- It is better to give up dental floss and choose brushes with soft and medium-hard bristles. The best option for oral care is a combination of a soft toothbrush, a special medicated paste, rinsing and cleaning with an irrigator. This method will effectively remove food debris from the oral cavity without damaging the mucous membrane.
- Take vitamins K and C. This will require a balanced diet or the inclusion of vitamin complexes in your daily diet.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. Proper brushing of teeth 2 times a day, regular preventive examination by the dentist.
- To prevent bleeding, it is better to use compounds with a therapeutic effect. It is recommended to change the brush every 3 months.
When your gums bleed, it is not only unpleasant, but also dangerous. The wounds can get infected, which can cause serious complications. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
Author of the article