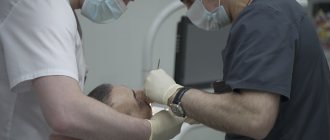
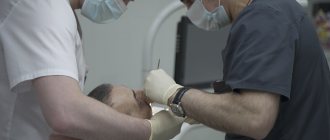
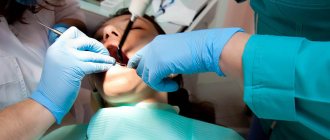
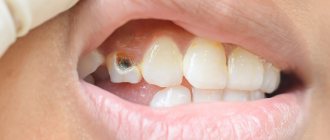
Methods of modern dentistry are aimed at preserving the dental unit. Removal is resorted to as a last resort if gentle treatment techniques are ineffective. Resection of the apex of the tooth root (apicoectomy) is a microsurgical intervention for excision of tissue affected by infection with part of the injured tooth root. The operation is performed if the inflammation has taken the form of a cyst or granuloma. The main condition for the success of such a surgical intervention is the timeliness of the patient’s visit to the dentist. If the pathological process spreads to most of the root, the tooth will have to be removed.
Indications for surgery
- Poor endodontic treatment leading to inflammation of the root apex;
- the presence of a cyst, granuloma or other neoplasm, no more than 1 cm in diameter;
- perforation of the root walls during filling;
- pin or stump inlay in the dental canal;
- obstruction of the dental canal due to a congenital developmental defect;
- a crown or bridge placed on a tooth.
Stages of the operation
Resection of the apex of a tooth root is a complex operation that does not tolerate even the slightest mistakes. After careful preparation, the following occurs:
- Anesthesia (local, in rare cases, general anesthesia);
- Removal of the nerve and filling of the root canal of a diseased tooth;
- The surgeon cuts the gum and drills a small hole in it;
- The part of the bone that prevents access to the apex of the tooth root is removed;
- The infected granuloma or cyst is eliminated;
- Cleaning the operated area, its irrigation;
- Removal of the apex of the tooth root;
- The cavity in the bone (through which the root apex was accessed) is filled with the patient’s blood plasma and bone material;
- The gums are sutured.
When surgery is not performed
Like any other surgical intervention, apicoectomy has limitations and contraindications. These include:
- Mobility of teeth II-IV degrees;
- destruction of the crown part of the tooth (more than 50%);
- the presence of cracks in the affected root;
- severe curvature of the root canal (impossible to fill);
- crowding of teeth, which does not allow identifying the affected root;
- acute infectious, viral disease;
- severe bleeding disorders;
- decompensated diabetes mellitus;
- severe immunodeficiency;
- oncology in the active stage.
Some of the limitations to root resection are the indication for removal of the affected unit. The second part refers to general contraindications to any surgical intervention. The risk of surgery for the patient is assessed individually.
The specialists at the Ilatan Clinic make every effort to save the dental unit, if possible. But if there are direct indications for removal, for example, extensive damage to dental tissue, the doctor will not suggest apicoectomy.
Contraindications (when root apex resection should not be performed)
Alternative treatment methods are prescribed in cases of:
- The patient has deep damage to the periodontal tissue; exposure of the neck of the tooth or its root;
- Acute form of periodontitis;
- If there is damage to a large part of the root system, for example, due to inflammatory processes;
- Too high tooth mobility (grade 3-4);
- The top of the tooth or the tooth itself are destroyed;
- The size of cysts and granulomas exceeds 10 mm (other methods of surgery are used);
- Malignant formations in the oral cavity;
- The close proximity of healthy and diseased tooth roots, which significantly increases the risk of tissue damage during surgery.
You should also pay special attention to the state in which a person approaches the operation.
Surgery is strictly not recommended if:
- The patient feels unwell, there are signs of somatic diseases (autoimmune diseases; blood diseases; diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- The patient’s condition does not allow for surgery (acute period of illness; fever; respiratory viruses, etc.);
- The presence of severe pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Resection stages
- Formation of access
- the dentist cuts through the gum, exposing the jaw bone. Forms a small hole in the bone tissue (in the projection of the root apex), gaining access to the pathological focus. Often, the bone tissue has dissolved in the projection of the cyst; there is no need to cut out a hole. - Excision of tissues and correction of the apex
- the doctor removes the source of inflammation along with the dead apex of the root, cutting it off perpendicular to the upper dental axis (to the level filled with the filling mass). The empty space is filled with osteoplastic material (bone volume is restored faster). - Suturing
- suturing the wound area is sometimes performed with the installation of drainage for the outflow of ichor. Drainage is installed between the seams and is removed after 1-2 days.
Root resection takes 40-60 minutes, depending on the location of the tooth. It is easier to intervene on canines and incisors than on multi-rooted units.
Root apex resection: patient reviews
All patients note that the operation is absolutely painless. However, postoperative pain will occur immediately after anesthesia (severe pain after resection is not typical). The next morning you may see swelling of the soft tissues of the face in the projection of the operation, sometimes a hematoma. In rare cases, suppuration of the surgical wound occurs, but this does not happen often. Prophylactic antibiotics help prevent this complication.
After surgery, they are usually prescribed -
- antibiotic Amoxiclav 625 mg (1 tablet – 2 times a day, 6-7 days),
- NSAID-based analgesics,
- rinsing with a solution of 0.05% Chlorhexidine.
Relapse and reoperation - the percentage of relapses according to official statistics is about 1-3%. If the operation is performed according to all the rules, then there should be no complications. There are 2 main points that determine the quality of the operation. Firstly, the cyst shell must be completely removed (since even a small fragment of the cyst shell remains, it will appear again).
Secondly, this is the quality of root canal filling. If the root canal was poorly prepared, for example, it was not sealed tightly, this will lead to the spread of infection along the canal walls and a new cyst formation. And retrograde root canal filling, which we described above, can also help here.
Recovery period
The entire operation lasts about an hour, the recovery period takes up to six months or more, depending on how quickly the bone tissue regenerates. In the first 1-2 days after the surgical procedure, the patient is bothered by moderate pain, swelling, and redness of the gums. After 3-4 days, the unpleasant symptoms decrease and the condition improves. To ensure that the postoperative period passes quickly and without problems, the doctor will give the necessary recommendations for care, prescribe painkillers, as well as a short course of antibiotic therapy.
When is it recommended to remove part of a tooth root?
Most often, resection is performed when:
- the formation of a cyst on or near the root of the tooth;
- proliferation of granulomas or multiple granulomas on the root part or in the area nearby;
- anatomically incorrect position of the tooth canals.
It is important! To successfully perform the operation and rehabilitation after it, a prerequisite is the presence of a sufficient volume of bone tissue in the operation area (approximate tissue thickness - from 5 mm). If these indicators are lower, there is a high risk of bone injury during the removal of granulomas or cysts.
What is important, the manipulation is performed under local anesthesia; If the patient is very distressed, premedication may be administered. In any case, the procedure is not accompanied by discomfort and is easily tolerated.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Care after tooth resection
- Do not chew on the operated side.
- Until the wound heals, avoid irritating, solid foods (food should be warm and soft).
- Do not use a hard toothbrush, aggressive pastes, or mouthwash.
- Take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor to prevent infection.
- Rinse your mouth after eating with an antiseptic solution.
- For the first week after surgery, limit physical activity to moderate, and exclude extreme, contact sports.
- Do not visit the bathhouse, swimming pool, sauna until the wound is completely healed.
- Avoid eating too hard foods until the bone is completely restored (at least 3 months).
- Visit your surgeon regularly to evaluate the results of the operation.
Recommendations after surgery, what you definitely shouldn’t do
After surgery, you should not additionally load the area of the dental system that has undergone surgery with food. It is important to follow all the dentist’s recommendations and not self-medicate. It would not hurt to take several control radiographs (for example, after 3, 6 and 12 months). You can disinfect the oral cavity with antiseptics or soda solution to prevent the development of purulent processes in the gums.
It is necessary to follow a gentle diet - do not eat solid foods: nuts, dried fruits, sweets, etc. Avoid sour and sticky foods.
Possible complications
Root resection is a micro-operation, the purpose of which is to preserve the full functionality of the affected tooth. Usually, the risk of complications is minimal, but they cannot be completely excluded. Sometimes the following complications are possible:
- Bleeding due to injury to nearby vessels;
- infection of a postoperative wound;
- recurrence of cysts, granulomas (if all affected tissues were not removed);
- perforation of the maxillary sinus, nasal passage;
- damage to the nerve passing along the alveolar ridge;
Sometimes complications are caused by structural features of the jaw, for example, the proximity of the roots to the maxillary sinus. Complications caused by non-compliance with medical recommendations include swelling and tissue inflammation. Ignoring advice on limiting physical activity is fraught with the development of bleeding, and failure to maintain hygiene can lead to wound infection.
Possible complications after cyst removal
Removing a cyst is a necessary procedure; the longer the treatment of a cyst is delayed, the more likely complications are to develop. There is no need to be afraid of removing a cyst; according to statistics, the percentage of possible adverse consequences is immeasurably less than complications from an unoperated cyst (abscess, phlegmon, sepsis).
After cystectomy, the service life of the tooth is not reduced. Both after therapeutic and surgical treatment of cysts, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the bone tissue is required.
To avoid complications, it is important to maintain oral hygiene, follow your dentist's recommendations, as well as eat a healthy diet and avoid alcohol, smoking, carbonated drinks and solid foods in the first days after surgery.
Cost of tooth root resection
The price of root resection is determined depending on the volume of surgical intervention, the cost of consumables, and anesthesia. The result of the procedure fully justifies the money spent. After all, it is cheaper than removal with further implantation and prosthetics. The doctor will tell you exactly how much tooth resection costs after examination and diagnosis.
Pain relief during tooth root resection
The bone tissue of the upper jaw has a more porous structure. Therefore, if the operation is planned on the upper teeth, then infiltration anesthesia is used. By injection, an anesthetic drug (lidocaine, ultracaine, etc.) is injected into the submucosa of the gums.
Thanks to diffusion, the solution penetrates through the soft tissue into the bone, blocking the nerve fibers of these deep areas.
Conduction anesthesia is used for the lower jaw. The injection is made in the area of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, the anesthetic drug permeates the nerve fiber itself, as well as the tissues surrounding it.
Contraindications to the procedure
Surgery is not performed in the following cases:
- Inflammation of periodontal tissues.
- An advanced stage of periodontal disease, when the neck of the tooth is exposed and the unit itself has become mobile.
- Tight adherence of the roots of adjacent healthy teeth to the source of infection.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Excessive tooth mobility.
- Weakened immunity.
- Cancerous formations in the tooth area.
- Active form of the inflammatory process.
- Pregnancy period.
Types of surgery
At the preparatory stage, professional teeth cleaning is required. This is necessary to destroy plaque and food debris trapped in periodontal pockets. Immediately before the operation, local anesthesia is administered. The dentist performs a series of sequential actions in accordance with the chosen method. There are three main ways to perform a gingivectomy.
Simple means:
- Wave-like dissection of the gums and periosteal tissue at the site of inflammation.
- A similar cut is made from the inside.
- At the ends of each of the incisions, vertical cuts are made.
- The gum is separated and needs to be eliminated.
- Curettage of the bone cavity and wound surface is performed.
- A bandage is applied, which the patient wears for up to 48 hours.
Gentle - almost the same as the previous one. The difference is that in this case, not the entire wall of the pocket between the tooth and the gum is cut, but only part of it (no more than 3 mm). Then curettage is also carried out on the remaining part of the gum tissue.
Radical - refers to complex surgical procedures, since the tissue of the alveolar arch of the jaw is involved in the process. In this case, wave-shaped incisions are also made, after which the gum edge is removed along with epithelial cords, granulation tissue and affected areas of bone. At the last stage, a gum bandage is applied to promote rapid healing.
Therapeutic treatment of cyst/granuloma
Do not be afraid to go to the doctor if you suspect that you fall under the described symptoms of a cyst. Firstly, only x-rays can accurately show whether this is actually the case; secondly, the sooner you see a dentist, the higher the chances that you can do without surgery. Extreme measures are resorted to only when therapeutic treatment has not brought the desired result, or the source of inflammation is in an advanced stage.
However, there is no guarantee that the treatment will have a positive outcome and that surgery will not be necessary. In addition, this process is long and has many stages. To reduce and resolve a cyst or granuloma, the source of infection must be neutralized. At this stage, the doctor works with the root canals: if they have not been sealed, he removes the pulp and carries out treatment; if fillings have been installed, he removes and rinses the canal with an antiseptic.
After this, the doctor installs a temporary medicated filling paste based on calcium hydroxide for several months. To determine the effectiveness of therapy, it is necessary to take another x-ray. In case of successful treatment and reduction of the source of inflammation, the patient will receive a permanent filling.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Wound healing time
The oral mucosa takes approximately 2 weeks to heal. After this period, all symptoms of surgical intervention disappear, and chewing loads do not cause pain. Complete healing of bone tissue requires more time - from 6 to 12 months. During this period, the hole in the bone heals. To monitor this process, radiography should be performed regularly. This diagnostic procedure is prescribed a few days after resection and 6-7 months later.
Alternative options
- Cleaning teeth using ultrasound . Tartar is destroyed, the integrity of the unit is preserved.
- Drug treatment using antiseptics. The best option is Chlorhexidine in the form of rinses or compresses.
- A course of antibiotics . Allows you to quickly relieve the inflammatory process and alleviate the human condition.
Conservative treatment is not always effective. If characteristic symptoms reappear or the situation worsens, gingivectomy becomes mandatory.