Why does cheek swelling occur?
A common cause of edema is odontogenic periostitis, or gumboil. The inflammatory process of the periosteum is accompanied by the formation of purulent contents at the base of the root. The causes of gumboil are the spread of infection from a diseased tooth - carious or pulpy. In this case, only surgical treatment of periostitis, an incision in the gum and cleaning out the pus will help relieve swelling.
Another cause of cheek swelling is gingival cysts. If the cystic formation is localized not strictly under the root, but on the side, the gums and along with it the patient’s cheek swell. Getting rid of cysts involves performing tooth-preserving operations or, in advanced cases, tooth extraction. Often the cyst itself does not cause swelling, but after surgery to resect it, the patient receives swelling, which goes away within 2-3 days.
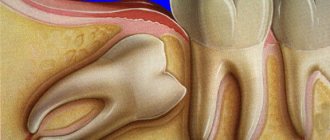
Patients with impacted and dystopic wisdom teeth often suffer from swelling during periods when the tooth is actively trying to erupt.
Causes of the pathological condition
There are many reasons that lead to a swelling of the cheek from a tooth. Among them are:
- Toothache. A tooth hurts due to caries or pulpitis. Swelling may also occur after the element is removed. With proper treatment, the symptom goes away on its own within 2-3 days.
- Inflammation of the salivary glands and ducts. The cheek swells due to improper oral care or infection with viral and infectious pathogens.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses. Swelling spreads to other areas of the face - eyes and cheeks.
- Damage to the lymphatic system. This factor is the most common cause of cheek swelling without tooth pain.
- Neuritis of the facial nerves. Pathology develops due to hypothermia of the body. Additionally, the problem is accompanied by impaired facial expressions and pain when talking and eating.
- Mumps is a viral disease that leads to damage to the salivary glands. One of the symptoms of mumps is swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes and cheeks. Swelling can manifest itself both unilaterally and bilaterally.
- Infectious mononucleosis. In terms of symptoms, the disease is similar to a sore throat and occurs in an acute form.
- Diphtheria. Occurs due to damage to the body by the Loeffler bacterium. Diphtheria is accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the tonsils and fever. Antibiotic therapy does not give a positive result in treatment.
- Traumatic injuries to the soft tissues of the cheek. The healing period after injuries takes 2 to 3 weeks.
- Allergic reactions. There are situations when the cheek is swollen due to individual intolerance to food or oral hygiene products. You can get rid of the problem only by eliminating the provoking factor.
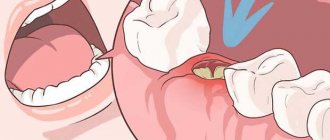
Cheek swelling as a complication after tooth extraction
If a patient has had a tooth removed, then swelling is a natural phenomenon. However, it often indicates that the operation was performed incorrectly or the development of a pathological process due to the patient’s failure to comply with the recommendations in the postoperative period. To recognize the problem and contact a specialist in a timely manner, it is important to know that:
- Swelling is considered normal after removal of an upper wisdom tooth. In this case, the swelling spreads to the upper part of the face. Swelling of soft tissues is very natural, because the area where the tooth roots are located in this case also contains a large number of blood vessels of various sizes.
- Swelling is predictable after complex removal of lower wisdom teeth. If the problematic “eight” was sawed out or split and removed in parts, with a high degree of probability we can talk about subsequent swelling of the soft tissues of the face.
You can understand that swelling does not indicate pathology by the nature of the phenomenon. As a rule, it does not occur immediately after extraction, but the next morning. The swelling increases throughout the day, causing serious discomfort, and remains at the same level the entire next day. On the fourth day after tooth extraction, the swelling should subside and the discomfort caused by it should decrease. Against the background of “normal” edema, there is no fever or throbbing pain.
Symptoms that require urgent help
You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if your cheek is swollen from a tooth. The condition can be fatal.
The list of dangerous signs includes:
Headache after tooth extraction
- Unbearable toothaches that appear constantly. The condition indicates that an infection has attached to the surgical field. Severe pain is acceptable only after operations involving cutting out part of the bone tissue. Pain sensations decrease after 1-2 days, otherwise urgently contact the dentist.
- Temperature rises to 38 degrees and weakness.
- Pain when opening the mouth, swallowing and eating food.
- A compaction revealed by palpation of the problem area.
- Absence of a blood clot in the socket. A clot does not form due to intensive mouth rinsing on the first day after surgery or other illiterate actions of the patient that provoked a violation of soft tissue regeneration. The condition threatens the occurrence of acute symptoms and infection of the maxillofacial tissue.
Also, immediate consultation with a doctor is required in cases where the tumor is rapidly growing in size.
Due to the lack of blood clot formation, infectious complications develop after a tooth has been removed (pulled out).
When is swelling a sign of pathology?
- If swelling does not appear the next morning, but much later (on the third or fourth day);
- If swelling is accompanied by increasing pain;
- If, against the background of edema, the patient’s temperature rises;
- If the swelling is so severe that it makes speech and swallowing impossible;
- If there is a putrid odor from the mouth.
The listed symptoms may indicate that the patient has developed alveolitis. When wisdom teeth are removed, this phenomenon is not so rare, and according to statistics it happens in 20% of cases.
Causes of swelling
A common situation is when a tooth hurts or a swollen cheek. An inflammatory process begins to develop in the inner part of the tooth. Sometimes the reason lies in incorrect surgical intervention by a specialist.
In general, we can identify the following factors of unpleasant sensations that are localized in the oral cavity:
- changes in pathological illness in the mouth area;
- diseases associated with disruption of the functional functioning of neighboring organs (for example, the maxillary sinus or trigeminal nerve);
- factors of discomfort in the oral cavity include the wrong course of treatment.
Unpleasant sensations may appear temporarily or be permanent. External irritants, such as sweet, hot or cold drinks, also have a huge impact. With slight pressure, an aggravation of this situation is observed.
If you suffer from a swollen cheek, you need to understand the reasons for this process. First of all, this concerns the diagnosis of periodontal disease. As you grow older, your gums lose their former elasticity and bleed constantly. Tooth enamel loses its former resistance to external irritants. This means that teeth and gums are quite easily susceptible to infection.
Sometimes the cheek becomes swollen from this infection. Use medications prescribed by your doctor for the course of treatment. Experts recommend removing the tooth, after which a prosthetic procedure should be performed.
The next disease that provokes swelling is an inflammatory infiltrate. Patients often encounter a situation where their cheek is swollen after dental treatment. For example, after therapy aimed at getting rid of apical periodontitis or pulpitis. A symptom that appears before the onset of swelling is a fairly severe toothache.
The main manifestations of inflammation are characterized by softening of soft tissues, or the gradual accumulation of pus. Subsequently, it penetrates into neighboring areas, and cases of entry into the circulatory system are possible. This process negatively affects the patient’s health and general well-being. In severe cases, death is possible. To protect yourself, you should seek help promptly.
The next option is that the wisdom tooth is growing in the wrong way. Due to the development of the eighth teeth or if the normal process of teething is disrupted, swelling of the cheek is possible. A mucous sac often appears at the site of inflammation. Leftover food often gets into its interior.
It is quite difficult to remove food from this area, so irritation of the mucous membrane occurs. This condition causes discomfort and the patient suffers from severe pain. In some cases, body temperature rises.
If the wisdom tooth grows partially, then the patient may suffer from discomfort while eating. After all, food particles injure the soft tissues of the cheek, and the size of the tumor increases.
There are cases when the cheek becomes swollen after tooth extraction. This situation is explained by unprofessional treatment. For example, if a nerve remains during filling. Even in the absence of pain, this situation is dangerous. If the patient does not take appropriate measures, in most cases he will lose a tooth.
Sometimes swelling may occur as a result of an allergic reaction. If this situation arises, the doctor must promptly remove the filling and replace the material that provoked the allergy with another (more neutral) material.
When the gum is cut, swelling may occur. This surgical intervention is performed if pus is present. At first, the tumor may increase in size.
Separately, it is worth noting the situation when a tooth was removed and the cheek became swollen. To minimize negative manifestations, experts advise not to touch the affected area with your tongue or hands for at least 24 hours. Also at this time it is prohibited to consume alcoholic beverages and hot dishes.
It is important to contact a qualified specialist if you notice the presence of one or more symptomatic signs:
- after your tooth was pulled out, your cheek became swollen;
- excess of normal body temperature;
- after you have had a tooth removed, you observe a constant increase in pain;
- swelling gradually expands its boundaries. In the future, if the patient does nothing, this can lead to suppuration.
Why does alveolitis occur after wisdom tooth removal?
Edema, as a consequence of alveolitis, can occur for various reasons, namely through the fault of the doctor or the patient himself.
Causes of edema when the doctor is to blame:
- A cyst remained under the extracted tooth.
- The doctor incorrectly applied stitches, which came apart and exposed the alveolar bone.
- The doctor did not prescribe an antibiotic to the patient after the removal of a wisdom tooth due to a purulent process.
- The doctor left a foreign body in the hole - pieces of a tooth, bone, instrument, etc.
- Causes of edema, when the patient is to blame:
- The patient did not comply with recommendations for oral hygiene in the postoperative period.
- The patient rinsed his mouth vigorously, which led to the flushing out of the blood clot covering the wound.
- The patient chewed hard food on the side of the extracted tooth, which led to suture dehiscence and exposure of the alveolar bone.
- The patient did not take antibiotics prescribed by the doctor after a complex wisdom tooth extraction.
Whatever the cause of pathological swelling, it is necessary to get rid of it under the supervision of experienced specialists. Call ICDI ROOTT toll-free at 8 800 775–26–37 and make an appointment with a doctor at any of the clinics – on Dmitrovskaya and Proletarskaya. We will provide high-quality treatment - therapeutic, physiotherapeutic or surgical - to stop the processes that cause swelling of the soft tissues of the face.
Tumor due to improper treatment
Why else can pathology be observed? Separately, it should be noted the swelling of the cheek, which arose as a result of illiterate therapy. If the cheek is swollen after a complex tooth extraction, then this is a variant of the norm. The symptom disappears on its own after a few days. Typically, such swelling is small in size and does not cause pain to the patient. The situation does not require repeated surgery.
The opposite situation arises if we are talking about an infectious process that has begun after medical care has been provided. Complications are more often observed after the removal of wisdom teeth or a retained element. Such operations cannot be performed without significant damage to soft tissue. Complications arise due to doctor errors or when the patient fails to comply with the dentist’s recommendations during the recovery period.
The impacted tooth is located in the deep tissues of the gums due to incomplete eruption or incorrect location
The gums also swell due to improper sanitation of the diseased tooth. In this case, repeated assistance from a specialist is required, followed by taking medications and local treatment of the affected area. After complex removal of an element, swelling can be observed for up to 2 weeks.
Swelling also often develops due to allergic reactions to painkillers used by the dentist during treatment. In this case, additional symptoms are observed (heavy breathing with whistling, shortness of breath), but the tooth does not hurt. A person requires urgent hospitalization to cleanse the body of the allergen.