Inflammation of the facial nerve is an unpleasant ailment that does not go away painlessly. The main complaints of patients are sharp attacks of pain in the face, in the upper and lower jaws.
This inflammation is considered one of the most common among facial pains. Most often, the disease proceeds without a trace, but if treatment is neglected, paralysis may occur.
The disease most often occurs in women over 50 years of age; men are treated with this disease much less frequently. People with a genetic predisposition, such as a narrow bone canal, are also at risk. Due to this anatomical feature, there is an increased risk of pinching due to impaired blood supply and various inflammations.
What is the facial nerve?
The trigeminal nerve, also known as the facial nerve, is the largest of the twelve cranial nerves. It originates in the ear, after which it branches, the first path reaches the frontal part, the second is located at the jaw. The nerve goes around almost the entire surface of the human face; it literally controls it.
Every person has two facial nerves - one on each side of the head. It is in contact with other cranial nerves and has supersensitive fibers.
Doctors divide the disease into two types - primary and secondary. The primary one manifests itself as a complication from a cold, in this case the normal nutrition of the nerve is disrupted. Secondary occurs with severe intoxication against the background of inflammatory or infectious diseases, as well as tumor processes.
Trigeminal nerve, anatomy, innervation, where the trigeminal nerve is located
The trigeminal nerve, nervus trigeminus, the 5th pair of human cranial nerves is a mixed nerve that contains sensory, motor and autonomic fibers. The functions of the trigeminal nerve are varied.
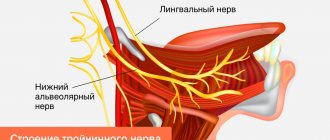
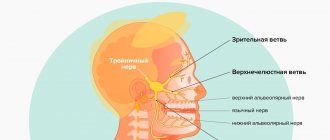
The sensory fibers of the trigeminal nerve originate from the cells of the trigeminal ganglion, which is called the ganglium trigeminale. It is located in the recess of the pyramid of the temporal bone. The dendrites of these cells form 3 branches and 3 trunks.
1 branch of the trigeminal nerve, the first branch (nervus ophthalmicus) - the ophthalmic nerve passes in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, later through the superior orbital fissure into the orbit. Then it breaks up into branches, innervates such structures as the outer part of the conjunctiva, the skin of the outer corner of the eye, the upper eyelid, the lacrimal gland, the skin of the scalp to the temporal and parietal regions, the skin of the forehead, the skin of the root of the nose, the cornea, the frontal sinus, the main sinuses , nasal mucosa, nasal skin, posterior cells of the ethmoid bone.
2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve, second branch (nervus maxillaris) - the maxillary nerve passes (exit) through the round foramen and the pterygopalatine fossa. It further breaks down into branches and innervates the following sections: the skin of the temporal region (temporal region, temple), the skin of the zygomatic region (cheekbone), the mucous membrane of the posterior ethmoid cells and the main sinus, the vault of the pharynx (pharynx), the nasal cavity (nose), the soft palate, hard palate, mucous membrane of the tonsils (tonsils), skin of the infraorbital region (infraorbital region), wings of the nose, upper lip, gums of the upper jaw, upper teeth.
3rd branch of the trigeminal nerve, third branch (nervus mandibularis) - the mandibular nerve leaves the skull through the foramen ovale (exit point, exit point), innervates the following areas: mucous membrane of the cheek, mucous membrane of the lower gum (lower gum), skin of the corner of the mouth (angle mouth), skin of the external auditory canal, anterior part of the auricle, temple, all lower teeth, skin and mucous membrane of the lower lip.
The motor fibers of the trigeminal nerve originate from the motor nucleus nucleus motorius nervi trigemini. The core is located in the bridge tire. Fibers extending from the nucleus leave the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. They innervate the masticatory muscles and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. The axons of the trigeminal ganglion cells form a root and go to the bridge, where they divide into 2 branches.
The descending branch forms the descending spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for conducting temperature and pain sensitivity. It ends in the nucleus spinalis nervi trigemini. The descending spinal tract and its nuclei are analogous in their function and structure to the posterior horns of the spinal cord. The nuclei and path are divided into 5 segments, as a result of which the innervation of the facial skin in the Zelder zones is located in a ring.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on the face
Usually the disease is caused by infection or bacteria. List of reasons why inflammation of the facial nerve may occur:
- Temporomandibular joint injuries
- Tumors (benign and malignant) of the brain and facial area
- Anomalies of skull development
- Skull injuries - birth, fracture, base, damage to the face or jaw
- Polio
- Pulmonary tuberculosis
- Otitis
- Sinusitis
- Chronic caries
- Inflammation after tooth extraction or treatment
- Hypertension
- HIV and AIDS
- Poisoning
- Inflammation of the middle ear
- Severe hypothermia of the head
- Changes in hormonal levels in women
- Gum inflammation
- Ramsay Hunt syndrome
- Stroke
- Bell's palsy
Causes range from minor to life-threatening illnesses. Each of the reasons determines the further treatment of the patient. In some cases, special tests are performed for diagnosis - auditory, lacrimal, infectious, salivary or gustatory. In this way, the functioning of the receptors and sensory organs is checked.
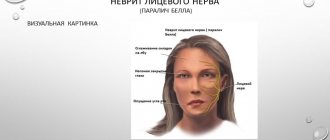
Symptoms of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Experts include short-term, but acute and intense pain in different parts of the head as the main symptoms of facial neuralgia. Shooting attacks spread over the entire surface of the face - lips, eyes, nose, upper and lower jaw, gums and tongue.
Patients also report the following symptoms:
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Muscle weakness
- 2-3 days before facial expressions are affected, pain occurs behind the outer ear, spreading to the face, back of the head and eyes
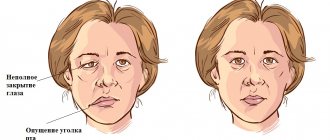
- Facial asymmetry
- Inability to close the eye on the affected side
- Drooping corner of the mouth
- Dry mouth
- Slurred speech
- Cross-eyed strabismus
- Uncontrollable tearing
- Disorders of taste buds
- Increased drooling
- Facial muscle spasms
- Increased or decreased facial sensitivity
- Temperature increase
Due to discomfort and pain, the patient begins to develop a phobia and increased anxiety. He tries to avoid poses and movements that provoke discomfort.
Traumatic neuropathy. Etiology.
Traumatic neuropathy most often occurs in the case of surgical interventions on teeth (traumatic extraction of teeth, removal of filling material beyond the apex of the tooth root, anesthesia with injury to the nerve trunks, removal of bone or tumor of the jaws), as well as in cases of surgical interventions on the paranasal sinuses and infraorbital canal.
Damage to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve, as a rule, is practically not observed. Most often, the third branch of the trigeminal nerve is affected, which is apparently due to the anatomical location of the inferior alveolar nerve, which makes it easily accessible during a variety of traumatic dental procedures. This is especially true for dental interventions on third molars. The cause of traumatic neuropathy of the inferior alveolar nerve can also be filling the mental canal during the treatment of pulpitis of the 4th and 5th teeth of the lower jaw.
Combined damage to the I and II branches of the trigeminal nerve can occur after inflammatory diseases of the brain with the development of adhesions or in the case of sinusitis, when the maxillary and frontal sinuses are simultaneously involved in the inflammatory process.
Clinic.
Patients complain of constant aching, sometimes pulsating pain in the area of innervation of the injured nerve, a feeling of numbness and “crawling goosebumps”. In case of injury to the mandibular nerve, tooth alignment occurs, which is associated with damage to the motor part of the nerve; patients cannot eat or talk. Trigger zones on the face and in the oral cavity are not identified.
During an objective examination, hypoesthesia or anesthesia (hyperpathy is also possible) of the skin and mucous membrane in the area of nerve innervation is detected. On palpation, pain is noted at the exit points of the II and III branches of the trigeminal nerve, as well as in the case of vertical percussion of the teeth and deep palpation of the lower jaw.
Diagnostics.
The main diagnostic criterion is the occurrence of pain after interventions on the dental system. The disease is characterized by clinical polymorphism and significant duration. During weather changes, stressful situations and in the presence of somatic diseases, exacerbation of the pain syndrome may occur.
In the event of scar changes in the nerves or retraction of the nerve into the scar of soft tissues (after gunshot wounds, in the case of defects of soft and bone tissues after resection of the jaws), constant aching pain of unexpressed intensity with persistent sensory disturbances is observed.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Depending on the affected area and the set of symptoms, the strategy for diagnosing the disease is determined. To determine the location of nerve damage, the severity and dynamics of recovery, doctors prescribe a hardware diagnostic method, for example, electromyography. MRI and CT scans are used to determine the presence of tumors in the brain.
The patient may also be referred for a general or biochemical blood test, x-ray of the lungs, ultrasound of soft tissues or ophthalmoscopy.
You can be confident in the quality of the procedures performed in the clinic and the high accuracy of the results of MRI, CT and other methods of diagnosing various diseases. Medunion performs magnetic resonance imaging of all types: head, spine, abdominal cavity and joints using modern equipment.
Diagnostics
The neurologist makes a diagnosis based on the clinical picture, the patient's medical history, the results of a neurological examination and a physical examination. The doctor must rule out diseases that may manifest as facial pain (herpes, headaches). An accurate diagnosis is necessary in order to choose the right tactics for treating neuritis. With neuritis, palpation of the exit points of the trigeminal nerve is accompanied by painful sensations. Diagnosis includes MRI. This is necessary in order to exclude tumors and demyolinating diseases. The diagnosis can be confirmed by the positive effect of low-dose anticonvulsants or tricyclic antidepressants.
Treatment for inflammation of the facial nerve
Drug treatment
Treatment of trigeminal neuritis is complex. The disease is first treated with medication - the patient is prescribed drugs that will alleviate the situation. These include painkillers, decongestants, vasodilators and B vitamins. Most often, the recommended medications are tablets, but you can speed up the recovery process by using ointments and gels. Sometimes doctors prescribe intramuscular injections.
In special cases, the recovery process of the facial nerve may be slowed down. Then the patient is prescribed glucocorticosteroids, which improve the metabolic processes of nervous tissue. Various biostimulants and hyaluronidases also contribute to a speedy recovery.
You cannot prescribe medications for yourself. Be sure to see a neurologist or neuropathologist at the first symptoms to determine the diagnosis and treatment strategy. Recovery medications are recommended to patients on a case-by-case basis, paying attention to the presence of chronic diseases, symptoms, and so on.
Surgery
Another way to treat the facial nerve is surgery. However, doctors turn to this option quite rarely - only when the trigeminal nerve is ruptured. Surgery is also required if there is no effect from the conservative method after six months or a year. Surgical intervention is only relevant during the first year of the presence of the disease; later, the muscles on the face irreversibly atrophy.
The surgical process involves suturing the damaged area of the facial nerve to restore its motor function.
Massage
The next treatment method is massage for the treatment of the facial nerve. The purpose of this method is to remove swelling, improve blood circulation, restore sensitivity and conduction of nerve impulses. Massage is contraindicated for tuberculosis, oncology, atherosclerosis and elevated temperature.
Initially, the massage therapist works only with the healthy side of the face, collar area, neck and area above the shoulders. Basically, the master uses rubbing, stroking, kneading and vibration.
For noticeable desired changes, it is necessary to conduct ten to twenty massage sessions from five to fifteen minutes. The duration is determined based on the degree of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, the goals of therapy and the dynamics of recovery.
Physiotherapy
The next treatment method is physical therapy. It alleviates the severity of symptoms, helps to activate metabolic processes in tissues and restore the functions of the facial nerve.
Doctors prescribe this course of treatment from the first days of the onset of neuritis. The list of physical procedures includes:
- Ultrasound
- Laser irradiation of blood
- Electrophoresis of drugs
- Microwave therapy
- Exposure to ultra-high frequency electricity
- Ozocerite treatment
- Myoelectrostimulation
- Darsonvalization
This complex is indicated for the first week of treatment. Doctors prescribe it together with medication. This tandem helps speed up the process of restoration of the facial nerve. And its most important advantages are the absence of side effects and painlessness.
Alternative Methods
There are also alternative treatment methods. These are procedures aimed at restoring facial muscles and eliminating the symptoms of facial neuritis. Such procedures include:
- Clay or paraffin masks
- Acupuncture
- Reflexology
- Injections to eliminate muscle disorders
- Therapeutic baths
- Taping – stretching the face using adhesive plasters
- Immunosorption – purification of blood from antigens and antibodies
- Biofeedback – facial muscle training
Gymnastics for the face
Also, in conjunction with complex treatment, you can do facial exercises. Before this, you need to consult with a specialist; the doctor will draw up an individual list of exercises based on the severity of the process, location of the lesion and symptoms. Typically, such gymnastics takes about ten minutes a day.
A standard set of exercises includes relaxing and tensing individual facial muscles. For example, to restore articulation, it is recommended to pronounce the sounds “u”, “o”, “and”. Afterwards, you need to bring your lower lip under your upper teeth and reproduce the sounds “v” and “a”.
Gymnastics for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve:
- Close eyes
- Raise your eyebrows
- Frown
- Squint
- Smile with your mouth closed
- Smile with your mouth open
- Puff up your cheeks
- Pull them back
- Whistle
- Widen your nostrils
- Curl your lips
- Raise your upper lip and return to the starting position
- Lower your lower lip and return to the starting position
- Take water into your mouth
- Rinse your mouth
- Close your mouth
- Run the tip of your tongue along your gums
- Move your tongue right and left
Treatment
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is carried out depending on the severity of symptoms. First, conservative therapy is prescribed. If this does not help, doctors resort to surgical methods. Their essence is to eliminate the cause of neuralgia. This may be compression of the nerve by the vessel. Surgical treatment is carried out using radiofrequency destruction, microvascular decompression or percutaneous surgery.
What drugs are most effective for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia:
- antibiotics. Prescribed for infectious nature of the disease;
- glucocorticosteroids. Relieves severe inflammation in the body;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Helps suppress inflammatory processes;
- painkillers. Relieves soreness in the facial muscles;
- muscle relaxants.
To improve metabolic processes in the nervous tissue, the patient is prescribed B vitamins. How to relieve acute pain with trigeminal neuralgia:
- use anticonvulsants;
- provide physical rest, preferably bed rest;
- Apply an anti-inflammatory ointment or a warm compress to the site of pain.
Disease prevention
Doctors recommend eliminating effects on the body that cause inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Here are some recommendations to help avoid illness:
- Avoid drafts and hypothermia
- Keep your head warm during the cold season
- Monitor your blood pressure
- Timely treatment of infectious and bacterial diseases
- Have a routine check-up with an oncologist
- Avoid skull and head injuries
You can sign up for an individual consultation, take tests or undergo treatment at the Medunion private clinic. You can easily make an appointment with us by calling 202-95-54 or online, directly on the website, by clicking on the “Online booking” button.
We have been working in Krasnoyarsk since 2006 and provide high-quality medical services to the population. The staff consists of highly qualified doctors of broad and narrow specialization.
INDICATIONS FOR REMOVAL:
- the molar is impacted (unerupted) or dystopic (occupies an incorrect position in the jaw), which injures the soft tissues and neighboring teeth, interferes with their normal development or contributes to destruction;
- extensive damage by caries, the crown is significantly destroyed (while the tooth itself occupies an incorrect position in the dentition);
- pulpitis, periodontitis; (if access to the root canals is limited and the doctor obviously sees that it is not possible to properly process the canals)
- the presence of chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane of the “hood” - pericoronitis;
- the trigeminal nerve is pinched;
- orthodontic treatment is planned
- cysts or tumor-like neoplasms detected