Causes of inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve
Factors contributing to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve are:
- surgical interventions on the jaw bones;
- fractures of the base of the skull, lower and upper jaws;
- tumors;
- complex tooth extraction;
- hypothermia;
- surgery on the maxillary sinus;
- improperly administered anesthesia;
- incorrectly performed dental prosthetics;
- metabolic disorders;
- the presence of foreign bodies that irritate the nerve trunk or injure nerve endings;
- bacterial or viral infection;
- various types of intoxication of the body;
- hypovitaminosis;
- weakening of the immune system.
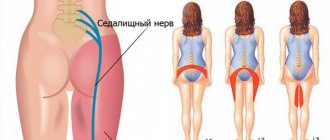
Treatment of sciatic neuralgia at home
Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, or sciatica. With this type of inflammation, pain occurs in the lower back, back of the thigh or lower leg. Discomfort increases during movement, especially under load. When a person is in a calm state, the pain syndrome decreases or disappears altogether. The cause of the disease, which affects the largest nerve in the human body, is arthritis or pinched nerve roots. An attack of neuralgia can begin unexpectedly, for example, due to an unsuccessful turn of the body, as well as from hypothermia.
A decoction prepared from viburnum flowers, calendula inflorescences, thyme, and horsetail will help relieve the acute phase of inflammation. These plants are taken in equal quantities. After mixing all the ingredients, pour 500 ml of hot water, boil over low heat for 5 minutes, cool and filter. Take 100 g of decoction orally 3 times a day.
Externally, to relieve suffering, the same means are used as in the treatment of intercostal neuralgia with herbs. A decoction of hot chili peppers is especially effective. An extract prepared from birch buds is also used for rubbing. The kidneys are infused for 7 days, first filled with a glass of vodka. The finished product does not even need to be filtered. Rub it into the sore spot before going to bed.
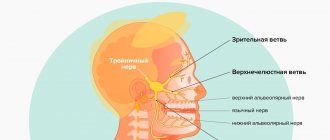
Symptoms of trigeminal neuritis
The maxillary trigeminal nerve consists of three types of nerve fibers:
- vegetative;
- motor;
- sensitive.
The symptomatic picture of neuritis may vary depending on which fibers were affected by the inflammatory process.
Damage to sensory fibers
In particular, with inflammation of the sensory fibers, the patient may complain of a tingling sensation, numbness, and weakened sensitivity in the area innervated by the trigeminal nerve.
Damage to motor fibers
When motor fibers are damaged, there is a partial or complete decrease in strength in the innervated muscles, their atrophy and deterioration of tendon reflexes.
Damage to vegetative fibers
When the vegetative fibers are inflamed, the patient experiences cyanosis and swelling of the skin, dryness and thinning of the skin, and the potential risk of developing a trophic ulcer increases.
Pain relief for occipital neuralgia
Damage to the nerve fibers of the cervical plexus - this disease occurs most often due to a complex of dystrophic disorders in the articular cartilage (cervical osteochondrosis). Shooting acute pain, manifested in paroxysms, goes from the neck to the back of the head. Thyme tincture helps to remove it. To do this, pour 50 g of thyme into 100 g of vodka and leave for 5 days. Take 15 drops of the prepared solution orally, after diluting it in 100 g of water, three times a day.
For external use, oil made from fir cones and young shoots is used. The oil is rubbed into the local area of pain using a gauze pad 6–8 times a day. For the same purposes, an infusion of marshmallow root is suitable, which is prepared as follows: 10 g of raw material is crushed and poured into 1 tbsp. warm water, then leave for 6–8 hours. Moisten a soft cloth with the decoction and apply it to the place where the pain is felt the most. A warming bandage is applied on top.
Pain due to inflammation
In addition, a disease such as inflammation or neuritis of the facial trigeminal nerve makes itself felt with attacks of pain of a very diverse nature:
- cutting,
- burning,
- pricking,
- tearing
- shooting, etc.
In this case, the area of pain does not always correspond to the area of innervation and can spread to the lower jaw, cheeks and chin.
Pain may be accompanied by:
- muscle spasms (facial, chewing),
- the appearance of nasal discharge,
- development of hypersalivation,
- increased lacrimation.
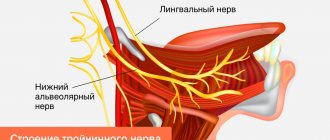
Lack of sensation in the tongue, lips and chin
With inflammatory damage to the trigeminal nerve, not only the entire nerve can be damaged, but also its individual branches. This is why numbness and pain can occur in various areas of the face. For example, when the lingual branch of the nerve is inflamed, patients complain of pain and sensitivity disturbances in the anterior part of the tongue, and when the mental branch is damaged, in the area of the lips and chin.
Pain when laughing, chewing, brushing teeth and shaving
Pain due to neuritis of the maxillary trigeminal nerve can intensify with touching, chewing, laughing and with changes in temperature. That is why patients, trying to prevent the recurrence of painful attacks, avoid excessive mobility and prolonged conversations, and refuse brushing their teeth and shaving.
Treatment of intercostal neuralgia with folk remedies
Damage to the intercostal nerves is an inflammatory disease, usually accompanied by shooting sharp pains that are localized in the sternum on the left. They are often mistaken for cordial ones. This type of neuralgia can be provoked by the consequences of injury, complications of an acute infectious disease of a viral nature, or severe hypothermia (cooling) of the body.
A tincture of hot aromatic seasoning (chili) will help reduce pain. It is prepared like this: 2 tbsp. l. raw materials from crushed fresh pods (without seeds) are poured with 1 glass of strong alcoholic drink (40°), left for 10 days, filtered and stored in a dark container. Apply the resulting product externally. Apply warming compresses as needed 4–6 times a day.
In the evening before bed, to relieve pain, rub your chest with black radish juice, cover yourself with a cotton cloth and a shawl or blanket on top. In the same way, a gruel made from horseradish is used. Don't forget to cover the compress with cellophane and wrap yourself up. A mixture of fresh lilac buds with melted butter also has a warming effect.
A decoction of peppermint is taken internally. Recipe: 20 g of leaves pour 500 ml of boiling water, 60 min. insist, then filter. Drink it half a glass 3 times a day before meals. Raspberry leaves and stems are also brewed. The decoction is taken in 50 g doses.
Treatment of neuritis of the maxillary trigeminal nerve
Therapy
The treatment program for trigeminal neuritis is drawn up taking into account the causes of the disease and its clinical signs. The main goals of treatment are:
- achieving a sensitizing effect;
- fight against bacterial and viral infection;
- increasing the body's immune forces;
- elimination of swelling of the nerve trunk;
- restoration of natural adaptive and compensatory reactions;
- normalization of the patency of nerve impulses.
Healing procedures
The set of procedures aimed at blocking the inflammatory process and eliminating all manifestations of neuritis includes:
- antibacterial therapy;
- antiviral therapy;
- elimination of factors contributing to the occurrence of intoxication;
- removal of tumor-like neoplasms or dissection of adhesions compressing the nerve;
- prescribing vitamin and mineral complexes to the patient;
- stimulation of nerves and muscles;
- acupuncture;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, UHF, ultrasound, paraffin therapy).
People suffering from trigeminal neuritis are advised to regularly visit dental clinics and have their oral cavity sanitized.
Diagnostics
If trigeminal neuralgia is suspected, the neurologist interviews the patient - clarifies the nature and frequency of pain, asks what preceded these pains, what diseases were suffered shortly before their onset, whether there are any chronic diseases at the moment, whether injuries have occurred in the facial area.
By palpation (palpation), areas of decreased/increased sensitivity and local pain are detected.
Before treating inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it must be diagnosed and separated from other possible diseases. The symptoms of neuralgia are similar to frontal sinusitis, dental pathologies, otitis media and sinusitis.
Diagnostic methods include the following procedures:
- consultation with a dentist to identify possible dental diseases, poor-quality filling or removal, unsuccessful prosthetics;
- X-rays of the skull and teeth allow you to see the pinching of the facial nerve and the formations that caused it;
- to determine the nature of the passage of impulses along the nerve, electromyography is performed;
- To exclude viruses that cause the disease, the patient must undergo a blood test.
Trigeminal neuralgia manifests itself with pronounced symptoms that make it possible to distinguish this disease from similar pathologies. At the initial stages, inflammation manifests itself as primary symptoms.
If the disease progresses, then secondary signs of neuralgia appear.
Primary
In addition, spasms of the affected area, numbness or increased sensitivity of the skin, and neurotization are noted. Let's look at all the symptoms in more detail.
In many cases, a specialist is able to diagnose trigeminal neuritis during the first examination. But to clarify the diagnosis or the reasons for the development of pathology, some tests may be required:
- electroneurography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- electromyography;
- blood test for the presence of the virus and the state of immunity;
- dental x-ray;
- panoramic shot of the jaws.
In order to understand the root of the problem and completely eliminate it, a neurologist can refer the patient for examination to other specialists: an infectious disease specialist, an immunologist, a dentist, an ENT specialist, an ophthalmologist, an allergist.
Note! Pathologies of the trigeminal nerve are characterized by a high degree of difficulty in finding the causes. In view of this, in most cases, treatment is aimed only at relieving pain and inflammation and preventing re-exacerbation
And a complete cure is rarely possible.
You can understand that inflammation of the trigeminal nerve has begun by the first symptoms, which manifest themselves quite quickly. Its main features are:
- Muscle spasm - develops more often on one side of the face and is accompanied by severe pain. Outwardly, this symptom looks like unnatural facial asymmetry.
- Pain of a sharp, intense nature, intensifying when talking or eating. The area of localization depends on which of the 3 branches inflammation develops in.
Pain can be of 2 types:
- typical - the pain is acute, throbbing, has a wave-like character of attacks with different frequency of manifestation, affects only one side of the face.
- atypical – it occurs rarely, has a nagging, monotonous course, may be accompanied by muscle contraction, and is difficult to relieve.
Important: symptoms can appear at any time for no apparent reason. Habitual procedures and actions can lead to their development: brushing teeth, washing, shaving, laughing, talking.
To identify the affected area and determine the affected nerve branch, he palpates the face. Additionally, an examination is prescribed to determine the presence of inflammation in the facial part - sinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis.
To differentiate neuralgia from other conditions with similar symptoms and to determine the causative factor, the following examination methods are used:- CT,
- MRI,
- Angiography,
- Ultrasound,
- ECG,
- Examination of the oral cavity,
- Serological examination of blood.
Only based on the results of these examinations and after they identify neuralgia, treatment is prescribed by a specialist.
Traditional medicine recipes
To treat the trigeminal nerve, doctors recommend trying special recipes from traditional medicine. Of course, they cannot help everyone and at the same time they will only relieve pain, but will not cure it completely. Therefore, if you experience any pain, you can try to relieve it at home and immediately go to the dental clinic for help.
So, the following recipes can help relieve pain:
- Compresses from boiled beets, which are grated on a coarse grater, add black radish juice and use the resulting mass to make a compress on the trigeminal nerve.
- Make a rinse using an infusion of chamomile and honey. Rinse your mouth with the prepared solution.
- Lotions made from horseradish grated on a coarse grater. You need to wrap the resulting mass in a clean cloth and apply it to the place where the pain occurs.
If pain occurs in the temporal part of the face, you should immediately make an appointment with a neurologist, who can determine the cause of the trigeminal nerve disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.