What is the trigeminal nerve
The human face has many muscles and nerve endings. Not only the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx, and conjunctiva, but also the nerve endings can become inflamed. This is most often associated with neurological disorders that change the sensitivity of the fibers that conduct impulses.
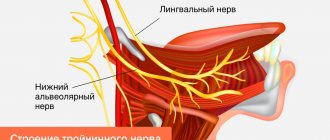
With neuropathy of the facial area, acute shooting pain occurs on the right or left. Mirror inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is extremely rare. It is located in the temporal region, near the base of the auricle. And from it there are branches along the entire half of the face:
- jaw nerve (upper and lower);
- optic nerve;
- infraorbital nerve.
The trigeminal nerve passes through the bone tissue in several places, which plays an important role in the occurrence of inflammation associated with pinching. Thus, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve can result in acute pain both in the upper and lower jaw, and in the forehead area, covering the eye sockets.
Causes and symptoms of facial neuritis
The facial nerve is a long nerve fiber, which, located on both sides of the face, regulates the functioning of all facial muscles. Some of its branches are responsible for the sensation of taste, as well as for the secretion of saliva and tears. When the large branches of this nerve fiber become inflamed, it is called facial neuritis. This is usually a one-way process.
The causes of facial neuritis are mainly infectious: it is caused by viruses or bacteria that have entered the body. The manifestations of the disease are very specific, so diagnosis is not a problem. Treatment of neuritis of the facial nerve is carried out by a neurologist.
Facial neuritis occurs due to:
- hypothermia of the face;
- herpetic infection;
- polio virus;
- mumps virus;
- inflammation of ear structures close to the nerve as a result of a bacterial infection or infection with ARVI viruses;
- nerve injury;
- disruption of nutrition of the central parts of the nerve (it leaves directly from the brain) as a result of stroke, encephalitis.
The first symptoms of facial neuritis are pain and discomfort in the postauricular area. After 1-2 days the following develop:
- weakness of the muscles of half the face (facial expressions become “poor”);
- facial asymmetry: “crooked smile”, drooping one corner of the mouth;
- asymmetry of the lips when baring or smiling;
- inability to close the eye, and a white portion of the sclera is always visible between the iris and the eyelid;
- inability to stretch out the lips, puff out the cheeks (one cheek sags and air escapes), raise one eyebrow;
- disturbance of the sense of taste on the front part of the tongue;
- lacrimation from one eye: it can be present constantly, or appear only during meals, and the rest of the time the eye will dry out from lack of tears.
A herpetic lesion is characterized by the addition of severe pain in the ear to the above symptoms, which will “shoot” in the back of the head and face, ringing in the ears, dizziness, and involuntary movements of the eyeballs. Herpes-specific “bubbles” can be detected not from the first day of the disease on the auricle, on the mucous membrane of the pharynx and tongue.
With parotitis, the main symptoms of facial neuritis appear against the background of weakness, increased temperature, and the appearance of swelling behind and under the ear (while the skin color does not change).
What symptoms facial neuritis will have will depend on where the lesion is located: in the central part, or one of the peripheral branches is inflamed. So, if the nerve is inflamed at the point where it exits the trunk, then hearing impairment is added to the symptoms described above. If the lesion is in the brain stem, then convergent strabismus will be added to the main signs of neuritis. Based on the symptoms, the neurologist understands where the pathological process is located and prescribes appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
There are several reasons leading to inflammation of the nerve ducts:
- Poor blood supply associated with physical compression of the nerve. First of all, this is swelling caused by diseases of the ENT organs. The resulting tumor can also pinch the nerves.
- Inflammation associated with dentistry. This includes gingivitis, periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and eruption of wisdom teeth. Each of these diseases can lead to suppuration, abscesses, swelling and bacterial infections of tissues.
- Medical error by an anesthesiologist - if the injection was given unsuccessfully and the needle got into a nerve, pain cannot be avoided.
- Hypothermia causes muscles to lose their elasticity, which leads to pinching of the nerves passing between the fibers.
- Bacterial infections, in particular tetanus and polio.
- The cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, which is difficult to diagnose, is the psychological state of a person - frequent experiences, stress, and nervous disorders.
To determine the cause of inflammation, you need to consult a specialist.
Causes of the disease
Coldening the facial nerve means giving access to pathogenic microbes into the body. They disrupt the supply of nerves to tissues. Statistically, in 90 percent of cases, when a person cannot control the movements of the facial muscles during a cold and experiences pain, this is a sign of a cold facial nerve.
The causes of the disease are also serious lesions, such as:
- head injury;
- middle ear disease;
- hypothermia;
- lesions during pregnancy;
- diabetes;
- borreliosis;
- spinal paralysis;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- tumors;
- ischemia;
- stroke;
However, most facial nerve paresis occurs due to hypothermia. Therefore, during the cold season, you need to be especially careful about yourself, dress warmly, and avoid hypothermia.
Treatment methods
Depending on what caused the inflammation, a course of treatment is prescribed. For bacterial lesions, the emphasis is on antibacterial therapy through systemic administration of drugs.
However, regardless of the reasons, the doctor prescribes painkillers to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. It could be:
- ibuprofen;
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- ketorol;
- diclofenac.
All of the listed drugs can be prescribed either in the form of tablets for oral administration, or prescribed in the form of solutions for intramuscular administration.
When conservative methods are not possible, the help of a surgeon may be needed. This primarily concerns abscesses due to the eruption of wisdom teeth, pulpitis or other dental diseases. In this case, the abscess will be opened, pus will be removed, the wound will be treated with antiseptic, and the tooth will be removed, if necessary. If a pinched nerve occurs as a result of pathologies in the structure of the skull, the surgeon will perform an operation to correct the situation and free the nerve bundles.
As a complex therapy, massage, heating or exposure to a magnetic field and electric current can be prescribed. You cannot massage or warm the inflamed area yourself, because this can lead to complications associated with rupture of the purulent capsule, blood poisoning and paralysis of the facial nerve.
Separately, you may need to consult a neurologist who will determine the cause of the inflammation if other specialists have not found obvious foci of infection and abscesses.
Traditional methods of treatment are permissible only as an addition to the main therapy. For example, rinsing with chamomile decoction will relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. But you can resort to such procedures only with the permission of the attending physician.
Diagnosis of inflammation of the facial nerve
If the doctor is properly qualified, then only based on the patient’s complaints will he be able to make a diagnosis and identify the severity of the pathological process. But even if the clinical picture is typical, the patient will have to undergo a series of diagnostic examinations:
- take blood and urine tests;
- undergo magnetic resonance imaging;
- do electroneurography.
The results obtained will help determine what treatment for inflammation of the facial nerve will be. In addition, such an examination will allow the doctor to identify the body’s perception of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - these are the drugs that will be used for therapy.
Possible complications
Doctors call facial paralysis the first complication that appears in the absence of adequate treatment. This means that a person who does not receive medical care in a timely manner is deprived of the opportunity to express his emotions through facial expressions on one side of his face. This condition can no longer be corrected, which will certainly affect the quality of life. Distortion of facial expressions will lead to the development of depression and constant dissatisfaction with one’s appearance. Not every patient can come to terms with irreversible changes in their appearance without deep distress.
One of the most unpleasant manifestations of paralysis is the inability to close the eyelids on the injured side of the face. In this case, the eye will have to be regularly instilled with artificial tears to prevent the cornea from drying out, since natural hydration through blinking becomes unavailable for this eye.
Reasons for development
Facial nerve neuropathy can develop for the following reasons:
- progression of herpes, polio, mumps, enterovirus;
- hormonal imbalances (the disease appears especially often in the first half of pregnancy);
- tooth infections;
- sudden and severe hypothermia;
- injuries of the skull and jaws;
- sinusitis, otitis;
- diabetes;
- poor circulation in the blood vessels of the face;
- multiple sclerosis.
Most often, the disease in question develops when the facial nerve is cold - a short stay in a draft is enough for the inflammatory process to begin its progression.
Prevention of inflammation
To prevent the risk of developing inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to follow a number of measures:
- monitor oral hygiene and consult a dentist in a timely manner;
- do not stay in the cold for a long time or protect your face from freezing with a scarf;
- do not self-medicate otitis media.
At the first manifestations of pain on the face, you should immediately consult a doctor. This will stop the development of inflammation. In addition, early diagnosis allows for conservative treatment methods.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in treatment
Due to the fact that neuralgia does not affect the general condition of the body, many patients postpone visiting a doctor and treating the trigeminal nerve. In fact, this is the wrong approach, since the disease can lead to paralysis and muscle paresis. In addition, it has a significant impact on psychological and social aspects of life.
No less important is the fact that painkillers for trigeminal neuralgia provide only a temporary effect. Over time, anticonvulsant medications may also stop working as they become addictive. Therefore, you should not abuse medications. They only relieve the symptoms of neuralgia, and its cause can only be identified by a qualified specialist.
How to recognize
In fact, it is impossible to miss the symptoms of a head cold. As experts note, the first signs appear quite quickly - already in the first days, and then only increase. Symptoms include:
- general weakness;
- increase and decrease in pressure, often spasmodic;
- increase in body temperature;
- pain when trying to look at the light;
- chills;
- feeling of body aches;
- pain in the head, often with a feeling of throbbing;
- paroxysmal pain in the forehead and face.
Those who have suffered from such a cold often report that the headache was similar to a migraine. And pain in the head can be felt right down to the hair roots.
The main defender is immunity. How to keep children healthy during cold season? More details
Treatment
If a patient has a cold lymph node, treatment is selected taking into account the underlying disease. The treatment regimen depends on the type of pathogen.
Treatment methods:
- Antibiotic therapy - for bacterial infection.
- Antiretroviral drugs - for HIV and AIDS.
- Antiherpetic drugs - for herpetic infection.
- Antimycotics - for fungal infections.
- Bed rest and plenty of warm drinks - for mild ARVI.
Self-medication is dangerous not only due to the incorrect selection of drugs, but also the development of the underlying disease. It is better to detect it early and treat it than to waste time and money on inappropriate medications.
Read also: Dry paroxysmal cough
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
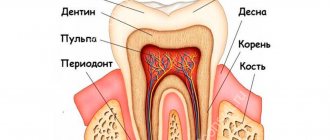
Symptoms of dental nerve inflammation
What are the most common symptoms if the nerve has a cold:
- possible hypersensitivity of the eyes, eyelids and forehead;
- the occurrence of constant aching pain in the jaw area;
- the appearance of shooting pain;
- constant severe pain, which worsens when teeth come into contact with cold or hot food;
- it hurts to smile.
The inflammatory process during hypothermia of the dental nerve occurs from the penetration of pathogenic microflora into the pulp, which is the cause of shooting pains when there is a large temperature difference or during physical contact (pain when chewing).
If pathogenic processes develop very quickly or the patient delays visiting the dental clinic, then inflammation can spread beyond the damaged tooth in the form of swelling, which everyone is accustomed to calling “flux.” Its medical name is periostitis. The second possible complication is periodontal inflammation. Unlike flux, it does not have an external expression in the form of noticeable swelling and is not accompanied by purulent formations.
This cold, in which the dental nerve hurts, occurs equally in men and women. Therefore, when the question arises: “What to do if your tooth gets a cold?” or “Is it possible to catch a cold on the facial nerve?”, consult a doctor immediately so as not to get even more unpleasant complications.
If you do not do this as soon as possible, the inflammatory process will develop, and this can lead to the appearance of multiple purulent foci, and subsequently to the death of first the tissue, and then the dental nerves. Over time, severe pain stops, but inflammation continues, and the longer you postpone a visit to the hospital, the more difficult the treatment will be.
Reasons for the onset of the disease
If you regularly visit the dentist and pay enough attention to dental care, then most likely you are not in danger of developing inflammation of the dental nerve. But if you neglect the condition of your teeth, such a disease is not uncommon. There are several reasons that can trigger nerve inflammation:
- neglected and not cured in time caries, especially when the remote control is damaged;
- There are chips, injuries, and fractures on the teeth;
- with a previously acquired infection due to improper treatment;
- during previous treatment, low-quality materials or medications were used;
- When installing the prosthesis, the tooth was processed incorrectly;
- Perhaps the body, at this time, was weakened by another infectious disease.
Treatment at home
What to do if your nerve has already caught a cold, but you won’t be able to visit a doctor in the near future for some reason. Is it possible to treat a tooth without the help of a dentist, and most importantly, how to treat it?
The first step is to carry out antibacterial therapy, which will prevent the development of the inflammatory process. Next, you need to deal with pain relief if professional help is not available.
The main rule that must be observed when treating any foci of inflammation is that you cannot apply warm compresses and in general do not warm the site of inflammation. The most you can do is cover your cheek with a scarf.
The following drugs can be used for pain relief: coffedon, dexalgin, oxadol, lidocaine .
ethnoscience
There are many traditional ways to treat a tooth without expensive medications. All of them belong to the so-called alternative medicine, which uses herbs, fruits or other very accessible and inexpensive remedies.
- you can try rinsing with strong alcoholic drinks, preferably regular vodka, at room temperature;
- you can apply a compress of chopped onion wrapped in a thin cloth to the ear on the opposite side of the diseased tooth;
- very good results were shown by rinsing with a lukewarm soda solution or sage infusion (15 mg of sage per 200 mg of hot water, leave for 15 minutes, strain before use);
- crush a regular analgin tablet and apply it to the painful area, this relieves acute pain well;
- Salted lard was considered an excellent remedy for toothache. Apply a small slice of lard to the sore spot;
- many traditional healers advise using a cut clove of garlic, like lard, and applying it to the affected tooth;
- make a small cotton ball, soak it in alcohol and apply it to the sore spot, trying not to touch the gum, as long-term exposure to alcohol can cause a burn;
- dilute a few drops of Chlorhexidine in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth with this solution at least three times a day;
- Another remedy is to chew a sorrel leaf;
- pour birch buds (25 g) with alcohol (100 g), leave for 10 days. Moisten a cotton ball with this tincture and place it on the sore tooth;
- cloves have long been considered an excellent remedy for toothache, so simply moisten a cotton ball with clove oil and apply it to the gum, and if there is an open cavity in the tooth, then put the cotton wool directly into it;
- Hydrogen peroxide has long become a popular component of many folk recipes, and in this case, rinsing with a solution of peroxide and water can effectively disinfect the oral cavity, stop inflammation and, as a bonus, remove plaque from teeth.
All these folk recipes will help relieve an attack of acute pain only for a short time, but will not solve the problem itself. Only a professional doctor will help you cure inflammation.
Prevention
Of course, such unpleasant conditions can be avoided using fairly simple prevention methods. “You should not go outside without hats, especially in winter and in windy weather. It is also necessary to use scarves to avoid blowing through the neck and back of the head. You should also avoid hypothermia of various kinds by dressing appropriately for the weather. In addition, special attention should be paid to supporting the immune system - there are a lot of ways, and quite diverse. You can also use vitamin therapy to strengthen the body’s defenses, but it must first be agreed upon with your doctor in order to take exactly those microelements and nutrients that you need during this period of time,” notes the immunologist.
You shouldn’t let the disease take its course, and you shouldn’t count on the fact that your immune system is strong, so running down the street without a hat is no big deal. There are always risks. And it’s better to take care of your health in advance.
Break up with ARVI. How to properly recover from a cold? More details
There are contraindications, you should consult your doctor