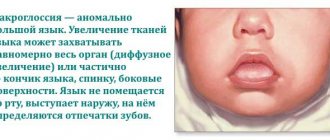
We are used to the fact that we need to go to the dentist if we have problems with our teeth or gums. What to do if you have inflammation of the tongue or glossitis? Dentists identify more than 10 types and subtypes of infection. The infection can be caused by both fungus and bacteria. Viral infection is less common. Inflammation can be caused by a lack of certain vitamins and minerals, or hormonal changes. There are many reasons for the disease, so it is important to identify what exactly caused the inflammatory process.
Causes of glossitis
- improper oral hygiene;
- bacterial infection;
- fungal infection;
- heavy metal poisoning;
- bad habits (smoking, alcoholism);
- congenital pathologies of the tongue (folded tongue);
- allergic reaction;
- tongue injury (often caused by malocclusion);
- oral infections;
- lack of iron in the body;
- burn of the mucous membrane (hot food or drinks);
- infectious diseases (AIDS, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, measles).
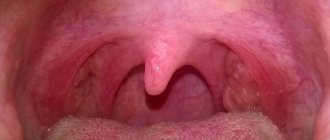
Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
The most common types of glossitis
The most common occurrences in dental practice are:
- acute catarrhal glossitis;
- tongue abscess;
- desquamative glossitis.
Acute catarrhal glossitis is the most common type of inflammation. Inflammation can be caused by microbes or mechanical damage to the tongue. The predominant symptoms are pain, redness and swelling.
A tongue abscess is the appearance of an abscess in the tongue. The abscess can be superficial, under the mucous membrane, or maybe in the thickness of the tongue. Abscesses in the thickness of the tongue, in addition to pain in the tongue, can cause a disturbance in the general condition. A person develops a fever, a headache, and weakness. Most often occurs due to injury to the tongue.
Desquamative glossitis, also known as “geographic tongue,” most often appears in children. It appears in the form of various spots on the tongue, which look like a white coating, alternating with areas of pink mucous membrane. There are no changes other than appearance. Scientists have identified a clear reason for it. The main factors are believed to be bacteria, allergic reactions and hormonal imbalances.
Why do ulcers appear under the tongue?
An ulcer under the tongue occurs due to an inflammatory process of an erosive nature. An abscess can be caused by various factors. It is very important to identify the cause that provoked the disease. After all, this is the only way the doctor will be able to prescribe effective treatment to the patient.
The most common causes of mouth ulcers include:
Leukoplakia under the tongue - the spot cannot be removed
Development of stomatitis
It can be of three types, namely candidal, aphthous and herpetic. The second option is more common. This stomatitis is chronic, so it cannot be completely cured. Therefore, from time to time the patient will experience a sore under the tongue and in other parts of the oral cavity.
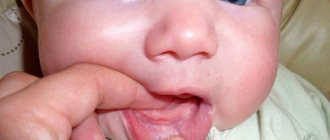
Mechanical damage to the oral mucosa
This reason is often explained by the appearance of ulcers on the frenulum of the tongue in a child. He may get hurt on cutlery or scratched by candy. Simply biting your tongue is enough to create a wound on it.
Just one microcrack can cause serious inflammation in the mouth. It develops into an abscess due to the active activity of bacteria. Within a few hours, the first symptoms of the disease will begin to appear in a child or adult. If you do not provide first aid to the patient, the infection will spread throughout the entire oral cavity.
READ ALSO: Herpes on the lips dream book
Hematoma on the frenulum after trimming
Somatic disease
Often a white sore is one of the symptoms of a dangerous disease that affects the human immune system. These diseases include tuberculosis and HIV. Ulcers will begin to appear due to poor personal hygiene, as well as decreased immunity.
Varicose veins under the tongue with inflammation
To find out why ulcers appeared under the tongue in an adult or child, you need to ask the patient about his health and find out if he was injured several hours before the onset of the inflammatory process.
Symptoms of glossitis
- increased salivation;
- swelling and redness;
- pain and burning when eating;
- plaque on the tongue in the form of spots;
- bad breath;
- papillomas or warts on the tongue;
- speech disorder;
- foreign body sensation.
Prevention of glossitis - high-quality oral hygiene and no bad habits. It is important to undergo timely preventive examinations and also eat well. All these factors actively contribute to the development of the disease and bring a number of problems.
Pimples on tongue
Pimples on the tongue are painful and cause discomfort, but they are easily treated and do not cause complications. A pimple on the tongue can appear for many reasons, most often due to microtrauma of the tongue, stomatitis or herpes. In principle, there cannot be acne on the tongue, since there are no sebaceous glands on it. Those formations that are mistaken for pimples are not actually pimples - they are not filled with purulent exudate. These are small swellings and ulcers on the surface of the tongue. They are white, pink, red, yellow, depending on the complexity of the disease and the cause of formation. Small pimples are very painful, they interfere with eating, talking and even bother the patient at rest.
White pimple on tongue
A white pimple on the tongue most often appears as a result of stomatitis or candidiasis. These two diseases are treated completely differently; you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms in order to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment. Candidiasis is characterized by white pimples and a coating on the tongue, which in appearance resembles cottage cheese and covers the entire surface of the oral cavity. There are also white pimples on the base, tip and under the tongue.
With stomatitis, small pimples appear on the tongue. There are usually many of them, they can merge with each other. These small white pimples at the tip or root, at the base or underneath are very painful and itchy. The pain intensifies after eating. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Treatment consists of antiseptic treatment of the surface of the oral cavity and lifestyle correction, since the main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene.
Red pimple on tongue
Red pimples on the tongue are the main sign of glossitis, an inflammatory disease. Outwardly, they look like inflamed red dots that hurt.
Glossitis can appear for many reasons:
- Allergic reaction;
- alcohol abuse;
- eating too hot and spicy food;
- the presence of the herpes virus.
The appearance of yellow pimples on the tongue is usually not an independent disease. Often with stomatitis or candidiasis, the coating on the surface of the tongue takes on a yellowish rather than white tint. Yellow pimples most often also mean either candidiasis or stomatitis.
Pink pimples on the tongue , like yellow ones, are not an independent disease. Usually they are an early stage of glossitis, when the inflammatory process has not yet reached its peak. If pink acne appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for advice.
The main causes of acne:
Mechanical damage
In the process of chewing or biting food, we bite our tongue, resulting in a slight mechanical injury. The risk of surface damage increases when consuming hard foods with sharp edges (crackers, chips, seeds). A small painful swelling or bump forms at the site of the injury, which after some time turns into a white pimple.
You should exclude spicy and hot foods from your diet, carefully monitor oral hygiene, and after a few days the pimple will disappear on its own.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction is possible to food, medicine or toothpaste. This causes small white pimples and sores to form that hurt and irritate when eating or drinking liquids. If your doctor suspects an allergy, it is very important to identify the allergen and eliminate it from your diet.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is a common cause of white or red pimples on the surface of the tongue. The main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene, exposure to pathogenic bacteria on the mucous membranes due to dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables. Most often, children suffer from stomatitis, because they tend to put everything in their mouth. At the first suspicion of stomatitis, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe medications that relieve itching and soreness of the tongue, as well as promote the speedy healing of ulcers and pimples.
Herpes
Herpes can affect all mucous surfaces of the human body, including the oral cavity. In this case, watery pimples may appear on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks. Without proper treatment, herpes can eventually affect the entire body, including the brain. Therefore, if you have a herpes virus, you should consult a doctor and undergo a course of antiherpetic therapy.
Poor nutrition
If you eat too much spicy and hot food, inflammation of the tongue, or glossitis, may occur. Drinking alcohol in large quantities, as well as smoking, can cause inflammation of the tongue. Therefore, when the first problems appear, you should immediately try to get rid of bad habits.
Pathologies of the patient's internal organs
Pimples on the tongue can be a manifestation of various diseases, including candidiasis or tuberculosis. If a pimple does not go away for a long time, be sure to consult a doctor.
Weakened immunity
If the immune system is weakened as a result of a previous illness or due to a lack of vitamins and microelements, small painful pimples may appear on the surface of the tongue. It is necessary to take immunomodulators, as well as drugs with lactobacilli to normalize intestinal function and correct the activity of the immune system.
You can only get rid of a pimple on your tongue using comprehensive measures. It is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the true cause of its occurrence. The oral cavity should be kept clean, preferably rinsed with a soda solution or a decoction of St. John's wort. It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system and limit the consumption of spicy and too hot foods so as not to irritate the inflamed nodule.
A pimple at the base of the tongue makes it difficult to swallow and even talk; it hurts and causes a lot of trouble. It could be stomatitis, a fungal infection, a sore throat or pharyngitis. Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis.
A pimple on the tip of the tongue can pop up at the site of a microtrauma as a result of an infection entering the wound.
In any case, it is advisable to consult a doctor and get tested to make an accurate diagnosis.
For any questions, please call: +7 (343) 2000 730; +7 We work daily, without breaks: Mon-Sat 09.00-21.00 Sun 10.00-20.00 We are waiting for you at the address: Ekaterinburg, st. Gottwald 14a, office 6. Dentistry "MK DENT"
Treatment of glossitis
A specialist must make an accurate diagnosis and identify the cause of the disease. If you suspect that you have glossitis , and all symptoms indicate this, contact your dental clinic. This is the only way to create the right treatment plan and provide timely assistance. Quite often in such cases, doctors prescribe antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and rinsing the mouth with special antiseptic solutions. In advanced stages, glossitis is treated surgically. Deep abscesses must be opened in the maxillofacial department. Under no circumstances should you take medications without a doctor’s recommendation.
You can cure glossitis, caries or any other diseases of the oral cavity right in your sleep. Family Dentistry Center "Medexpert" provides dental treatment under medicinal sedation. Thanks to this approach, the patient falls into a healthy sleep, ceases to feel pain and discomfort, while the vital functions of the body remain unchanged. Sedation is widely used in pediatric dentistry and even helps fight dental phobia. Dental treatment can be comfortable and painless - tested for yourself.
Which doctor should I contact?
If a lump appears under the tongue on the frenulum, you need to find out what factors provoked its formation. Only a doctor can correctly determine the cause. After all, the ball can be filled with liquid or consist of epithelial cells. The degree of discomfort depends on the size of the formation. When papillomas are soft, the patient may not feel them, but large inflammatory growths interfere and begin to hurt. Contact your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- The mucous tissues of the oral cavity constantly dry out;
- The deficiency of saliva and its composition is clearly expressed;
- The taste sensations have changed a lot;
- Increasing pain appeared;
- Swelling on the face increases;
The affected tissue around the lesion may become red and begin to bleed. First of all, you should consult with your local therapist. To confirm the suspected diagnosis, it is most often necessary to visit a dermatologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, venereologist, or gastroenterologist. If the need arises, the patient is referred to a surgeon or oncologist. During the examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a thorough examination, and performs laboratory diagnostics and histology. In complex cases with abscesses, patients are referred for ultrasound examination, as well as computed tomography. The pathogen is detected using a cytological analysis of saliva.
Which people are at risk for stomatitis?
As already noted, children are primarily susceptible to stomatitis, since their immune system is just learning to fight infections and diseases and respond to irritants appropriately. Therefore, if, with timely consultation with a doctor and proper treatment, your baby still chronically develops stomatitis in the mouth, then perhaps the reason is due to age, and over time these problems will disappear.
But besides age, there are other factors that increase the risk of stomatitis ulcers in a person’s mouth. They are associated with various reasons, some of which we have already named when characterizing the types of stomatitis, but now we will try to specify each factor separately.
Those at risk for possible development of stomatitis include:
- People with a hereditary predisposition to the disease. Scientists have proven that the likelihood that stomatitis will develop in a person’s mouth (on the palate, mucous membrane, throat or tongue) increases if one or both parents have ever encountered similar problems. The best way out in this situation is to follow the rules of oral hygiene and take vitamin and immunomodulatory complexes as prescribed by your doctor.
- People with current somatic diseases. Quite often situations arise when stomatitis chronically develops in a person’s mouth without any obvious reason. During a complete examination of the body of such a person, any diseases are usually revealed, in particular, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (giardiasis or helminthic infestations). Parasites, while in the body, may not manifest themselves in any way and not bother a person for years, but they reduce his immunity and prevent resistance to infections and other diseases. In this case, in order to get rid of stomatitis in the oral cavity, a person should undergo a course of treatment that will allow him to get rid of other concomitant diseases.
- People with reduced immunity. Human immunity is reduced not only by somatic diseases, but also, for example, by factors such as stress. Therefore, if you have a hard job or tense family relationships, this can cause chronic stomatitis, localized on the oral mucosa. In addition, frequent occurrence of ulcers in a person's mouth may indicate more serious problems with the immune system caused by a disease such as AIDS. Therefore, in this situation, a person is recommended to get tested, undergo a full examination of the body and get plenty of rest.
- People with bad habits. Bad habits such as alcohol, smoking and drug use can cause stomatitis and the formation of painful ulcers in the mouth. The fact is that such a lifestyle weakens the immune system and undermines human health. In addition, cigarette smoke and alcohol create favorable conditions in the oral cavity for the development of bacteria, viruses and fungal infections, which provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers on the human mucosa.
If you have seen photographs of people with stomatitis in the mouth, then you have probably noticed how unattractive this disease looks, not to mention how much discomfort it causes to a person. Therefore, if you are at risk for the possibility of developing stomatitis ulcers on the mucous membrane, palate, throat or tongue, then you should take measures to reduce the chances of getting stomatitis: quit bad habits, undergo a course of treatment for somatic diseases, increase your immunity and take vitamin complexes. But these measures should be taken only after consulting a doctor.
How does the infection manifest and why is it dangerous?
The most striking symptom of oral candidiasis is a white, loose coating on the mucous membrane. It mainly covers the tongue, cheeks, and may affect the gums and palate. Plaque can be easily scraped out; the tissue underneath is prone to redness and may bleed. Other signs of the disease include:
- unpleasant taste;
- dry mouth;
- burning;
- the appearance of cracks in the corners of the lips;
- difficulty or painful swallowing;
- unpleasant sensations with habitual movements of the tongue.
Candidiasis can be acute or chronic. In most cases, it is the acute form that manifests itself; the chronic form is typical for carriers of HIV infections and smokers. Depending on the degree and form of the disease, other symptoms may be observed, so even if one or two appear, you should immediately contact your dentist.
Features of treatment of stomatitis
The therapeutic regimen is selected taking into account the cause of the disease. The approach must be comprehensive. To relieve pain symptoms, you need to use medications containing lidocaine. These can be gels, tablets, rinsing solutions.
If it turns out that the pathology is caused by herpes, you need to use antiviral drugs, including oxolin and acyclovir. In case of severe inflammation, medications with the addition of solcoseryl, vitamins, and oils help. If the culprit of the pathology is bacteria, the use of dental ointments based on chlorhexidine, miramistin, furatsilin, metronidazole, chlorophyllipt is indicated.
When a disease is of a fungal nature, antifungal compounds come to the rescue. Their active substances are nystatin, clotrimazole, miconazole. Rinsing your mouth with a weak soda solution helps with fungus.
If during the examination it is determined that the tongue is damaged as a result of the progression of an allergic reaction, general-spectrum antihistamines are prescribed. In the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the activity of the stomach and intestines is first of all normalized. Usually, after eliminating the underlying disease, cases of stomatitis also disappear.
In order for positive dynamics to emerge as quickly as possible, the patient must follow all medical prescriptions and not stop treatment ahead of time. Then the ulcers will heal within three to seven days, the pain will be a thing of the past.