The hemostatic sponge is an important tool in the home and travel first aid kit and the best assistant to the surgeon. When used, it is possible to quickly stop bleeding. Today, hemostatic sponges come in a huge variety. They can be easily selected in size depending on the conditions of use.
Features of wound healing after tooth extraction
Before moving directly to hemostatic sponges, what they consist of and how to use them, you need to understand how the wound heals after removal and what can go wrong here. More on this later.
Why is there bleeding after removal?
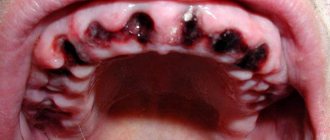
Bleeding is a natural reaction to surgery. After all, when a tooth is removed, the smallest capillaries that penetrate the gums and ligamentous apparatus - the periodontium, which attaches the roots to the bone socket - are torn. And with difficult removal, the bleeding may be even stronger, because... The dentist makes incisions in the gums and drills into the jaw bone - the tissue is more damaged.
Bleeding is a natural reaction to surgery
Read on the topic: How long can a tooth hurt after extraction - normal and pathological.
How long does bleeding last normally?
Normally, the blood stops within 15-20 minutes (less often, within 45 minutes) and a blood clot forms in the socket. It seals the hole like a cork, preventing germs from penetrating inside. If the patient has problems that affect blood clotting, then the bleeding time is prolonged, and a clot may not form at all. And this is already fraught with inflammation of the bone socket (the pathology is called “alveolitis”). Therefore, according to indications, the dentist applies a hemostatic drug to the area of the extracted tooth.
On a note! Bleeding may appear again for a short time (and there will be quite a bit of blood) after the anesthetic wears off - if it contained adrenaline. This substance narrows the blood vessels in the intervention area, and as they expand normally, slight bleeding occurs. It goes away quickly.
Why does the bleeding not stop for a long time?
As a rule, after tooth extraction, the dentist says that you should not eat or drink for 2 hours. But few people say that you should not rinse your mouth or suck drinks out of a straw. In the first days, only oral baths are allowed, and it is better to drink in the usual way. Also, do not touch the wound with a brush. It is better to chew food on the healthy “side” of the jaw. Otherwise, there is a risk of moving or “pulling” the clot out of the hole - which will provoke new bleeding or even inflammation, which will result in long-term treatment.
The following groups of patients are also at risk:
- who has not formed a blood clot,
- with blood diseases,
- who takes blood clotting medications,
- having high blood pressure,
- women during menstruation or menopause,
- exposing themselves to physical activity immediately after removal and during the recovery process,
- if there was already inflammation at the extraction site (for example, pericoronitis above a wisdom tooth),
- during complex operations: when several teeth were removed at the same time, or manipulations were performed with increased tissue trauma.
Bleeding may occur during physical exertion after removal.
When you need urgent help
If the bleeding is profuse and does not stop for a long time, if after normalization of the condition the blood begins to ooze heavily again, this is a reason to consult a dentist. In a situation where the patient, in the presence of continuous bleeding, feels weakness, apathy, if the temperature has risen sharply (above 39 degrees Celsius), it is better to call an ambulance or go to the hospital on your own.
Modern hemostatic materials in surgery
Lecture transcript
XXV All-Russian Educational Internet Session for doctors
Total duration: 20:01
00:00
Oksana Mikhailovna Drapkina, Secretary of the Interdepartmental Scientific Council on Therapy of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor:
— We are starting a new section - the surgical section. The only lecture in this section will be: “Modern hemostatic materials in surgery.” Shreiner Igor Vladimirovich. Please.
Igor Vladimirovich Shreiner:
— The need to achieve adequate hemostasis during surgery is a necessity that the surgeon faces from the moment the operation begins until the very end. In principle, on the first day of the early postoperative period.
In modern surgery, the number of surgical interventions on organs that can cause active bleeding (surgeries on the heart, blood vessels, parenchymal organs, liver, pancreas, kidneys) is increasing. The use of traditional methods of hemostasis (mechanical, thermal hemostasis) can lead not only to failure to achieve hemostasis, but also to the development of serious complications.
They are being replaced by new methods of local hemostasis: chemical and biological hemostasis.
What requirements need to be developed for new local hemostatic agents? These are application products.
- Induce complete cessation of capillary and parenchymal bleeding in the shortest possible time (preferably up to two minutes).
- Possess high adhesiveness.
- Adhere tightly to the wound surface.
- Prevent recurrent bleeding.
- Do not have an irritating effect on surrounding tissues or undesirable effects on the body of the breakdown products of this hemostatic agent.
- Do not affect the function of hemostasis in the general bloodstream.
- Be easy to use: cover the wound surface evenly and simultaneously. It is easy to remove from the wound surface in the absence of its resorption.
01:58
Several mechanisms of chemical hemostasis can be distinguished.
Hygroscopic. The mechanism is quite clear: due to the active absorption of water and low molecular weight substances by the hemostatic material, an increased concentration of coagulation factors and formed elements occurs in the area of the vascular defect, which contributes to the achievement of hemostasis.
The adhesive effect is an increased ability to fix the formed elements of blood, as well as procoagulant proteins on its surface.
The vasoconstrictor mechanism is self-explanatory.
Participation of coagulation factors - that is, the achievement of biological hemostasis.
Many means of hemostasis are most often of a mixed nature.
Modern hemostatic agents include a fairly wide range of drugs. They can be called modern conditionally, because these are most often drugs that began to be used for this purpose in recent years, although they have been known in themselves for a long time. These are clotting factors: thrombin, fibrin and synthetic glue.
Traditional hemostatic agents include materials based on gelatin, cellulose and collagen. There are several additional types of hemostatic agents. These are alginates and wax.
As we can see, hemostatic agents have a wide range of effects on the coagulation cascade and can affect all its stages. This makes it possible to achieve adequate hemostasis in almost any situation with the combined use of these agents.
The most well-known and long-used traditional hemostatic agent is collagen. Being a structural protein of the body, it is the first to stand in the way of blood and formed elements during bleeding. Contacts them in the subendothelial layer, causing their adhesion and platelet degranulation. It has a procoagulant effect.
This mechanism was transferred to the use of collagen as a local hemostatic agent. In addition, when using a sponge, this material can also cause hemostasis due to the hygroscopic effect.
These hemostatic materials are produced from bovine dermis.
There are various forms of collagen release that allow you to actively use it in various situations: from solutions and powders to sponges and pastes. There are often combinations of collagen with various substances. These can be both antibacterial and hemostatic substances (allowing the effectiveness of collagen preparations to be increased 4-5 times). This is thrombin, fibrin, which I will talk about later.
Collagen is effective against capillary bleeding from soft tissues. Using it without any additional combinations on parenchymal and venous bleeding is ineffective. It is in this group of bleeding that it is effective compared to gauze packing (a physical method of hemostasis). Allows you to stop bleeding 1.5-2, sometimes 3 times faster.
05:57
Oksana Drapkina: Igor Vladimirovich, in what form should collagen be? Is this a sponge? What is she like? Or are there different forms?
Igor Shriner: As I already said, there are different forms of drugs. The most common one is still a sponge due to the additional hygroscopic effect.
Oksana Drapkina: The sponge is probably not very convenient? It won't dissolve, will it?
Igor Shreiner: Firstly, collagen itself is difficult to absorb and contributes to the further formation of dense scar changes in the area where it is applied.
Secondly, the sponge itself does not always help stop bleeding, because the shape of the wound and the depth of the wound vary. This is difficult to do with a sponge. In this situation, it is more effective to use some liquid forms of other drugs (this is impossible with collagen)…
Oksana Drapkina: Or powder.
Igor Shriner: Yes, or powder materials.
06:52
Oksana Drapkina: In surgery, is this, in principle, a big problem? Is the problem of stopping bleeding even a problem in surgical practice?
Igor Shriner: This is a problem during large and serious operations, most often accompanied by bleeding. Oncological operations, liver operations. It is not always easy to achieve some kind of coagulation. It is impossible to achieve hemostasis by suturing or ligating blood vessels. Of course, these materials are actively used.
Oksana Drapkina: Sorry for interrupting.
Igor Shriner: I think that now any major oncological operation requires additional use...
Oksana Drapkina: Hemostatic drugs.
Igor Shriner: Yes. This significantly reduces the risk of postoperative problems (bleeding) and, accordingly, the risk of complications.
Another traditional hemostatic agent is gelatin. The mechanism of its action is not entirely clear. Most likely, the most common possible mechanisms include damage to the platelets themselves upon contact with gelatin and the release of coagulation factors. Also, when using the “sponge” shape, a hygroscopic effect is possible.
The main positive aspect of using gelatin is the possibility of its complete degradation within 4-6 weeks.
It is also effective for capillary bleeding in soft tissues. Often comparable in effectiveness to, and in some cases superior to, collagen derivatives. The effectiveness of gelatin use is enhanced in combination with other hemostatic agents.
08:27
Oxidized regenerated cellulose is actively used as a hemostatic agent. Its mechanism of action is quite diverse. It both adsorbs and fixes coagulation factors and platelets on itself, and due to the low pH of cellulose, it causes vasoconstriction in the area of its application.
Most often it is used in the form of fabric plates. This is a convenient form because it is softer than a sponge and allows you to place it on a wound of any configuration.
Completely disintegrates after 1-3 weeks. However, due to the risk of granulomas in this area, many recommendations indicate the need for its removal after hemostasis has been achieved.
This is a fairly effective hemostatic agent. It surpasses the effectiveness of collagen and gelatin. Helps achieve hemostasis not only with capillary and parenchymal bleeding, but also with venous and arterial bleeding. Used in operations accompanied by severe bleeding (uterus, bones, after resection of the liver, kidneys).
Another long-term remedy is a combination of albumin and glutaraldehyde. The mechanism of its action is associated with the formation of bonds between albumin and the wound surface (mechanical closure of the vascular defect). It is this mechanical effect that makes it possible to achieve hemostasis regardless of the patient’s coagulation status.
It is often used in cardiovascular surgery for bleeding from vascular anastomoses at the puncture site, when patients can use acetylsalicylic acid, heparin, and where mechanical closure of defects is needed.
Thrombin can also be classified as a hemostatic agent used intraoperatively. Both bovine thrombin and recombinant human thrombin are used. Both show a high hemostatic effect, although bovine thrombin induces a high immune response and antibody production. This limits its reuse.
I would like to note that the largest number of cases of complications described when using local hemostatics is associated with the local use of thrombin. Its entry into the bloodstream causes serious coagulopathies.
As a combination: thrombin and gelatin. This is an effective and widely used combination of gelatin matrix and thrombin coating. Effectively reduces blood loss after liver resections. Actively used in vascular operations. The effectiveness of this particular combination has been proven in randomized, controlled trials, where it has proven to reduce the volume of blood loss and the volume of blood transfusion.
11:38
The most currently discussed and used material is fibrin glue. The mechanism is clear. This is the direct formation of a fibrin clot at the site of application of the drug. To achieve hemostasis and prolong it, it is combined with antifibrinolytic drugs: tranexamic acid, aprotinin. For fibrin glue, controlled regulation of the rate of fibrin clot formation is possible due to different concentrations of thrombin in this mixture.
Another combination drug is a combination of collagen and fibrinogen. This is most often a collagen sponge coated with fibrinogen. It is more effective than most of the above-mentioned drugs.
For liver resections, this can be called a reference drug for hemostasis. It has been studied in many randomized trials after liver resection, where its effectiveness has been proven. Everything else that is used in this area is precisely compared with the effectiveness of these drugs.
Synthetic adhesives are understandable: mechanical sealing of vessels (defects in them). These are both cyanoacrylate adhesives and polyethylene glycol polymers.
I would like to say a little about the local use of systemic drugs. This is often used in our practice.
These drugs cannot stop bleeding, however, studies have shown that with the routine planned use of these drugs in operations accompanied by large blood loss, such as joint replacement, cardiovascular surgery, the use of tranexamic acid, aprotinin can significantly reduce blood loss and the volume of further blood transfusion.
13:40
Of the modern drugs that are entering the arena of local hemostatic therapies, I would like to note the emerging large number of reports and studies with new drugs that are polysaccharides in their structure. This is chitin and its derivative – chitosan.
Causing an active adhesive effect due to the ionic interaction between the positive charge of the polymer and the negative charge of the erythrocyte cell membrane, they ensure the formation of a clot in the area of the vascular defect.
As a positive point, it is also revealed that their action in connection with the mechanism is not related to the classical coagulation pathways. This helps surgeons use them in patients with bleeding disorders and platelet dysfunction.
These drugs are more effective than oxidized cellulose. Accordingly, they are more effective than traditional drugs such as gelatin and collagen. They have comparable effectiveness to the drug "Tachocomb" (a preparation of collagen and fibrinogen). Its effectiveness is even higher in compromised groups - that is, in experimental, heparinized animals.
It is possible to create a microcrystalline bulk form of drugs that can stop bleeding in difficult areas of vascular punctures.
Not only the drugs themselves are being modernized, but also their forms and mechanisms. In addition to the direct adhesive effect, preparations are created that, due to their physical structure (these are microporous polysaccharide hemosphere preparations), adsorb water and low molecular weight substances, concentrating protein coagulation factors, platelets, and other blood cells on their surface, thereby enhancing the coagulation mechanism.
It is the powder form of release that allows these preparations to be coated with deep and complex surfaces.
16:00
There are isolated reports of new possibilities for hemostatic therapy. This is a dosed release of hemostatic drugs: the creation of a hemostatic material with microspheres embedded in it, which contains either thrombin or oxidized regenerated cellulose. They do not immediately exhibit their hemostatic effect, but as the material is destroyed.
A fairly proven approach: the creation of combination drugs that act at various stages of the hemostatic cascade. One of such drugs produced in our country is the drug “Algigemostat”. This is a local hemostatic agent, available in powder form.
It contains calcium alginates, epsilon-aminocaproic acid, oak bark extract, chlorhexidine.
Calcium alginate is a drug that has proven itself as a wound cleansing and wound healing agent. It was during its use as a wound-healing agent that its pronounced hemostatic effect was noted.
In addition, the calcium salt of alginate allows you to maintain a high concentration of calcium in the bleeding area. This drug is effective for capillary bleeding from soft tissues.
Additional components of Algigemostat can enhance the effect of calcium alginate. This is epsilon-aminocaproic acid, which, being an inhibitor of fibrinolysis, prevents the destruction of the formed fibrin clot. Oak bark extract causes partial coagulation of plasma proteins, thereby also stimulating the hemostatic cascade. The addition of chlorhexidine, an antibacterial drug, prevents further infection of the area where the hemostatic agent is applied. This is important when stopping bleeding from deep wounds, where it is impossible to adequately remove elements of infection.
18:17
We can name such indications for the use of Algigemostat.
- Stopping capillary bleeding in soft tissues in wide practice (surgical, gynecological, urological and traumatological).
- Hemostasis and, due to the capabilities of alginates, healing of open wound surfaces.
- Hemostasis of postoperative wounds with an antibacterial effect to avoid further wound suppuration.
The advantage of Algigemostat compared to other hemostatic agents is the combined effect on various stages of the hemostatic cascade.
In addition, the form of its release, as I have already indicated earlier for other drugs, is powder. This allows you to increase the adhesive properties of the hemostatic agent, prevent it from being washed away by blood or exudate later during the wound process, and allows you to apply the drug to wound surfaces of any configuration.
Also, unlike drugs in the form of a sponge or plate, it allows you to additionally apply the drug if the dose that we have already applied is ineffective. All this allows you to effectively stop bleeding and achieve the necessary hemostasis.
In conclusion, I would like to say that, despite such a wide range of drugs, their use is still complementary to other mechanical methods of hemostasis and is not a panacea for bleeding. First you need to try to achieve mechanical hemostasis, and only then use hemostatic agents.
Thank you.
What is a hemostatic sponge
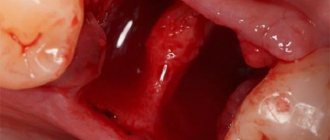
Now let's move on to why a hemostatic sponge is placed in the hole left after tooth extraction? Let's first understand the terminology. “Hemo” means “blood” and “stasis” means stopping. Those. a hemostatic sponge is needed to stop bleeding. In simple terms, this is a kind of replacement for a blood clot. The hemostatic sponge in the tooth socket not only seals the open cavity, but also has a hemostatic effect. Firstly, it puts pressure on small vessels, stopping bleeding. Secondly, it absorbs excess blood, increasing several times. The bleeding stops within 2-3 minutes.
On a note! By the way, local hemostatic agents are used not only in dentistry, but also in other areas of medicine - for example, hemostatic bandages successfully replace tourniquets that are applied for bleeding.
Hemostatic collagen sponge (hemostatic)
The collagen hemostatic sponge is intended for use as a wound covering in surgery, traumatology, dermatology, dentistry and at home as a local hemostatic agent for capillary and parenchymal bleeding. Collagen hemostatic sponge (biodegradable collagen plate) is designed to provide local hemostatic and antiseptic effects, stimulate tissue regeneration. The hemostatic collagen sponge is used as a hemostatic agent for capillary and parenchymal bleeding, for tamponade of the dural sinuses, to stop bleeding from the bone marrow canal, to stop alveolar bleeding after tooth extraction, to fill defects of parenchymal organs (in particular, after resection liver), to close the gallbladder bed after cholecystectomy. There are no indications for limiting the use of collagen plates in children, the elderly, pregnant women and nursing mothers . Contraindications: - Increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug; — Intolerance to nitrofuran drugs (furacilin, furagin); - Arterial bleeding; — Purulent wounds, pyoderma.
The hemostatic sponge is a plate from yellow to brown in color, with a specific odor of acetic acid, with a porous structure, with a relief surface, absorbs liquid well, and swells slightly. The collagen plate is prepared from a collagen solution and is produced at two domestic enterprises. Hemostatic sponge composition: The composition of hemostatic plates produced by JSC Luzhsky includes : collagen, boric acid and furatsilin. The composition of the collagen sponge produced by Zelenaya Dubrava JSC includes: collagen no less than 80%, boric acid no less than 0.1%, aminocaproic acid no less than 1%, argovite no less than 0.01%. Technical characteristics: The hemostatic plate is insoluble in cold water and organic solvents, stable at temperatures not exceeding 75 °C. At higher temperatures and a humid environment, partial dissolution of the hemostatic plates occurs. pH of the water extract is from 4.5 to 6.5 ( Green oak forest: within 5.0-7.5); moisture content not more than 18%. Moisture absorption is at least 5 grams per 1 gram of dry matter. Hemostatic plates are made in dimensions: (50±5) x (50±5) x (7±2) mm, (90±10) x (90±10) x (7±2) mm, (97±10) x ( 97±10) x (7±2) mm, diameter (11+1) x (7+2) mm Application:
Immediately before use, observing the rules of asepsis, open the packaging with scissors. The hemostatic plate (collagen sponge) is removed, applied to the bleeding area and pressed against it for 1-2 minutes, or the bleeding surface is tightly tamponed, followed by bandaging. After soaking in blood, the hemostatic plate fits tightly to the bleeding surface. To close damaged areas of parenchymal organs (liver) or the gall bladder bed after cholecystectomy, a hemostatic plate is applied to the damaged surface. If the bleeding does not stop, a second layer of hemostatic plate can be applied. After stopping the bleeding, the hemostatic plate is fixed with a U-shaped suture. Further operation is carried out according to accepted methods. To stop bleeding from a vascular suture, the bleeding area is covered with a hemostatic plate. After the bleeding has stopped, the hemostatic plate is not removed, as it subsequently completely dissolves. The size and number of hemostatic plates used are selected in accordance with the size of the bleeding surface or the volume of the cavity. Packaging: No. 1 - Pack hemostatic plates (sponges) with dimensions 50x50 mm, 90x90 mm, diameter 11 mm, 1 pc. in sterile packaging made of polyform and laminated paper or other materials approved for packaging medical products. Individually packaged plates along with instructions for use are placed in a cardboard box. No. 10 - Individual sterile packaging - containers made of Poliform film and laminated paper, packed in 10 pieces in cardboard packs. Sterilization: radiation Guaranteed shelf life of the plates from the date of sterilization: 3 years. Manufacturers: OJSC Luzhsky, Russia CJSC Zelenaya Dubrava , Russia
Hemostatic sponge (plate) price from RUB 48.50:
| Name | Price with VAT | Package | Manufacturer |
| 50 x 50 mm | 48,50 | №1 | "Luzhsky, Russia |
| 58.00 rub. | "Green oak grove" , Russia | ||
| 90 x 90 mm | 97.00 rub. | "Luzhsky, Russia | |
| RUB 115.00 | "Green oak grove" , Russia | ||
| 97 x 97 mm | RUB 115.00 |
Appearance and release form
The hemostatic sponge looks like a cube or plate, which looks like a small sponge or a piece of yellow or white foam rubber. Although in fact it consists mainly of natural collagen with various medicinal additives. The plate is quite soft and easy to cut, which allows the dentist to cut the desired size according to the shape of the hole.
The plate is quite soft and easy to cut
Manufacturers produce both small (1x1 centimeter) and large sponges (10x10 cm). The plates are tightly sealed in transparent bags, and the cubes are sealed in dark, opaque bottles. Hemostatic powders and gels are also produced. Absolutely all collagen hemostatics dissolve on their own in the wound over time.
Types of hemostatic sponges
According to the manufacturing method, hemostatic sponges for teeth are of the following types:
- from donor blood plasma - amben,
- from bones/tendons/blood of cattle - collagen and gelatin.
You need to understand that a hemostatic agent not only stops bleeding (due to aminocaproic acid, for example) and stimulates the formation of a blood clot, but also has an antiseptic effect. It can also accelerate regeneration and relieve inflammation. It all depends on the active components that make up the hemostatic sponge. The drug can be impregnated with the following substances:
- antiseptics: chlorhexidine, furatsilin, silver suspension, boric acid, iodoform,
- local anesthetics: for example, lidocaine,
- preparations for bone regeneration: calcium phosphate,
- antibiotics: metronidazole, chloramphenicol, neomycin, gentamicin, etc.,
- natural substances: propolis, eugenol, etc.
Hemostatic sponges for teeth come in different types
What is she?
So, a hemostatic sponge is an effective hemostatic agent, widely used in various medical fields, in particular, by dentists when removing teeth. The sponge has pronounced antiseptic and sorbing properties, and therefore not only stops bleeding, but also protects the wound from bacteria. In addition, thanks to the described remedy, damaged sockets heal faster.
Main types of hemostatic sponges
So, the described remedy is intended not only to stop bleeding, but also to prevent the occurrence of inflammatory processes if a complex surgical intervention was performed (for example, a wisdom tooth was removed). In standard cases of extraction, bleeding is stopped with the help of a collagen sponge that stops the bleeding.
After surgery, if there is a risk of inflammation in the tooth socket, dentists often recommend using “Alvostaz” - this is a special alveolar compress made in the form of a sponge. "Alvostaz" has an antiseptic and hemostatic effect, in addition, the drug is often used for the prevention/therapy of alveolitis.
About release forms
So, what is a hemostatic sponge? Essentially, it is a yellowish pressed powder that has a faint aroma of acetic acid. These sponges are sold in the form of small rectangular elastic plates (their sizes can be 5x5 cm and 9x9 cm) with a porous dry structure. During production, sponges are placed in PET bags, which are tightly closed, and then placed individually in cardboard packaging.
These sponges - just like regular sponges - perfectly absorb liquid, swelling at the same time. Sponges do not dissolve in cold water, as well as in substances of organic origin, but can partially dissolve in water whose temperature is more than 75 degrees. To make pressed plates, a collagen solution is used - it is obtained from the tendons/skin of cattle. There are also additional components - boric acid and nitrofural.
The above-mentioned “Alvostaz” is considered one of the most effective remedies. The product is sold in the form of small (dimensions - 1x1 cm) hemostatic sponges soaked in a special solution, packaged in plastic jars of 30 pieces. "Alvostaz" is produced in three versions; it contains propolis, eugenol, tricalcium phosphate, iodoform, lidocaine and thymol.
Effect of hemostatic sponges
The product described in the article is used locally (it is used to pack wounds) and has a wide spectrum of action, namely:
- stops bleeding;
- accelerates wound healing;
- protects the hole from bacterial infection;
- prevents swelling of gum tissue;
- stops the focus of the inflammatory process;
- eliminates painful sensations.
Note! The hemostatic sponge is effective for several hours after tooth extraction. After a certain time (indicated by the manufacturer), the sponge placed in the hole dissolves completely.
Manufacturers of hemostatic sponges
Popular manufacturers of hemostatic agents used by dentists in our country are domestic companies. Let's consider them further:
- Alvostaz compress from Omega-Dent: available in the form of cubes, flagella, powders and solutions. The compresses are numbered - “1” with iodoform, “2” with metronidazole and chlorhexidine, “3” with neomycin and chloramphenicol,
- "Gemasept" with gentamicin from the Russian Research Institute of Hematology and Transfusiology of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency",
- “Collagen hemostatic sponge” with silver and boric acid from “Zelenaya Dubrava”,
- “Hemostatic sponge” with furatsilin and boric acid from “Belkozin”.
Indications for use
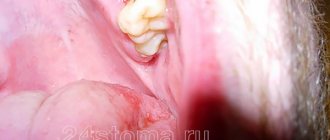
A hemostatic sponge can be useful after tooth extraction, especially wisdom teeth. Because the “eights” often do not erupt completely, and the dentist has to perform a mini-operation to get to them and remove them along with the roots. When a tooth is removed, a hemostatic agent is placed 3-4 months before implantation to completely eliminate the possibility of complications and problems with the formation of new bone in the socket.
Also, hemostatic sponges or powders are used during operations on the gums1 - plastic surgery, curettage of gum pockets (removal of deep “deposits” of tartar), and when cutting off dead areas of the jaw bone due to osteomyelitis. In the latter case, bone blocks and materials for regeneration of bone substance are additionally planted. In general, the doctor always assesses the patient’s condition in advance - asks about diseases and other conditions, and about the medications taken. If there is a risk of bleeding or poor regeneration, then rest assured, a hemostatic sponge will definitely be placed in the hole.
These sponges are used for bone augmentation
It is important to know! A few days after tooth extraction, it may be necessary to apply a hemostatic sponge if the dentist sees a tendency to worsen. For example, a clot has fallen out or the gums/bone have become inflamed.
How to use the drug correctly
How to use the sponge? The hemostatic sponge is placed into the socket of the extracted tooth only by the dentist. Home use is not recommended due to the risk of infection deep into the tissues. The application procedure is given step by step below:
- tooth extraction or treatment of the hole a few days after removal: in the latter case, purulent masses are removed, irrigation is carried out with an antiseptic,
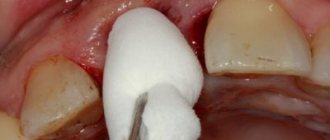
- a piece of the hemostatic plate is cut off with sterile scissors or a hemostatic cube is taken with tweezers,
- the drug is placed in the hole and pressed with a flat instrument: if the hemostatic agent is pre-saturated with thrombin, the hemostatic effect is enhanced,
- if necessary, an additional piece of hemostatic is applied,
- if necessary, a small tampon is placed on top of the hole (it will be removed the next day),
- suturing the gums - a seam in the shape of the letter “P”: also, if necessary, in most cases you can do without stitches.
A piece of the hemostatic plate is cut with sterile scissors.
Dental sponge
Dental sponge "Stimul Oss" with chlorhexidine based on hydroxyapatite and collagen is used for filling bone defects and intraosseous implantation, for contour osteoplasty, in the surgical treatment of periodontitis, periodontal disease, etc.
The dental hemostatic sponge “Stimul Oss” is unique. The collagen sponge, in contact with the wound surface, stimulates the growth of connective tissue, i.e. wound healing. Designed to optimize reparative osteogenesis, prevent jaw atrophy after removal of teeth, cysts, benign tumors, sequestration, as well as increasing bone volume (contour osteoplasty) in order to eliminate its deformation and prepare the mouth for prosthetics. It is also used for intraosseous implantation of supports for dentures and surgical treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease. Dental sponge “Stimul Oss” is a dry porous material with a base in the shape of a circle or square, soft elastic consistency, white color, diameter 11 mm, welding temperature in water is not less than 45.0 ° C; pH of aqueous extract 5.0–7.5; sorption activity no more than 10 minutes; mass fraction of moisture no more than 18.0% Contains: hydroxyapatite, chlorhexidine, formaldehyde. Hydroxylapatite, which is part of the drug, has a stimulating effect on the activity of reparative osteogenesis in the socket of the extracted tooth. Chlorhexidine is introduced to increase antibacterial activity, and the dosage is selected so that it does not reduce the osteoinductive properties of the entire product as a whole. Indications for use:
- After tooth extraction in order to reduce atrophy of the alveolar edge of the jaw.
- After tooth extraction for the purpose of osteoreparation, which allows earlier intraosseous implantation of supports for dentures.
- During resection of the apex of the tooth root for chronic periodontitis, cystogranulomas.
- After removal of jaw cysts (odontogenic and non-odontogenic) and removal of benign jaw tumors (fibroma, adenoma, etc.)
- During sequestrectomy for destructive osteomyelitis of the jaws.
- For radical flap operations for periodontal disease and for filling the periodontal pocket after its curettage for local periodontitis in order to restore the walls of the alveoli.
- When implanting denture supports (to achieve osseointegration).
- For alveoplasty with atrophy of the alveolar process.
- To raise the floor of the maxillary sinus in order to create conditions for intraosseous implantation.
- For contour plastic surgery (hernioplasty, in particular for dentofacial deformities).
The warranty shelf life is 3 years from the date of manufacture. Packaging: double bag made of polyethylene film, combined material or other materials approved for packaging medical products. The product is sterilized upon release by gamma rays at a dose of 1.5 MRAD. Contraindication:
- Polyallergy.
- Allergy to chlorine-containing substances.
- Allergy to collagen-containing drugs.
Instructions for use: After removing a tooth, cyst shell, sequestrum, benign tumor or other pathological tissue, blood clots are removed from the resulting bone defect with a stream of saline solution, a curettage spoon or a gauze swab. After treating the outer surface of the outer package - container with an antiseptic solution (furacilin, chlorhexidine, etc.), it is opened with sterile scissors and the small packaging bag containing a dental sponge is removed with sterile tweezers, the small package is opened with sterile scissors, the GSK-X-GA block is removed with tweezers -50 and inject it into the bone tissue defect. The number of blocks used is determined by the volume of the bone defect. Having ensured hemostasis, the edges of the soft tissue wound over the bone defect are brought together with sutures. After its removal, the tooth socket is filled with 1–2 GSK-Kh-GA-50 blocks to 1/4 of its depth. The edges above the hole are brought together with sutures or applied for 20–30 minutes. gauze swab. The patient is not recommended to eat for 4 hours. With contour osteoplasty and alveoplasty, the periosteum is peeled off from a small soft tissue incision. The resulting cavity (tunnel) is tightly filled with GSK-Kh-GA-50 blocks. The edges of the soft tissue wound are brought together with sutures. STORAGE CONDITIONS "Stimul Oss" in packaging of the enterprise is stored in protected from light, closed, clean warehouses without foreign odors. Manufacturer: JSC Luzhsky, Russia Price: 48.00 rub.
Is it necessary to remove the hemostatic agent?
Patients often wonder what to do with a hemostatic sponge after it has been placed in the socket of an extracted tooth? How long should I keep it on, and will it dissolve on its own? The rules of conduct are as follows: carefully but thoroughly observe oral hygiene, and also take medications prescribed by the dentist. There is no need to specially remove the hemostatic agent - after all, it consists of components that will completely dissolve during wound healing. And instead of a hemostatic agent, its own tissues form in the hole.
“When my wisdom tooth was removed, they stuffed it into the wound like a piece of foam rubber. I then saw the houses through the seams. I was also surprised - what is it? And at the next appointment, my dentist told me that this is a special sponge that absorbs blood and protects against infection. And when it resolved, I didn’t even notice)) It probably completely disappeared in a couple of weeks.”
Ekaterina R., review from irecommend.com
Contraindications and side effects
The only contraindication to the use of a hemostatic sponge after tooth extraction is an individual allergy to any of the components of the drug. In particular, for antibiotics that are used to impregnate the hemostatic agent. Therefore, be sure to tell your dentist if you are allergic and to what medications. Hemostatic agents should also be used with extreme caution in children.
There are no side effects, because There are no toxic substances or components that affect perception in hemostatics. But if itching, inflammation, or swelling appears, feel free to contact your dentist. These manifestations can be caused either by a newly manifested allergy or by incipient complications - if, for example, the treatment was carried out poorly or the patient did not follow the doctor’s instructions.
1Skulean A. Periodontal regeneration, 2012.
Precautionary measures
Absorbable GG is not used for heavy bleeding resulting from damage to large vessels. A contraindication to the use of a sponge is the patient’s individual intolerance to certain components of the product (for example, Furacilin). When used independently, it is not allowed to place (remove) GG into the inner layers of the socket; only surface application is permissible. When the hemostatic effect is achieved, the sponge is carefully removed from the postoperative wound.