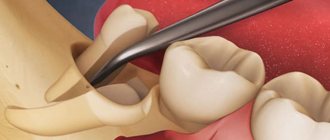
Bleeding gums after tooth extraction is a natural process that usually does not require medical intervention. But in some cases, this phenomenon indicates serious tissue damage or other pathologies, and it will be almost impossible to stop the bleeding on your own. What to do if there is severe bleeding from the socket and when should you consult a specialist?
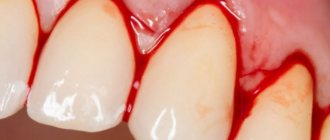
Gums bleed after tooth extraction
How long does it take to bleed after surgery?
Any surgical intervention, including tooth extraction, is associated with tissue trauma and damage to blood vessels - the teeth “hold” tightly to the tissue with their roots, so the doctor has to separate them using physical force. For this reason, it is simply impossible to do without blood during the procedure.
If your gums bleed after tooth extraction while you are at the dentist, the surgeon will help you on the spot
Normally, bleeding stops within 10-30 minutes after surgery - during this time the blood clots, and a clot forms in the socket, protecting it from infection. When removing teeth in the lower jaw, which dentists often call difficult, bleeding may take a little longer. After the initial bleeding stops, ichor may be released from the wound (do not mistake it for blood), so the saliva will be colored pink.
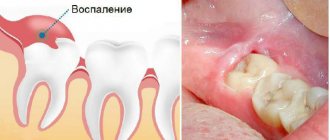
Removal of a wisdom tooth on the lower jaw
It should be noted that in some patients bleeding does not occur at all - this is due to the fact that adrenaline, which is released in the body or contained in anesthetics, causes temporary vasospasm. In such cases, there is a serious risk of developing alveolitis or the “dry socket” effect, since a protective clot does not form in the wound.
If the bleeding is strong enough and does not stop after using simple remedies, you should contact your dentist - you may need medical help to stop the bleeding.
There are many different reasons that lead to prolonged bleeding from a wound.
First aid at home
In order for the bleeding to stop, it is necessary to compress the blood vessels, but in such a way as not to cause additional trauma or damage to them and not to introduce an infection into the wound. Before carrying out procedures, wash your hands thoroughly with soap. Follow all the recommendations listed below with care.
At home, you can try to get rid of the problem in the following ways:
- tamponade the hole: for these purposes you can use a piece of sterile bandage or gauze. It is necessary to apply a tampon to the wound and close your jaws tightly. There is no need to apply pressure. Normally, the bleeding should stop within 15–20 minutes. For better effect and antiseptic treatment of the hole, you can pre-moisten the swab with hydrogen peroxide or in a solution of “Furacilin”,
- use a hemostatic collagen sponge: this is a specialized material impregnated with medications. You can purchase the product at the pharmacy. It’s better to stock up on it before the procedure, so that if necessary, everything you need is at hand. The advantage of such a sponge is that it has an immediate effect, disinfects, relieves signs of the inflammatory process, promotes rapid tissue healing, and also dissolves on its own. Price – from 100 rubles,
- take medicine for hypertension (for example, Captopril): if you have high blood pressure, then you need to bring your condition back to normal,
- apply a cold compress to your cheek: this is an excellent preventive measure against swelling and bleeding. Compresses constrict blood vessels and prevent the appearance of hematomas. Cold compresses are especially effective on the first day after extraction. Ice or any product from the freezer is suitable as cold, but before using it you need to wrap it in a towel or soft cloth. The time of one procedure is 10–15 minutes, then you need to take a break for half an hour and repeat according to the same scheme up to 4–6 times in a row.
Methods can be combined. You can combine socket tamponade with the use of cold compresses. Try to relax during the procedures. Don't be nervous, lie down. If there is no positive dynamics within an hour, then you need to call an ambulance or ask someone to take you to a doctor. Do not drive yourself, as general weakness due to blood loss can lead to decreased concentration.
Why is bleeding from a socket dangerous?
Intense bleeding from the gums often frightens patients - they fear dying from blood loss. However, the risk of death after tooth extraction surgery is minimal - this happens in isolated cases, and only with people who suffered from serious illnesses, alcoholism or drug addiction. But problems with internal organs and systems as a consequence of severe bleeding from the gums are quite likely, so it is not recommended to ignore severe bleeding.
Blood clot after tooth extraction
Causes of bleeding after tooth extraction
Bleeding after dental surgery is usually divided into primary and secondary - in the first case, blood flows immediately after the procedure, and secondary bleeding can develop several hours, sometimes several days after the visit to the clinic.
Bleeding after tooth extraction
There can be several reasons for primary bleeding, most of them are associated with pathological conditions of the body.
Table. Causes of primary bleeding after tooth extraction.
| Causes of bleeding | How to prevent |
| High blood pressure | Before going to the dentist, you need to measure your pressure and also take a sedative that will reduce the risk of it (pressure) increasing during the operation |
| Poor blood clotting in certain diseases (leukemia, hepatitis, hemophilia) | People with serious pathologies and hematopoietic diseases should report their problem to the doctor, who will choose the safest method of performing the operation |
| Taking medications | 2-3 days before tooth extraction, refrain from taking aspirin, heparin and other blood thinning drugs, as well as oral contraceptives (increased concentrations of estrogen in the blood in women can also cause bleeding) |
| Severe stress | If a person has a strong fear of dental procedures, a surge of adrenaline in the body can provoke bleeding - to prevent it, before visiting the dentist you need to try to calm down, and if necessary, take a sedative |
| Anatomical features of the dentofacial apparatus (large blood vessels on the surface of the gums) | Closely monitor the condition of the socket after surgery, avoid physical activity and follow the doctor’s recommendations |
- Why do my gums hurt after tooth extraction?
Another common cause of severe gum bleeding after tooth extraction is medical errors during extraction. Careless or too rough operation causes severe tissue trauma, which causes intense bleeding, and this situation is especially dangerous when large branches of the arteries are damaged.
Severe bleeding may be the result of a medical error
The main cause of secondary bleeding is patients’ failure to comply with the dentist’s recommendations: drinking hot drinks, solid foods, exposure to other traumatic factors, smoking, etc. In addition, blood from the socket can ooze in the event of complications developing - suppuration, alveolitis, the presence of cysts or granulomas. They impair coagulation at the site of inflammation, which leads to large blood loss both during and after surgery.
Alveolitis in the tooth socket
Professional assistance in dentistry
If you could not stop the bleeding at home on your own, then you need to go to the dentist. The doctor will examine the hole, clean it if necessary, and treat it with an antiseptic. Further, depending on the clinical situation and indications, iodoform turunda or a hemostatic sponge can be applied to the wound.
A specialist can also cauterize the vessels with an electric current using a procedure such as electrocoagulation. Another effective measure to stop bleeding and minimize possible complications is suturing the edges of the wound and applying sutures. If large blood vessels were damaged during the extraction process, the doctor will compress and bandage them.
If the bleeding has not stopped for too long, the doctor will definitely prescribe you medications and antibiotics to avoid further complications. Additionally, the dentist may prescribe hemostatic drugs that promote rapid clot formation (for example, Dicynone), but only if you have no contraindications (thrombosis, thrombophlebitis).
“I once returned home from dentistry after a planned operation, and my extracted tooth was bleeding, quite heavily. It's good that I'm on the phone with my doctor. She advised me to take a Tranexam tablet if there are no contraindications. I quickly read the instructions on the Internet and sent my husband to the pharmacy. I took it at home, the bleeding stopped after 20 minutes and there was no more…”
Vera, review from otzovik.com
When should you see a doctor?
In most cases, bleeding can be stopped using simple measures, but sometimes it requires immediate consultation with a doctor. You need to contact an emergency dental clinic if:
- the blood flows too intensely (the oral cavity fills with blood literally every few seconds);
- along with bleeding, a person experiences weakness and dizziness;
- the affected area is very swollen and painful;
- bleeding is accompanied by fever, difficulty breathing or swallowing;
- the patient experiences a severe headache and numbness in the areas adjacent to the affected area.
Phlegmon - acute extensive (spread) inflammation of fatty tissue
A variant of the norm is considered to be mild or moderate bleeding, which lasts no more than 24 hours; after the removal of third molars, this period increases to three days.
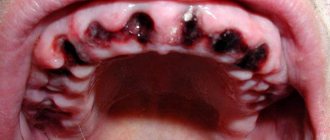
Photo of holes after tooth extraction
What can a doctor do?
In cases where it was not possible to stop the bleeding on your own, you should call an ambulance or go to the dental office. Doctors will examine the sore spot and prescribe one of the procedures aimed at stopping the bleeding:
- packing or suturing;
- cauterization of blood vessels;
- taking medications that improve blood clotting.
Tamponade bleeding
If the bleeding was not stopped in a timely manner, inflammation may begin in the hole - blood stops oozing from the wound, but the soft tissues begin to swell and hurt. If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to clean the hole, then fill it with a special anti-inflammatory agent and undergo a course of antibiotic treatment. If all of the above measures are ineffective, the patient is indicated for hospitalization.
After tooth extraction
Consequences of perforation
Perforation of the maxillary sinus is a fairly serious pathology that often has to be treated in a hospital. Attempts to independently treat it with folk remedies at home without medical assistance can lead to the development of serious and dangerous consequences:
- The development of a pronounced inflammatory reaction in the sinus cavity with the spread of infection to the surrounding bone tissue and the formation of foci of osteomyelitis of the upper jaw.
- Spread of inflammation to other sinuses of the skull (frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid).
- Loss of healthy teeth located in the area of untreated perforation.
- Formation of purulent foci (abscesses, phlegmons).
Due to the close location of the maxillary sinus and the brain, after perforation, infection may spread to the meninges with the development of meningitis or meningoencephalitis, which threatens the patient’s life.
How to prevent bleeding?
To avoid postoperative bleeding, you must refrain from the following actions:
- eat hard, rough, hot and cold foods;
- rinse your mouth intensively, especially with hot water;
- take a hot bath or visit a sauna;
- engage in heavy physical labor;
- actively use facial expressions (open your mouth wide, etc.);
- clean the affected area with a toothbrush, touch the wound with your tongue, fingers or foreign objects;
- smoke, drink alcohol;
- apply warm compresses to the cheek.
Normal socket healing
The above conditions must be observed for at least 24 hours (ideally 3 days) - this will help avoid not only bleeding, but also serious postoperative consequences.
In most cases, bleeding after tooth extraction is a normal physiological phenomenon that can be eliminated with simple home remedies, and if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the pain, fear and blood that accompany any operation will soon be left behind.
- What medicine is put into the hole after tooth extraction?