What do we do when a tooth is pulled out? Even under the office, many examine the traces of the operation, fearing for its consequences. The fear intensifies after the end of the painkillers: how long should the wound hurt, and when will the bleeding stop?
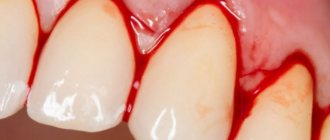
Blood clot after tooth extraction
On the first day, a blood clot appears at the site of the pulled out tooth - an important condition for high-quality wound healing. In order for recovery to proceed without serious consequences, it is important to know what the wound should look like during extraction, what should and should not be done with it during the recovery period.
A few words about the procedure
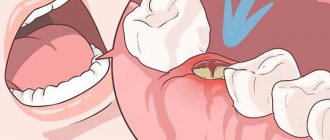
Tooth extraction is a full-fledged surgical procedure. The operation consists of four stages.
- Treatment of the area around the tooth that is to be removed.
- Anesthetic injections - ampoules in carpules, where an anesthetic is combined with drugs to constrict blood vessels. Usually local anesthesia is used in the area where the nerve that innervates the problem tooth exits; if this is not enough, anesthetics are added without additional effect. When the medicine is injected into the inflamed gum with an acidic environment, part of it is inactivated, so additional anesthesia is used.
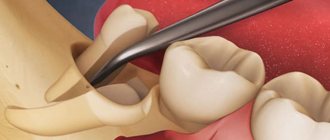
- Tooth extraction after the anesthesia has started working (the gums become numb, the blood vessels narrow). A scalpel is used to cut off the ligaments that fix the tooth. The choice of instruments and duration of the procedure depend on the condition of the tooth.
- Treatment of the oral cavity after removal: sutures (if the wound is torn or its edges are located far from each other) and a gauze swab soaked in a hemostatic agent (it must be held in the teeth for 20 minutes, since the effectiveness of the hemostatic drug increases compression of the wound). Do not rush to remove the tampon.
Gum section
Preparing for removal
Removal of a tooth
Installing a tampon
Stitching
Bleeding from the hole itself does not pose a mortal danger. In medical practice, only one case of death was recorded when blood from a wound entered the respiratory tract because the patient was intoxicated. The bleeding was complicated by cirrhosis of the liver, which interferes with clotting, and the woman had three teeth removed at once.
When should the bleeding stop?
It is absolutely normal for blood to appear immediately after a tooth is removed from its socket. However, dentists and surgeons unanimously claim that bleeding should stop after a few minutes, that is, while the patient is in the dental chair. But this does not always happen so quickly; many patients experience the appearance of blood from the socket even after the end of the operation.
The reason for this may be several factors, the main of which are the characteristics of a particular person’s body and the complexity of the manipulations performed. Even when a wisdom tooth is removed, which is usually accompanied by severe dissection of soft tissue, the bleeding should stop flowing after 30-40 minutes. All other manifestations are not normal and require consultation with a professional.
Why is it important for the bleeding to stop? Immediately after the operation, it turns into a dense clot, which will have to protect the exposed bed from infection and bacteria until it is completely healed. After the blood has clotted, ichor may begin to ooze from the operated area, causing the salivary fluid to take on a slightly pinkish tint. This process can last 2-4 days.
After operation
After three hours, the painkillers are still strong, so patients do not feel pain or it is mild. All this time, pure blood or ichor may be released from the hole. If a figure eight was removed, this can last all day, since the surgical area of the wisdom tooth is larger than that of other teeth.
Bleeding from the socket
On the second day, the hole has an unattractive appearance: a blood clot with a grayish coating. It looks like pus, but you shouldn’t be afraid of it: it’s fibrin, a substance that facilitates wound restoration. If everything goes well, the pain will be aching and will subside by the end of the day. If the nature of the pain is different - sharp, pulsating, and there is scarlet blood from the wound, you should urgently see a dentist.
At first, the hole may smell foul. There is no need to be afraid of this: blood accumulates there, and since it cannot be rinsed out, bacteria settle in the wound. If you feel normal, there is no fever, there is no reason to worry.
The rehabilitation process is normal if:
- What medicine is put into the hole after tooth extraction?
- when touching the wound, the ichor does not appear;
- the aching pain gradually disappears;
- feeling normal (temperature up to 38° is possible only in the first two hours);
- swelling on the cheek decreases (if it was not there before extraction, it should not appear at all);
- after 3 days the wound no longer bleeds.
2 weeks after removal
To reduce bleeding, you can make a tampon yourself. Positioning it so that the edges do not injure the blood clot, hold the napkin for half an hour. In the pharmacy chain you can buy a hemostatic sponge, which can be used in cases of heavy bleeding, for example, in liver failure.
Hemostatic sponge
The hole is closed with a hemostatic sponge.
You can take one or two tablets of Dicinone or Etamzilate (no more than 8 pieces per day).
Dicynone tablets
You cannot experiment with hydrogen peroxide: it reacts with blood components, destroying the blood clot and increasing blood flow.
Edema
Swelling is another unpleasant consequence of tooth extraction. As a rule, it appears the next day after surgery and reaches its maximum value on the third day, after which it begins to decrease.
Cold compresses can be used to reduce swelling. To do this, you need to prepare ice cubes in advance, wrap them in cloth and apply them to the operation site for no more than twenty minutes. After a twenty-minute break, the procedure can be repeated. But it should be remembered that this method is effective in combating edema only in the first thirty-six hours after surgery.
How does the healing process work?
Even if there are no complications, the wound heals completely within four to six months.
- On the 2nd day, a blood clot appears in the socket - a protective gate against mechanical damage and infections.
- If healing proceeds normally, on the third day you can already see granulation tissue at the operation site.
- In the second week, the epithelium actively grows, and granulation tissue appears instead of a clot. Primary restoration of bone structures occurs.
- In 2-3 weeks, it displaces the blood clot and bone tissue is visible around the perimeter.
- Recreation of new tissues takes 30-45 days.
- In about 60 days, the hole is closed by osteoid tissue impregnated with calcium.
- After 4 months, the bone becomes an “adult”, with a porous structure.
- When the bone is fully formed, the wound should resolve to a third of the length of the root.
- After extraction, the gums atrophy and the process of subsidence continues for 6-12 months.
Stages of tissue healing after tooth extraction
Healing of the tooth socket after extraction
Tooth extraction is a surgical intervention with the formation of a wound after extraction, therefore, as after any intervention, the wound formed at the site of the tooth must also undergo a healing process, and its tissue must recover and fill the voids. This process lasts for 4 months. The stages of tooth socket healing are as follows:
- a blood clot forms immediately after removal;
- 2-3 days - epithelization of the hole begins;
- 3-4 days - the first signs of granulation tissue formation appear;
- 7-8 days - part of the blood clot is replaced by granulations, gum cells begin to form an epithelial layer; the process of bone tissue formation begins;
- Days 14-18 - granulation tissue completely fills the socket, and the socket itself is completely covered with new epithelium. New bone cells are actively forming on the walls of the socket;
- 1-2 months - active process of bone tissue formation;
- 2-3 — filling the hole with bone tissue; tissue saturation with calcium;
- 4th month - bone formation ends, the structure becomes spongy.
If, when a tooth is removed, a blood clot does not form in the socket, the healing process of the socket occurs thanks to its walls - they are the ones who contribute to the development of granulation tissue. Otherwise, the further stages of healing are the same as those described above.
Healing after removal of an inflamed tooth
We have described a 4-month process of tissue restoration, however, they are restored so quickly only if there is no injury, inflammation or infection in the tooth and surrounding tissues. If the listed processes take place, tissue regeneration does not proceed so quickly. As a rule, it is prevented by the formation and course of the inflammatory process, the time period increases and the stages of healing look like this:
- epithelization and formation of granulation tissue occur in 10-15 days instead of 3-5 days;
- Bone tissue formation begins only on the 15-16th day instead of the 7-8th.
- closure of the hole by the epithelium is 2 times slower and ends only on the 30th or 50th day;
- only at 2 months the hole is completely filled with osteoid cells, which then become full-fledged bone;
The process of epithelium and bone formation can be even longer if the walls of the socket and/or gum tissue were severely damaged during tooth extraction.
Possible complications
Since tooth extraction is a surgical procedure, unpleasant consequences may arise after it is performed—complications of various kinds. In this case, the causes of such complications can be either the patient’s negligence in hygiene after surgery or the incorrect actions of the surgeon. Another category of etiology of adverse consequences is the complex course of the operation (with increased bone strength, non-standard shape or size of the tooth root).
Alveolitis
Alveolitis often forms when, after removal, a blood clot does not form in the socket for some reason. Without a clot, the socket is deprived of a protective barrier from external influences and is therefore susceptible to the appearance of an inflammatory process. The first and main symptom of this disease is pain immediately after removal or after 2 days. There is swelling of the gums, inflammation of the edges of the socket, due to the fact that a blood clot has not formed, the cavity is filled with food, which further contributes to the development of the inflammatory process. Other characteristic signs: temperature, unpleasant odor from the hole, poor health, pain and swelling of the mucous membrane at the extraction site.
The etiology of the development of alveolitis is considered to be an infection caused by oral microbes entering the socket. The body is not able to form a protective barrier in the hole, so inflammation rapidly develops in it.
The following causes of alveolitis are distinguished:
- chronic inflammation in the tissues of the oral cavity, its exacerbation;
- high degree of tissue trauma due to complex tooth extraction;
- a blood clot did not form during or after the operation (for example, due to the patient’s violation of the doctor’s recommendations);
- disorders in the immune system, chronic fatigue, chronic diseases;
- long removal process (longer than 40 minutes).
Treatment of alveolitis
Depending on the severity of alveolitis, both local and general treatment can be prescribed. Local methods are usually used using antiseptic rinsing and treating the socket with an antimicrobial agent. In addition to this treatment, vitamins and antibiotics may be prescribed.
In the case of general treatment, physiotherapy is also added, and the overall period of treatment and healing of the hole is increased.
Socket bleeding
Bleeding can occur both immediately after the operation and some time after the operation: from 1 hour to 24 hours or more. The period of manifestation of alveolar bleeding varies depending on the reasons that cause it. An earlier manifestation may be caused by vasodilation, later - due to injury to the socket by the patient after surgery. However, the etiology of the complication may also include injuries during removal (gums, alveoli, blood vessels) and diseases of the body (sepsis, hypertension, leukemia, the first 2 days of the menstrual cycle in women, taking aspirin and its analogues, diabetes).
The process of preventing bleeding depends on what causes it: local causes are eliminated by applying sutures to the rupture sites or applying cold, using a tampon. If the bleeding is caused by low blood clotting, medications are used to increase clotting.
Paresthesia
Sometimes after tooth extraction, patients complain of numbness in the oral cavity. Symptoms can be expressed over a period of 1 to 30 days or even more. The cause of paresthesia lies in nerve damage. Dentists can speed up the restoration of damaged tissue by prescribing vitamins B and C to the patient in combination with injections of galantamine and dibazole.
Neighboring teeth change position, Popov-Gordon effect
The body does not tolerate emptiness, therefore, after a tooth is removed and there is no analogue in its place for a long time, the neighboring teeth (and the tooth on the opposite jaw) tend to fill the resulting space, leaning towards the socket. Obviously, in such a situation, the dentition changes, which leads to curvature, changes in chewing load and bite.
The problem can be solved by replacing the missing tooth with an analogue after the hole has healed and tissue restoration: an implant, a prosthesis.
Communication of the oral and nasal cavities
When extracting molars and premolars of the upper jaw, the floor of the maxillary sinus may be injured, which will lead to the formation of a connection between the oral cavity and the nasal cavity.
It is noteworthy that this complication occurs even if all actions were performed correctly by the dentist. Its causes are usually:
- absence of a bone septum or close adherence of the roots to the sinus;
- bone destruction due to chronic inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root;
The complication requires surgical intervention by a specialist, since the entry of food and drink into the nose through the oral cavity usually leads to inflammation in the sinus (sinusitis), which in itself is a very unfavorable consequence and requires long and complex treatment.
Intervention is not carried out only if acute purulent sinusitis of the upper jaw has developed.
Other complications
Other complications are caused by: incorrect actions of the doctor and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
First category of reasons:
- improper use of forceps and, as a result, damage to the crest of the alveolar tissue;
- erroneous extraction of a tooth germ due to the ignorance of the doctor during milk extraction;
- injuries to adjacent teeth due to careless work of a dental surgeon;
Second category of reasons:
- weak or defective teeth located nearby may break during surgery on the causative tooth;
- low strength of the causative tooth, which causes its fracture and the need to remove parts;
- weak jaw tissue, which increases the risk of fracture and complications;
- individual features of the structure of the roots, jaw and location of nerves.
Rules of care
To prevent complications due to the patient’s fault, it is very important to follow all the dentist’s instructions, namely:
- The first day after surgery: keep the installed tampon in the mouth for 30 minutes, do not eat for 2 hours; do not load food and do not touch the socket area with your tongue or toothbrush;
- 2-3 days after surgery, minimize the load on the teeth located in the extraction area, limit the intake of solid and hot foods, giving preference to soft and liquid foods;
- Refrain from smoking (to prevent a vacuum from occurring in the socket) and try not to drink alcoholic beverages;
- Buy a soft toothbrush to gently clean the area of the extracted tooth a few days after the operation; in the first days it is better not to brush the injured area at all;
- The next day after the operation, make oral baths for the socket (do not rinse under any circumstances) with warm salted water (but not with special rinses).
- Do not exercise for 2-3 days;
- Do not take a hot bath on the first day after removal;
- Do not take aspirin and its analogues.
What determines the rate of tissue regeneration?
The indicated time frames are indicative information, since the restoration process is influenced by many factors:
- doctor's qualifications,
- condition of the roots,
- hygiene procedures,
- gum health
If a tooth is removed during an exacerbation of the disease, healing slows down. A lacerated wound also tightens it, especially during operations on figure eights. Particular attention is paid to high-quality treatment after the procedure. If tooth fragments remain in the hole, they will interfere with the formation of a protective blood clot, and in the end everything will end in an inflammatory process, lengthening the recovery period.
Healing socket in place of a wisdom tooth
After removal, the surgeon will definitely give advice on proper care of the wound. If you ignore advice or follow it irregularly, complications are inevitable.
Since the blood clot covers the vulnerable hole, it is important not to disturb it. If you rinse immediately after visiting the dentist, you can wash it. An unprotected wound easily becomes infected.
Rinsing after tooth extraction is prohibited
If there are problems with changes in blood pressure, sometimes the wound bleeds for a long time. Once the blood pressure normalizes, bleeding usually stops.
Signs of inflammation
The inflammatory process in the socket occurs when a blood clot is damaged and the wound becomes infected. The following signs indicate its development:
- pain of varying intensity - aching, throbbing,
- fatigue and severe weakness,
- rise in temperature to subfebrile levels,
- unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth,
- pain when touched, contact with hot and cold,
- discharge of pus,
- difficulty chewing, swallowing, opening the mouth.
With alveolitis, the socket may become dry and a greenish or yellowish coating may form. If a blood clot falls out and pain occurs, do not put off visiting the dentist. It is easier to stop the inflammatory process at its beginning. The doctor will curettage the hole, treat the wound with an antiseptic solution, and prescribe antibacterial drugs.
Complications during extraction
All unfavorable conditions lead to alveolitis - inflammation that develops after infection of the wound. Most often, problems begin after a blood clot falls out. Sometimes a clot does not form at all.
- Ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal
Alveolitis of the tooth socket
If you rinse your mouth, alveolitis is diagnosed after 1-3 days. The water pressure washes away the protection and inflammation is guaranteed. Its signs:
- increasing pain, gradually affecting neighboring areas;
- as inflammation spreads, general signs of intoxication intensify: fever, aching joints, loss of strength;
- swelling spreads to nearby areas;
- the mucous membrane turns red-blue due to impaired blood supply;
- bad odor from the problem area in which food debris accumulates.
All other complications also develop after the wound becomes infected. It is convenient to present their features in a table.
| Type of complication | Description |
| Dry socket | The blood clot has not formed, recovery time is delayed, and there is a risk of alveolitis. Most often it happens during active rinsing. A dry socket should be shown to the dentist. |
| Osteomyelitis | A serious consequence when alveolitis spreads to the jaw bone. Inpatient treatment is required. |
| Nerve damage | If the tooth has massive roots, there is a possibility of nerve damage. All tissues near the tooth lose sensitivity. For treatment, a vitamin complex and medications are used that accelerate the transmission of nerve impulses to muscle tissue. |
| Cyst | A serious complication requires surgical methods of elimination. |
After recovery, there is no need to delay prosthetics, since the absence of any unit of the dentition has a bad effect on the condition of the entire oral cavity.
Prosthetics
Causes of untimely appearance of a blood clot
When a blood clot forms within half an hour after tooth extraction, this is normal. But it happens that a blood clot forms only several hours or even days after the operation, or the socket generally remains dry and unprotected. Why is this happening:
- long-term unstoppable bleeding: occurs against the background of some chronic diseases associated with impaired blood hemostasis and metabolic processes in the body, for example, diabetes mellitus. The problem is also caused by the patient taking drugs containing acetylsalicylic acid (for example, Aspirin) the day before or for a long time. In women, the pathology may be associated with surgery during menstruation. Read about all the causes of the problem and methods for solving it in the feature article on the website,
- vasoconstriction caused by the use of anesthesia: in this case, bleeding can begin only 1-3 hours after the operation,
- medical errors: a clot may not form because the specialist performed the operation too traumatically, cleaned the hole poorly and left tooth fragments inside. In general, experienced doctors, seeing that there are no prerequisites for the formation of a blood clot, resort to additional measures, for example, provoking bleeding or simply stitching the edges of the wound so that infection does not get inside.
Prosthetics after removal within 24 hours or several days: indications
Some situations and diagnoses require dentists to act quickly. In this case, it no longer matters how long the gums take to heal after tooth extraction for dental prosthetics - the indications are important.
Within 24 hours after removal, the doctor will place a pre-fabricated temporary prosthesis in the following cases:
- loss of anterior units - due to potential mental and physical discomfort;
- edentia in children - otherwise rapid deformation of the jaws will begin;
- complete edentia in adults - usually we are talking about the removal of all teeth immediately before immediate prosthetics;
- loss of the last molars on both sides - in case of deep bite or diseases of the jaw joints;
- removal of antagonists - teeth of the upper and lower jaws located opposite each other.
In the first two weeks, prosthetics are indicated if an express protocol is followed - dentures are not always installed immediately, but 5-7 days after implantation - painlessly and quickly. After implantation, you can live a normal life - restrictions are minimal.
Removable dentures are placed in a similar period of time.
Doctors providing this service
Modern surgical dentistry makes it possible to avoid tooth extraction in most cases, but tooth extraction is still sometimes necessary.
An operation to remove a tooth should be performed only as a last resort, when other methods to save the tooth are no longer possible or when the tooth may cause other, more serious complications.
Indications for tooth extraction
A fairly common indication for tooth extraction is the need to sanitation the oral cavity in the presence of chronic periodontitis in the acute stage, when it is impossible to eliminate the inflammatory focus at the apex of the tooth.
In some cases, tooth extraction is performed to avoid more serious complications. For example, if you have teeth that can cause a cyst, inflammation or neuritis of the trigeminal nerve. If a tooth constantly injures the tongue or the mucous membrane of the cheek, and also interferes with a normal bite, it is also better to remove such a tooth. Multi-rooted teeth, which are the cause of odontogenic osteomyelitis, are removed. When fitting a removable denture, sometimes it becomes necessary to remove teeth, but there must be strict indications for this.
Surgical operations to remove a tooth are performed under effective anesthesia, taking into account all contraindications.
Teeth are removed when they are severely damaged by caries, affected by advanced periodontal disease (“sick gums”), have been broken so that they can no longer be restored, are incorrectly positioned in the mouth (for example, an embedded wisdom tooth), or in preparation for orthodontic treatment.
Before starting tooth extraction, the dentist examines the oral cavity, takes x-rays of diseased teeth, and evaluates their condition.
After a tooth is removed, the teeth adjacent to it begin to gradually shift, sometimes quite significantly, and this can greatly affect the general condition of the teeth. Removing even a single tooth can create serious chewing problems. To avoid these complications, the dentist will recommend replacing the extracted tooth with an artificial one.
Considering all the advances in operative surgery today, most patients prefer to replace the existing dentition defect by placing a dental implant (advantages of using dental implants), dental bridges or removable partial dentures.
How to remove a tooth
There are two extraction methods used in dentistry: simple and complex. Their choice depends on which teeth are being removed - premolars and molars with tangled branched roots are removed using a complex method. It is very difficult to pull out such elements entirely due to the fact that the tooth socket is penetrated by retaining ligaments and alveolar processes. Errors during the procedure or insufficient experience of the specialist lead to serious complications. Therefore, even despite the acute condition, always find out in advance where you can have a tooth removed from a good doctor with positive recommendations.
Factors complicating the operation:
- complete destruction of the coronal part;
- high fragility;
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- Unerupted or misaligned wisdom teeth.
The technology of the procedure depends on which teeth are removed. In some cases, tissue incision and suturing are performed.
Whether it is painful to remove a tooth or not depends largely on the condition of the element. Anesthesia is performed in all cases, with the exception of severe allergic reactions to all types of painkillers. With the development of extensive purulent lesions, the effect of the drug may be reduced.
How long it takes to remove a tooth depends on the complexity of the operation. On average, this takes no more than 5-10 minutes (including waiting for the anesthesia to take effect). In general, the procedure includes the following steps:
- anesthesia;
- if necessary, an incision is made into the mucous membrane to access the cervical area, or the doctor lowers the gum with an instrument;
- Use forceps to fix the tooth at the lowest point without excessive pressure;
- rocking and extraction from the hole is performed;
- returning the gum flap to its place.
If inflammatory processes are diagnosed in the oral cavity, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. In some cases, extraction is performed under general anesthesia.
In case of multiple lesions, the doctor determines how many teeth can be removed in your case during one visit, but more often it is 1–2 elements. This is because extraction is a traumatic operation that will take time to recover from. Too large areas of damage increase the likelihood of complications several times and take much longer to heal.
If after surgery the extracted tooth, or rather the hole left after it, hurts, this is a reason to consult a doctor. After the procedure, minor pain is allowed during the first 24 hours. Visit the dentist if your temperature rises, swelling increases, bleeding occurs, or pain spreads to the lymph nodes. These are symptoms of a wound infection. Untimely treatment can lead to alveolitis.