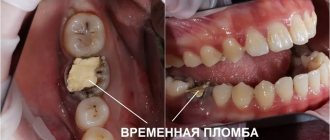
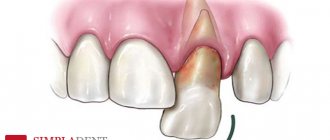
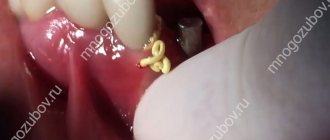
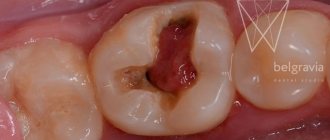
When is root removal required?
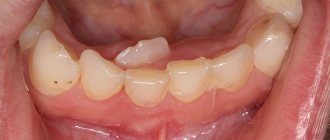
It happens that only the root remains in the gum, and its crown part has been completely lost due to mechanical stress or untreated caries. After an X-ray examination, CELT specialists determine the possibility of treating such roots and their further use as a support for the crown. If this is not possible and the tissue surrounding the root is changed, a decision is made to remove it. Indications for root removal of front, broken, baby and other teeth are:
| Indications | Reasons for deletion |
| Serious damage to the crown of the tooth | Complete fracture of the crown, complex transverse fracture, fracture along the lobar axis, as well as destruction of the tooth crown below the gum level |
| Inflammatory processes | Development of inflammation in the root area in the form of a cyst, granuloma, abscess or phlegmon |
| Dentofacial anomaly | The tooth that is to be removed has an atypical location and prevents other teeth from growing, injures the gums and causes discomfort |
| Movable root | Third degree of tooth mobility |
It is worth noting that the crown part of the tooth can be destroyed both on a tooth with a nerve and on a pulpless tooth. If the tooth is “alive” and the destruction of its coronal part is not severe, its preservation is quite possible. As for a tooth with a removed root, the latter, as a rule, are seriously damaged and their restoration is quite difficult. In this case, the doctor may recommend removal of the tooth root and subsequent implantation.
Indications for removal of lower teeth
Conventionally, all indications for surgical intervention in the lower jaw can be divided into groups:
- Chronic intoxication resulting from advanced dental disease. It can lead to sepsis, myocarditis, endocarditis and other dangerous connective tissue lesions.
- Purulent processes in the periodontium, if they cannot be stopped using conservative methods.
- Acute osteomyelitis, perimaxillary abscess, phlegmon, sinusitis caused by a destroyed tooth. Extraction is carried out only if the disease cannot be eliminated by therapeutic methods.
- Longitudinal fracture, splitting of the crown into 2-3 parts with exposure of deep layers of the pulp (if it is impossible to close the defect with filling material).
- The presence of units that are positioned incorrectly and injure the surrounding mucous membranes, but are not subject to orthodontic treatment.
- Detection of elements that have not fully erupted, causing inflammatory reactions in adjacent areas.
- To eliminate malocclusions before starting an orthodontic course.
- The presence of supernumerary lower units that interfere with proper oral hygiene, prosthetics, disrupt chewing function, or cause constant pain.
Removing the root of a decayed tooth
Cases where a root remains after tooth extraction are not uncommon. Its removal is a difficult and unpleasant procedure for the patient, even despite the effectiveness of modern anesthesia. Fortunately, the need to remove tooth roots does not always arise. If the root is healthy enough, it is treated and prosthetics are performed. However, removing a rotten tooth root is simply necessary, since its preservation will entail a number of problems:
- Halitosis (bad breath);
- A breeding ground for infection in the oral cavity, possible damage to neighboring teeth;
- The appearance of subgingival stone;
- Spread of infection to the maxillary sinuses, development of osteomyelitis;
- The appearance of cysts and granulomas at its apex ( removing a tooth with a cyst on the root
is a complex procedure); - A decrease in the body’s overall immunity due to the fact that it is forced to constantly fight the source of inflammation.
In order to properly plan the operation, our dentist performs an x-ray examination. The operation itself is performed using local anesthesia, dental forceps or an elevator. Removing the roots of the front teeth
is carried out using rotational movements, and lateral movements using rocking. The most complex cases may require additional manipulations, the use of burs and special microsurgical dental instruments. Removing the roots of the teeth of the lower and upper jaw is a more complex procedure than removing a whole tooth. It requires special training, which consists of examination, diagnosis and sanitation of the oral cavity. The treatment plan is drawn up based on diagnostic studies and the patient’s indications.
Modern methods of dental treatment
Many patients traditionally associate dental treatment in a clinic with the buzzing sound of a drill. This device is really necessary for the preparation of dental tissues. But modern methods make it possible in some cases to do without it. Such technologies, in particular, include:
- Remineralizing therapy. This non-invasive treatment method is based on the use of external calcium and fluoride preparations at the very first stage of caries, when there is no obvious defect yet, but softening of the enamel is already noticeable.
- Ozone therapy. The essence of the method is to treat dental tissues affected by caries with triatomic oxygen. At the same time, healthy enamel is preserved, and pathogenic microorganisms are completely destroyed by ozone.
- Icon Method. The damaged area is treated with a polymer composition that destroys bacteria, seals the affected area and restores the density of tooth enamel.
Innovations also include dental treatment under a microscope. When used, it is possible to save even seemingly hopeless units from removal.
Root removal steps:
- Carrying out activities for the administration of a local anesthetic drug;
- Separation of the circular ligament from the neck of the tooth, moving the gum tissue away from the edge of the alveolus;
- Cutting the gums and drilling out the bone tissue to provide access to the root (if necessary);
- The process of removing the root using forceps or a dental elevator. If a tooth has several roots, removal is carried out in parts;
- Treatment of the hole, suturing (if the gum is cut), treatment of the operated area.
It is important to understand that removing roots located on the upper jaw is different from removing roots located on the lower jaw. In the first case, special forceps are used, in the second - elevators. The technique for removing the roots of the upper jaw involves twisting single roots and dislocating parts of one root. As for the roots of the lower jaw, they are twisted.
Easy removal
If the wisdom tooth has erupted correctly, grows evenly and has straight, untwisted roots, then there is every chance of getting by with a simple operation, which is carried out in 4 stages.
- Diagnostics
, including examination and x-ray, allows the doctor to get a more accurate idea of the upcoming operation. - Anesthesia.
Generally, local anesthesia is used for simple wisdom teeth removal. - Tooth extraction.
The doctor applies forceps, gently rocks the tooth and removes it using a special tool - an elevator. If fragments of roots remain in the hole, they are also carefully removed. - Treatment of the hole and suturing of the gums.
Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions are used. In some cases, stitches are placed to protect the wound from bacteria, and the patient is sent back for rehabilitation. As reviews show, in the case of simple removal it takes very little time.
How much does tooth root removal cost in Moscow?
The cost of tooth root removal is determined individually, as it depends on how complex the case is. In the dental department of the multidisciplinary clinic CELT, it starts from 800 rubles for a simple removal and ends at 10,000 rubles for a complex removal of a 2nd degree dystopic tooth. You can view our basic prices in this section of our website. In order to find out the exact cost of tooth root removal in our clinic in Moscow, consult our specialist.
In the dentistry of the CELT clinic, you can get a consultation with a dental surgeon, undergo an examination and remove the roots of the teeth, if there are indications for this. We will eliminate any dental problems effectively and absolutely safely.
The result of implanting a wisdom tooth in place of a six
The chance of such a tooth to take root with autotransplantation is almost 100 percent
. Why? Because the transplanted tooth has a large number of its own living tissues, which fully correspond to the tissues of the patient’s body. This is not a foreign body like, for example, a titanium implant. And it is absolutely its own piece of the body, which, subject to the transplantation technology, will not be rejected in the future.
The results of computed tomography show excellent survival of the transplanted tooth.
All 4 canals in the transplanted wisdom tooth are treated and hermetically sealed.
Based on the results of observation after 6 months, it is clear that the bone tissue is fully formed
, there are no empty spaces in it.
The bone around a tooth is identical to the bone around adjacent teeth. The patient was very happy about this possibility of implantation, which was successful and will delight him for many years. The patient learned about the benefits of wisdom teeth. According to the patient, the wisdom tooth transplant was initially unexpected for him, and he was very surprised by its prospects and opportunities provided by the doctors of the German Implantology Center.
Reviews of doctors providing the service - Tooth root removal
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
When is it better not to remove a wisdom tooth?
It seems that removing the lower wisdom tooth is the best solution to all problems, but this is not always true. In many patients, the eruption of “eights” occurs without complications, and in the future these teeth do not cause inconvenience, so there is no need for surgery. Also, you should not pull out your lower wisdom tooth if:
- dental prosthetics are planned and the third molar can become a support for a bridge;
- "seven" is missing. In this case, the wisdom tooth will take its place;
- caries affects only the upper part of the wisdom tooth. Then, instead of a traumatic removal operation, you can perform a regular filling, the price of which will be lower.
Relative contraindications to wisdom tooth removal are:
- infectious and inflammatory processes affecting the oral cavity
- for example, periodontal disease. In this case, you first need to stop the inflammation and take a course of antibiotics, and only then proceed to remove the molar; - respiratory diseases
- influenza, ARVI. They can provoke postoperative complications; - pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- cardiovascular diseases
in the acute stage.
Causes and consequences of losing the seventh teeth
Tooth loss usually occurs due to chronic diseases. Sevens are at risk - they are subject to heavy loads when chewing food, and their location does not allow for high-quality hygiene at home. Together, these factors lead to the rapid development of caries, pulpitis and crown destruction. Following the crown, inflammation moves to the root, periodontitis occurs, the formation of granulomas and cysts. If not treated in a timely manner, the inflammatory process spreads over large areas, which leads to the removal of the source of infection. Other reasons:
- periodontitis;
- jaw injuries;
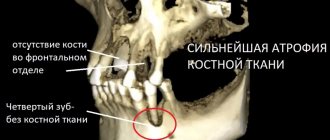
- bone atrophy due to age-related changes;
- congenital anomalies.
The loss of even one unit of dentition leads to the following consequences:
- malocclusion - voids in the dentition lead to a displacement of neighbors towards the missing unit, while the jaws will no longer close as tightly as before;
- diseases of neighboring teeth - when tilted towards the defect, the necks become exposed, sensitivity and inflammation occur;
- diseases of the digestive system - food is not chewed properly, pathologies of the stomach and pancreas develop;
- bone atrophy - due to root loss, the load on the jaw decreases and it becomes thinner;
- change in appearance - tired appearance due to sunken cheeks and wrinkles.