Every person experiences tooth extraction sooner or later. The first experience was with baby teeth, but, as a rule, no problems arise with them, and they fall out safely even without medical assistance. But with permanent teeth the situation is different. Due to their complex root system, it is sometimes very difficult to remove them, and various additional techniques have to be used. Fortunately, modern dentistry has a whole range of modern methods that are low-traumatic and allow you to cope with even the most complex cases.
What are the indications for tooth extraction?
Tooth extraction in dentistry is always a last resort procedure. Doctors make every effort to save the tooth or at least part of it, but in some cases extraction cannot be avoided. We are talking about many conditions.
- Chronic periodontitis, which is in the acute stage. As a rule, if the inflammatory process continues to recur, it is recommended to remove the tooth to prevent further spread of the infection.
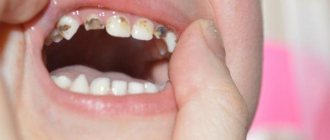
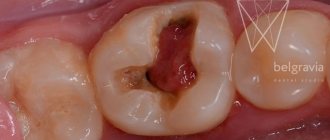
- Very strong and deep carious lesion of the tooth.
- Odontogenic osteomyelitis, which usually develops as a complication of infection and is characterized by damage to bone tissue.
- The tooth constantly injures soft tissues. This happens especially often if the tooth is in an incorrect position. Permanent trauma is very dangerous, therefore, if the problem cannot be solved in another way, removal is recommended.
- Fracture of a tooth root or any other mechanical damage.
- Late stages of periodontitis, when the teeth begin to become very loose.
- An impacted tooth that cannot erupt and is covered on top by gum tissue. Most often this happens with wisdom teeth.
- Carrying out orthopedic treatment or prosthetics that cannot be done without removing one or more teeth.
Reasons for performing tooth extraction surgery
Indications for an operation that involves removing the incisor from the alveolar socket are divided into two groups:
- emergency;
- planned in advance.
Emergency indications for performing tooth extraction are:
- acute inflammatory processes of a purulent nature (including those spreading to bone tissue);
- severe damage of no functional significance;
- severe acute pain in the absence of opportunities for conservative therapy;
- damage to the dental crown that cannot be repaired by placing a filling or dental prosthetics.
Indications for planned tooth extraction are:
- the formation of basal cysts and the development of periodontitis in the tissues surrounding the incisor with impassable root canals;
- periodontitis, accompanied by severe tooth mobility;
- the presence of supernumerary, impacted or incorrectly located teeth that injure the mucous epithelium of the oral cavity, promote the development of inflammation, provoke pain, impair diction or interfere with food intake;
- tumor growths in jaw tissues;
- the presence of teeth that prevent prosthetics or orthodontic treatment.
Contraindications to tooth extraction
Of course, if the situation is urgent and tooth extraction is inevitable, the doctor will perform the procedure immediately after the patient seeks help. But if the operation is planned, then in some cases it is recommended to refrain from it. Contraindications include the following conditions:
- acute viral disease, pneumonia;
- oncology;
- some blood diseases;
- recent myocardial infarction;
- tumors and other lesions in the oral cavity.
In addition, tooth extraction is a procedure undesirable for pregnant women. But if it cannot be avoided, then doctors recommend, if possible, to carry it out in the second semester.
How to pull out a tooth root at home
Despite the availability of modern surgical techniques and effective pain relief methods, some patients refuse to visit the clinic and prefer to perform the removal themselves. Pliers and other tools designed for everyday use, but not for dental work, come to the rescue. The base of the root part is picked up and removed. Doctors categorically do not recommend doing this under any circumstances. The fact is that the process is associated with a high risk of complications and can lead to irreversible consequences.
Is it possible to pull out the root of a tooth on your own, as experts explain?
As stated above, dentists agreed that extraction at home poses a serious threat to the health of the person who decides to do it. What happens if you ignore these recommendations:
- the open wound becomes infected, which can subsequently lead to sepsis;
- traumatic shock occurs from pain, severe stress develops;
- fragments remain in the hole, it is very rarely possible to get them completely at home, suppuration occurs, and the risk of serious dental pathologies increases;
- intense bleeding appears.
Before removing an overgrown tooth root if it is broken, it is necessary to undergo a high-quality diagnosis and develop a treatment regimen together with a doctor. Only a specialist can choose the appropriate technique and recommend a method of pain relief. Complications after extraction are rare if the procedure is performed in a clinical setting. Self-pulling can lead to serious problems, including sepsis.
Preparing for tooth extraction
For many people, tooth extraction is a very unpleasant and even frightening procedure. In fact, such fears are a consequence of those times when this manipulation was done without anesthesia using rough instruments. Today dentistry has stepped far forward, so removal takes place in much more comfortable conditions. You should not be afraid of the procedure, because the right psychological attitude is also one of the important conditions for the success of the operation.
To ensure that no incidents occur during tooth extraction, you must inform the surgeon about your state of health. If you have allergies, chronic or acute illnesses, be sure to tell your doctor. The same goes for the medications you take. Avoiding complications will also help avoiding alcohol and cigarettes the day before the procedure.
It is important to remember that you will not be able to eat or drink for some time after tooth extraction. Therefore, it is recommended to eat well before the procedure.
Anesthesia for tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a rather painful procedure, so it is almost never performed without anesthesia. The exception is people with allergies to anesthetic drugs. Most often, when extracting teeth, local anesthesia is used using an injection. Usually we are talking about the so-called conduction anesthesia, which is injected directly into the nerve and has an increased concentration of the active substance. Naropin, ultracaine, ubistezin, etc. are used as the latter.
In addition to local anesthesia, general anesthesia may also be used during tooth extraction. Today, sedation is the most popular. This is a procedure in which the patient is given a strong sedative. He is in fact conscious, but does not feel pain and remains as if in a dream. Anesthesia is a more serious procedure that involves complete loss of consciousness, which in turn entails a longer recovery period.
General anesthesia for tooth extraction is used if the patient is intolerant to drugs for local anesthesia. In addition, it is used if a person has mental disorders, as well as if he experiences severe fear of the procedure. It is also justified if several teeth are to be removed at the same time. For example, sedation is often used when wisdom teeth are extracted. The procedure is done under the supervision of an anesthesiologist. Before the manipulation, the patient undergoes tests, performs a cardiogram and other procedures to diagnose the condition of the body.
Removal steps
Before you pull out the root of a tooth, you need to prepare for this. The procedure is carried out in several successive steps. All of them are mandatory and, subject to medical recommendations, as well as general rules, guarantee a good result and quick recovery.
Preparing for removal
At the preparatory stage it is necessary:
- It is good to examine the oral cavity, especially near the pathological area. A panoramic photograph should be taken, the condition of the periodontal soft tissues should be assessed, and the presence of an inflammatory process should be confirmed or refuted.
- Develop a therapeutic regimen together with your doctor.
- Select pain relief methods and specific medications, taking into account contraindications and individual characteristics of the body.
- Prepare the necessary equipment.
- Perform hygienic treatment of the oral cavity, remove plaque and stone.
- Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution. Chlorhexidine is most often used for this.
- Do not neglect anesthesia.
- If necessary, cut the gum.
Proper preparation is a guarantee of a successful procedure. In this way, possible complications can be minimized as much as possible.
Tools
Dentists, before pulling out, remove the root of the molar tooth from the gum, select special devices, without which high-quality extraction is impossible. The doctor comes to the aid of:
- Forceps. They capture the visible part protruding above the surface of the gums. The periodontium is first separated from the root system, and the mucous membranes are peeled off from the boundaries of the alveoli. Dental units from the upper jaw are pulled out with a tool with wide bayonet-shaped blades, and from the lower jaw - with wedge-shaped models.
- Elevator. It is used as a lever, first inserted into the cavity between the walls of the hole and the root body. Used when the root part is deep, when forceps are powerless.
- Drill. Using a bur, the outer alveolar wall is removed, and the remains are removed with forceps.
Extraction methods
There are several methods that dentists resort to:
- Amputation. Indicated if surgical intervention on the upper jaw is necessary. The visible periodontal layer is mechanically separated, the drill trims the root system, which is then removed with forceps. The empty hole is filled with a special composition.
- Hemisection. Most often used on mandibular molars. The doctor takes out the diseased root and the coronal part that is adjacent to it. After this, filling is performed.
- Cystectomy. Indicated for cystic neoplasms. First, the upper section is opened, the cyst is excised, and the resulting void is filled with medical composition.
Regardless of the method chosen, local anesthesia is used. The patient will not feel pain or other discomfort.
Further processing of the alveoli
This is a mandatory step after extraction of a dental unit. The hole must be thoroughly washed with an antiseptic solution, then anti-inflammatory drugs are placed in it for the purpose of prevention or for treatment if inflammation does appear. In this case, the wound will heal much faster.
Features of tooth root extraction in different jaws
When removing fragments from the upper and lower dentition, there are some differences in the instruments used and the manipulations performed. From above, molars, canines and incisors are removed with bayonet-shaped forceps and C-shaped pliers. The dentist performs rotational movements and pulls out the tooth. When difficulties arise, a drill or elevator is used.
With the lower jaw everything is much simpler. Typically, curved dental forceps are sufficient. The exception is when “eights” are removed.
What methods of tooth extraction are used?
In modern dentistry, different methods of tooth extraction are used. In most cases, the choice of one method or another depends on the characteristics of a particular situation.
Simple method
In this case, we are talking about removing a tooth with a well-preserved crown, which is located in an accessible place. And although extraction is carried out exclusively by surgeons, such manipulation, especially in public clinics, is often performed by dental therapists.
During tooth extraction, a specialist uses different instruments. First of all, these are tongs. They vary depending on what teeth they are used for. For example, there are S-shaped forceps that are used to remove premolars and molars in the upper jaw, or forceps that are used to remove exclusively lower molars. In addition to forceps, luxors and elevators are also used, which perform the functions of lever tools.
Direct tooth extraction can occur in different scenarios. So, when extracting a single-rooted tooth, the doctor uses a technique called rotation. It involves rotating the tooth around its axis, which allows you to quickly remove the element. If the tooth is multi-rooted, then luxation or rocking is necessary. Thanks to gradual loosening movements, the doctor gradually extracts the tooth along with the root.
Complex method
Complex extractions are usually performed on multi-rooted teeth. The fact is that sometimes even prolonged swinging of the tooth does not produce results. In such a situation, the specialist uses a drill and saws the tooth, separates the roots and gradually removes all the parts. A similar procedure is also often used when the crown of the tooth is severely damaged or there are other serious problems, for example, the root system is too thin and fragile. The situation is even more complicated if the tooth is completely or partially impacted or is in an incorrect position. In particular, this often happens with wisdom teeth. In such a situation, it is necessary to first cut through the soft tissue and only then saw the tooth itself.
Piezosurgery
This method is innovative, so it is not yet widespread. Piezosurgery is usually used to remove complex teeth. In this case, the tissue incision is made with an ultrasonic scalpel. This method is much less traumatic, since ultrasound in no way directly comes into contact with tissues. Thus, the patient recovers much faster than after conventional surgery.
Laser tooth extraction
As in the case of piezosurgery, in this case the tooth is removed not with conventional instruments, but with the help of a laser beam. This is also a non-contact technique associated with less blood loss and less risk of injury. In addition, the pain of the procedure itself when using a laser is much lower, so this option is suitable for people who suffer from allergies to anesthetics. Unfortunately, both piezosurgery and the use of laser are quite expensive manipulations, so they are not yet performed widely.
Impacted wisdom tooth
These are usually the hardest eights to remove out of all the others. We have already numbed the surgical field. What's next?
It's under the gum! So, we take a scalpel in our hands and make a delicate incision in the area of the tooth being removed. This creates access to the wisdom tooth being removed. It is isolated from the surrounding tissues using special instruments, and now we can visually assess its position and choose a removal technique.
If the tooth does not erupt, it means that something is preventing it. This “something” will also interfere with its removal, and this “something” could be a neighboring tooth, a bony protrusion, etc. However, you won’t also remove the seven to get to the wisdom tooth, right?
Special surgical tip for removing wisdom teeth. Rotates at the right frequency, provides the right torque, does not burn tissue or inflate emphysema. In surgery, we use only such devices.
Therefore, we divide the tooth into parts. Using a special tip with a cutter speed of 150,000 rpm - this is no longer a simple angle cutter, but not yet a turbine cutter. The latter, by the way, is highly undesirable to use for removing teeth, because at 500,000 rpm it is easy to burn everything with a hellish flame, and with air from the cooling nozzle you can also inflate emphysema over half your face. In general, for removal you need to choose the right tools; there are no trifles or compromises here and cannot be. And you should think a hundred times before removing such problematic teeth in a one-chair dental office at a rural club on the “Half-Empty Bins” collective farm.
Impacted teeth are removed mainly with an elevator, and not with forceps, as many are accustomed to thinking
So, we divide the tooth into 2-3 parts in order to remove it carefully and with little trauma to the surrounding tissues. And teeth are usually removed using an “elevator” (in the picture on the left). Forceps, which everyone associates with removal, are actually used extremely rarely.
Well, the tooth has been removed. Next, we clean the tooth socket from “sawdust” and small tooth fragments that might remain. Using a curette.
When removing wisdom teeth, no biomaterials are used; the hole is filled with a blood clot on its own, this is quite enough for normal healing.
Moreover, “pushing” biomaterials into the hole can complicate the healing process, so let the regeneration process take place naturally and simply, and not fancy, as some doctors suggest.
After removal, resorbable (absorbable) sutures are placed on the hole; most often they do not need to be removed.
The clot is in place. Next, we bring the edges of the wound together and put stitches so that food doesn’t get stuck in the wound, it doesn’t bleed too much, and it heals faster. But at the same time, the sutures should not be tight, because the wound may bleed significantly during the first 24 hours. And if you don’t create an outflow, edema often develops.
Tooth extraction procedure: what is important to know?
The removal of each tooth can take place according to a different scenario. To predict it, the doctor conducts an examination and also takes an x-ray. In most cases, removing teeth from the upper jaw is easier and faster, but teeth on the lower jaw can create certain problems. This is explained by the fact that the lower chewing teeth have a much more complex root system. In addition, the bone tissue itself is denser here.
Also, before the procedure, it is important for the patient to prepare for how long it may last. As a rule, simple tooth extraction goes very quickly. The doctor needs 5-10 minutes to carry out all the manipulations. However, if we talk about complex removal, then in this case the time spent in the office may last for 20-60 minutes.
Contraindications
It is prohibited to carry out manipulation during pregnancy, diabetes, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, or the impossibility of anesthesia due to allergies.
Laser exposure does not cause bleeding. Despite this, the use of laser techniques is not recommended for blood diseases.
Advantages
Laser therapy for extraction has a number of advantages:
- It is performed under anesthesia and is not accompanied by pain.
- Reduced likelihood of complications. Under the influence of a laser, the edges of the wound are sealed and disinfected.
- Fast execution.
- Wound sterilization.
- Short rehabilitation.
The device operates silently. There is no drilling sound or vibration.
Flaws
Like any treatment method, the laser method has disadvantages. Since the procedure is new, not all dentists are equipped with the necessary equipment. The operation must be performed by a qualified and experienced doctor. This is due to the high cost of the service.
Preparatory stage
Before the procedure, the dentist carefully examines the oral cavity. The set of preparatory measures includes:
- The location of the element to be deleted is determined.
- The patient's medical history is studied. Chronic pathologies are identified.
- X-ray diagnostics and general clinical blood tests are performed.
- The patient is prohibited from taking painkillers on the eve of the intervention.
- It is recommended to eat a large meal a couple of hours before surgery.
The dentist selects the appropriate anesthesia and sets up the laser equipment.
Carrying out the procedure
The laser extraction technique is almost identical to traditional tooth extraction. Initially, the doctor applies anesthesia. The laser beam does not cause pain when making incisions. Anesthesia helps eliminate discomfort during surgery.
Step-by-step operation:
- Dissection of the mucous membrane. Required if the tooth is hidden under soft tissue. The flaps are folded back to provide access to the unit.
- Breaking an element into pieces. A molar that has split on its own does not undergo crushing.
- Cleaning the hole from fragments. The doctor checks the socket for the absence of small bone fragments.
- Membrane installation. Prevents infection from entering the wound and the development of the inflammatory process.
- Returning the mucosal flaps to their place and applying sutures.
The technology helps minimize trauma to bone and mucous membrane tissue.
Postoperative period
During the recovery period, the patient must adhere to medical recommendations:
- Refrain from eating food for two hours after the procedure.
- Do not eat solid food.
- Avoid intensive rinsing in the first days.
- Do not heat the damaged area.
- A cold compress will help relieve swelling.
- Avoid physical activity and visiting the sauna and swimming pool.
- Perform oral hygiene daily. When brushing your teeth, do not touch the post-operative area with a brush.
The recovery period lasts up to three days. For complex procedures, dentists prescribe antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Complications
Ignoring medical recommendations and rules for sanitation of the oral cavity leads to the development of complications. Swelling and inflammation occurs in the postoperative area. If you experience any warning symptoms, pain, swelling or discomfort, you should contact your doctor.
What care is required after tooth extraction?
Regardless of whether you had a simple or complex tooth extraction, such a situation requires monitoring your well-being and the wound surface on the gum. First of all, this concerns the proper healing of the hole. Ideally, a blood clot should form in it, which indicates that healing is proceeding without problems. It is for this purpose that the doctor immediately after the procedure places a gauze swab into the resulting cavity. It must be kept in the indicated place without removing it for 20-30 minutes, and only after that can it be removed. If the hole has formed correctly, then in a couple of days it will be covered with epithelium, and after a couple of months new bone tissue will appear in its place.
In order not to interfere with the proper healing of the wound, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Do not rinse your mouth for a couple of days or use a toothbrush in the area where the tooth was removed;
- For the first time after the procedure, avoid hot drinks and food;
- do not take a hot shower or bath for 2-3 days after tooth extraction;
- for the first few hours, completely abstain from food and drinks;
- Until the wound heals completely, try to chew on the other side of your mouth.
Many people experience swelling in the area where the tooth was removed, which can last for several days. To make it less pronounced, it is recommended to apply ice to the cheek after the procedure. Minor pain and low-grade fever may also be a concern. This is considered normal, and to alleviate the condition, the doctor prescribes painkillers. He may also prescribe an antibiotic if in a particular case he considers its use justified. In such a situation, it is extremely important to undergo a full course of treatment in strict accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
Stages of healing
The process of complete recovery after tooth extraction is quite long, but effective: all surrounding tissues are completely regenerated.
- 3–4 days - development of granulation tissue;
- 14th day - complete filling of the hole with granulation tissue;
- 45th day - filling the hole with spongy bone tissue;
- end of the 3rd month - transformation of spongy bone tissue into dense;
- after 4–6 months (8–10 in the presence of complications), the socket is radiologically indistinguishable from the surrounding tissue [2].
After the hole has healed, it is worth thinking about restoring the integrity of the dentition. Modern implantation technology makes it possible to obtain a prosthesis that does not differ from natural neighboring teeth either in appearance or in function.
List of sources
- Timofeev A. A. Guide to maxillofacial surgery and surgical dentistry. Kyiv: Chervona Ruta-Ture, 2002. // URL: https://studfile.net/preview/2767270/ (date accessed 08/08/2020).
- Propaedeutics of dental diseases. Propaedeutics of surgical dentistry: tooth extraction surgery: textbook / Ed. Garages S. N. Stavropol: St. State Medical University, 2022. // URL: https://stomfaq.ru/uchebnoe-posobie-pod-redakciej-prof-sn-garaji-stavropole-2017/index.html (access date 08.08.2020 G.).
- Orthodontist: “Sometimes orthodontic non-intervention is a respect for evolution. Unfortunately, modern dentistry often goes against nature,” interview with Yu. L. Denisova // URL: https://doc.by/vopros-vrachu/ortodont-inogda-ortodonticheskoe-nevmeshatelstvo-eto-uvazhenie-k-evolyucii- k-sozhaleniyu-sovremennaya-stomatologiya-chasto-idet-protiv-prirody/ (accessed 08.08.2020).
Possible complications after tooth extraction
In some cases, tissue healing after tooth extraction does not occur correctly, or an infection is observed. In this situation, we talk about complications after surgery. They are indicated by severe pain, great swelling, and elevated temperature. If pathogenic microflora gets into the wound, then bad breath and purulent discharge may also appear. The listed symptoms may indicate a cyst or fistula.
A common complication after tooth extraction is alveolitis. This condition is accompanied by a dry socket, that is, the absence of a blood clot. The main sign of pathology is quite severe pain. Alveolitis is most often diagnosed in women taking contraceptives and in people who smoke.
The development of complications after tooth extraction is often a consequence of neglecting the doctor’s recommendations. In addition, the reason may be related to poorly performed manipulation or low qualifications of the doctor. That is why it is always important to contact experienced specialists who master modern techniques and cope well with even the most complex and extraordinary cases.
come back
In what cases should teeth not be removed?
Contraindications to the operation are:
- acute infectious diseases;
- menstruation in women;
- hypertensive crisis, severe arrhythmia and other cardiac disorders;
- I and III trimesters of pregnancy;
- taking medications that reduce blood clotting;
- hemophilia and other blood diseases;
- epileptic seizures;
- schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.
If the listed pathologies and conditions are identified, the issue of tooth extraction is considered on an individual basis.