636
It is believed that fixed functional orthodontic appliances are not effective enough to treat people with a mature dental system.
Doctors often recommend that such patients resort to maxillofacial surgery to correct dental anomalies.
However, recently developed orthodontic devices can, in many cases, eliminate the need for invasive and expensive bone grafting. Such devices include the Forsus device.
General presentation and purpose
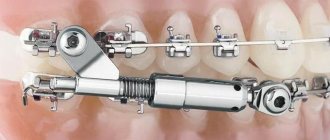
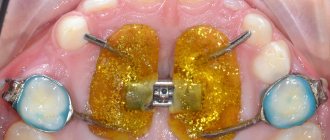
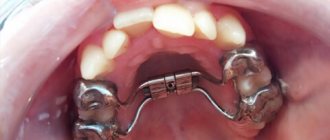
The Forsus device is a non-removable orthodontic device of a functional-mechanical type. This means that the corrective force is created in it both by a constantly operating mechanical device (spring) and by the work of the masticatory muscles.
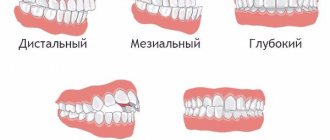
The device is intended for the correction of distal occlusion (class 2 anomaly), which is characterized by retraction of the lower jaw relative to the upper jaw.
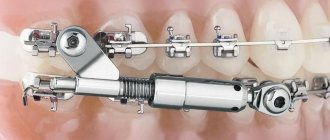
The orthodontic system assembled using the Forsus apparatus consists of the following elements:
- upper buccal tubes (right and left);
- maxillary arch with braces;
- mandibular arch with braces;
- EZ module;
- mandibular rod.
The corrective action of the device consists of stimulating growth (moving forward) of the lower jaw through the pressure of the mandibular rod on the mandibular vestibular arch.
At the same time the growth of the upper jaw is inhibited , thanks to the reactive force from the spring transmitted to the buccal tube, through it to the arch and all the teeth of the upper jaw.
The design can be supplemented with other elements, in particular, ligatures, which have the desired effect on individual teeth.
For what purpose is the bite height determined and the methods used.
Come here to review techniques for determining centric occlusion and centric relation of the jaws.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/mehanizm-stanovleniya-molochnogo.html we will talk about the features of the period of change in the primary occlusion.
Causes
In young children, distal occlusion is a physiological norm. The upper jaw protrudes above the lower jaw by a distance of 1 to 10 mm. This is necessary for sucking the mother's breast. Gradually, the distal bite becomes orthognathic.
Reasons for the development of prognathia:
- Vitamin D deficiency. Causes rickets at an early age, the consequence of which is distal or mesial occlusion.
- Premature loss of baby teeth or their removal.
- Genetic factor.
- Calcium and fluoride deficiency in the body of a pregnant woman causes prognathism in the child.
- The influence of external factors - the use of a pacifier, sucking of fingers and other objects in childhood.
- Chronic pathologies of the respiratory system, causing disruption of normal nasal breathing. This leads to improper jaw development.
- Poor posture. A bent back and a head down provoke the development of jaw pathology.
- Injuries that damage the jaw bones.
- Some types of speech defects, due to which distal occlusion develops.
Specifications
The Forsus device is a universal system that can be adjusted to the jaw of any adult. Its main parameters are the pressure force on the lower vestibular arch and the distance from the edge of the buccal tube to the surface of the bracket installed on the lower canine (that is, the length of the intermaxillary traction).
The pressure of the rod on the arc should be about 200 g. It is regulated using stoppers installed on the mandibular rod to change the degree of compression of the spring.
The length of the intermaxillary rod varies depending on the size of the jaw and is established by selecting a rod of the required length, as well as by installing stoppers on the lower vestibular arch.
All structural elements are made of durable material with high fatigue strength.
Purpose of individual system elements
- Spring assembly. Consists of three telescopic springs that provide the necessary correction force. The consistency of its action makes the treatment independent of the patient’s behavior, with the mouth open and closed.
- Clip . It is used to attach the EZ module to the buccal tube. Thanks to a special design (presence of an anti-rotation shoulder), the clip prevents the occurrence of torque on the buccal tubes, which prevents rotation of the abutment tooth and increases the comfort of wearing the device.
- Buccal tube. It is the base (support) against which correction is carried out.
It consists of a ring put on a tooth (molar or premolar) and 2 soldered tubes. The upper one is used to attach the maxillary facebow, the lower one, located at the level of the occlusal surface, is for attaching the EZ module clip. The length of the down tube ranges from 3.6 to 4.3 mm. - EZ module .
This is the main element of the system. It is a prefabricated unit that includes a spring unit and a clip, the elements are connected to each other by a lever. According to their function, the EZ module is an intermaxillary rod that transmits force from a compressed spring to the lower vestibular arch. This creates a constant correction force independent of the patient. - Mandibular rod .
Transfers force from the spring to the lower vestibular arch. Available in five sizes - 25, 29, 32, 35 and 38 mm. The connection of the rod to the arc is carried out using a loop located at its end. The latter is thrown onto the arc and compressed with pliers to prevent it from falling off. - Inferior vestibular arch . Receives pressure from the mandibular rod and transmits it to the teeth of the lower jaw, through glued braces. The force is directed forward to advance the lower jaw.
- Superior vestibular arch . Connects the teeth of the upper jaw into a single supporting system. Receives reactive correction force and transmits it to the upper jaw, inhibiting its development.
Indications and contraindications
The Forsus appliance is used to correct moderate class II anomalies (distal occlusion).
In particular, the following clinical cases are indications for its use.
- The need for skeletal correction in mild and borderline distal occlusion. (Reference: Skeletal correction, unlike dentoalveolar correction, involves influencing the entire jaw bone, and not just the dentoalveolar process).
- Dentoalveolar anomaly class 2.
- Unilateral class 2 anomaly (distal bite + displacement of the midline of the lower jaw). In this case, different correction forces are set for different sides of the jaw. The result of treatment is the correction of the distal bite with simultaneous correction of the position of the midline.
The Forsus device is contraindicated if there is a risk of negative changes in facial aesthetics.
Reasons for distalization of lower molars and features of the device.
In this publication, read how orthodontic tooth traction is performed.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/ortodontiya/prikus/deprogrammator-koysa.html all the most important things about using the Koysa deprogrammer in dentistry.
Fixation stages
Installation of the device, if it is used at the very beginning of treatment, begins with fixation of buccal tubes on the second molars of the upper jaw.
The maxillary and mandibular arch with braces are installed using standard technology - the adhesive method. The ends of the mandibular arch should be curved after the outermost brackets (installed on the second molars). For reliability, you need to attach the arches to the locks not with elastic, but with wire ligatures.
After fixing the arches, begin installing the EZ module. Using Weingard forceps or another instrument, insert the module clip from the mesial side into the lower tube until it clicks.
Using a special tool in the form of a ruler, measure the distance from the rear edge of the tube to the distal surface of the bracket installed on the canine. If a stopper installed on the arch is used as a support for the mandibular rod, then the distance to it is measured.
When measuring, the lower jaw should be in its natural position (without moving forward). Based on the measurement results, a mandibular rod of suitable length is selected.
The loop of the selected rod is placed on the lower vestibular arch in the intervals between the first premolar and the canine. The point of application of the rod can be changed using a stopper installed on the vestibular arch (the stopper serves to stop the rod and is installed at the point where it is necessary to apply force).
When the patient's mouth is open, the module spring is compressed and a rod is inserted into it. If it is discovered that when the teeth are closed, the rod comes out from the far edge of the spring, you need to use a smaller standard size.
The final manipulation is to compress the rod loop with pliers to prevent it from falling off the arc.
The device is activated (if necessary) by installing a locking ring on the rod in front of the spring (to do this, it must be compressed). The correction step is 2-3 mm.
Watch the video to see how the Forsus device is installed and operates.
Subtleties of removal
The decision to remove Forsus is made by the doctor after achieving the desired treatment result.
The whole process takes place in the following sequence:
- Compressing the spring, the doctor removes the rod.
- Holding the distal part of the structure with Weingard forceps, the EZ module is removed from the facebow tube in the mesial direction.
- Disconnects the rod by holding its distal end with your fingers and using forceps to unbend the loop at the end of the rod.
Important! Removal, like installation of Forsus, is carried out quickly, without discomfort for the patient.
Duration of wearing
The duration of treatment varies widely, depending on the severity of the abnormality. The device can be used not from the beginning of treatment, but at some stage (installation of the EZ module on a previously installed brace system).
It is also possible to remove the module before the end of treatment, and continue correction with braces without it. In general, the duration of treatment can range from 1 month to 2 years.
Control inspections of the system are recommended at least once every 6 weeks.
Price issue
The cost depends on the configuration. It can be supplied with a lower vestibular arch with braces (in this case, the price starts from 17,000 rubles), and without an arch (about 10,000 rubles).
Treatment with the device, in addition to its price, includes diagnostics, drawing up a treatment plan, sanitation of the oral cavity, professional cleaning and other therapeutic measures.
The cost of treatment also includes installation of the device, repeated activations, control of the correction process, removal of Forsus after its completion. As a result, the total amount for treatment, depending on the configuration of the device, ranges from 20,000 to 32,000 rubles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantage of the Forsus apparatus is its effectiveness in correcting distal occlusion in people with a mature dental system.
In addition, a number of advantages are due to the design features of the device.
- Predictability of the result, thanks to the efficiency of the system and the elimination of the human factor. The adjustment does not require patient participation. The constant action of the corrective force is ensured by the presence of a spring.
- Easy to install. The EZ module attaches to the buccal tube with one click. This became possible thanks to the special design of the clip. The mandibular rod is also easily attached to the vestibular arch. The loop is thrown onto the arc and compressed with pliers to prevent it from jumping off the arc.
- Easy to use , does not require long-term staff training.
- Compatible with any braces ; it is possible to simultaneously use rigid and elastic ligatures to move an individual tooth in the desired direction.
- High adaptability , adaptability to different jaws. The magnitude, application point and direction vector of the corrective force can be easily changed.
- Structural strength. Breakdowns cannot be completely ruled out, but the device is quite reliable.
- Comfortable to wear. In most cases, patients do not complain of discomfort. This is ensured by the design of the device itself. The close location of the spring and the rod to the teeth, as a rule, relieves the cheek mucosa from irritation.
- Practical invisibility.
Flaws:
- volumetric design , in rare cases, due to the structural features of the jaws, irritation of the mucous membranes by the spring and rod is possible;
- relatively low degree of correction for skeletal (jaw) anomalies (dental-alveolar movement occurs more easily).
Installation Rules
The Forsus device is installed and removed by an orthodontist specialist. Preliminary activities include the following:
- Diagnosis of anomaly.
- Drawing up a treatment plan.
- Sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Cleaning the oral cavity.
- Attaching bandage rings with mandibular rods to the first maxillary molars (without grinding them down) using a cement base.
- Installation of braces systems on both jaws. To securely fix them, especially on the fangs, a wire ligature is used.
Reviews
The Forsus device has been used in orthodontics relatively recently. If you had to undergo treatment with its help, share your impressions about it.
Was a positive result achieved, how long did it take? The comment form is at the bottom of the page.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags devices: bite correction
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
The use of aesthetic abutments in dental practice
Next article
Is it possible to do dental implantation without a sinus lift?