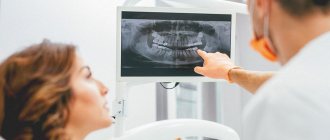
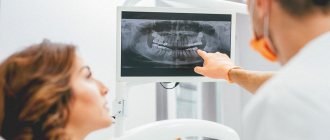
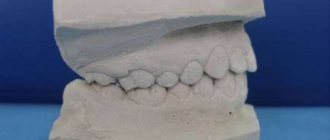
Dentistry today works real miracles. Despite this, keeping teeth intact in old age is not so easy. As a rule, older people need prosthetics. At the same time, it is important to choose the right orthopedic design, since at the moment the choice of prostheses is huge. Each material and product has both its advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, it is necessary to proceed from the individual characteristics of the patient, as well as from the clinical picture of his oral cavity.
Orthopedic dentistry
Orthopedics is a large branch of dentistry that deals with the elimination of violations of the integrity and defects of the maxillofacial area. The basis of orthopedic dental treatment is prosthetics.
There are two main treatment methods :
- Dental restoration. Suitable for situations where the tooth is not completely lost. The area of the missing tooth is filled with special orthopedic structures (stump inlays, pins, etc.). Thus, the damaged dentition is restored to its original appearance.
- Prosthetics. This option is used for complete tooth loss. An orthopedic dentist selects an individual denture. There are several types of structures, differing both in the materials from which they are made and in the installation methods.
Types of orthopedic structures
To correctly choose a prosthesis, you need to take into account a number of factors. First of all, the product must fully restore the functions of lost teeth. Also, the choice of the type of orthopedic product depends on the patient’s preferences and financial capabilities. The doctor will tell you which option to choose.
Let's figure out what types of dentures there are.
Main types:
- metal crowns;
- metal-ceramic products;
- ceramic structures.
These products are usually manufactured in two types:
- single crowns;
- bridge structures.
Determining which type of product is better is quite difficult. Each prosthesis has its own characteristics. The main differences are price and aesthetic indicators.
Among other things, dentures are divided into two types: removable and fixed. Let's take a closer look at what removable orthopedic structures are.
Dentures
Dentures are structures designed for full or partial restoration of the dentition. There are three types of prostheses:
- Removable;
- Fixed;
- Partially removable.
For each individual case, the orthopedic dentist selects an individual type of design. Its choice depends on many factors: the health of the patient’s body as a whole, structural features of the maxillofacial area, the presence of other oral diseases, treatment methods used in this clinic.
Innovative materials and the latest technologies in the field of orthopedic treatment allow us to achieve excellent results. The service life of modern prostheses reaches more than 10 years. They are distinguished by excellent aesthetic qualities, comfort and ease of wearing.
Artificial teeth used on modern structures are almost impossible to distinguish from natural teeth.
The development of orthopedic dentistry does not stand still; new developments and materials are constantly appearing. However, classical prosthetic methods are not excluded. Methods are emerging that combine various areas of dentistry.
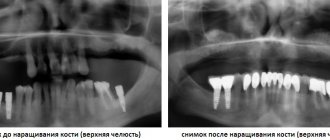
For example, modern dentures are often fixed on mini-implants. Thus, the treatment uses the best practices of both implantology and orthopedics.
The main task of dental prosthetics is to restore lost dental tissue, missing teeth, and the structure and function of the masticatory apparatus.
Depending on the existing problem, the dentist may offer several solutions.
Based on the nature of fixation, prosthetics are divided into 2 types:
- Fixed prosthetics
– used to restore lost tooth tissue, as well as in complete or partial absence of teeth (edentia):- Microdental prosthetics: inlays, pin inlays, veneers;
- Crowns;
- Bridges;
- Prosthetics using implants (in cases of partial or complete edentia).
- Removable prosthetics
– used for partial or complete edentia. Divided into:- Partially removable dentures
are a dental orthopedic structure that restores part of the missing teeth in the presence of two or more natural teeth on the jaw, on which a partially removable denture can be secured using clasps (hooks) or attachments (locks); - Conditionally removable
are structures that got their name because of the method of fixation on implants. Such dentures cannot be removed independently; this can only be done in a dental setting. In this case, the prosthesis is firmly fixed, but if necessary, it can be properly cleaned, replaced, or modified; - Complete removable dentures
are an orthopedic design that is used in the absence of teeth. The patient can easily remove and clean the prosthesis on his own.
Let's look at each type in more detail. Let's start with fixed prosthetics.
Fixed orthopedic structures have a number of advantages over removable ones, namely they are comfortable, aesthetic, do not interfere with diction and taste, and do not require special hygiene.
The most commonly used fixed prostheses include:
- Single crowns
- used to replace lost tooth tissue or to replace 1 lost tooth with an implant. It is also possible to prosthetize 2,3 or more adjacent teeth, but each of them will be covered with a separate crown (the need to connect these crowns to each other is decided by the doctor, depending on the clinical situation). The most frequently asked question in this area is: “Are adjacent teeth ground down?” No, only those teeth are subjected to preparation, the destruction of the crown parts of which requires prosthetics. - Bridges
are when abutment teeth or implants are covered with crowns, and between them there are 1-2 artificial teeth). The main disadvantage of this type of prosthetics is the loss of bone structures in the area of the missing tooth, followed by exposure of the roots of the supports of the bridge (but this only applies to one’s own teeth). - Inlays (onlays)
are orthopedic structures made in the laboratory, used in case of significant destruction of the crown parts of the teeth. They are a priority because they are stronger and more wear-resistant than fillings. They are installed on both vital and pulpless (dead) teeth. - Stump inlays
are used when the coronal part of a tooth is completely destroyed, as a more durable alternative to a pin structure. They are a metal structure that includes the coronal part of the tooth along with a pin; the coronal part can be lined with ceramics in the case of further coating with a ceramic crown. Use in multi-rooted teeth is not recommended due to the risk of tooth and root fractures. - Veneers
are microprostheses, (especially relevant recently) the main task is aesthetics! With the help of veneers, you can solve problems with the shape, color, and size of teeth. The thinnest dentures. They have a number of contraindications for use.
Fixed dentures also differ in the materials from which they are made:
- Solid (metal) crowns
- consist of metal, come in silver or golden color (if the patient would like coated crowns). Recently, spraying has practically not been used due to the harmful effects on the body. The most budget option for fixed prosthetics. Leads to disruption of dentogingival attachment. There is a risk of an allergic reaction to the metal. - Metal-ceramic crowns
- have a metal base, then covered with an opaque layer and ceramics, the color of which is selected individually. Due to the multi-layer structure, it is necessary to remove a large amount of tissue during grinding, which reduces the service life of the tooth. Aesthetic properties are also questionable; after fixation, we often observe a dark edge of the gum, as the metal edge of the crown is visible. The dentogingival attachment also suffers. - Metal-free (zirconium dioxide, pressed ceramic E-max) crowns
are highly aesthetic and durable structures consisting of either ceramics or zirconium dioxide with ceramic lining (the type of material is selected depending on the location). Crowns are thinner than metal-ceramics, so prosthetics can be applied even to “living” teeth. Highly aesthetic due to light refraction and transparency of the structure. Biocompatible with the gum, which reduces the risk of recession of the gingival margin, increasing the service life of crowns. - Plastic (temporary) crowns
are the most short-lived structures, therefore they are used only for a short period of time (for example, during orthodontic treatment or for monitoring a tooth after complex endodontic treatment).
Next, we will consider the most commonly used types of removable prosthetics.
- Plate (acrylic, plastic dentures)
- the base is made of hard plastic (acrylic), on which artificial teeth are installed. The longest adaptation! The prosthesis is quite voluminous, as a result, patients often notice a violation of the diction of patients (mainly during the period of adaptation), and a possible disturbance of taste. The advantages include good fixation and the lowest cost. The advantage of this type of prosthetics is the possibility of relining (adjusting) the prosthesis. - Nylon
– soft removable dentures, thinner and lighter. Made from nylon. Getting used to them is easier. But due to their structure, they absorb water, which leads to their deformation and replacement, since the relining process is not possible for them. Nylon dentures accumulate odors and dyes, which also leads to replacement. - Clasp
- this prosthesis is based on a metal frame on which an acrylic base with artificial teeth is installed; the fixation of these prostheses can be clasp, locking, telescopic or using pelots. Clasp dentures are used only in cases of partial absence of teeth. They do not affect diction and are comfortable when chewing. The advantages include speed of production. Abutment teeth are mostly covered with crowns. It is important to know that restraint devices may be visible when talking and smiling.
We looked at the most commonly used types of dentures at a dental appointment. The doctor will tell you which of these structures you need during a consultation after an examination and all the necessary studies.
Removable dentures
Removable dentures are structures that can be removed and installed independently. Modern dentures are comfortable to wear and have an attractive appearance, indistinguishable from real teeth.
There are two types of removable structures: clasp and plate.
According to the method of fixation, prostheses are distinguished:
- With a clasp fixation system (a clasp is a kind of hook shape);
- With fixation on attachments (on locks and hinges);
- With telescopic fixation system.
Popular Orthopedic Treatment Options
Each situation has its own optimal prosthetic option. There can be no universal solutions here. Orthopedic dentistry today offers many ways to treat dental disorders and anomalies.
The most popular are:
- Tabs. Replace fillings. Made from individual casts. They fill the existing carious cavity and fit tightly to its sides. They make the tooth beautiful and very durable, do not shrink over the years, and do not change the original color.
- Veneers. Overlays glued to the front surface of the crown. Requires minor preliminary grinding. They only cope with minor changes - chips, cracks, unsightly fillings, changes in the shade of enamel.
Prosthetics on implants. This type of dental orthopedics is indicated for complete or partial loss of fangs, molars, and incisors. It makes it possible to restore chewing function, eliminate problems with “lisping” diction, and make the smile area beautiful.- Crowns. Optimal if the crown part is severely destroyed and the roots are in satisfactory condition. They are made from metal, plastic, ceramics, zirconium oxide, and precious metals. The material is selected taking into account the required strength and the desired visual effect.
- Dental bridge. Used if there is no one or several adjacent units. Its edges are crowns, and the center is artificial teeth. Requires, as a minimum, two reliable supports.
- Removable structures. They can be lamellar or clasp. They are used if there is no large number of dental units. They are usually preferred by older people due to their low cost and ease of use.
Orthopedic dentistry is rightfully one of the most popular dental branches. After all, even children with primary malocclusion often become clients of an orthopedist.
Fixed dentures
This type of prosthesis is permanently in the oral cavity. Using various fixation methods, they are securely fixed and do not require daily manipulations to remove and install them. This mounting option is most comfortable for the patient. After installing the prosthesis (provided that the procedure was performed by a competent orthopedic specialist), you can forget about it. And remember during routine dental examinations.
Non-removable structures include:
- Restorative crowns;
- Bridges.
Materials for prosthetics.
A few years ago, orthopedic dentistry could only offer uncomfortable removable structures. Today, different methods of prosthetics are available to patients using high-quality materials. Unpractical plastic has been replaced by flexible nylon. It is much more practical and reliable than acrylic plastic. Orthopedic systems created on the basis of a nylon base have a number of advantages:
- They are durable.
- Their shade matches the color of the enamel and gums.
- Can be secured using suction cups.
- The patient gets used to flexible structures much faster.
- When used, do not injure the oral cavity.
To create permanent systems, namely crowns, modern prosthetic dentistry offers several types of materials. Most often, patients use ceramics to restore their front teeth. It perfectly imitates the appearance of incisors, but unfortunately, it is not sufficiently resistant to mechanical stress. To replace molars, stronger dentures are needed that can withstand heavy loads. In this case, crowns made of metal or composite are suitable.
- Zirconium dioxide is a durable material that is completely biocompatible with the human body and does not cause allergic reactions or inflammatory processes. A patient with such teeth has nothing to fear; they will not break or crack. To create crowns from zirconium, special equipment is required, since the material is very hard and cannot be processed by hand. Today this is the most durable and aesthetic method of prosthetics.
- Metal-ceramics is a permanent structure made of a metal base, covered with ceramics on top. This is the best option if you are looking for reliable and inexpensive crowns. They can be used to restore both chewing and front teeth. Their only drawback is that the frame is translucent, so the color of the enamel darkens over time.
Depending on the clinical case, the patient himself chooses the basis for the prostheses, based on his financial capabilities. A variety of materials allows you to install high-quality products at an affordable price.
Partially removable dentures
Partial removable dentures are made to fit a portion of the toothless jaw and are secured with discreet clasp hooks. After each meal, the denture should be removed and rinsed with running water.
Some people find it difficult to get used to removable dentures, but if you follow the tips that can be found at this link, the adjustment process will be much easier. The main advantage of removable dentures is that in order to remove or put on the denture you do not need to go to the dentist, the process of cleaning and caring for the structure becomes easier.
At the Consilium Dent dental clinic, all work on the selection, manufacture and installation of prostheses is performed by experienced orthopedic dentists who are capable of solving the most complex clinical problems.
When you contact the clinic, our doctors will make temporary prostheses on the same day, which can be used until the end of treatment. This will provide our patients with maximum comfort and help hide aesthetic imperfections.
Tab
An inlay is a microprosthesis used to replace tooth defects and restore the anatomical shape of crowns. It can serve as a support for a short bridge (the so-called Maryland bridge), a splinting structure.
Dental inlays
Indications for production:
- Pathologies of hard dental tissues that cannot be replaced by filling: caries , increased abrasion, wedge-shaped (abfraction) defects , crown fractures, enamel hypoplasia, fluorosis;
- Defects in the dentition of 1–2 teeth (as a fixing element in temporary structures with an extended service life);
- Pathological mobility of teeth (splinting elements during orthopedic treatment of periodontitis - inflammation of periodontal tissues).
Advantages of inlays over direct restorations (“fillings”):
- Elimination of incorrect cavity formation (on the model and in the tooth it will have tight, precise contact with the walls and a single direction of insertion due to steep walls and a flat bottom);
- The possibility of more accurate and correct restoration of the correct anatomical shape and individual characteristics of the crown, the functional component (chewing);
- High-quality restoration of the contact point - the part of the crown in contact with adjacent teeth (optimal shape and position, smoothness) - this is important for the healthy condition of the gums;
- Possibility of additional correction before fixation (visually, radiologically, instrumentally);
- High color stability and durability.
Restrictions and contraindications:
- Very deep and hard-to-reach cavities (submerged under the gum);
- Low natural crown.
Classification:
- Inlay – completely surrounded by hard tooth tissues;
- Onlay – cover the internal slopes of the tubercles (protective overlay);
- Overlay – covers all surfaces except one (usually the outside);
- Pinlay – reinforced into tissue using pin(s).
For the manufacture of inlays, the following are used: metal alloys (cobalt-chromium, silver-palladium, gold), composite materials, ceramic masses, zirconium oxide.
Clinical and laboratory stages of making an inlay (indirect method):
- Creation of a cavity within the enamel and dentin with preventive expansion to avoid secondary caries ;
- Obtaining impressions and models;
- Making a wax reproduction of the future design;
- Conversion into a permanent material (casting, firing, milling, pressing);
- Checking the accuracy of manufacturing on the model and in the clinic, fixation.
With the direct manufacturing method, the formation from wax occurs directly in the cavity prepared in the tooth. The indirect method is most often used.