Content:
- How do they manifest themselves?
- Where do they come from?
- Consequence of dental diseases
- Aphthae of traumatic nature
- Result of common diseases
- How to cure
Defects of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity are not uncommon.
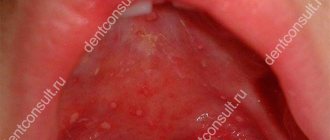
Many people encounter them. They can occur due to infectious and viral diseases, mechanical damage to tissues. Most often, dentists encounter white sores on the gums. These are painful areas that prevent the patient from enjoying life. They make eating problematic and do not allow for high-quality hygiene measures. Any touch to the affected area provokes acute pain.
It is important not to ignore the presence of white patches on the gums. If they appear, you should contact your dentist. The doctor will determine the cause of the disease and tell you how to eliminate it.
Ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis
Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis is an infectious disease. Its causative agents are Vincent's spirochete and spindle-shaped rod. It can affect only the gums, cover the entire mucous membrane of the mouth, and spread to the tonsils.
Degree of damage
The diagnosis is made depending on the degree of damage to the mucous membrane:
- Vincent's gingivitis or gingivostomatitis (only the gums are affected).
- Stomatitis (gums and other areas of the oral cavity are affected).
- Vincent's tonsillitis (the pathological process spreads to the oral mucosa and involves the palatine tonsils).
Causes
The main reason for the development of the disease is improper oral hygiene. The causative agents of the disease are present in the oral microflora of all healthy people. If hygiene rules are not followed, their number increases, resulting in the development of a pathological process.
The rapid development of ulcerative necrotic stomatitis can also be provoked by a general weakening of the body’s immunity and resistance. For this reason, the disease often accompanies colds.
Other reasons that can cause the development of stomatitis include:
- Hypothermia.
- Overwork.
- Severe stress.
- Exhaustion as a result of insufficient nutrition (for example, with strict diets).
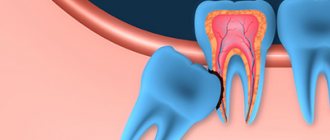
The risk of developing stomatitis increases with the presence of injuries to the mucous membrane. The risk group includes patients whose mucous membranes are constantly injured, for example, by tooth fragments, poorly placed fillings, dentures, etc. Often stomatitis occurs during the eruption of wisdom teeth, since the gums are severely injured during the process.
Despite the abundance of reasons that can lead to the development of necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis, careless hygiene and poor dental care remain the most common provoking factors. The likelihood of developing the disease increases if:
- Plaques and tartar.
- Inflammatory processes in periodontal canals.
- Chips and cracks, etc.
Depending on the nature of the disease, acute, subacute and chronic stomatitis are distinguished. The disease can occur in varying degrees of severity.
Symptoms
At the initial stages of the disease, both specific (bleeding, burning, dry mouth) and general symptoms (weakness, fever, joint pain) occur. Often the patient considers them to be signs of other pathologies and does not associate them with the inflammatory process in the mouth. The duration of this stage differs depending on the severity of the disease. The disease can progress quickly and the condition worsens in just a few hours. In a chronic course, the first stage can last several days.
As the pathological process develops, the general condition worsens, and the following symptoms appear:
- Sharp pain in the mouth.
- Difficulty moving the tongue.
- Increased salivation.
- The appearance of putrid odor from the mouth.
Gradually, lesions develop on the gums. Subsequently, they spread to other areas of the mucosa. The gums swell and turn red. Severe pain and bleeding occurs. It becomes almost impossible to eat. As the disease progresses, the gums become covered with gray necrotic tissue.
General health depends on the severity of the disease. In a mild form, the patient’s general condition remains normal, the ability to work remains, and the person can lead a normal life. A severe course is always accompanied by a strong increase in temperature. The ulcers are deep and can reach tendons and bones. In this form, stomatitis can lead to another serious disease - osteomyelitis.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Treatment
If signs of stomatitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. During diagnosis, the doctor examines necrotic ulcers, determines the depth and extent of the lesion. After this, treatment is prescribed.
During treatment, it is important to ensure thorough sanitation of the oral cavity. The disease must be treated comprehensively:
- Rinse with antiseptic solutions.
- Taking antihistamines.
- Taking general strengthening medications and vitamin C.
- Ointments and applications for the treatment of necrotic ulcers.
- Removal of necrotic tissue and dental plaque.
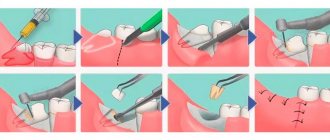
Surgical intervention is indicated in cases where the development of stomatitis was provoked by the eruption of wisdom teeth. If treatment is started correctly and in a timely manner, the entire process takes 6 days. If the patient does not receive the necessary treatment in time, complications, gangrenous processes, and irreversible changes in the bones and periodontium begin to develop.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Sources:
- Personal experience as a periodontist;
- Diseases of the teeth and oral cavity; GEOTAR-Media - Moscow, 2012;
- Diseases of the oral mucosa; Phoenix - Moscow, 2007;
- Clinical manifestations of infectious diseases in the oral cavity in patients with HIV infection; Publishing house of the Russian Peoples' Friendship University - Moscow, 2013;
- Therapeutic dentistry. Diseases of the oral mucosa. In 3 parts. Part 3; GEOTAR-Media - Moscow, 2013;
- Therapeutic dentistry. Diseases of the lacrimal membranes of the oral cavity. In 3 parts. Part 3: GEOTAR-Media Moscow, 2013;
- Banchenko G.V., Rabinovich I.M. Syphilis and its manifestations and oral cavity. Clinic, diagnosis, treatment; Medical Information Agency - Moscow, 2008;
- Bark K., Burgorf V., Hede N. Diseases of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and lips. Knika. Diagnosis and treatment. Atlas and guide; Medical literature Moscow, 2011;
- Brad W. Neville - Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology (2016).
Where do they come from?
Conventionally, all provoking factors can be divided into the following groups:
- mechanical or thermal damage to tissues;
- dental diseases;
- systemic pathologies.
In other words, the problem may be much more serious than it seems at first glance.
Consequence of dental diseases
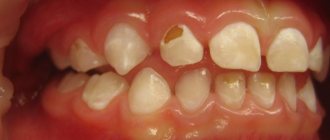
Among the diseases of the oral cavity that cause the appearance of painful white spots are:
- Aphthous stomatitis. Has a relapsing course. A person develops painful aphthae. They can be located on the cheeks, tongue, palate, lips. They always hurt a lot. Heal within 7-10 days. If such an aphtha is damaged by carelessness, the regeneration processes will proceed very slowly and after the end of regeneration, a non-absorbable scar will remain. Until now, scientists have not established why aphthous structures appear. Most researchers believe that reduced immunity is to blame.
- Herpetic stomatitis. Caused by the herpes virus. A huge number of small white erosions appear in the patient’s mouth. Women over the age of thirty are prone to the disease. Aphthae occur on the tongue and on the surface of the floor of the mouth. They do not have clear boundaries. “They drag on” for one to a week and a half. In addition to ulcers, this form of stomatitis causes increased body temperature, enlarged subcervical lymph nodes, and general weakness.
- Necrotizing periadenitis. Another name for this pathology is Setton's aphthae. The disease is difficult to correct. It often takes several years to treat it. First, compactions appear under the mucous membrane. Soon, instead of them, ulcers with protruding edges form. They can be strewn with the surface of the cheeks, tongue, lips. Setton's aphthae are always very painful. They interfere with normal conversation and eating.
- Vincent's ulcerative necrotic stomatitis. Infectious lesion. It is caused by associations of fusobacteria and spirochetes. Painful areas form in the patient's mouth. The condition is aggravated by muscle pain and headaches. To eliminate tumors in the mouth, doctors carry out local etiotropic therapy, use antibiotics and antiprotozoal drugs. It has been noticed that Vincent's disease is more often encountered by men over the age of thirty with reduced immunity and vitamin deficiency.
Causes
The exact cause of the origin of this disease is still in question. Doctors are inclined to several probable versions: an allergic reaction, a viral infection, streptococci and staphylococci, immunodeficiencies and genetic abnormalities. The possibility of the formation of CRAS due to disruption of the digestive tract, liver, and nervous system (which may be due to regular stressful situations), as well as due to hazardous production and the environmental situation in the area of residence, cannot be ruled out.
In allergy sufferers, frequent manifestations of this type of stomatitis are accompanied by migraines, asthma, skin rashes and itching. Patients with chronic colitis, gastritis and helminthic infestations may suffer from recurrent aphthous stomatitis due to the large amount of toxins in the blood.
In any case, a relapse of the disease can be triggered by a weakening of the body’s defenses and a malfunction of the immune system. Prerequisites for this may be previously suffered severe forms of influenza, tonsillitis, chronic intestinal diseases, severe allergic reactions to flowering, food products, prosthetic materials, fillings and much more.
Aphthae of traumatic nature
Ulcers resulting from trauma include:
- Afty Bednar. Happens only to small children. They are traumatic ulcerations. They arise due to the habit of constantly gnawing hard objects, poor hygiene, and gross mechanical irritation of the upper palate. Usually such white areas are covered with a yellowish coating, which can be easily removed.
- Traumatic aphthae. These include ulcers formed due to sudden movements with a toothbrush, carelessly performed dental treatment, rubbing of dentures, exposure to acids, alkalis, and medications. Treatment of such neoplasms does not take much time and is not complicated. The main thing here is to remove the influence of the provoking factor, then the tissues will recover fairly quickly.
Result of common diseases
Some diseases have a systemic effect on the body. This means:
- Tuberculosis. When the lungs are affected, negative symptoms can spread to the mucous membranes of the mouth. This occurs due to the penetration of the pathogen into the oral cavity through damaged epithelium. Then the patient develops ulcers on the cheeks and under the tongue. First, these are always specific tuberculous tubercles, and then aphthae. They grow quite quickly. At the same time, an increase in the amount of plaque on the tongue, weakness, and loss of body weight are recorded.
- Syphilis. Pathology caused by Treponema pallidum. During the incubation period, which lasts about three weeks, aphthae occur. They are round or oval. Their edges are usually raised, swollen, and the color is red. Such damage takes a long time to heal - up to three months. Syphilis erosions are not as painful as tuberculosis ones. After their healing, retracted scars form.
- HIV infection. It has been noticed that every third HIV-infected person has inflamed oral tissues. In this case, therapy must be specific. It is not the dentist who is responsible for its implementation, but the infectious disease specialist. As soon as the patient’s health improves and the immune system is strengthened, the aphthae will disappear on its own.
How to cure
Treatment for damage to the mucous membranes is always selected individually. There is no single regimen that is suitable for every clinical situation. First, the doctor determines the cause of the complication, and only then tells how it can be eliminated. The emphasis is on the area of the affected surface and the features of its localization, the presence of concomitant diseases, and the severity of symptoms.
To stimulate local regenerative processes the following can be used:
- topical agents - gels, solutions, creams, ointments;
- medications administered orally, intravenously or intramuscularly (broad-spectrum antibiotics, painkillers, immunostimulants, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins);
- physiotherapy.
In some cases, it is necessary to carry out professional hygiene, treat identified dental diseases, and replace old prosthetic systems with new ones. If necrotic tissue needs to be removed, the doctor uses anesthetics. They make the intervention painless.
It is very important that a person does not ignore painful areas on the gums. If they appear and do not go away within three to five days, you should definitely consult a dentist. After all, it is possible that the disorder is not associated with stomatitis, but with some serious pathology of the internal organs. In any case, you won’t be able to find out at home.
Of course, it is easier to prevent the development of a dental disorder than to treat it. Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of erosion on the gums come down to following the rules of hygiene, undergoing specialized dental examinations, timely treatment of all diseases, and proper nutrition. People who care about their health encounter gum ulcers much less frequently.
Treatment
Due to the likely allergic nature of this disease, treatment of chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis can take a long time. Identifying an allergen is not so easy, since first it is necessary to take tests for a large number of possible pathogens, and then eliminate it from the patient’s daily life.
Various antihistamines do not treat this type of disease, but only temporarily eliminate some of the symptoms, which is why treatment of CRAS should primarily be aimed at eliminating the cause of stomatitis. If a patient is found to have a helminthic infestation and the body is poisoned with toxins, treatment will consist of completely cleansing the body of parasites and the results of their vital activity.
Before prescribing any medications, the doctor should refer the patient for a complete blood test. In parallel with the tests, local treatment can be used to eliminate painful symptoms in the oral cavity. Aphthae must be regularly treated with antibiotic solutions with anesthetic, as well as wound-healing ointments, gels and oils.
If there is no informative indication in the analyzes of the cause that caused CRAS, it is recommended to prescribe immunomodulatory drugs in complex therapy with vitamins, as well as adherence to a certain diet. It is also recommended to treat chronic diseases of internal organs, nervous system, teeth and gums.