In the practice of dentists, there are often cases when a patient’s tooth is fully formed, but does not erupt. It is called “retained”, and the problem is treated with special methods. Teeth that are formed but “stuck” inside the jaw can cause inflammatory processes: pericoronitis, periodontitis, periostitis, abscess, phlegmon, etc. Treatment is carried out using various methods, from removal to wearing specialized braces. Reduce the risk of impacted tooth Prevention helps, for example, wearing trainers that prepare the jaw for the appearance of new teeth.
What is retention? Why does pathology develop? Symptoms and diagnosis
Retention is considered one of the most common teething anomalies. Most often, problems arise with the lower and upper “wisdom teeth”, which grow incorrectly. They are usually encountered by adults. In children, a common impacted tooth is the canine of the upper jaw. The second premolars of the mandible often present unpleasant surprises.
Symptoms of unerupted teeth vary by owner. The problem may not manifest itself at all, or it may cause constant visits to the dentist. The variety of symptoms and their absence is due to the fact that the incorrect position of a tooth or its incomplete eruption is an almost natural phenomenon for humans. Approximately 35-45% of “wisdom eights” in adults are impacted teeth . Difficulties begin to arise when such a molar or premolar causes irritation of the soft tissue around it. Based on indirect signs - pain or inflammation - the doctor identifies the “wrong” tooth.
Semi-retinated teeth are visible immediately at the first examination: they partially grow, but not completely. Such partially erupted molars and premolars cause many more problems: being partially located in the soft tissues, they almost always cause inflammation. There is no need to specifically diagnose them: the doctor almost always finds such teeth during a routine examination.
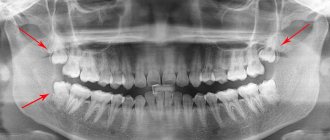
Finding completely impacted teeth is a real quest. They may not be visible at all, because they are located under the existing elements of the dentition. In this case, there is only one diagnostic option: you need to take a full picture of the jaw, which will clearly show the whole picture. Below in the picture is a selection of examples. Impacted teeth are marked in red or with arrows.
Examples of impacted teeth on x-ray
What complications do impacted teeth cause and why do they need to be “extracted”?
It is difficult for the patient to immediately understand what danger “hidden” teeth can pose, but it is really serious.
Semi-retinated teeth cause inflammation of the “hood” with which they are covered and adjacent tissues, and this provokes purulent inflammation.
Fully impacted teeth that lie in the jaw can behave like a foreign body; they put pressure on neighboring teeth, causing their displacement and a number of other problems.
In this case, the patient experiences pain and fever in case of inflammation, a feeling of pressure and discomfort in the jaw, neuralgia or numbness of part of the face.
If we list the diseases that can result from impacted teeth, it will become clear that this is a real “time bomb” that can detonate at any moment.
What diseases can be caused by an impacted tooth:
- periodontal cyst,
- caries of neighboring teeth and their roots,
- pulpitis,
- pericoronitis,
- periostitis,
- periodontitis,
- purulent lymphadenitis,
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve,
- odontogenic sinusitis,
- abscess,
- phlegmon,
- resorption (resorption) of the roots of adjacent teeth,
- bad habits: mouth breathing, infantile swallowing, inserting the tongue into a dental defect,
- problems with biting food,
- malocclusion, displacement of interdental contacts, crowding of teeth.
Types of dental retention
There are many classifications of dental retention. One of the most popular methods of division is by degree of eruption. Thus, there are semi-impacted teeth , which are partially visible in the gum, and completely hidden - located under the gum or bone tissue. The latter are not available for palpation. If the impacted tooth is located in the gum tissue, the diagnosis will say “with tissue immersion,” but if it is located in the bone, “with bone immersion.”
Another classification method takes into account the position of the molar, canine or premolar:
- vertical,
- horizontal,
- corner.
Horizontal teeth can also be transverse, sagittal or oblique, and angular teeth can be mesial, distal, lingual or buccal angular. Rarely, but still there are reverse impacted teeth - these are elements that grow “upside down”, that is, their crown is directed towards the jaw.
Impacted and dystopic teeth
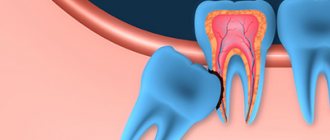
Impacted tooth
- this is a tooth that has already fully formed, but cannot fully erupt, since it is partially or completely covered by either the gums, the jaw bone, or another tooth located nearby. As a result, such a tooth gets stuck in the jaw, the gums become swollen and inflamed, causing severe pain.
This is one of the most common dental anomalies. The most common impacted “wisdom teeth” are the eights in the lower jaw. In fact, this is why wisdom teeth are most often removed. While they are in their rudimentary, “dormant” state, they do not cause pain or discomfort, but if they begin to erupt incorrectly, they can not only provoke inflammation, but also damage other teeth.
In this regard, dentists recommend removing the impacted tooth immediately after it begins to cut, without waiting or delaying. Retention of a wisdom tooth before age 25 is not considered an anomaly.
, but normally after 25 these teeth still erupt. Sometimes they are removed at an early age to prevent them from erupting in the future.
Often, an impacted tooth is also called a dystopic tooth, in which it is displaced inside the gum and grows into the cheek, palate or gum, and not as it should.
Causes of impacted teeth. Is it possible to prevent retention?
The most popular reason for impacted teeth is genetic predisposition. Moreover, what is inherited is not the desire of the canines and molars to grow “some into the forest, some for firewood,” but the structure of the jaw. It can be narrow, which is why there is simply not enough space for all the necessary elements of the dentition. But there are other reasons:
- malocclusion, which has formed due to harmful myofunctional habits or mechanical injuries;
- early loss of baby teeth, due to which permanent teeth do not have guidelines for growth;
- “extra” teeth – atavism, called polyodontia;
- initially diseased tooth germs.
In some cases, retention problems can be prevented. Some orthodontists and pediatric dentists recommend the use of trainers to develop the dental arch and give growing canines and molars a guideline for eruption. If the problems are hereditary, only timely treatment will help.
You can read more about trainers in the article: Trainers for straightening teeth: description, varieties, tips for use
Main reasons for retention
- genetic predisposition;
- artificial feeding of a child using bottles and pacifiers;
- long-term use of pacifiers in childhood;
- too dense gum tissue;
- past viral and infectious diseases;
- the presence of so-called “supernumerary” dental units next to impacted ones;
- abnormal location of buds in the bone;
- delay in the development of teeth - late change of milk teeth to permanent ones;
- jaw injuries.
With retention, the patient experiences swelling and redness of the gums, pain in the eruption area, which intensifies when pressing on the area. The temperature may also rise, general malaise and weakness may occur.
Why are impacted teeth dangerous?
Despite the fact that sometimes unerupted teeth do not interfere with a person in any way, you need to understand that every impacted tooth is a potential cause of serious and unpleasant diseases. They lead to the following problems:
- inflammatory processes;
- non-healing ulcers on the gums and cheeks;
- constant appearance of caries, pulpitis;
- the appearance of gum pockets, which can cause periodontitis;
- infectious processes, often leading to osteomyelitis (purulent infection of the jaws).
The absence of symptoms is almost always the result of a happy accident, and not a normal development of events. Therefore, with such a diagnosis, it is very important to constantly see a doctor.
Symptoms
Due to continuous trauma to the mucous membrane, swelling may occur. The crown of an unerupted tooth often leads to inflammation of the adjacent soft tissue of the gums, resulting in the development of pericoronitis or gingivitis. In the place where impacted teeth come into contact with normal teeth, pulpitis, cervical caries, and chronic apical periodontitis can develop. Irritation of the nerve fibers may also occur, resulting in pain, paresthesia, and trigeminal neuritis. In some cases, more dangerous complications develop, accompanied by increased body temperature and intoxication:
- Purulent periostitis;
- Pericystic osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- Abscess;
- Purulent sinusitis;
- Phlegmon.
The course of any type of retention is often asymptomatic and is determined by chance as a result of preventive diagnostics.
Principles of treatment: is it possible to avoid surgery?
Many patients are sure that an impacted dystopic tooth is necessarily a reason for surgical intervention. But dentists try not to cut without a good reason. Therefore, if your extra teeth are not inflamed and do not interfere with your life, it is quite possible to avoid surgery. The doctor may also prescribe the installation of hard metal braces, which will “pull” the partially erupted tooth from the gum tissue and fit it into the dentition.
Typically treatment proceeds as follows:
- A diagnosis is carried out, which includes a visual examination and the creation of a panoramic image of the jaw.
- The doctor examines the results and decides whether the tooth needs to be removed. If yes, then surgery is prescribed.
- If the dentist sees other ways to solve the problem, he prefers them. First of all, the installation of a bracket system is considered. To do this, it is necessary that there is a place in the dentition where a new element could be placed.
- If braces are not required or cannot yet be placed, the doctor will try to help the tooth erupt. For this purpose, medications and surgery are used. Teething assistance is often used when the wisdom tooth is partially left under the gum, but is positioned correctly.
Modern doctors have many treatment methods in their arsenal, but everything completely depends on the specific case.
Stages of treatment for an impacted tooth
How is surgery performed to expose the crown of an impacted tooth?
- As a preliminary stage, preparation for the operation is carried out. The patient undergoes professional hygiene and sanitation to reduce the amount of infection in the oral cavity and speed up postoperative healing.
- The operation to expose an impacted tooth is performed under local infiltration anesthesia and is considered a fairly serious surgical intervention.
The operation to expose the crown of an impacted tooth and install an orthodontic element on it can be carried out according to 2 schemes:
I Delayed bracket installation.
- The mucous membrane in the projection of the crown of the impacted tooth is excised, the entire crown of the tooth is exposed, and a special tampon is installed in the wound.
- After 2-3 days, a button or bracket is installed on the crown of the exposed tooth, which is tied to the orthodontic arch and traction begins.
II Bracket installation during surgery
- The dentist-surgeon peels off a small mucoperiosteal flap and exposes part of the crown of the impacted tooth, onto which the locking element is immediately fixed.
- The bracket is tied to an orthodontic arch or additional devices.
- After installing the orthodontic element, the flap of tissue is placed in place and the wound is sutured.
The disadvantage of this method is that in this case, repeated surgical intervention is possible if the bracket on the tooth comes off.
After surgery, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and antiseptic rinses, if necessary, to speed up healing. Light, non-traumatic food is recommended.
When is it necessary to remove an impacted tooth? Why remove impacted teeth?
Even an experienced surgeon will say that removing an impacted dystopic tooth is a serious and complex operation that should not be performed unnecessarily. Therefore, it is indicated in the following cases:
- inflammation of the soft tissues (pericoronitis) or jaw (osteomyelitis);
- the tooth is located in a follicular cyst or grows horizontally;
- a cyst or benign formation is diagnosed;
- pus or bacterial infection is detected.
Removal technique
Removal should be carried out by an experienced doctor who knows the specifics of working with impacted teeth. The main problem here is their inconvenient location, so it’s difficult for a beginner to cope with the problem. Removal takes place in several stages:
- Performing local anesthesia (in case of complex tooth position, general anesthesia can be used).
- An incision in the mucous membrane.
- Drilling into bone tissue to create a hole.
- Tooth extraction.
- Removal of tooth or bone fragments.
- Treatment of the wound.
- Stitching.
- Sutures are removed one week after surgery.
Often, the doctor has to first crush and then remove the tooth so as not to damage the adjacent molars and mucous membrane.
Contraindications
The operation will have to be postponed for the following reasons:
- the patient's serious condition due to any kind of illness;
- hypertensive crisis;
- nervous problems or mental disorders;
- viral infections;
- blood diseases;
- serious heart problems.
For women, this operation is not performed 2-3 days before the start of menstruation and after an abortion (at least 2 weeks must pass).
What complications occur after removal of impacted teeth? How to avoid them
Any operation can cause complications, and surgical treatment of an impacted tooth is no exception. Most often, the consequences manifest themselves as severe bleeding, pain, swelling of the gums or cheeks. If nerves are affected, increased sensitivity or insensitivity of the mouth and face may occur. Due to the incorrect actions of doctors, the patient faces a dislocation of the jaw or even a fracture.
The patient can avoid problems after surgery if he goes to a trusted clinic (excluding the human factor) and carefully takes care of the wound that appears in the mouth. Immediately after surgery, the patient should:
- refuse food for 3-4 hours;
- do not smoke for at least 3 hours;
- Avoid alcohol until the stitches are removed.
It is important to come back for a follow-up appointment with a surgeon or therapist. It is necessary to monitor the bleeding: if it does not stop for too long or painkillers do not work, you should contact the dentist immediately. Timely help will help avoid unpleasant consequences.
Postoperative care after removal of an impacted tooth
The doctor is obliged to advise the patient on how to properly care for the wound on the gum. Since removing an impacted tooth is a full-fledged operation, it is imperative to follow the rules of care. The patient needs:
- reduce physical activity to a minimum for 2-3 days after surgery;
- refuse hot and cold foods and liquids;
- change your toothbrush to a soft one;
- take only a warm shower or bath, do not visit baths and saunas;
- take all medications prescribed by your doctor (antibacterial therapy is usually prescribed).
It is important not to rinse your mouth so as not to disrupt the healing. You can make neat baths (liquid or herbal decoction is taken into the mouth, held without rinsing and spitting), but coordinate all procedures with your doctor.
Recommendations after removal of an impacted wisdom tooth
The consequences of removing an impacted wisdom tooth may not be positive, but negative, if you do not follow the doctor’s instructions in the postoperative period. This procedure, like any other surgical intervention, does not go away without leaving a trace, so it takes time for complete healing.
As a rule, in the first days after treatment, the patient may experience swelling and pain, and the temperature and blood pressure may also increase. In addition, temporary articulation problems and difficulty eating are common after surgery.
What to do after removing an impacted wisdom tooth:
- do not remove the gauze pad for half an hour after surgery;
- do not eat or drink in the first three hours after tooth extraction;
- apply cold compresses in the first one or two days;
- do not eat hard, spicy or hot foods, avoid physical activity, and do not visit the sauna or swimming pool during the healing period.
After removing an impacted wisdom tooth, the doctor may prescribe the patient to take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as vitamin complexes. Do not forget that the rehabilitation process lasts about two weeks: during this period it is necessary to make at least one preventative visit to the dentist.
Conservative methods of treating retention
If the tooth is located correctly in the gum and there is minimal interference with eruption, doctors try not to remove it, but to return it to its intended place by nature. Different methods are used for this:
- laser correction;
- current pulses;
- gum massage;
- electrophoresis;
- some medicines.
All these treatment methods are aimed at making the tooth crown get rid of the gum hood on its own. They partially imitate the natural process of eruption of canines and molars. But the availability of such treatment depends on the situation.
How to stimulate tooth eruption
Stimulating the eruption of an impacted tooth is also one of the ways to treat the problem. The doctor prescribes specialized procedures if he sees that a molar or canine is positioned correctly, but its roots have not yet formed. Then the orthodontist recommends:
- Carrying out vacuum massage with special equipment;
- light finger massage at the site of eruption;
- electrical stimulation;
- exposure to ultrasound, laser, vibrating vacuum devices, etc.
Such methods are aimed at restoring blood circulation and accelerating metabolic processes in the gums.
Removal steps
The procedure can be divided into three stages:
- preparatory;
- The operation itself;
- After surgery.
Preparatory stage.
At this stage, the doctor visually examines the patient's oral cavity. Then a computed tomography is done to look at the length and shape of the roots, the depth of the tooth, etc.
Surgery
Complex wisdom tooth removal is divided into several stages. Let's consider a generalized operation scheme:
- A painkiller is given. To do this, a needle is inserted into the lower jaw to the nerve bundle so that the patient does not feel pain. Lips, chin, tongue are numbed. If sensitivity does not disappear, an additional injection is given. After anesthesia, the course of a complex extraction procedure depends on the location of the tooth.
- An incision is made with a scalpel.
- The tooth is sawed down to make it easier to remove.
- Take out the crown and roots.
- The wound is treated and sutured.
This completes the surgical stage.
Postoperative stage
This stage is very important, its duration is 7 – 10 days. During this period, the surgical wound heals, and a clot first forms in the hole and then resolves. Patients must follow our doctor's instructions exactly to avoid post-operative complications.
Tooth extraction: how long does the procedure take?
With a simple type of extraction, the procedure is carried out in 10 - 20 minutes. The process of complex removal lasts from 30 minutes or longer, depending on the specifics of the operation. For example, removing a horizontal tooth can take up to 2 hours or more. At the same time, sometimes additional preparatory procedures are necessary, which also take time.
After tooth extraction in the lower jaw antibiotics to prevent the entry and spread of infection. Such complex manipulations are contraindicated for pregnant and nursing mothers. Painkillers are prescribed to reduce pain after the procedure.
For complex removal, the patient is asked to come back again in five days or earlier if a fever appears. If the tooth has come out halfway (semi-retinated tooth), removal is carried out in the same way, but it is easier to pull it out, since part of the molar is on the surface.
Conclusions. Expert advice
An impacted tooth is a molar, premolar or incisor that is hidden in bone or gum tissue. If part of the tooth is visible, it is called semi-impacted. Many children and about 40% of adults face this problem when they lose their eights. The appearance of incorrectly positioned teeth itself may go unnoticed – the symptoms are associated with related diseases. Thus, caries in a tooth hidden in the gum almost always causes inflammation of nearby tissues.
It is believed that impacted dystopic teeth are a hereditary problem. But they can appear due to an incorrect bite. Retention can be improved using surgical intervention or conservative methods: massage, electrophoresis, etc. Some dentists recommend wearing trainers, which help develop the dental arch and reduce the risk of improper eruption.
Almost always, the orthodontist tries to return the tooth to the dentition using braces and other methods of influence. If this does not work, the doctor removes the foreign element. The operation is complex, so it is important to contact a specialist. Success largely depends not only on the doctor, but also on the patient: failure to comply with the rules of postoperative care leads to complications.
What to do if you suspect you have a similar problem? See a doctor and be constantly monitored by him. The dentist will prescribe treatment and help prevent complications.
Prices for surgical services at the clinic
| Service | Price |
| Tooth extraction | |
| Removal of a tooth | RUB 3,900 |
| Removal of a tooth of III degree of mobility | 2,000 rub. |
| Wisdom tooth removal | 5,500 rub. |
| Simple tooth extraction | RUB 3,900 |
| Surgery to remove an impacted tooth | 7,500 rub. |
| Other | |
| Bone grafting | 25,000 rub. |
| Sinus lift closed | RUB 18,900 |
| Open sinus lift | 26,500 rub. |
| Excision of the tooth hood | 2,800 rub. |
| Resection of a single-root tooth | 9,500 rub. |
| Resection of a multi-rooted tooth | 7,000 rub. |
| Alveolar ridge correction | RUB 5,900 |
| Opening a periodontal abscess | RUB 3,800 |
| Lip frenuloplasty | 5,500 rub. |
| Plastic frenulum of the tongue | RUB 5,900 |
| Socket curettage | 800 rub. |
| Treatment of alveolitis | 2,500 rub. |
| Dental implantation | |
| Adin implant installation | RUB 21,500 |
| OSSTEM implant installation | RUB 26,700 |
| Installation of the Nobel Replace Select implant | 40,000 rub. |
| Ankylos implant installation | 41,000 rub. |
| Installation of Hi-Tech implant | RUB 29,500 |
| Implant installation Mis | 32,000 rub. |
Removing an impacted (unerupted) wisdom tooth is a complex operation that is performed by an experienced dental surgeon with mandatory anesthesia.
Sign up Duration 15-60 minutes Cost from 840 rub. All prices
One of the common pathologies in dentistry is an impacted tooth. An impacted tooth is a tooth that, for some reason, cannot erupt on its own and take its place in the dentition. Removal of an impacted tooth is the most likely outcome of having such a tooth in the oral cavity. Very often, upper or lower “wisdom teeth” or, as they are also called, “eight teeth,” grow in this way.
Removing an impacted wisdom tooth is a rather complex operation that is performed only by an experienced dental surgeon with mandatory anesthesia. An impacted wisdom tooth can cause malocclusion, serious misalignment of teeth in a row, and can also negate efforts to straighten and correct teeth. Additionally, if this tooth becomes infected, it can become a source of infection for other teeth and lead to serious problems. Removal of an impacted tooth is carried out in EXPERT dentistry painlessly and without complications for patients!