- home
- Articles
- Causes of gum inflammation and treatment
Complaints of increased sensitivity and bleeding gums are quite common among patients in dental clinics. At the initial stage, the patient feels slight discomfort, but if measures are not taken in time, the gums begin to bleed and hurt, and the teeth begin to become loose. In this case, you need to visit a doctor, determine the causes of the inflammatory process and get advice on further treatment.
What is gum disease
This is a lesion of periodontal tissues, that is, the tissues surrounding the tooth. This general definition combines deep and superficial inflammatory processes.
Damage to soft tissue occurs gradually. At the initial stage, only the marginal part of the gum is inflamed. If the inflammation is not cured at this stage, the infection penetrates deeper, the deeper layers of the periodontium are affected, and the disease becomes severe.
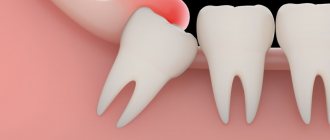
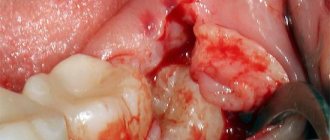
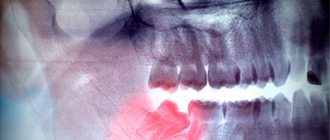
When should a tooth be removed?
Direct indications for wisdom tooth removal are the following pathologies and conditions.
- There is no place in the dentition for a number eight.
- Dystopic tooth (molar occupies an anatomically incorrect position).
- The appearance of wisdom teeth threatens the molars in front.
- Severe forms of caries that destroy the tooth.
- The third degree of mobility of the figure eight.
- Upcoming installation of braces.
If removal is not carried out, the development of complications is inevitable. The number eight will destroy adjacent teeth and provoke the development of pulpitis, periodontitis, and extensive caries. Eventually it will fall out on its own, but at too great a cost to the patient.
There is no need to be afraid of wisdom tooth removal. Depending on the complexity of the problem, third molar extraction will last from 20 minutes to 2 hours. The operation is performed using local anesthesia or sedation, which ensures that the procedure is painless.
Why does inflammation occur?
Plaque is the main cause of the first stage of gum disease, gingivitis. It contains bacteria that irritate soft tissues, causing inflammation and redness. At the initial stage, this does not cause severe pain, but if the inflammation is not treated, it can progress and develop into periodontitis, a more severe stage of the disease that can cause tooth loss.
Injuries - brushing your teeth too intensely or aggressively can injure the soft tissue, causing inflammation and pain.
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy or puberty make gums more sensitive and prone to developing gingivitis.
Systemic diseases change the composition of saliva, disrupt the composition of the blood, metabolism, and therefore can affect the condition of the gums. These include cancer, HIV, and diabetes.
Medicines can affect oral health because some of them reduce the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on teeth and gums. Some medications cause abnormal growth of gum tissue.
Bad habits such as smoking make it difficult for soft gums to heal themselves.
Poor oral hygiene , for example if a person brushes their teeth irregularly or does not floss.
Heredity - a family history of dental diseases - is a factor contributing to the development of periodontitis.
Harmful effects of microorganisms . Various microorganisms form the natural microflora of the oral cavity. However, when the immune system is weakened or due to poor nutrition, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply in the mouth, which negatively affects the soft tissues of the mucous membrane.
Where can the pain go?
Quite often, the process of growth of eights is accompanied by uncharacteristic symptoms. Moreover, some of them are due to the growth of the molar itself, and the other part indicates the development of complications. Let's take a closer look - can a wisdom tooth give into...?
- Head
- in case of complicated teething it can. - Eye
– with complicated eruption of the upper molars and the development of an abscess, it can. - Tongue
- a symptom indicates the presence of purulent inflammation of the soft tissues closer to the tongue. - Ear
– indicates the development of inflammation, pulpitis or dental cyst. - Throat
- most likely we are talking about pulpitis. - Jaw
- a symptom characteristic of complicated teething and inflammation. - The neck
is unlikely, unless we are talking about the spread of infection and inflammation of the lymph nodes. - Temple
– Clicking and pain in the temple may be present due to tension in the temporomandibular joint, which occurs from constant pain. - The teeth are nearby
- of course, because the figure eight can put pressure on them.
Important! The above list is a serious signal to contact a dentist. Don't delay your visit to the clinic!
Types, symptoms and treatment of gum diseases
The initial stage of the disease usually takes place in the form of gingivitis. Untreated inflammatory processes progress and lead to the development of more serious pathologies, such as periodontitis.
| Disease/Symptoms | Gingivitis | Periodontitis | Periodontal disease | Periostitis (flux) |
| Gum color | Bright red/purple | Bright or dark red | Close to natural | Red (in the area of the diseased tooth) |
| What happens to the gums | Inflamed, swollen. Growth of gum tissue (in pregnant women) | Inflammation, swelling, pus from under the gums, exposure of the necks of the teeth | Gum recession with virtually no signs of inflammation | Painful lump with a purulent tip (abscess) |
| Painful sensations | Moderate to strong, depends on shape | Strong during exacerbation, weak during chronic course | No, but there is an itch | Severe pain, radiates to other parts of the jaw, neck, head |
| Bleeding while brushing teeth | Eat | Eat | No | No |
| Unpleasant smell | Eat | Eat | No | Eat |
| Other symptoms | Increased salivation, gray-green film on the gums (in advanced forms) | High temperature, intoxication, loosening of teeth, interdental spaces | No obvious signs | Swelling of the face, neck, ear, lymph nodes, fever up to 38-39°C, intoxication |
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a form of gum disease that causes inflammation of the marginal tissue of the gums. In mild cases of gingivitis there may be no discomfort or visible symptoms, but in more severe cases the symptoms are more severe.
How is gingivitis treated?
Treatment begins with diagnosis. To do this, a specialist conducts an instrumental and visual inspection. Subsequently, the optimal treatment plan is selected taking into account the clinical picture of the development of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
In standard situations, treatment of gingivitis occurs in stages:
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Treatment of caries (if necessary).
- In severe clinical situations, hormonal therapy or surgery may be indicated (in the presence of hypertrophic gingivitis).
Read more about the cost of treatment for gingivitis.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more serious inflammation of the gums, which damages not only the soft, but also the hard periodontal tissues that support the teeth. Their destruction can cause loosening and loss of teeth.
Non-surgical treatment methods are used if periodontitis is not in advanced form. This treatment involves less invasive procedures:
- Hygienic teeth cleaning. Eliminates bacteria and hard deposits from the surface of teeth. The procedure is carried out using mechanical tools, sandblasting, and an ultrasonic device.
- Curettage. During the procedure, deposits under the gums and on the tooth roots are removed, and their surfaces are polished to prevent the re-accumulation of soft/hard deposits.
- Local antibiotics in gels are injected into periodontal pockets after cleaning. However, oral antibiotics may be required to completely eliminate the microorganisms causing the infection.
Surgery. If the patient has advanced periodontitis, more invasive procedures may be required:
- Flap surgery. The dentist cuts the gum to lift the edge of the gum, thereby exposing the roots of the teeth. Thanks to this, he can efficiently remove plaque and, if necessary, build up bone tissue.
- Transplantation (transplantation) of soft tissues. If gum tissue is lost, it may need to be strengthened by grafting a small amount of tissue from the surface of the mouth (palate). This will help stop tissue recession and restore lost tissue.
- Osteoplasty. This procedure is performed when the bone around the root is destroyed. A bone graft preserves the tooth by holding it in place. In addition, it serves as the basis for the restoration of natural bone.
- Regeneration of destroyed tissues. A special gel is applied to the root of the diseased tooth. This gel contains proteins that stimulate the restoration of destroyed bone and connective tissue.
To increase the chances of successful treatment of periodontal disease, and to reduce the likelihood of developing it, it is recommended that you brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss every day, and it is also important to see your dentist regularly.
Learn more about the types of periodontitis.
Periodontitis and Periodontitis: what is the difference?
Periodontitis is a pathological inflammatory process in which harmful microorganisms penetrate the periodontium through the root canals. Unlike periodontitis, which affects the gums, periodontitis develops against the background of caries, pulpitis, or tooth trauma. That is, periodontitis is actually a disease of the teeth, not the gums, and only subsequently can the pathology spread to the soft tissues in the form of a purulent lump or fistula.
The first symptoms are a feeling of discomfort and tension in and around the affected tooth. When suppuration occurs, the pain becomes throbbing, the tooth visually appears higher than the rest. In severe cases, the lymph nodes become enlarged and there is malaise or fever.
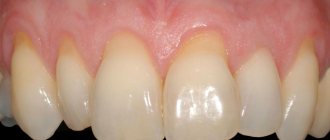
Periodontal disease
The disease is very similar to periodontitis. It is essentially a form of periodontitis. The key differences are:
- No obvious signs.
- No bleeding as opposed to periodontitis.
- Itchy gums (as opposed to periodontitis, where there is increased sensitivity).
Reasons for development:
- malocclusion;
- metabolic disorders or hormonal changes.
The choice of treatment method depends on the main cause of the disease. The dentist’s first task is to eliminate the root cause of the pathology.
Prevention of periodontal disease is: normalization of hormonal levels, vitamins, careful hygiene, gum massage.
Learn more about the stages of periodontal disease and the cost of treatment.
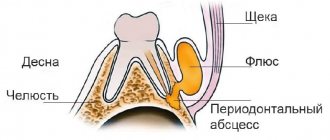
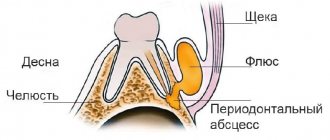
Periostitis (Flux)
Periostitis is an inflammatory disease that occurs due to infection from the periodontium into the area between the bone and the periosteum. Occurs as a complication of periodontitis.
Within a few hours, severe swelling of the face and neck may occur. Associated symptoms are unbearable pain and tumor formation. The pus is located in a sac, its location is also very individual, most often it appears in the form of a protruding lump.
Periostitis can occur even after extraction (pulling out) of a tooth. In addition, it occurs as a result of severe sore throat, colds, and also after injury to the teeth, soft tissues or jaw.
During surgical treatment, the pus must be drained, and the periodontal pocket must be cleaned and disinfected.
How and with what to relieve inflammation
⛔ Only a doctor can prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy. There is no point in trying to heal yourself. If you can't see a dentist right away, here are some effective home remedies to reduce pain and inflammation before you can see a doctor:
- Rinse with salt water. Reduces the number of bacteria, which means it slows down damage to the oral cavity. At least 2 times a day until the swelling subsides.
- Cold compress. Wrap the ice pack in a clean cloth and apply it to the sore area. This will prevent swelling or at least reduce it.
- Herbal poultice. Some herbs and spices can be used as home remedies to relieve inflammation and pain. The analgesic effect is exerted by: clove and spilanthes powder; anti-inflammatory - turmeric. Apply a paste of herbal powder and water to your gums, wait until the pain subsides, and rinse.
- Tea bags. Brew a tea bag in boiling water (5 minutes). Cool, apply the cool bag to the sore gums for at least 5 minutes. Simple black or green tea or anti-inflammatory herbs (chamomile, ginger) are better suited.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers. Regular pain relievers and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as aspirin, acetaminophen, ibuprofen can help in a pinch. Follow the directions on the bottle labels to determine dosage.
Are folk remedies effective? Dentists do not recommend treating gum disease at home. If an oral infection is suspected, the patient is advised to contact a dentist and immediately visit an emergency dental care office. Painkillers in such cases are unnecessary and ineffective. Home remedies won't help either.
Preventive measures
To prevent a negative reaction after the installation of dentures, you should follow the strict instructions and recommendations of the dentist. It is necessary to maintain oral hygiene to reduce the risk of inflammation.
To do this, the specialist recommends adhering to the following prevention methods:
- Removable structures must be removed at night. Thus, the gums “rest.” This clause does not apply during the first week of installation.
- You should periodically massage your gums. Using your finger will speed up blood flow and relieve tension from soft tissues.
- When brushing your teeth daily to remove plaque, you need to pay attention to the interdental space and tongue. It is necessary to clean out food debris in the cracks, otherwise an inflammatory process will develop over time. A brush with fine soft bristles and a irrigator should be used to prevent stones. Cleaning time is at least 2 minutes.
- When eating food, you need to distribute the load evenly on both sides of the jaw.
- Rinse after every meal. Herbal infusions and purified water can be used.
- Avoid foods such as chewing gum, nuts, crackers, gummy candies, and hard fruits.
- If indicated, complete absence of dentition, bone tissue atrophy or anatomical features of the jaw, use fixing gels, creams, powders.
Following these dental care rules will allow your gums to quickly adapt to the structure. If cracks, breaks, or loose fit of the plates to the gums appear, you should contact a professional.
What are the dangers of gum disease?
Untreated inflammation is fraught with penetration of infection into the deeper layers of the periodontium.
Periodontal pockets create a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria, which causes their abnormal expansion and receding gums. Harmful microorganisms also penetrate hard dental tissues, corroding them. These processes can lead to exposed roots, loosening or tooth loss. In the future, the infection can cause tonsillitis, bronchitis, pharyngitis, adenoiditis, and spreads hematogenously throughout the body.