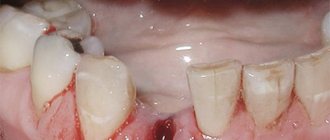
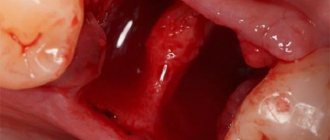
Pain after tooth extraction: how long does it last, and is it normal? These and other questions concern patients after dental procedures. Pain syndrome is normal in several cases: early postoperative period, complex removal, simultaneous implantation.
Normally, pain can persist from several days to a week, and its intensity should decrease. The appearance of symptoms such as increased pain, swelling, inflammation, bleeding or the appearance of purulent exudate is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
How does a postoperative wound heal?
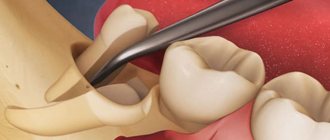
How long the area hurts after tooth extraction depends on many factors. The healing process after tooth extraction is a complex and lengthy process. Removal occurs with a rupture of the dentofacial connection, namely the connection with the alveolar process and the jaw bone.
The recovery process lasts about two to three weeks. Much depends on the surgical protocol, the clinical situation and the characteristics of the body.
Main stages:
- Formation of a blood clot. Forms 1.5-3 hours after extraction. The function of the clot is to protect the wound area from pathogens and secondary infection.
- Active tissue regeneration. The affected mucous membranes are restored, after 3-4 days swelling and inflammation decrease.
- Formation of granulation tissue. After 4-6 days, granulation tissue forms on top of the clot - the basis of a new epithelial layer.
- Granulation proliferation. After a week, the granulation tissue grows, completely covering the socket.
Already on the eighth to tenth day, the wound is completely healed and by the end of the second week a new epithelial layer is formed.
After two weeks, bone tissue begins to renew. After six months, the bone tissue in the area of removal becomes completely healthy.
On the lower jaw
Standard and non-standard complications after pulling out figure eights on the lower jaw occur more often than on the upper jaw. The lower jaw has a number of features, and there are many obstacles in the area where the wisdom teeth are located.
Nerve damage
The mandibular and lingual nerves are at risk of injury, since they pass close to the wisdom tooth. Such damage causes paresthesia, which is manifested by impaired sensitivity:
- sensory;
- painful;
- taste;
- temperature
In the most severe cases, nerve damage negatively affects vision, hearing, and also provokes paralysis. Patients compare paresthesia with numbness of the jaw in the area of the removed molar. In most cases, this complication disappears on its own within a few days, but sometimes additional drug treatment is required.
Alveolar ridge fracture
A fracture of the alveolar process of the lower jaw occurs when the dentist does not grip the jaw correctly and applies more force than necessary. This is an unlikely complication as the mandible is quite strong. Treatment is carried out under conduction anesthesia and involves repositioning and fixing the fragment in the correct position.
Jaw damage
snapshot of the jaw
Jaw injuries (dislocations and even fractures) also often occur due to the fault of the doctor if the tooth is pulled out too intensely or abruptly. During surgery, it is necessary to remove a significant amount of lower jaw bone to provide access to the problematic molar. Because of this, the sections of the jaw are weakened, which increases the risk of fracture if excessive force is applied. A crack or fracture does not always appear immediately. It happens that the patient notices the first symptoms in the form of pain, swelling, and impaired mobility already at home. Sometimes it takes a week before they appear. Statistics show that jaw injuries during medical procedures account for no more than 0.2% of all jaw fractures.
Soft tissue injuries
By pulling out a molar, the doctor can injure the soft tissues surrounding the molar. We are talking not only about the gums, but also about the cheek, tongue, lips. Injuries are caused by dental instruments (scalpel, drill, forceps). The lip is also often injured by the thread used to suture the gums. This happens due to the carelessness of the doctor or the restlessness of the patient. To avoid complications, you need to sit quietly in the dental chair and not distract the doctor.
Causes of pain
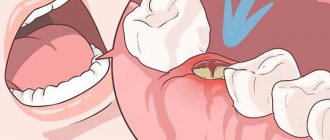
The occurrence of pain after tooth extraction is associated with damage to nerve endings, vascular structures and soft tissues. The peak intensity of pain occurs in the first hours after the cessation of anesthesia. The symptom persists for about 12 hours.
In case of incisions in the gums or damage to the bone tissue, as well as after implantation after removal, toothache may persist for 2-3 days. Pain syndrome also occurs in the case of displacement of the dentition towards the formed void. Therefore, doctors recommend prosthetics as soon as possible after extraction.
Additional physiotherapy treatment (click to expand)
Physiotherapeutic treatment is an important addition to drug therapy; with the help of physiotherapy, the intensity of inflammation can be significantly reduced and healing time can be accelerated. For alveolitis, the following techniques are used:
- UV therapy - the hole is irradiated with short-wave ultraviolet light, which kills pathogenic microorganisms and reduces the level of inflammation.
- SMV therapy is a method of treatment with an electromagnetic field, based on the effect of centimeter waves on the area of inflammation. The procedure helps improve blood circulation and metabolism, due to which toxic substances are removed from tissues faster and regeneration processes are accelerated. SMV therapy also has an analgesic effect.
- UHF therapy – the body is exposed to a high-frequency electromagnetic field. For alveolitis, UHF therapy is used if the patient's regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
- Electrophoresis – medications are injected into inflamed tissue using electrical impulses. For post-extraction alveolitis, electrophoresis is used to reduce pain. For this purpose, solutions of novocaine, lidocaine, trimecaine are used.
- Fluctuarization is a treatment technique with pulsed currents of a sinusoidal shape with a low frequency. As a result of the procedure, blood circulation and lymph flow improves, swelling resolves, and the level of inflammation decreases.
- Laser therapy - the hole is exposed to infrared laser radiation, which has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces swelling and redness of soft tissues, and accelerates healing.
Pain during difficult removal
The duration of pain after complex extraction (wisdom teeth, impacted or dystopic incisors) is associated with damage to a larger tissue area. Often such an operation involves making an incision in the gum, sawing out the roots, extracting tooth fragments, and draining an abscess, which increases the scope of the surgical intervention. If your ear hurts after wisdom tooth removal, this may indicate nerve damage.
In some cases, patients complain of persistent discomfort and pain for up to a week. Clinical manifestations such as swelling, swelling of the gums, enlarged submandibular lymph nodes, fever, and malaise are also common.
Contraindications to extraction
There are situations when wisdom teeth cannot be removed, at least not immediately. This can cause complications regardless of the condition of the dental crown and the presence of infection.
- There is an acute infectious disease not related to dentistry, for example, influenza, meningitis, pneumonia.
- There is any pathology of the heart or blood vessels.
- A heart attack suffered by the patient no earlier than six months before the proposed extraction.
- The likelihood of a stroke or ischemic attack.
- Mental illnesses in the acute stage.
Even for tooth extraction there are a number of contraindications, for example, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, high blood pressure
By the way. For diseases in which blood clotting is impaired, the third molar extraction operation can be performed, but in the hematology department of the hospital, so that if uncontrolled bleeding occurs, it can be stopped in time.
Types of pain
The nature and type of pain depends on the type and surgical intervention, the duration of the operation, and the complexity of the clinical process. Clinicians distinguish the following types:
- Aching. It is felt immediately after the anesthesia wears off. Keeps for about 2-4 days. The jaw may ache when opening the mouth or chewing.
- Intense, enduring. Occurs during extraction of a complex tooth with drainage or opening of a purulent cavity.
- Phantom. Occurs after traumatic surgery and may be felt from time to time. Phantom pain occurs with weak immunity and a low pain threshold.
It is difficult to say how intense the pain will be in each specific case, which is why it is so important to follow medical recommendations to prevent complications.
When to see a doctor
About 25% of patients experience a return visit to the surgeon after extraction of a posterior molar. This occurs due to the development of complications after surgery. When is it time to go for a follow-up appointment to prevent serious problems?
- The pain lasts longer than a week, does not decrease, on the contrary, it increases.
- New symptoms appear, the temperature rises, pain spreads to the entire jaw, to the ear area, to the temporal part.
The pain began to spread to the ear
- The swelling of the cheek intensifies and does not subside, occupying a larger area.
- Putrid odor from the mouth.
A putrid odor appeared and pus began to leak
- Any discharge from the socket, especially purulent discharge.
All this may mean the presence of a disease that began as a result of infection of the socket, the presence of foreign bodies in it (fragments of dental bone or other objects). The doctor will again order an x-ray, clean the hole, treat it with an antiseptic, and, if necessary, apply drainage. He will prescribe medication and give recommendations for gum care that will help normal healing.
What else can pain indicate?
Severe pain after removal may indicate the development of complications. Pulsating pain that radiates to the ears and submandibular lymph nodes is not normal. The most common causes of complicated postoperative pain are the following factors:
- Violation of treatment protocol. Unfortunately, mistakes do occur, especially in the removal of complex teeth. The techniques and approaches used in different clinics may differ from the standards. Errors include leaving fragments of materials or a splintered tooth root behind.
- Alveolitis. Occurs in the absence of a blood clot. The disease complicates natural healing and interferes with normal tissue regeneration. That is why doctors do not recommend touching the wound with your tongue or rinsing your mouth intensively.
- Dry hole. One of the common complications and the cause of long-term pain after tooth extraction. Despite the moisture of the mucous membranes, bone tissue is visible at the bottom of the wound opening. This problem is typical for smokers during periods of hormonal surges. The doctor seals the wound with a swab containing medication.
- Trigeminal neuritis. Long-term pain persists when a tooth in the mandibular row is removed if the trigeminal nerve is damaged during the manipulation. Damage may be accidental due to structural anomalies or multiple branching of nerve structures.
The likelihood of complications developing is low if the removal protocol, medical recommendations after extraction, and timely response to alarming manifestations are followed.
On the top
The most common complication of extraction of figure eights in the upper jaw is a puncture of the base of the maxillary sinus (maxillary sinus).
Puncture of the bottom of the maxillary sinus
The dental roots of molars number three in the upper jaw are located too close to the base of the sinus, and sometimes even grow into it. Chronic inflammation of the periapical tissue provokes resorption of the axillary septum, due to which the roots of the molars fuse with the mucous membrane inside the sinus. It is this part that most often ruptures during the extraction of the right or left tooth. This complication can be noticed by the following symptoms:
- nasal sound, bleeding air bubbles;
- blood from the nose on the side of the figure eight.
In such a situation, urgent medical assistance is necessary.
How can you reduce pain?
In the early postoperative period, it is important to follow basic recommendations that reduce the risk of negative manifestations:
- maintain the integrity of the blood clot - do not touch the wound with your tongue, rinse vigorously with solutions or water, just take an antiseptic or herbal decoction into your mouth, hold for a few minutes and spit;
- after a complex removal, take broad-spectrum antibiotics - this is important to prevent the infectious process;
- taking symptomatic medications for up to 2-3 days - in the first days, medications help reduce pain and inflammation;
- use a gel with a cooling effect for intense pain;
- do not eat for two hours after surgery, and eat solid food in the area of manipulation for 5-7 days.
You can reduce the pain if you chew a piece of ginger or propolis on the healthy side of the jaw, apply ice through a handkerchief to your cheek or chin, and rinse with the following ingredients:
- tea tree (10 drops per 500 ml of boiled water);
- steep chamomile decoction;
- decoction of eucalyptus and string;
- soda-salt solution (1 tsp soda, 1 tsp salt, 500 ml water).
The temperature of rinsing solutions should be comfortable - neither cold nor hot. Herbal solutions are best used as an alternative 3-5 days after surgery. In the early period, it is better to rinse the wound and oral cavity generously with water-based antiseptics.
The appearance of pain after tooth extraction is associated with trauma to the deep layers of the jaw structures. The tooth can hurt from several hours to 3-7 days, depending on the severity of the clinical situation and the scope of medical intervention. If questionable symptoms or other signs indicating complications appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Procedures for continuing treatment at home
Treatment of alveolitis at home is carried out when acute symptoms have been eliminated, antiseptic turundas are no longer needed and the goal is to speed up the healing of the hole. For this use:
- Mouth rinses with infusions of chamomile, calendula, and sage. These medicinal plants have anti-inflammatory properties and accelerate healing processes. Rinsing is carried out several times during the day, always after meals.
- Applications with dental adhesive paste Solcoseryl. The drug belongs to the group of tissue regeneration stimulators: it accelerates healing, improves the supply of cells with oxygen and nutrients. The paste has a pleasant mint taste and contains the anesthetic component polidocanol 600. To properly apply the paste, you need to dry the hole with a gauze swab and fill it with Solcoseryl, lightly moisten the paste with water on top. The procedure is repeated several times a day as necessary; the paste is able to protect the socket throughout the day from mechanical and chemical influences.
- Taking vitamin preparations. You can purchase any vitamin and mineral complex at the pharmacy (Vitrum, Duovit, Complivit); Vitamins are taken to increase the body's defenses and shorten the recovery period.