Why are sutures required after wisdom tooth removal?
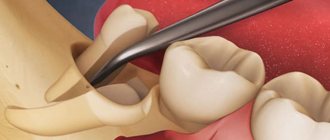
Extraction of the third molar requires suturing. It is not always possible to save the patient from the procedure described above. Even when working with high-quality equipment, a competent dentist will encounter problems. The third molar is secured with the help of two roots, the removal of which requires making a few incisions, and then removing the tooth body from the gum. Sutures are also applied if there are clinical signs of gum inflammation. Swelling is considered a natural process for the body, due to damage to the gums during incisions. The suturing procedure is also a preventive measure, which reduces the risk of infectious pathological syndrome; pathogenic bacteria do not penetrate into the open wound. The smaller the size of the wound, the lower the likelihood of infection, the age the rate of regeneration. Regardless of the type of thread used, suturing takes a short period of time. Self-absorbable threads are a more preferable option; they do not need to be removed and re-injure the gums.
What happens to the gum after removal?
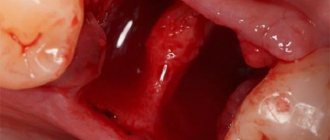
The intervention associated with the operation requires sutures. After all, it is often impossible to remove a tooth that sits deep in the gum without surgical manipulation. The gums react quite sensitively to such things, they can become inflamed and almost always bleed.
If a wisdom tooth is to be removed, it is often necessary to cut a section of the gum and then apply stitches to quickly heal the wound. The gum is a mucous membrane, it covers the processes next to the lower and upper jaws, and is located directly next to the teeth.
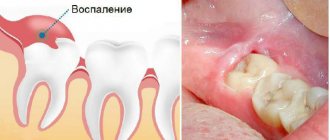
After the dentist removes or simply pulls out a tooth, the gums become more sensitive and easily vulnerable to various microbes. For many people with periodontal disease, the gums are generally very irritated, and the slightest intervention leads to severe bleeding, purulent discharge and an unpleasant burning sensation.
How to understand that complications have arisen after suturing?
Alarming symptoms after removing the “eight” are as follows:
- heavy bleeding that lasts more than a day;
- severe pain, throbbing pain that prevents you from sleeping or leading a normal life;
- very large swelling;
- redness in the intervention area;
- blood in saliva in the first three days after the intervention;
- elevated body temperature.
In all these cases, you must consult your doctor. It is possible that stitches will have to be stitched again to avoid complications.
Complications after osteoplasty and sinus lifting
The main postoperative complications include the appearance of pain, swelling at the surgical site and surrounding tissues, bleeding, numbness and paresthesia
Suture dehiscence after sinus lifting and bone grafting is not as common as pain and swelling, but is also a rather unpleasant condition. Typically, suture dehiscence occurs due to mechanical damage or trauma at the surgical site when the doctor’s recommendations are not followed. The cause may also be a manufacturing defect in the thread or incorrectly chosen tactics in using knots. But this happens extremely rarely, only among insufficiently experienced specialists. Violation of the regime in the postoperative period:
- Using a straw when taking food and water;
- Puffing out cheeks, whistling, singing and screaming;
- Constant tugging at the surgical site and nodes with the tongue;
- Excessive rinsing with antiseptics and other solutions, which can cause unnecessary pressure in the mouth;
- Intensive use of a toothbrush to clean the tongue, cheeks and teeth;
- Rough food that is difficult to chew, which can cause injury to the suture;
As a result, the wound will open and, most likely, infection will occur at the osteoplasty site and in the surrounding tissues. This will naturally cause local inflammation, pain, fever and astheno-vegetative syndrome. All this is one side of the coin, the other side is that after the infectious agent enters the wound, an inflammatory reaction will occur and the stitches will separate. What can cause an inflammatory reaction:
- Non-compliance with the regimen after surgery;
- Refusal of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, which will reduce pain and protect against the development of infection;
- Poor or lack of oral hygiene;
- Visiting sports sections, saunas, baths, swimming pools;
- Smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages.
If this situation occurs, you should immediately seek medical help, as all this can lead to the loss of the implant. And then there is a long period of rehabilitation of the bone and soft tissues, repeated osteoplasty, a period of healing and recovery. Therefore, you should only contact qualified specialists who, in addition to a first-class operation, will also be able to correctly explain the importance of the recovery phase after surgery in order to eliminate all possible complications.
Useful tips for oral care
- hold the cotton swab applied by the doctor for 20-30 minutes;
- within 2-3 hours after surgery, be sure to apply cold compresses to reduce tissue swelling;
- carry out oral baths (not to be confused with rinsing) with antiseptic drugs for 3-5 days: “Miramistin”, “Chlorhexidine 0.5%” or other drugs prescribed by a doctor can be used as medicinal solutions;
- after 3-5 days, start using a toothbrush - only a soft one for the operated area, as well as a new one, without bacteria on it. The teeth of the opposite jaw can be brushed immediately, the main thing is to avoid the area of the extracted tooth;
- chew food on the side opposite the injured area;
- You can drink water immediately, preferably warm;
- You can eat only after the anesthesia wears off, that is, after 2-3 hours;
- Lead a quiet lifestyle, try to avoid physical activity and heavy lifting for 5-7 days.
Types of suture materials
To close the hole after tooth extraction, modern dentistry uses various suture materials.
- Absorbable - sterile natural or synthetic threads that do not require removal. During the healing process, wounds resolve completely.
- Non-absorbable - silk and polymer threads. They are characterized by ductility and high strength. They need to be removed one week after the procedure.
The choice of suture material depends on the degree of tissue damage during surgery. After suturing, slight swelling and discomfort when chewing may be observed for 3 days. If the pain intensifies and the stitches come apart, you need to urgently seek help.
What not to do after suturing.
- don't rinse your mouth! Mouth baths in the first 3-5 days are more than enough;
- do not use hot compresses! This is fraught with the appearance of edema and the development of inflammation;
- do not create a vacuum in your mouth: do not puff out your cheeks, sneeze, blow your nose and spit very carefully;
- do not pick the wound, do not touch the clot with your tongue;
- do not drink or eat hot or cold food, only warm food;
- try to quit smoking for at least 2-3 days after surgery;
- Do not drink alcohol for 2-3 days - it does not promote tissue repair. Also rule it out if your doctor has prescribed a course of antibiotics;
- Do not overcool or overheat - give up sports exercises, swimming pools, saunas for 5-7 days.
Types of seams. Types of threads
In each case, when the dental surgeon sutures the gum, he decides which suture to use.
Seams can be intermittent or continuous.
The first type is more common and is characterized by the overlapping of separate, unrelated stitches (pictured below), and each is secured with its own knot.
This maintains the integrity of the fabrics, even if one of the stitches fails and falls off.
There is continuous suturing. All stitches are made with a single suture thread, securing them with a common knot. It's faster, but any damage to one stitch can ruin the entire thread construction.
Absorbable and non-absorbable threads are used to suture the gums.
Sutures that dissolve
Natural (Catgut) and synthetic (Vicryl, Dexon) threads are used. When suturing the gums with Catgut, it can stay on the wound for at least 2 weeks. It is dissolved by saliva substances, but due to its protein base it often causes allergies with inflammation of the gums.
Catgut is contraindicated if there is a high risk of inflammatory complications. Dental surgeons are using this material less and less.
Synthetic Vicryl is safe in terms of tolerability, adheres tightly to the gum, and does not change its strength properties during disinfection. If the doctor does not prescribe a time limit for removing the threads, they will still dissolve within 3 months.
Dexon will last on the gums a little longer than Vicryl, otherwise their properties are similar.
No one can say for sure how long it takes for threads to dissolve in a particular patient. This depends on individual factors: characteristics of the wound, the chemical environment of the oral cavity, general immunity, and the patient’s hormonal status.
When absorbed, the thread does not disappear without a trace, but gradually disintegrates into particles, which are spat out or swallowed by the patient. It is not dangerous to health.
Threads that do not dissolve
Non-absorbable threads are nylon, silk, polyamide fiber (nylon). Synthetic threads are completely hypoallergenic.
Sutures made from non-absorbable sutures are called non-absorbable or non-absorbable sutures. Their removal after the stitches have healed is mandatory. If such threads are used and there are no complications, the surgeon will release the patient from them 7–10 days after the tooth has been pulled out or another operation on the gums has been performed.
Indications for the procedure
Removing the remaining tooth from the alveolar socket is a surgical procedure that affects the tissue around the root part. The decision to apply suture material is determined by the doctor’s intention to prevent infection from entering the wound - according to statistics, suturing the hole reduces the likelihood of infection by 98%.
The residual that forms in the gum structure after extraction is a blood clot, which acts as a protective barrier to protect the socket from bacteria. Applying sutures eliminates the possibility of its displacement, preserving the area from the negative influence of the pathogenic environment. Suturing reduces the risk of the formation of inflammatory processes, as well as purulent areas that arise due to food particles stuck inside the wound cavity. In addition, the procedure is recommended at the first symptoms of edema formation, and promotes accelerated healing and fusion of wound edges.
Clinical indications considered as a basis for the procedure include the following situations:
- Extraction of wisdom teeth, accompanied by profuse bleeding that persists for several hours after the operation;
- The absence of a blood clot acting as a barrier to potential infection;
- Removal of completely destroyed elements, as well as impacted or dystopic units of the dentition.
The decision to apply sutures and suturing the alveolar socket is made based on the clinical picture observed in the postoperative period.