general characteristics
A pathological disorder of taste perception is called dysgeusia.
Such a “perversion” of taste sensations can be a sign of the development of neurological, hormonal, mental disorders and other diseases, including those caused by a deficiency of certain substances in the body. If the taste of the products remains unchanged, this diagnosis can be excluded. In this case, we are talking about the temporary persistence of an unusual taste in the mouth, and most often the problem disappears when the cause of its appearance is eliminated.
Causes of taste in mouth
Throat diseases may be accompanied by an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Photo: imagepointfr / Depositphotos Reasons for an unusual taste in the mouth may include:
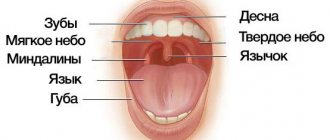
- diseases of the teeth, gums and oral mucosa;
- pathologies of the ENT organs (nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses);
- unbalanced diet;
- diseases of the stomach and gall bladder;
- hormonal and neurological disorders;
- intoxication with chemicals.
In women, a change in taste can be a sign of pregnancy; in men, it is rarely associated with physiological conditions and hormonal surges. At the same time, diseases of the nervous, respiratory systems, or even cancer can lead to the development of symptoms. Doctors will help you understand the cause of the symptom: in this case, an integrated approach to examination and treatment is necessary.
Causes of blood taste in mouth
The characteristic taste of blood most often indicates increased bleeding of the gums. Also, such a taste can be a symptom of diseases of the nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, sinusitis).
Other reasons for feeling blood in the mouth:
- diseases of the bronchi and lungs (acute bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy, lung abscess);
- disorders of the hematopoietic system;
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- oncological diseases;
- internal bleeding.
In addition, the sensation of blood in the mouth may be associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT):
- esophagitis;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- chronic gastritis;
- liver pathologies.
The taste of blood may occur due to biting the mucous membranes of the cheeks or tongue. In this case, it is enough to actively rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions, for example, chlorhexidine, throughout the day.
Causes of bitter taste in mouth
An unpleasant bitter taste may appear in the morning after waking up or several hours after eating.
Common causes of a bitter taste in the mouth:
- Pathologies of the liver and gallbladder (hepatitis, cirrhosis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, gallbladder kinks), stagnation of bile - at a certain point, its excess leaves through the bile ducts, enters the stomach and penetrates the esophagus.
- Indigestion. Slowing intestinal motility leads to retention of undigested food in the gastrointestinal tract. This leads to fermentation processes and the appearance of a characteristic taste in the mouth.
- Neurological pathologies (Alzheimer's disease, consequences of traumatic brain injury).
- Pregnancy.
Symptoms can also be caused by hormonal disorders, parasitic infections, or taking certain medications (antibiotics, antiallergic drugs, chemotherapy drugs).
At home you can get rid of the symptom with:
- eating small meals frequently;
- compliance with the water regime;
- rinse your mouth with a spoon of baking soda.
However, after eating, the sensations usually disappear for some time.
Causes of a metallic taste in the mouth
This symptom is often confused with the taste of blood, but other conditions can cause a strong sensation of “metal” in the mouth:
- chemical poisoning with heavy metals (mercury, copper, lead, arsenic);
- taking certain medications (iron supplements for anemia, antiparasitic drugs, pills to lower blood pressure);
- galvanosis - disruption of electrochemical processes in the oral cavity due to metal prostheses, implants, piercings;
- “burning mouth syndrome”, insufficient salivation and dry mouth;
- impaired kidney function (excessive accumulation of metabolic products);
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, Fig. 1);
- period of hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause).
The symptom can also appear due to everyday reasons:
- insufficient purification of drinking water;
- storing food in aluminum containers.
To relieve the metallic taste, you can try rinsing your mouth with salt and water, eating foods with intense flavors, and adding more natural spices. It is also important to temporarily switch to cutlery made from non-metallic materials.
Figure 1: A metallic taste in the mouth may indicate a serious medical condition. Source: Verywell Health
Causes of sweet taste in mouth
A sweetish taste that is not associated with an excess of desserts in the diet may be a sign of:
- dental pathologies;
- diabetes mellitus;
- pregnancy;
- problems with the thyroid gland;
- neurological pathologies (stroke, epilepsy);
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease);
- bacterial infections - some microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci) produce enzymes with a specific taste;
- pesticide poisoning.
You can try to get rid of this feeling by giving up sweets. Also, in the fight against taste, it is necessary to avoid smoking, drink enough fluids throughout the day and carefully observe the rules of oral hygiene.
Causes of acetone taste in the mouth
The reason for this taste and smell of “nail polish remover” from the mouth is most often the excessive content of special substances of fat metabolism - ketone bodies.
As a rule, the symptom appears with diabetes mellitus, but can also accompany other conditions:
- following a keto diet (Fig. 2);
- fasting or drinking too much fluid;
- kidney damage (glomerulonephritis, renal failure);
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- liver pathologies.
Figure 2: Following a keto diet may cause your breath to smell like acetone.
Source: Sewcream / Depositphotos You can get rid of the characteristic smell of acetone using natural breath fresheners, using dental floss and drinking water with lemon.
Important! If you experience a taste of acetone in your mouth, you should reconsider your diet and abandon alternative foods that do not contain sugar - a carbohydrate-free diet often leads to ketoacidosis.
Causes of taste disorders
A violation of taste makes it clear about the pathological processes that occur in the body. Often the cause can be serious injuries or latently developing diseases. In addition to taking medications and basic causes, this is how severe pathologies manifest themselves.
| Cause | Description | Mouth sensation |
| Fracture of the base of the skull | Disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems of the body. Accompanied by nausea, fainting, noise and pain in the head. | Metallic Bloody Ammonia |
| Oral Oncology | Tumors that disrupt the functioning of receptors. The pathology develops with damage to taste perception. | Purulent Moldy Ammonia |
| Sjögren's disease | The activity of the salivary glands and taste buds decreases. Accompanied by cough, pain, inflammation of the pharynx, pressure. | Bloody Metal |
| Purulent lesions of the larynx | Development of ulcers, inflammations with purulent processes. It often occurs against the background of rising temperature. | Purulent Moldy Almond |
| Thalamic pain syndrome | Damage to the thalamus, causing a violation of taste perception. | Salty Sweet Sour Bitter |
| Hepatitis | The functioning of the receptors is disrupted only in the acute form. Accompanied by pain and inflammation. | Ammonia Metallic Bitter |
| Candidiasis | Fungal infection of the oral cavity. There is a thick white coating on the palate, tongue, lips and gums. | Purulent Sweet Moldy |
Delaying a visit to the doctor for a long time leads to the development of the disease into a chronic form. The only exception is a one-time taste, when nothing hurts against its background, there is no cough, sputum or coating on the tongue. It is impossible to diagnose pathology by the taste of saliva on your own.
Types of violations
Symptoms come in different etiologies and are provoked by pathologies and disorders. They often occur due to poor oral hygiene, poor diet, alcohol abuse or smoking. Partial loss of taste and the presence of aftertaste can be dictated by:
- Ageusia
. With severe damage to the nervous system, hormonal disruption occurs. Taste buds do not perceive food “correctly.” Often the opposite sensations are projected. Sweet foods taste salty and vice versa. - Hypogeusia
. Due to infectious and fungal diseases, the sensitivity of the tongue decreases. Taste sensations are more difficult to distinguish. Occurs when taking strong antibiotics, or with mechanical damage to the tongue. - Dysgeusia
. Erroneous taste recognition. Due to disturbances in the functioning of receptors, sugar seems salty, lemon tastes bitter. Against the background of hormonal imbalance, it often occurs in pregnant women and is temporary.
Neuritis, damage to neurons, can lead to complete loss of taste. Abnormalities of the thyroid gland provoke the same effect. In addition to taste, smell is lost. The patient feels similar sensations during strong anesthesia during tooth extraction.
Additional Information
You can avoid the sensation of blood, paint, and ammonia in your mouth by following basic rules. It is important to maintain oral hygiene, not take medications unless prescribed by a specialist, and visit the dentist regularly. Treatment of chronic pathologies will allow you to avoid unpleasant symptoms.
If an unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth is accompanied by dizziness, pain, or nausea, then immediate consultation with a doctor is required.
A persistent taste indicates serious chronic disorders. In pregnant women, tastes may indicate hormonal changes. They are usually temporary and do not require specialist intervention. If the feeling occurs only after eating, then you should spend more time on hygiene and visit the dentist.
A nutritious diet and regular preventive examinations minimize the risk of an unpleasant taste. If the sensations are accompanied by any additional symptoms, then they are part of the pathological process.
Help before diagnosis
In most cases, the following help to get rid of the symptom:
- keeping the oral cavity clean;
- regular and balanced nutrition;
- cessation of smoking, alcohol abuse;
- drink enough fluid during the day;
- moderate activity after meals.
You can temporarily remove the taste by thoroughly brushing your teeth, rinsing your mouth with water and lemon juice or baking soda, chewing gum, or special mouth fresheners.
Prevention of odor
Hygiene is an important point in preventing oral diseases. Teeth should be brushed twice a day. Circular movements are performed over the entire surface of the crowns. At the same time you need to clean your tongue. Its surface is cleaned with a soft brush. You can purchase a special brush.
If the doctor recommended a paste containing calcium, then you need to strengthen the enamel. Antiseptic agents will reduce bacterial activity. This will improve the condition of the gum tissue. After eating, you should rinse your mouth with clean water. It is important to visit the dentist regularly. Prevention of disease is the best treatment. If the oral cavity is in order, but your breath is not fresh, you need to make an appointment with a therapist. You can get rid of halitosis when the disease that caused it is eliminated.
When to see a doctor?
Eliminating the cause of the development of a symptom most often completely eliminates all its manifestations, so it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner (Table 1).
Table 1. Taste in the mouth: when should you seek medical help?
| Type of taste in the mouth | Reasons to see a doctor |
| Taste Blood | If the symptom is not associated with accidental damage to the oral mucosa, you should begin the examination with a trip to the dentist. If necessary, the specialist will refer you to other doctors for consultation. |
| Metallic taste | You need to undergo examination in the toxicology department if the taste appears after poisoning with chemical agents. It is also important to consult a doctor if you suspect bleeding of unknown location or galvanism. |
| Bitter taste | If bitterness in the mouth persists for several days, and is also accompanied by the appearance of plaque, nausea or vomiting, you should make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. This is probably how the body “signals” about disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. |
| Bitter taste | If your taste changes regularly without connection with the amount of sweets in your diet, you should consult a therapist or endocrinologist. |
| Taste of acetone | You should definitely see an endocrinologist if the symptom occurs due to diabetes. When following a low-carbohydrate diet, it is also important to choose a new diet from a nutritionist. |
Causes associated with diseases
An unpleasant taste of iron is very often a symptom of various diseases of the digestive system. In most cases, it indicates destructive changes in the upper digestive tract. For example, they may be associated with the development of erosive gastritis. This pathology is associated with increased production of gastric juice containing hydrochloric acid. As a result of exposure to an aggressive environment, the mucous membrane is damaged by hydrochloric acid. Against the background of damage to the mucous membrane, a characteristic taste of metal appears in the mouth and, in addition, severe heartburn occurs.
Dental diseases also often cause a characteristic metallic bitterness in the mouth. This:
- Stomatitis, which occurs when the mucous membrane becomes inflamed.
- Gingivitis, characterized by inflammation of the gums.
- Periodontitis, which is often a complication of gingivitis.
- Glossitis, the characteristic symptoms of which is the occurrence of inflammation of the surface of the tongue and the formation of a pronounced coating on it.
All of the above dental pathologies cause minor bleeding. Since blood contains iron ions, this leads to a metallic taste in the mouth.
A metallic taste may also be a sign of iron deficiency anemia. In this case, the sensations are constantly present and do not disappear after eating and drinking. Additionally, there is a change in taste preferences, and there is also a craving for eating inedible items: chalk, earth, ice, etc. But at the same time, they enhance the metallic taste.
Also, characteristic bitterness is observed against the background of B12-deficiency anemia. It leads to atrophic changes in the oral mucosa. Additionally, there is a violation of all taste perceptions.
Diagnostics
The first step in finding the cause of an unpleasant taste in the mouth should be a trip to the dentist: he will immediately determine the possible connection of the symptom with diseases of the teeth and surrounding tissues.
If the problem does not go away, you should consult a therapist: a specialist will help you understand the likely causes of the symptom. For an accurate diagnosis, the results of the following studies may be needed:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests (liver, kidney tests, glucose levels, lipid profile);
- tests to evaluate thyroid function;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS);
- pH-metry of the stomach;
- tests for Helicobacter pylori infection;
- electroencephalography (EEG), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the head.
The choice of diagnostic algorithm depends on the most likely cause of the development of an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Treatment
The best and most effective method of treating a symptom is to eliminate the cause of its occurrence. If the bad taste in your mouth is caused by a dental problem, it is important to get rid of tooth decay or other diseases as soon as possible.
If an unpleasant taste occurs due to pathology of certain organs and metabolic disorders, the doctor prescribes treatment for the underlying disease.
Conservative therapy
Depending on the characteristics of the symptom, to eliminate it, the doctor may prescribe drugs from the following groups:
- antiseptics;
- antacids;
- choleretic drugs;
- hypoglycemic agents;
- antidotes and detoxification drugs.
The doctor selects treatment individually. The treatment regimen depends on the causes of the taste, its severity, concomitant diseases and other features of the clinical case.
Sometimes, to get rid of the taste in the mouth, you have to resort to medications. Photo by JESHOOTS.com: Pexels
Physiotherapy
Methods of physiotherapeutic treatment in cases of unpleasant taste in the mouth help to cope with chronic inflammatory and metabolic processes, and eliminate other symptoms of pathology.
For example, for diseases of the ENT organs, rinsing with sea salt solutions, ultrasound treatment and UV irradiation, and therapeutic inhalations are used.
Warming procedures are contraindicated for patients with acute conditions - inflammation, likelihood of bleeding, severe pain.