Classification of the disease
There are four main types of miliaria, which differ in the nature of the rash, the duration of development and the severity of symptoms:
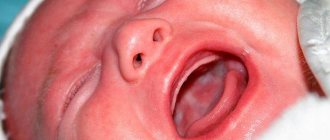
- Crystalline. It is accompanied by the development of a blistering rash, which most often appears on the head, behind the ears, and on the neck. Other localization of rashes is also possible. 2-3 days after the appearance, the blisters dry out and begin to peel off. Since irritation is not accompanied by inflammation or infection, the crystalline form is the simplest and most harmless.
- Red. A more complex type, in which sweat acts on the skin for a longer time and, accordingly, causes more severe irritation. A rash in the form of small inflamed tubercles provokes slight swelling and is accompanied by itching, burning, and discomfort. Lasts about two weeks.
- Miliaria alba, or vesiculopustulosis. With this type, blisters with a whitish or yellowish filling appear on the skin. When the bubble bursts, it leaves behind a light coating. The presence of color in the bubbly fluid indicates that the rash is accompanied by an infection, often staphylococcal.
- Deep. In most cases, prickly heat causes only superficial damage to the skin. With a deep form of pathology, the deep layers of the skin are affected. The disease is accompanied by blisters filled with light contents, which resolve or burst spontaneously.
Symptoms
The main and most obvious symptom of the pathology is a rash. Most often, rashes appear on the head, chest, back, groin, armpits, and buttocks. The rash appears as scattered blisters with clear, white or yellow contents, or as small grains with an inflammatory outline.
During the day, the rash may intensify or decrease, and the severity of its manifestation depends on changes in temperature and care for the baby’s skin. In some cases, the child does not show concern, but sometimes may experience itching, pain and demonstrate discomfort with whims, unstable sleep, and lack of appetite.
In mild forms of the disease, other symptoms may not occur. But in more advanced cases, which are accompanied by complications and infection, clinical manifestations may be supplemented by:
- elevated temperature up to 38 degrees;
- the appearance of light plaque, ulcers, ulcers;
- the formation of weeping cracks with an unpleasant odor;
- general deterioration of condition.
When assessing symptoms, it is important to prevent the development of advanced forms of prickly heat and consult a doctor promptly, without waiting for complications to develop. Source: Skin care for a newborn. Solntseva O.A. Medical Council, 2014. p. 35-39.
Causes
Most often, parents who do not adhere to the basic rules of caring for the child turn to doctors with complaints about heat rash in their baby: they bathe him with soap every day, wrap him up excessively without taking into account the real ambient temperature. Children with skin allergies, diabetes mellitus, rickets, seborrheic dermatitis or frequent diarrhea are also at risk. Chubby, overweight and bottle-fed babies are especially at risk of developing rashes.
Among other reasons for the development of prickly heat in children are:
- non-compliance with normal temperature conditions;
- too hot, tight clothes or shoes that do not allow air to pass through and do not create natural ventilation;
- excessive use of skin cosmetics that disrupt the acid balance and cause increased sensitivity (soaps, baby creams, oils, etc.);
- rare change of diapers or their poor quality, lack of care;
- viral diseases that are accompanied by fever.
Surgery
If all efforts made do not achieve the goal (and such a goal can only be the complete disappearance of the chalazion), surgical removal of the nodule is prescribed. This intervention is quite simple and is performed on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia in older children and under general anesthesia in young patients who are unable to control themselves on the operating table.
The problematic area of the eyelid is fixed with a special clamp, the capsule is opened (from the outside or from the side of the conjunctiva, depending on the location), its contents are removed, and the surgical site is treated with an antiseptic drug to prevent infection. If necessary, a drainage may be left to drain purulent contents. As a rule, a low-pressure bandage is applied.
How to distinguish heat rash in a child from allergies and other diseases
When a rash appears on the skin, the most difficult thing for parents is to distinguish prickly heat from other diseases: allergies, chicken pox, measles, etc.
First, you should examine the location of the rash. In the first case, the rashes are located in hard-to-reach places: in the area under the diaper, in the folds of the skin, in the hairline. In this case, the rash almost never appears on open areas of the skin that are well ventilated. But if the rash appears on the face, open parts of the arms and legs, most likely it is an allergy.
A simple home test will also help make a differential diagnosis. You just need to undress the baby and leave him without clothes or a diaper for several hours. If the rash appears as a result of prickly heat, during this time it will decrease and become paler. If it is an allergy, no changes will occur to it.
Additional symptoms will help distinguish the disease from measles, chickenpox and other viral pathologies. With infectious diseases, the temperature always rises, intoxication appears, and the rash quickly spreads throughout the body. In turn, the main symptom of prickly heat is just a rash.
Diagnostics
You should not self-medicate or try to diagnose your child yourself. Before you begin to treat prickly heat in a child, when the first rash appears, you should contact a pediatric dermatologist or pediatrician. The specialist will conduct an examination and distinguish the pathology from other diseases that are accompanied by a skin rash. For an experienced pediatric specialist, this is not difficult even with an initial visual examination.
In some cases, additional examination is necessary for a comprehensive diagnosis. The doctor may prescribe scraping for pathogenic fungal infections, as well as bacterial culture for microflora.
Eyesore
Syphilis
Herpes
13291 August 17
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. An eyesore: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
An eyesore, or leukoma, is externally manifested by clouding of the cornea of the eye that occurs after injury or an inflammatory process. The cornea is the anterior, most convex part of the eye capsule, consisting of a thin avascular membrane through which refracted light enters the posterior parts of the eye. There are three stages of corneal opacification depending on the size and depth of the lesion: a cloud, a spot and a cataract, but all of them affect visual acuity, and in some cases a person can become completely blind in the affected eye.
The success of treatment largely depends on timely seeking medical help.
Types of eyesores
There are congenital and acquired eyesores:
- congenital cataract is formed during the period of intrauterine development of the embryo and is often combined with other congenital eye diseases;
- the acquired form is the most common, occurring equally often in both men and women.
Depending on the depth of the lesion, the following types of cataracts are distinguished:
- corneal cataract without affecting other parts of the eye; there are scars of different shapes and lengths in the cornea;
- a thorn welded to the iris; a cloudiness appears on the cornea, sprouting with small vessels, spreading to the area of the iris;
- a cataract in combination with true clouding of the lens, that is, cataract;
- cataract with secondary cataract;
- intense clouding of the cornea of the eye, which is characterized by adhesions of the cornea with the iris and/or lens, clouding of the lens;
- a thorn complicated by retinal detachment and the development of eye atrophy.
Possible causes of eyesores
Doctors consider keratitis, an inflammation of the cornea of the eye, to be one of the possible causes. The most common cause of keratitis is a viral infection (herpes viruses, chickenpox). Often, bacterial infections, as well as non-compliance with the rules of wearing contact lenses, lead to an inflammatory process in the cornea.
Keratitis is characterized by redness of the eye, pain, lacrimation, photophobia, clouding of the cornea already in the initial stages of the disease, and decreased visual acuity.
If treatment is not started on time, the inflammation will spread deeper and an eyesore will begin to form.
Corneal injuries are another common cause of eyesores. Injuries can be mechanical, thermal or chemical (alkali or acid burns). Alkaline burns are the most dangerous.
The first symptoms of injury are pain, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign body, drooping of the eyelid.
Any injury to the cornea requires immediate medical attention.
Infectious diseases of the conjunctiva can lead to damage to the cornea and the appearance of a cataract. The conjunctiva is the connective membrane of the eye that covers the inner surface of the eyelids and extends from the outside to the cornea. One of the most dangerous diseases of the conjunctiva is trachoma. It occurs when a chlamydial infection enters the eye, is chronic and causes blindness in almost two million people in the world. Children are most susceptible to this eye disease.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that, despite the successes of domestic medicine, is still often diagnosed in patients of all ages. Tuberculosis can affect any organs and systems of the body, including the infection that can spread to the eyes, lead to deep damage to the cornea and cause the formation of a cataract.
Cases of cataract formation after eye surgery have been described. This is due to a violation of the integrity of the cornea, which increases the risk of infection.
Diseases leading to the formation of eyesores
- Congenital pathologies, for example, limbal dermoid, sclerocornea.
- Keratitis.
- Injuries (chemical, thermal burns, penetrating wounds).
- Trachoma.
- Corneal ulcers.
- Tuberculosis, syphilis.
Which doctors should you contact if an eyesore appears?
An ophthalmologist deals with the treatment of eyesores. He will order tests and conduct additional examinations. If you suspect an infectious etiology of the cataract, you may need to consult an infectious disease specialist or phthisiatrician.
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of an eyesore
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe the following examinations:
- a clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula will help identify inflammatory changes in various infectious and inflammatory diseases;
Treatment
The main method that allows you to remove rashes and cure skin pathologies is hygienic care. It is important to change the diaper immediately after a bowel movement and every three hours, washing the baby with running water. Between shifts you need to give air baths and leave the baby without clothes for a few minutes. At the same time, it is necessary to abandon synthetic clothing and low-quality children's cosmetics.
Bathing is carried out in water with a decoction of medicinal herbs. You can add chamomile, yarrow, and string. After bathing the child, dry thoroughly and powder the skin with powder.
In some cases, the doctor also prescribes treatment of rashes with drying antiseptics (“Furacilin”, “Chlorphilipt”), and creams containing panthenol (“Bepanten”, “Dexpanthenol”). White, red and deep miliaria are treated with antifungal and antibacterial ointments. However, it is not recommended to use any medications without prior consultation with a doctor. Source: Modern dermatological and cosmetic products for caring for the skin of children. Kotlukov V.K., Kuzmenko L.G., Antipova N.V. Medical Council, 2013. p. 8-12.
Doctors recommend setting the air temperature in the nursery at 20-22 degrees and monitoring the humidity, which should not exceed 50-70%. A good solution would be to purchase an air humidifier that will help create the right microclimate. These simple steps can help you get rid of the conditions that increase your risk of developing heat rash.
Preparations with zinc pyrithione
For mild to moderate seborrheic dermatitis on the head in infants, preference may be given to non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs based on zinc pyrithione. For example, Skin-cap shampoo containing activated zinc pyrithione has anti-inflammatory, sebum-regulating, and antimycotic effects. Skin-cap shampoo is prescribed as the main method of treatment to soften crusts and eliminate inflammation; in the future it can be used to prevent relapses of the disease. The activated zinc pyrithione contained in Skin-cap shampoo helps:
- reduce the intensity of inflammation;
- reduce the activity of fungi and bacteria;
- effectively moisturize the skin;
- eliminate peeling, feeling of skin tightness;
- reduce itching.
It is thanks to this combination of effects that Skin-cap shampoo can be used during an exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis in an infant, then the treatment will be more effective. You can combine the use of Skin-cap shampoo with accompanying medications, including it as part of complex therapy.
Treatment with medications is supplemented by general recommendations for changing diet and caring for the baby. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected on the face of a baby , it is recommended to exclude foods with potential allergens from the diet. You should not put synthetic clothing on your baby so that the skin is not subject to friction and irritation. Parents should pay special attention to the selection of laundry detergents, choosing products without aggressive substances in their composition.
The likelihood of stress for a child needs to be reduced as much as possible, so it is important to maintain a favorable psychological environment in the family.
Prevention
Effective prevention consists of proper and thorough hygienic care of the child: regular bathing, frequent changing of diapers or diapers. During the hot season, you can bathe your baby up to 2-4 times a day, but it is important not to use soap, oils, lotions and other products with each water procedure that can disrupt the acid balance and clog the glands.
It is also important to select clothes from natural, breathable fabrics and avoid synthetic and semi-synthetic fabrics that do not ensure normal evaporation of sweat. You need to dress your baby appropriately for the weather and not wrap him up in a warm blanket on a summer night. Source: Skin care for infants. Prevention of diaper dermatitis. Starostina L.S. Medical Council, 2022. p. 41-49.
Sources:
- Skin care for infants. Prevention of diaper dermatitis. Starostina L.S. Medical Council, 2022. p. 41-49
- Newborn skin care. Solntseva O.A. Medical Council, 2014. p. 35-39
- Modern dermatological and cosmetic products for the care of children's skin. Kotlukov V.K., Kuzmenko L.G., Antipova N.V. Medical Council, 2013. p. 8-12
Date of publication: 10/20/2017
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
How is seborrheic dermatitis treated in children?
If seborrheic dermatitis appears in newborns, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor. If seborrheic dermatitis is detected in an infant, treatment is carried out with external means. To loosen the crusts on the head and remove them painlessly, use products based on salicylic acid and oil compresses, which are applied about half an hour before water procedures. To treat seborrheic dermatitis in newborns , you can use drugs with a keratolytic effect. This will help remove excess gland secretion and cleanse the scalp. After softening and removing the crusts, anti-inflammatory agents may be prescribed.
For treatment to be more effective, it is necessary to ensure that the skin is well hydrated and supplied with nutrients in the right quantities. This helps restore and strengthen the water-lipid barrier and restore the proper functioning of the sebaceous glands. Suitable for care are dermatological creams created for children, which contain vegetable oils, sebum-regulating and wound-healing components. If treatment for seborrheic dermatitis in newborns turns out to be ineffective, the following may be included in the therapeutic regimen:
- topical corticosteroids;
- antibiotics and antiseptics;
- antihistamines for severe itching.